Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (4): 648-656.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.04.027
Prevention of vertebral and non-vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with anti-osteoporosis drugs: a network meta-analysis
Wang Jun, Ma Ting-ting, Zhang Yi-na, Zhang Jin-ping, Guo Jing-xue
- Department of Gerontology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Revised:2014-11-25Online:2015-01-22Published:2015-01-22 -
Contact:Zhang Yi-na, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Gerontology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Wang Jun, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Gerontology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jun, Ma Ting-ting, Zhang Yi-na, Zhang Jin-ping, Guo Jing-xue. Prevention of vertebral and non-vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with anti-osteoporosis drugs: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 648-656.
share this article
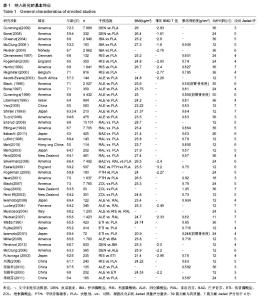
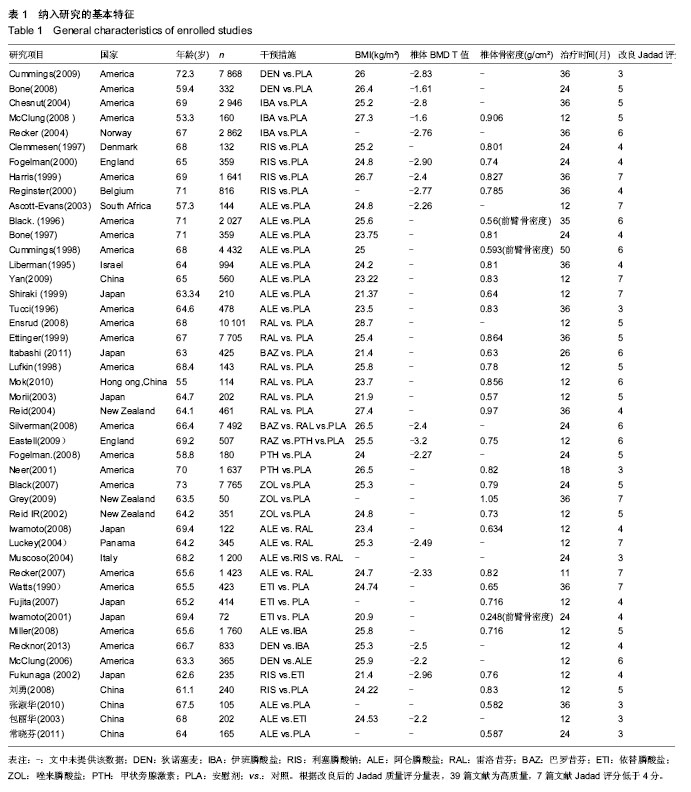
2.2 纳入研究的基本特征 纳入研究的基本特征内容:干预措施、体质量指数、椎体骨密度值、椎骨骨密度的T值及治疗期限。除了2篇文献[27,42],其他文献中提到均不同程度给予患者补充钙剂或维生素D。部分文献没有椎体骨密度和椎体骨密度T值,记录前臂骨密度值,纳入研究的基本特征及质量评价见表1。 2.3 纳入研究的方法学质量评价 42个纳入研究的基线均具有可比性。所有纳入研究均提及“随机”。其按照改良的Jadad量表对文献进行质量评价。根据改良后的Jadad质量评分量表,39篇文献为高质量,7篇文献Jadad评分低于4分[9,25,36,42,51-52,54],见表1。 2.4 椎体及非椎体骨折风险评价 2.4.1 网络Meta分析 椎体骨折风险网络Meta分析显示9种抗骨质疏松药物类药物及安慰剂两两之间的比较结果OR及其95%CI,见表2。"

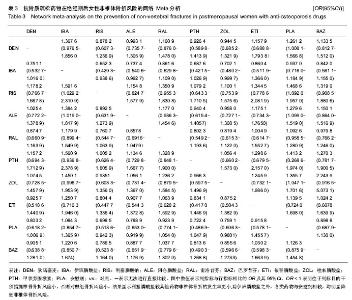
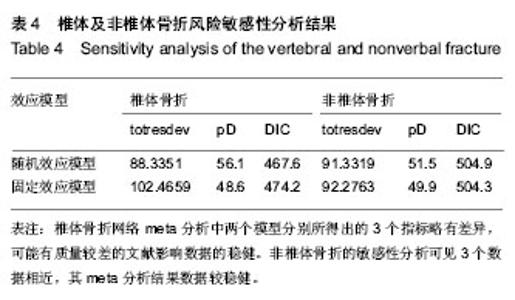
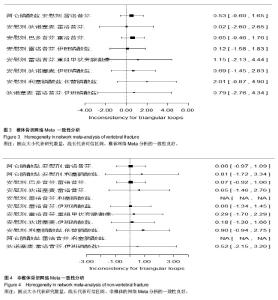
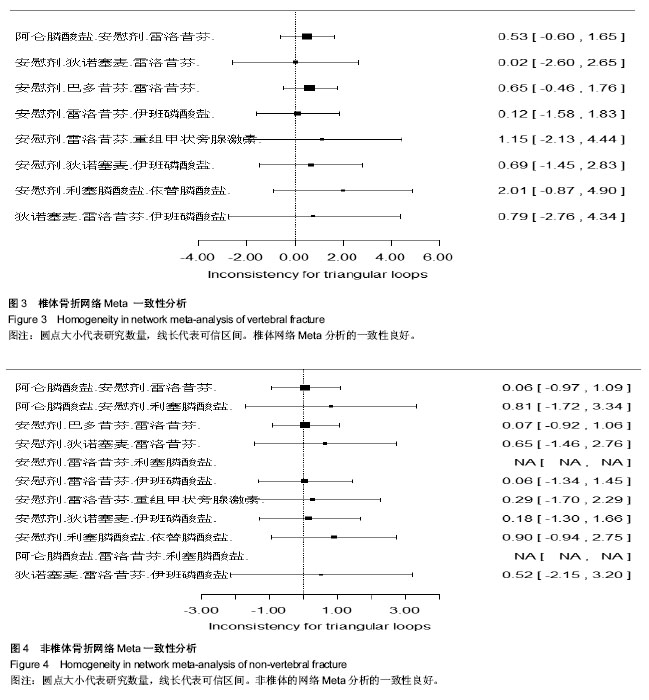
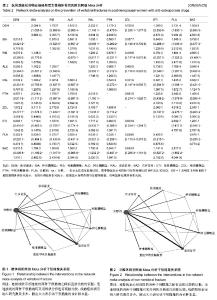
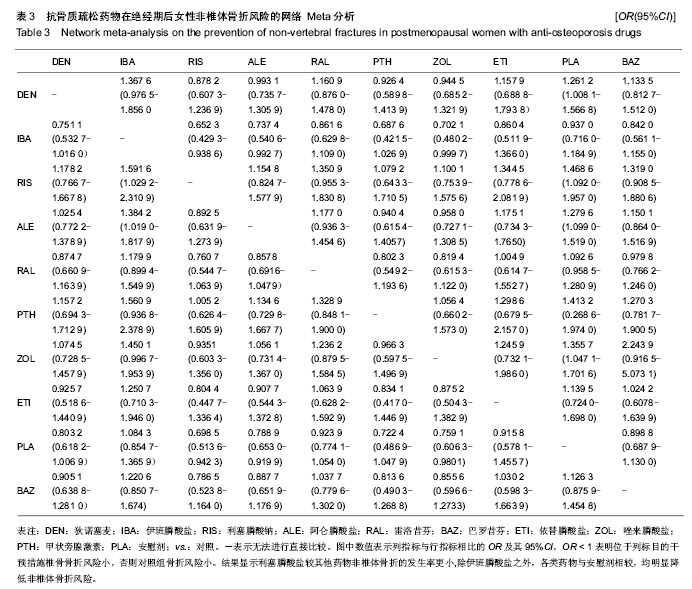
