• 组织构建基础实验 basic experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
电针对骶髓损伤后神经源性膀胱容量及其组织形态学的影响
李景兴1,张 泓2,艾 坤2,张雨辰2,匡静之2,鲍秋影2
- 1衡阳市中心医院儿童康复中心,湖南省衡阳市 421000;2湖南中医药大学针灸推拿学院,湖南省长沙市 410208
EIectroacupuncture effects on bladder capacity and tissue morphology of the neurogenical bladder after sacral spinal cord injury
Li Jing-xing1, Zhang Hong2, Ai Kun2, Zhang Yu-chen2, Kuang Jing-zhi2, Bao Qiu-ying2
- 1Rehabilitation Center for Children, Hengyang Central Hospital, Hengyang 421000, Hunan Province, China; 2College of Acupuncture, Moxibustion and Massage, Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410007, Hunan Province, China
摘要:
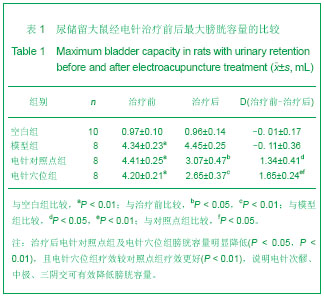
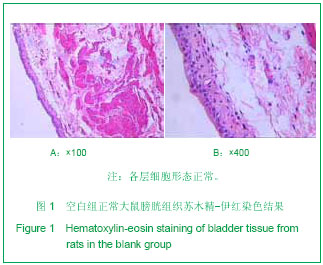
背景:骶段的脊髓和腰椎病变导致脊髓损伤使骶髓初级排尿中枢受损或其周围神经(副交感和体神经)病变引起逼尿肌无反射,会导致尿潴留,进而导致膀胱组织细胞形态学也发生了病理性变化。 目的:观察电针次髎、中极、三阴交穴对骶髓损伤后尿潴留模型大鼠最大膀胱容量及其组织形态学的影响。 方法:SD雌性大鼠40只,随机抽取10只为空白组,其余制备骶髓损伤模型后随机摸球法均分为模型组、电针穴位组和电针对照点组。模型组大鼠只捆绑不针刺,穴位组取大鼠“次髎”、“中极”、“三阴交”,对照点组取非穴对照点,针刺后加电针,均治疗20 min。且所有大鼠在治疗后第14天和第22天行膀胱容量检测,治疗结束后取膀胱组织行苏木精-伊红染色观察大鼠膀胱组织形态学变化。 结果与结论:①电针穴位组最大膀胱容量较治疗前明显降低(P < 0.01),并且较对照点组疗效更明显(P < 0.05),穴位组膀胱容量差值(d值)较对照点组差异更明显(P < 0.05)。②电针穴位组膀胱组织形态学较模型组及对照点组有明显改善。说明电针次髎、中极、三阴交穴可有效降低骶髓损伤后尿潴留大鼠最大膀胱容量并使受损的膀胱组织细胞得到一定程度修复。
中图分类号:

.jpg)