Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (31): 4934-4940.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2129
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fabrication of prevascularized osteogenic differentiated cell sheet based on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Chen Jia1, Yang Yiqiang1, Hu Chen1, Chen Qi1, Zhao Tian1, Yong Min1, Ma Dongyang2, Ren Liling3
1Stomatology Hospital of General Hospital, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Craniomaxillofacial Surgery, The 940th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force of Chinese PLA, Lanzhou 730052, Gansu Province, China; 3School of Stomatology, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-24Revised:2020-02-29Accepted:2020-04-03Online:2020-11-08Published:2020-09-03 -
Contact:Ma Dongyang, MD, PhD, Associate professor, Department of Craniomaxillofacial Surgery, The 940th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force of Chinese PLA, Lanzhou 730052, Gansu Province, China Ren Liling, MD, PhD, Professor, School of Stomatology, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Chen Jia, Master, Attending physician, Stomatology Hospital of General Hospital, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China Yang Yiqiang, Master, Attending physician, Stomatology Hospital of General Hospital, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81670969 (to MDY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jia, Yang Yiqiang, Hu Chen, Chen Qi, Zhao Tian, Yong Min, Ma Dongyang, Ren Liling. Fabrication of prevascularized osteogenic differentiated cell sheet based on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4934-4940.
share this article
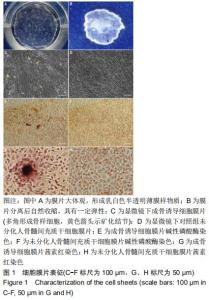
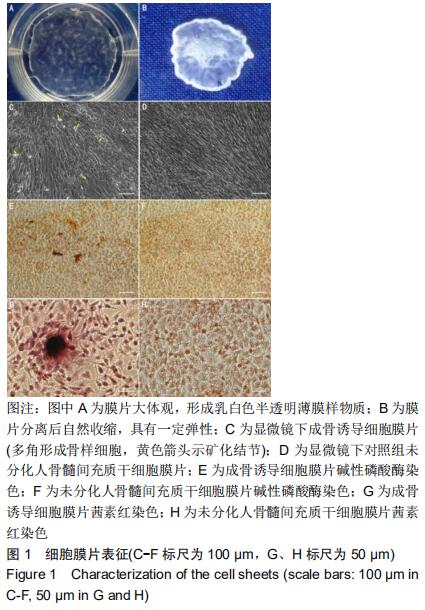
2.1 人骨髓间充质干细胞膜片表征 人骨髓间充质干细胞高密度接种后连续培养2周,培养皿底可见呈现乳白色半透明的薄膜样物质,见图1A,将该膜状物夹起后自然收缩,具有一定弹性,见图1B。镜下观察显示,高密度接种的人骨髓间充质干细胞迅速融合,5 d后细胞融合并持续生长形成致密的细胞膜片;继续培养,单个细胞形态消失,细胞逐渐融合成片,成骨诱导细胞膜片钙盐逐渐沉积,11-14 d时可见白色的矿化结节形成,见图1C。碱性磷酸酶染色发现,成骨诱导细胞膜片内有较多的大小不等的橘黄色沉淀,见图1E,茜素红染色发现数个大小不一的深红色结节,见图1G,而未分化对照组膜片碱性磷酸酶染色和茜素红染色均呈阴性,见图1F,H。 "

