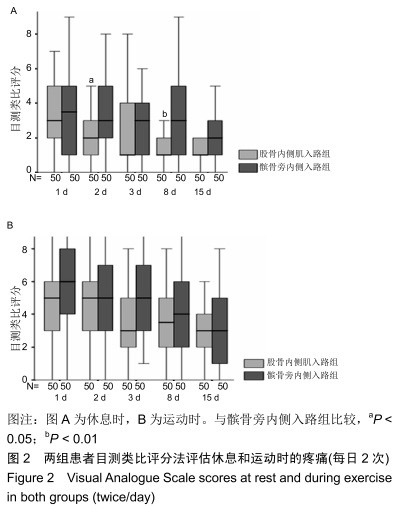
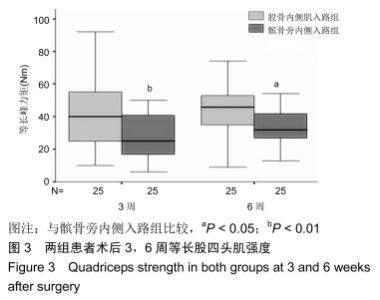
[1] 杨礼庆,马超,杜帅.人工全膝关节置换术围手术期疼痛管理现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(3):247-250.
[2] 史斌,安静,陈龙刚,等.人工膝关节置换术后疼痛影响因素的分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(7):993-997.
[3] 商杰,王业华,王海波,等.全膝关节置换术经股内侧肌下入路与经内侧髌旁入路临床疗效的META分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(1):38-44.
[4] THOMAS C, PATEL V, MALLICK E, et al. The outcome of secondary resurfacing of the patella following total knee arthroplasty: Results from the Trent and Wales Arthroplasty Register.Knee.2018;25(1):146.
[5] 张媛,魏应敏,马跃虎,等.改良髌骨轴位摄影在全膝关节置换术后X线检查中的应用[J].中国数字医学,2018,13(1):58-59.
[6] 姜辉,郑彦宏,孙百胜,等.急性髌骨外侧脱位后内侧髌股韧带损伤模式及其与髌股关节主要解剖参数的相关性[J].医学影像学杂志,2017,27(5):896-900.
[7] 谢明华,徐国健,翁东,等.缝合锚钉内固定治疗急性髌骨脱位后髌骨内缘撕脱骨折伴内侧髌股韧带断裂[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014, 29(6):603-604.
[8] 王瑞,陈哲峰,孙成,等.保留髌骨的全膝关节置换术后髌股关节过度充填现象[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(3):137-142.
[9] 戴祝,尤迪,廖瑛,等.髌骨复发性脱位伴陈旧性骨软骨骨折的治疗[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016(1):10-14.
[10] 王小康,潘玉才. 髌骨软化症的X线和MR对比研究[J].中国伤残医学,2017,25(23):16-17.
[11] 符培亮,李晓华,吴宇黎,等. 初次全膝关节置换股内侧肌中间入路与内侧髌旁入路置入假体的优势对比[J].中国组织工程研究, 2008,12(9):1793-1796.
[12] GRASSI A, COMPAGNONI R, FERRUA P, et al. Patellar resurfacing versus patellar retention in primary total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11):3206-3218.
[13] MARYA SK, AMIT P, SINGH C. Impact of Charlson indices and comorbid conditions on complication risk in bilateral simultaneous total knee arthroplasty. Knee.2016;23(6): 955-959.
[14] BOYD AD JR, EWALD FC, THOMAS WH, et al. Long-term complications after total knee arthroplasty with or without resurfacing of the patella.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(5): 674-681.
[15] LORD SR, MENZ HB, TIEDEMANN A. A Physiological Profile Approach to Falls Risk Assessment and Prevention. Physical Therapy. 2003; 83(3):237-252.
[16] SILVA M, SHEPHERD EF, JACKSON W O, et al. Knee strength after total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18(5): 605-611.
[17] 柯雪茹,赵莉,雷波,等.膝骨性关节炎病人全膝关节置换术后下行疼痛抑制功能与术后慢性疼痛的相关性研究[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2017,23(9):709-711.
[18] 黄小玲,唐金树,李岩,等.骨科康复一体化模式对全膝关节置换术后功能恢复影响的临床研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(8): 868-873.
[19] URQUART A, COLWELL CW JR. Influence of surgical approach on lateral retinacular releases in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(340):284.
[20] 刘军,孙振辉,田峥巍,等.股内侧肌下入路全膝关节置换术初步观察研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(9):649-652.
[21] WHITE RE JR, ALLMAN JK, TRAUGER JA,et al. Clinical comparison of the midvastus and medial parapatellar surgical approaches.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(367):117-122.
[22] DALURY DF, JIRANEK WA. A comparison of the midvastus and paramedian approaches for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(1):33-37.
[23] MAESTRO A, SUAREZ MA, RODRIGUEZ L, et al. The midvastus surgical approach in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2000;24(2):104-107.
[24] STEINBACH G. Evaluation of patella viability after disruption of the arterial circulation.Am J Sports Med.1987; 15(5): 490-493.
[25] 徐佩君,盛加根,徐镇,等.不断股直肌起点髋前侧入路行吻合血管游离腓骨治疗股骨头坏死的解剖学研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014(5):13-15.
|