| [1] Liu C, Shao H, Chen F, et al.Effects of the granularity of raw materials on the hydration and hardening process of calcium phosphate cement.Biomaterials.2003;24(23):4103-4113.
[2] Mainard D, Galois L.Treatment of a solitary calcaneal cyst with endoscopic curettage and percutaneous injection of calcium phosphate cement.J Foot Ankle Surg. 2006;45(6): 436-440.
[3] White E, Shors EC.Biomaterial aspects of Interpore-200 porous hydroxyapatite.Dent Clin North Am. 1986;30(1):49-67.
[4] Chang BS, Lee CK, Hong KS, et al.Osteoconduction at porous hydroxyapatite with various pore configurations. Biomaterials.2000;21(12):1291-1298.
[5] 郭大刚,徐可为,岳进,等.掺锶磷灰石骨水泥浆体的pH值及其固化体的体外细胞毒性评价[J].无机材料学报,2005,20(5): 1159-1166.
[6] Yamada Y, Ueda M.Regenerative medicine for bone using mesenchymal stem cells.Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2006; 43(3):338-341.
[7] GB/T16886.5-2003医疗器械生物学评价第5部分:体外细胞毒性试验.医疗器械生物学评价标准汇编[M].北京:中国标准出版社,2003:80-88.
[8] 陈德敏,傅远飞.不同含锶量的掺锶羟磷灰石陶瓷细胞毒性评价[J].现代口腔医学杂志[J].2003;17(6):501-503.
[9] Zhuang Z, Fujimi TJ, Nakamura M, et al.Development of a,b-plane-oriented hydroxyapatite ceramics as models for living bones and their cell adhesion behavior.Acta Biomater. 2013;9(5):6732-6740.
[10] 郭永锦.含锶磷酸钙骨水泥的改性研究[D].四川:四川大学,2004: 1-5.
[11] Qu Q, Perälä-Heape M, Kapanen A, et al.Estrogen enhances differentiation of osteoblasts in mouse bone marrow culture. Bone. 1998;22(3):201-209.
[12] Majors AK, Boehm CA, Nitto H, et al.Characterization of human bone marrow stromal cells with respect to osteoblastic differentiation.J Orthop Res. 1997;15(4):546-557.
[13] Coelho MJ, Cabral AT, Fernande MH.Human bone cell cultures in biocompatibility testing. Part I: osteoblastic differentiation of serially passaged human bone marrow cells cultured in alpha-MEM and in DMEM.Biomaterials.2000;21(11):1087-1094.
[14] 李峰.含锶磷酸钙骨水泥物理性能及生物相容性评价[D].陕西:第四军医大学,2006:1-5.
[15] 李峰,刘斌,赵信义,等.含锶磷酸钙骨水泥的细胞毒性[J].中国现代医学杂志,2006,16(20):3080-3082.
[16] 李峰,赵信义,吴军正,等.含锶磷酸钙骨水泥生物相容性评价[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2006,26(5):264-268.
[17] 叶冬平,周子强,梁伟国.一种可注射自固化含锶复合胶原磷酸钙骨水泥的结构和性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(38):7411-7416.
[18] 王华,管国平,杨业林,等.含锶羟基磷灰石骨水泥强化动力髋螺钉的极限载荷性能测试[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2011,8(1): 5-7.
[19] 倪国新,吕维加,曲广运,等.锶羟基磷灰石生物活性骨水泥应用于髋关节置换的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(8):708-710.
[20] 邝冠明,刘辉,郑召民,等.生物活性锶羟基磷灰石骨水泥应用于椎体后凸成形术的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(4): 362-366.
|
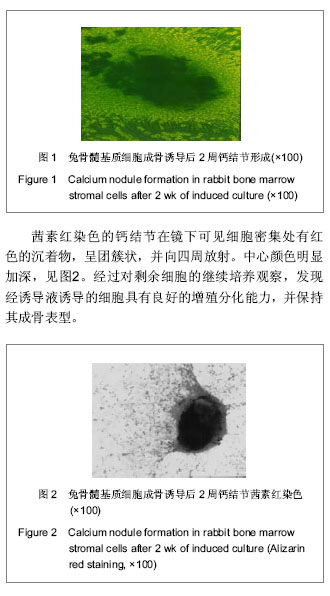


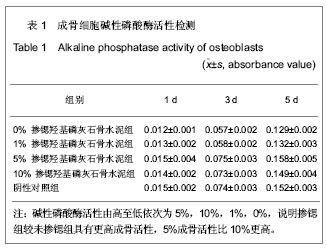
.jpg)
.jpg)