2.2 内皮血管网的形成 人骨髓间充质干细胞以9×104/cm2密度接种后第2天即迅速融合,经过14 d的连续培养及成骨诱导形成均匀致密的成骨诱导细胞膜片,见图2A,而人脐静脉内皮细胞膜片则成“铺路石”样排列,见图2B。将人脐静脉内皮细胞以5×104/cm2密度种在上述成骨诱导细胞膜片上,倒置显微镜下观察细胞形貌变化, 0 h时膜片未见明显变化,见图2C,3 d时人脐静脉内皮细胞逐渐发生迁移,排列变得有序,并且膜片中的细胞外基质随之发生重排, 可以观察到膜片上有整齐的微槽结构出现,见图2D;随培养时间的延长,人脐静脉内皮细胞进一步迁移,微槽结构也更加典型,见图2E,并开始形成小的空泡样结构,见图2F。 "

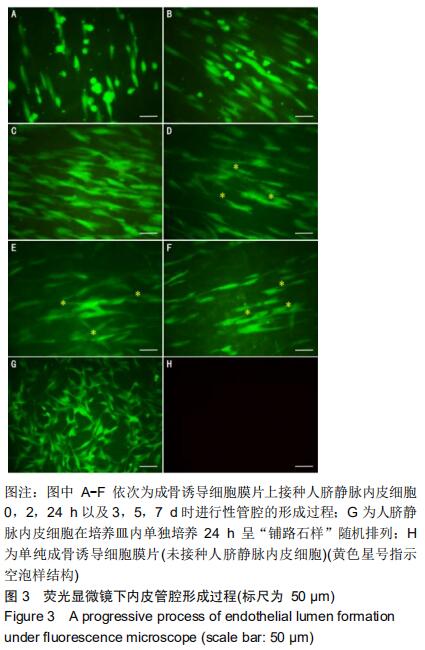
2.3 进行性管腔的形成 倒置相差荧光显微镜下观察成骨诱导细胞膜片接种人脐静脉内皮细胞(5×104/cm2密度)后血管网络结构的进行性形成过程。接种0 h时,内皮细胞呈单个的、形似带足突的圆形,见图3A;接种2 h后,内皮细胞逐渐开始变得细长,见图3B;接种24 h时,人脐静脉内皮细胞在膜片上发生迁移,排列变得有序,见图3C;随时间延长,人脐静脉内皮细胞进一步发生迁移,到第3天时内皮细胞之间互相连接、局部融合,并形成小的空泡样结构,见图3D;接种第7天时,可见细长的分支和细胞间管腔样结构,见图3F。然而, 在培养皿内单纯培养24 h的人脐静脉内皮细胞组则表现出内皮细胞“铺路石样”随机排列,并未发现有类似的改变,见图3G。 "
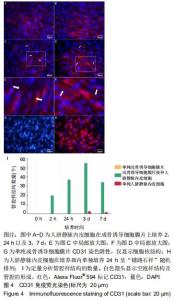
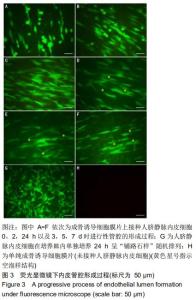
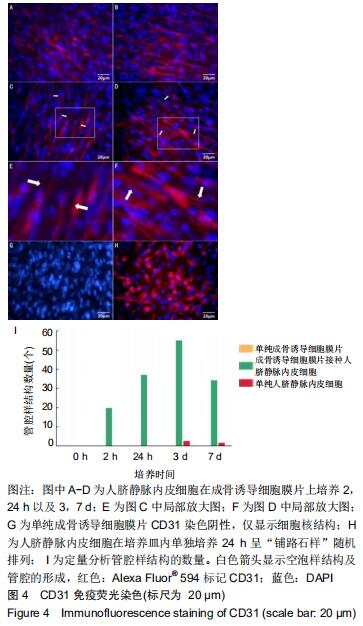
2.4 CD31免疫荧光染色结果 CD31免疫荧光染色检测显示成骨诱导细胞膜片接种人脐静脉内皮细胞后2,24 h以及3,7 d时进行性管腔的形成过程。接种人脐静脉内皮细胞至成骨诱导细胞膜片2 h时,人脐静脉内皮细胞变得细长,见图4A;24 h后,人脐静脉内皮细胞在成骨诱导细胞膜片上发生迁移并动态排列,见图4B;培养至3 d时,人脐静脉内皮细胞发生融合,形成空泡样结构,见图4C,此时形成的管腔样结构数量达最大,见图4I;随时间延长,更多的人脐静脉内皮细胞延长并且动态排列;培养至7 d时,一些空泡开始聚集,见图4D,形成的管腔样结构数量反而下降(P < 0.05)。单纯的成骨诱导细胞膜片(未接种人脐静脉内皮细胞)CD31表达阴性,见图4G;单纯在培养皿内的人脐静脉内皮细胞CD31表达阳性,但是该内皮细胞随机排列,无管网状结构形成,见图4H。 "
|
[1] NAKANO K, MURATA K, OMOKAWA S, et al. Promotion of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis in Vascularized Tissue-Engineered Bone Using Osteogenic Matrix Cell Sheets. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016; 137(5):1476-1484.
[2] MAIA FR, CARVALHO MR, OLIVEIRA JM, et al. Tissue Engineering Strategies for Osteochondral Repair. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1059: 353-371.
[3] BOYCE ST, LALLEY AL. Tissue engineering of skin and regenerative medicine for wound care. Burns Trauma. 2018;6:4.
[4] ASAKAWA N, SHIMIZU T, TSUDA Y, et al. Pre-vascularization of in vitro three-dimensional tissues created by cell sheet engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(14):3903-3909.