非椎体椎体网络Meta分析结显示比较结果OR及其95%CI见表3。 在椎体骨折风险的Meta分析中,各类药物与安慰剂相较,均明显降低椎体骨折风险。双膦酸盐药物中唑来膦酸盐的预防椎体骨折效果显著,唑来膦酸盐与其他药物进行比较,其次为狄诺塞麦、甲状旁腺激素、依替膦酸盐。伊班膦酸钠在比较中,其预防椎体骨折及非椎体骨折效果最弱。 非椎体骨折网络Meta析结果中,利塞膦酸盐较其他药物非椎体骨折的发生率更小,除伊班膦酸盐之外,各类药物与安慰剂相较,均明显降低非椎体骨折风险。在非椎体骨折的预防中,与安慰剂相较,除伊班膦酸盐外均明显降低椎体骨折风险,利塞膦酸盐的效果最突出,其次为唑来膦酸盐、甲状腺激素、狄诺塞麦。雌激素受体调节剂中,雷洛昔芬和巴多昔芬进行比较,椎体骨折巴多昔芬比雷洛昔芬预防椎体和非椎体骨折效果更好。 本文用了随机效应模型,对于多臂试验也采用了的拆分法。椎体的网络Mmeta干预措施之间关系图见图1,非椎体骨折网络Meta分析干预措施之间关系图见图2。图1和图2中的连接线表示相连接的两种干预措施之间有直接比较的证据,无连接线的两种干预措施可采用网状分析进行间接比较线的粗细表示纳入研究数目多少圆点大小表示该干预措施的合计样本量。 2.4.2 网络Meta模型收敛度检测 利用WinBUGS 1.4.3软件在R 3.0.3软件上建立模型绘制图片检测模型收敛度,椎体网络Meta森林图显示Rhat=1,非椎体网络Meta森林图显示Rhat=1,椎体及非椎体的随机效应模型的收敛度均良好。 2.4.3 网络Meta一致性分析 椎体网络meta一致性分析结果如图3及非椎体网络Meta一致性分析结果如图4显示数据中治疗措施形成三角关系,其可信区间与空白值相交,表明两项网络Meta分析计算所得结果与直接相比较所得的结果无明显差异,一致性较好。圆点大小代表研究数量,线长代表可信区间。椎体网络Meta分析和非椎体的网络Meta分析的一致性良好。 2.4.4 网络Meta敏感性分析 本文分别采用随机效应模型及固定效应模型分别计算totresdev、pD、DIC。以上3个检测指标网络Meta分析数据是否稳健,随机效应模型的以上3个指标分别于固定效应模型结果相近认为数据稳定性较好。 椎体及非椎体敏感性分析结果分别见表4。椎体骨折网络Meta分析中两个模型分别所得出的3个指标略有差异,可能有质量较差的文献影响数据的稳健。非椎体骨折的敏感性分析可见3个数据相近,其Meta分析结果数据较稳健。"
| [1] 王思成,杨雪骅,苏佳灿,等.抗骨质疏松药物临床应用的进展[J].中国组织程研究与临床康复,2009,13(46):9163-9166.
[2] Jadad AR,Moore RA,Carroll D,et al.Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials:is blinding necessary. Control Trails.1996;17(1):1.
[3] Jansen JP,Crawford B,Bergman G,et al.Bayesian meta-analysis of multiple treatment comparisons: an introduction to mixed treatment comparisons.Value Health. 2008;11(5):956-964
[4] 张天嵩,钟文昭.实用循证医学方法学[M].长沙:2012:433-442.
[5] 董圣杰,冷卫东,田家祥,等.Meta分析系列之五:贝叶斯Meta分析与WinBUGS软件[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(5): 395-398.
[6] 罗杰,冷卫东.系统评价/Meta分析理论与实践[M].北京:2013: 495-506.
[7] 曾宪涛,张超,郭毅.R软件R2WinBUGS程序包在网状Meta分析中的应用[J].中国循证医学杂志,2013,13(9):1137-1144.
