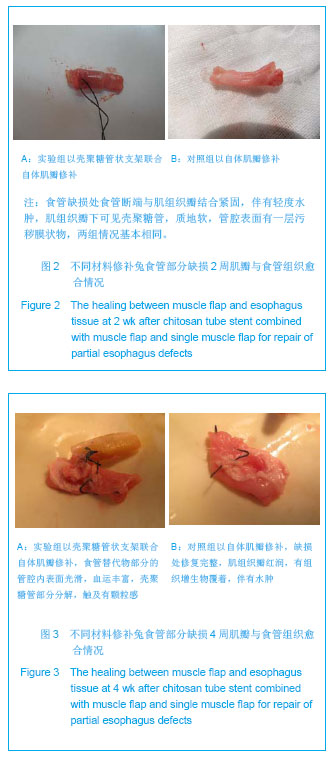
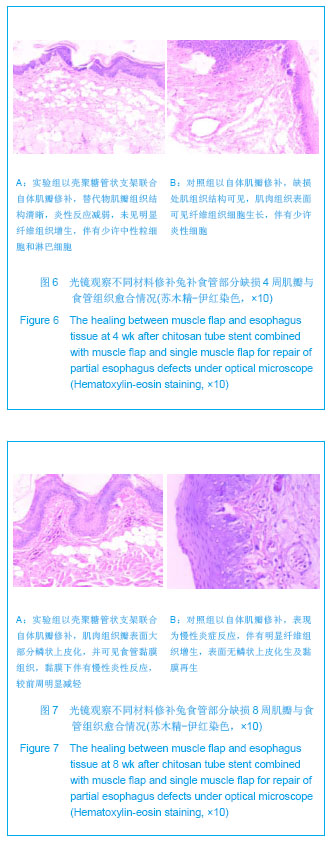
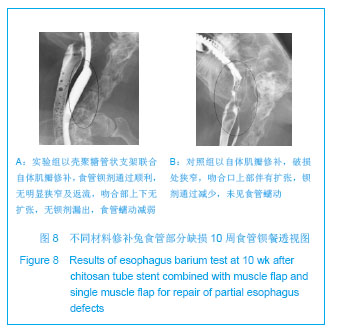
| [1]陈刚,石文君.食管替代物的研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2008,16(34):3855-3858.[2]Shen Q,Shi P,Gao M,et al.Progress on materials and scaffold fabrications applied to esophageal tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(4):1860-1866.[3]D’Journo XB,Martin J,Ferraro P,et al. The esophageal remnant after gastric interposition. Dis Esophagus.2008; 21(5):377-388.[4]Yasuda T,Shiozaki H. Esophageal reconstruction using a pedicled jejunum with microvascular augmentation.Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2011;17(2):103-109.[5]Chen HC,Kuo YR,Hwang TL,et al. Microvascular prefabricated free skin flaps for esophageal reconstruction in difficult patients.Ann Thorac Surg.1999; 67(4):911-916.[6]王如文,蒋耀光,龚太乾,等.颈阔肌皮瓣修复颈部食管狭窄的研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2007,29(9):749-751.[7]蔡英杰,柯孙葵,高惠川,等.肋间肌瓣在自发性食管破裂修补术中的应用[J].福建医科大学学报,2008,42(4):375.[8]韩云,刘军,赵俊刚,等.食管缺损经肺组织瓣和金属支架重建后黏膜爬行的光镜和电镜观察[J].中国医科大学学报,2012,41(5): 399-402.[9]Chen G, Shi WJ.Lung tissue flap repairing esophagus defection with an inner chitosan tube stent. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(12):1512-1517.[10]刘军,石文君,张苏宁,等.犬自体肺组织瓣替代胸段食管部分缺损的实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(5):507-510.[11]陈刚,石文君.简单快速制备壳聚糖支架导管的方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(23):4477.[12]Marks JL, Hofstetter WL.Esophageal reconstruction with alternative conduits. Surg Clin North Am.2012;92(5): 1287-1297.[13]洪志鹏.人工食管的基础研究进展及食管重建术的临床现状[J].昆明医学院学报, 2010,31(11):1-3.[14]智发朝,张兰军,彭秀凡,等.用生物型人工食管进行食管重建的实验研究[J].中华消化杂志,2003,23(3):137-141.[15]张兰军,智发朝,戎铁华,等.生物型人工食管的实验研究[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2001,4(3):157-160.[16]梁建辉,周星,梁显亮.人工食管脱落时间对猪新生食管通道功能形成的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(35):2509-2512.[17]陈宝林,王东安,封麟先,等.生物组织工程及高分子组织工程材料的应用[J].高师理科学刊,2007,27(1):24-26.[18]Saxena AK,Komann C,Ainoedhofer H,et al.Esophagus tissue engineering: Hybrid approach with esophageal epithelium and unidirectional smooth muscle tissue component generation in vitro.J Gastrointest Surg.2009;13(6): 1037-1043.[19]谭波,魏人前,杨志明,等.口腔黏膜上皮细胞与猪小肠黏膜下层体外复合培养的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2010,28(1): 176-180.[20]Kim MS,Ahn HH,Shin YN.An in vivo study of the host tissue response to subcutaneous implantation of PLGA- and/or porcine small intestinal submucosa-bases caffolds. Biomaterials. 2007;28(34):5137-5143.[21]Badylak S,Meurling S,Chen M,et al.Resorbable bioscaffold for esophageal repair in a dog model.Pediatr Surg.2000;35(7): 1097-1103.[22]刘军,石文君,张苏宁.肺组织瓣包埋金属支架重建气管、食管的动物实验研究[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(1):65-68.[23]赵俊刚,张苏宁,石文君,等.自体肺组织瓣内衬记忆合金支架替代长节段气管缺损:动物实验及临床观察[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(22):4209-4212.[24]Jain A, Gulbake A, Shilpi S,et al.A new horizon in modifications of chitosan: syntheses and applications.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst.2013;30(2):91-181.[25]潘炳坤,王挥戈.咽喉颈段食管癌术后节段性(近)环周缺损修复方法[J].中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志,2011,17(1):75-79.[26]吴平安,王先成,董忠根,等.游离股前外侧皮瓣在下咽及颈段食管肿瘤切除后组织缺损修复中的应用[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2009,23(21):961-962.[27]蔡英杰,柯孙葵,高惠川.肋间肌瓣在自发性食管破裂修补术中的应用[J].福建医科大学学报,2008,42(4):375.[28]梁建辉,周星,彭品贤,等.镍钛合金组合式人工食管替代食管的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(14):952-955.[29]张兰军,戎铁华,徐国良,等.改良人工食管结构预防新生食管狭窄[J].中国医学科学院学报,2006,28(3):325-328.[30]张兰军,戎铁华,吴秋良,等.“新生食管”再生过程的组织学观察[J].癌症, 2006,25(6):689-695. |

.jpg)