[5] 周震,王亚敏,任飞,等.骨髓间充质干细胞膜片和脐静脉内皮细胞共培养模型的构建及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(25): 3951-3955.
[6] LIU X, ZHANG G, HOU C, et al. Vascularized bone tissue formation induced by fiber-reinforced scaffolds cultured with osteoblasts and endothelial cells. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:854917.
[7] ANDERSON SM, SIEGMAN SN, SEGURA T. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) presentation within fibrin matrices on endothelial cell branching. Biomaterials. 2011;32(30):7432-7443.
[8] KOKEMUELLER H, SPALTHOFF S, NOLFF M, et al. Prefabrication of vascularized bioartificial bone grafts in vivo for segmental mandibular reconstruction: experimental pilot study in sheep and first clinical application. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;39(4):379-387.
[9] CHEN W, THEIN-HAN W, WEIR MD, et al. Prevascularization of biofunctional calcium phosphate cement for dental and craniofacial repairs. Dent Mater. 2014;30(5):535-544.
[10] DILLEY RJ, MORRISON WA. Vascularisation to improve translational potential of tissue engineering systems for cardiac repair. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;56:38-46.
[11] YUAN X, TSAI AC, FARRANCE I, et al. Aggregation of Culture Expanded Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Microcarrier-based Bioreactor. Biochem Eng J. 2018;131:39-46.
[12] FU WL, XIANG Z, HUANG FG, et al. Coculture of peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells on strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate scaffolds to generate vascularized engineered bone. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(5-6): 948-959.
[13] HOLNTHONER W, HOHENEGGER K, HUSA AM, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells induce vascular tube formation of outgrowth endothelial cells in a fibrin matrix. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(2):127-136.
[14] GUREL PEKOZER G, TORUN KOSE G, HASIRCI V. Influence of co-culture on osteogenesis and angiogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and aortic endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 2016;108:1-9.
[15] XING F, DUAN X, LIU M, et al. Construction and preliminary study on biological characteristics of composite cell sheets of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells derived from peripheral blood. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(1): 109-115.
[16] OKANO T, YAMADA N, SAKAI H, et al. A novel recovery system for cultured cells using plasma-treated polystyrene dishes grafted with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;27(10): 1243-1251.
[17] KOBAYASHI J, KIKUCHI A, AOYAGI T, et al. Cell sheet tissue engineering: Cell sheet preparation, harvesting/manipulation, and transplantation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(5):955-967.
[18] SATO M, YAMATO M, HAMAHASHI K, et al. Articular cartilage regeneration using cell sheet technology. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014;297(1):36-43.
[19] WANG C, HEI F, JU Z, et al. Differentiation of Urine-Derived Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells. Cell Reprogram. 2016;18(1):30-36.
[20] GAO H, LI B, ZHAO L, et al. Influence of nanotopography on periodontal ligament stem cell functions and cell sheet based periodontal regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:4009-4027.
[21] SASAGAWA T, SHIMIZU T, SEKIYA S, et al. Design of prevascularized three-dimensional cell-dense tissues using a cell sheet stacking manipulation technology. Biomaterials. 2010;31(7):1646-1654.
[22] MASUDA S, MATSUURA K, ANAZAWA M, et al. Formation of vascular network structures within cardiac cell sheets from mouse embryonic stem cells. Regen Ther. 2015;2:6-16.
[23] KADO M, TANAKA R, ARITA K, et al. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells enriched in endothelial progenitor cells via quality and quantity controlled culture accelerate vascularization and wound healing in a porcine wound model. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(7): 1068-1079.
[24] YANG J, YAMATO M, SHIMIZU T, et al. Reconstruction of functional tissues with cell sheet engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28(34): 5033-5043.
[25] SAWA Y, MIYAGAWA S, SAKAGUCHI T, et al. Tissue engineered myoblast sheets improved cardiac function sufficiently to discontinue LVAS in a patient with DCM: report of a case. Surg Today. 2012;42(2): 181-184.
[26] KARPOV AA, UDALOVA DV, PLISS MG, et al. Can the outcomes of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for myocardial infarction be improved? Providing weapons and armour to cells. Cell Prolif. 2017; 50(2):e12316.
[27] FAN Z, LIAO X, TIAN Y, et al. A prevascularized nerve conduit based on a stem cell sheet effectively promotes the repair of transected spinal cord injury. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:304-313.