[8] 张超,徐畅,曾宪涛.网状Meta分析中网状关系图的绘制[J].中国循证医学杂志,2013,13(11):1382-1386.
[9] Cummings SR, Martin JS, McClung MR,et al.Denosumab for Prevention of Fractures in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis.N Engl J Med.2009;361(8):756-765.
[10] Bone HG, Bolognese MA,Yuen CK, et al.Effects of Denosumab on Bone Mineral Density and Bone Turnover in Postmenopausal Women.Clin Endocrinol Metab.2008;93(6): 2149-2157.
[11] Chesnut IC,Skag A,Christiansen C,et al.Effects of oral ibandronate administered daily or intermittently on fracture risk in postmenopausal osteoporosis.Bone Miner Res.2004; 19:1241-1249.
[12] McClung MR, Bolognese MA, Sedarati F, et al. Efficacy and safety of monthly oral ibandronate in the prevention of postmenopausal bone loss.Bone.2009;44:418-422.
[13] Recker R,Stakkestad JA,Chesnut CH,Ⅲ, et al.Insufficiently dosed intravenous ibandronate iigections are associated with suboptimal antifracture efficacy in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bone.34:890-899.
[14] Clemmesen B, Ravn P, Zegels B, et al. A 2-year phaseⅡ study with 1-year of follow-up of risedronate (NE-58095) in postmenopausal osteoporosis.Osteoporos Int.1997;7: 488-495.
[15] Fogelman I,Ribot C, Smith R, Ethgen D, et al. Risedronate reverses bone loss in postmenopausal women with low bone mass: results from a multinational, double-blind, placebo- controlled trial BMD-MN Study Groiqx.Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(5):1895-1900.
[16] Harris ST, Watts NB, Genant HK, et al. Effects of risedronate treatment on vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. Vertebral Efficacy With Risedronate Therapy (VERT) Study Group. JAMA.1999;282(14):1344-1352.