[28] ZHANG H, LIU S, ZHU B, et al. Composite cell sheet for periodontal regeneration: crosstalk between different types of MSCs in cell sheet facilitates complex periodontal-like tissue regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):168.
[29] YAMAMOTO K, YAMATO M, MORINO T, et al. Middle ear mucosal regeneration by tissue-engineered cell sheet transplantation. NPJ Regen Med. 2017;2:6.
[30] ZHOU Y, CHEN F, HO ST, et al. Combined marrow stromal cell-sheet techniques and high-strength biodegradable composite scaffolds for engineered functional bone grafts. Biomaterials. 2007;28(5):814-824.
[31] CHEN F, ZHOU Y, BARNABAS ST, et al. Engineering tubular bone constructs. J Biomech. 2007;40 Suppl 1:S73-79.
[32] SYED-PICARD FN, LARKIN LM, SHAW CM, et al. Three-dimensional engineered bone from bone marrow stromal cells and their autogenous extracellular matrix. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(1): 187-195.
[33] MA D, REN L, LIU Y, et al. Engineering scaffold-free bone tissue using bone marrow stromal cell sheets. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(5):697-702.
[34] MA D, REN L, YAO H, et al. Locally injection of cell sheet fragments enhances new bone formation in mandibular distraction osteogenesis: a rabbit model. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(7):1082-1088.
[35] ZHANG R, GAO Z, GENG W, et al. Engineering vascularized bone graft with osteogenic and angiogenic lineage differentiated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Artif Organs. 2012;36(12): 1036-1046.
[36] TSIGKOU O, POMERANTSEVA I, SPENCER JA, et al. Engineered vascularized bone grafts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(8): 3311-3316.
[37] BAJPAI VK, ANDREADIS ST. Stem cell sources for vascular tissue engineering and regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18(5): 405-425.
[38] MASCARENHAS S, AVALOS B, ARDOIN SP. An update on stem cell transplantation in autoimmune rheumatologic disorders. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012;12(6):530-540.
[39] LIU Y, MING L, LUO H, et al. Integration of a calcined bovine bone and BMSC-sheet 3D scaffold and the promotion of bone regeneration in large defects. Biomaterials. 2013;34(38):9998-10006.
[40] MENDES LF, PIRRACO RP, SZYMCZYK W, et al. Perivascular-like cells contribute to the stability of the vascular network of osteogenic tissue formed from cell sheet-based constructs. PLoS One. 2012;7(7): e41051.
[41] STOPPATO M, STEVENS HY, CARLETTI E, et al. Influence of scaffold properties on the inter-relationship between human bone marrow derived stromal cells and endothelial cells in pro-osteogenic conditions. Acta Biomater. 2015;25:16-23.
[42] HUANG CC, PAN WY, TSENG MT, et al. Enhancement of cell adhesion, retention, and survival of HUVEC/cbMSC aggregates that are transplanted in ischemic tissues by concurrent delivery of an antioxidant for therapeutic angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2016;74:53-63.
[43] NAGAMORI E, NGO TX, TAKEZAWA Y, et al. Network formation through active migration of human vascular endothelial cells in a multilayered skeletal myoblast sheet. Biomaterials. 2013;34(3): 662-668.
[44] REN L, KANG Y, BROWNE C, et al. Fabrication, vascularization and osteogenic properties of a novel synthetic biomimetic induced membrane for the treatment of large bone defects. Bone. 2014;64: 173-182.
[45] REN L, MA D, LIU B, et al. Preparation of three-dimensional vascularized MSC cell sheet constructs for tissue regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:301279.
[46] KINO-OKA M, NGO TX, NAGAMORI E, et al. Evaluation of vertical cell fluidity in a multilayered sheet of skeletal myoblasts. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012;113(1):128-131.
[47] GARCIA-CARDEÑA G, COMANDER J, ANDERSON KR, et al. Biomechanical activation of vascular endothelium as a determinant of its functional phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(8):4478-4485.
[48] SOUCY PA, ROMER LH. Endothelial cell adhesion, signaling, and morphogenesis in fibroblast-derived matrix. Matrix Biol. 2009;28(5): 273-283.
[49] DEJANA E, LANGUINO LR, POLENTARUTTI N, et al. Interaction between fibrinogen and cultured endothelial cells. Induction of migration and specific binding. J Clin Invest. 1985;75(1):11-18.
[50] SENGER DR, PERRUZZI CA. Cell migration promoted by a potent GRGDS-containing thrombin-cleavage fragment of osteopontin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1314(1-2):13-24.
[51] SENGER DR, PERRUZZI CA, STREIT M, et al. The alpha(1)beta(1) and alpha(2)beta(1) integrins provide critical support for vascular endothelial growth factor signaling, endothelial cell migration, and tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2002;160(1):195-204.
[52] CHEN J, ZHANG D, LI Q, et al. Effect of different cell sheet ECM microenvironment on the formation of vascular network. Tissue Cell. 2016;48(5):442-451.
[53] MALAVAL L, MODROWSKI D, GUPTA AK, et al. Cellular expression of bone-related proteins during in vitro osteogenesis in rat bone marrow stromal cell cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1994;158(3):555-572.
[54] PETERS K, SCHMIDT H, UNGER RE, et al. Software-supported image quantification of angiogenesis in an in vitro culture system: application to studies of biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2002;23(16): 3413-3419.
[55] BOULETREAU PJ, WARREN SM, SPECTOR JA, et al. Hypoxia and VEGF up-regulate BMP-2 mRNA and protein expression in microvascular endothelial cells: implications for fracture healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(7):2384-2397. |
| [1] | Fan Haixia, Tan Qingkun, Wang Hong, Cheng Huanzhi, Liu Xue, Ching-chang Ko, Geng Haixia. Rabbit skull defects repaired by the hydroxyapatite/geltin scaffold combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1495-1499. |
| [2] | Wei Yashu, Liu Hongjing, Wang Huifeng, Wang Junduo, Zhao Wenjing, Chen Weiping. Cardiomyocyte-like differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by myocardial tissue lysates from different parts of the myocardium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 32-37. |
| [3] | Gui Xianwei, Jiang Huijiao, Wu Jie, Liang Xueqi, Xu Xiaodan, Wang Erqiang, Zou Hailiang, Chen Hejie, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Mesenchymal stem cell calcification induced by protoscolex of two species of Echinococcus: a differential analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 38-43. |
| [4] | Ye Dou, , Ma Xuexia , Guan Qian, , Luan Zuo , Yang Yinxiang , Wang Zhaoyan , Wang Qian , He Ying , Yao Ruiqin. Proportion and morphological characteristics of human oligodendrocyte precursor cells in different cell culture vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 44-49. |
| [5] | Gu Jingjing, Zhou Rui, Yang Tingting, Yang Xiaoping, Xu Fei, Zheng Bo. Supporting effect of human skeletal muscle-derived myoendothelial cells on hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 50-55. |
| [6] | Tao Guilu, Chu Tongbin, Zhang Lei. Proliferation and migration of endothelial progenitor cells promoted by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells conditioned medium with rosiglitazone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 56-60. |
| [7] | Zhu Bingbing, He Haibin, Deng Jianghua, Wang Wenqiang, Mu Xiaoling. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin 8 receptor inhibit inflammation and promote vascular repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 61-66. |
| [8] | Jing Yucheng, Wang Le, Wang Xianyun, Wei Mei, Li Min, Ji Lishuang, Ma Fangfang, Liu Gang , Zheng Mingqi. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic heart disease: a 3-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 6-12. |
| [9] | Yu Xingge, Lin Kaili. Application of nanocomposite hydrogels in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5441-5446. |
| [10] | Zhang Huxiong, Li Wei, Yang Wupeng, New Suyaratu. 3D-printed icariin/decalcified bone matrix material promotes the repair of femoral condyle defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5461-5466. |
| [11] | Hua Kunchi, Hu Yongcheng. Defatting effect of gradient alcohol treatment on cancellous bone allograft and the biomechanical properties of defatted cancellous bone allograft [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5502-5507. |
| [12] | Zhou Pengfei, Lin Jing, Chen Yuying, Lin Minkui. Canine dental pulp stem cells-polyglycolic acid scaffold complex for canine periodontal tissue defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5526-5531. |
| [13] | Liu Xin, Du Bin, Sun Guangquan, Cao Jinxing, Jiang Xiaohong. Porous beta-tricalcium phosphate-polypyrrole-biotin-icariin composite scaffold promotes recruitment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5532-5537. |
| [14] | Zhang Shuang, Xu Xiaomei, Zeng Yang, Yuan Xiaoping, Lin Fuwei. Rev-erbα’s effect on osteoblastogenesis of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4921-4926. |
| [15] | Xun Chong, Wang Qiang, Li Changzhou, Liu Xiaofeng. Potential molecular targets and therapeutic mechanisms underlying transplantation of autologous bone marrow stem cells for the treatment of spinal cord injury based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4927-4933. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