[17] Reginster JY, Minne HW, Sorensen OH, et al. Randomized trial of the effects of risedronate on vertebral fractures in women with established Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.2000;11:83-91.
[18] Ascott-Evans BH, Guanabens N, Kivinen S, et al.Alendronate prevents loss of bone density associated with discontinuation of hormone replacement therapy: a randomized controlled trial.Arch Intern Med.2003;163:789-794.
[19] Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, et al.Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures.Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet.1996;348:1535-1541.
[20] Bone HG, Downs RW Jr, Tucci JR, et al.Dose-response relationships for alendronate treatment in osteoporotic elderly women.Alendronate Elderly Osteoporosis Study Centers.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.1997;82(1):265-274.
[21] Cummings SR, Black DM, Thompson DE, et al. Effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with low bone density but without vertebral fractures:results from the Fracture Intervention Trial. JAMA.1998;280:2077-2082.
[22] Liberman UA, Weiss SR, Broll J, et al .Effect of oral alendronate on bone mineral density and the incidence of fractures in postmenopausal osteoporosis. The Alendronate Phase Ⅲ Osteoporosis Treatment Study Group.N Engl J Med.1995;333(22):1437-1443.
[23] Yan Y,Wang W,Zhu H,et al.The efficacy and tolerability of once-weekly alendronate 70 mg on bone mineral density and bone turnover markers in postmenopausal Chinese women with osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27: 471-478.
[24] Shiraki M, Kushida K, Fukunaga M,et al.A double-masked multicenter comparative study between alendronate and alfacalcidol in Japanese patients with osteoporosis. The Alendronate Phase Ⅲ Osteoporosis Treatment Research Group.Osteoporos Int. 1999;10:183-192.
[25] Tucci JR,Tonino RP,Emkey RD, et al.Effect of three years of oral alendronate treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.Am J Med.1996;101:488-501.
[26] Eastell R,Nickelsen T,Marin F,et al.Sequential treatment of severe postmenopausal osteoporosis after teriparatide: final results of the randomized, controlled European Study of Forsteo(EUROFORS).J Bone Miner Res.2009;24(4):726-736.
[27] Ensrud KE, Stock JL, Barrett-CE,et al. Effects of raloxifene on fracture risk in postmenopausal women: The raloxifene use for the heart trial.J Bone Miner Res.2008;23(1): 112-120.
[28] Ettinger B,Black DM, Mitlak BH, et al. Reduction of Vertebral Fracture Risk in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis Treated With Raloxifene: Results From a 3-Year Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA.1999;282(7):637-645.
[29] Itabashi A, Yoh K, Chines AA, et al. Effects of bazedoxifene on bone mineral density, bone turnover, and safety in postmenopausal Japanese women with osteoporosis.J Bone Miner Res.2011;26(3):519-529.
[30] Luflcin EQ,Whitaker MD, Nickelsen T, et al.Treatment of established postmenopausal osteoporosis with raloxifene: a randomized trial.Bone Miner Res.1998;13(11): 1747-1754.
[31] Mok CC,Ying KY,To CH,et al.Raloxifene for prevention of glucocorticoid-induced bone loss:A 12-month randomised double-blinded placebo-controlled trial.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70(5):778-784.
[32] Morii H, Ohashi Y, Taketani Y,et al.Effect of raloxifene on bone mineral density and biochemical markers of bone turnover in Japanese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from a randomized placebo-controlied trial.Osteoporos Int. 2003; 14:793-800.
[33] Reid IR, Eastell R, Fogelman I, et al. A conparison of the effects of raloxifene and conjugated equine estrogen on bone and lipids in healthy postmenopausal women.Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:871-879.
[34] Silverman SL, Christiansen C, Genant HK, et al. Efficacy of bazedoxifene in reducing new vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from a 3-year, randomized, placebo, and active-controlled clinical trial. Bone Miner Res.2008;23(12):1923-1934.
[35] Fogelman I,Fordham JN, Fraser WD,et al.Fox J.Parathyroid hormone(l-84) treatment of postmenopausal women with low bone mass receiving hormone replacement therapy.Calcified Tissue International. 2008;83:85-92.
[36] Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR, et al. Effect of parathyroid hormone (1-34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.N Engl J Med.2001;344(19):1434-1441.
[37] Black D, Delmas S, Eastell R, et al. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. NEJM. 2007;356(18):1809-1822.
[38] Grey A, Bolland MJ,Wattie D, et al. The antiresorptive effects of a single dose of zoledronate persist for two years; A randomized, placebo-controlled trial in osteopenic postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94(2): 538-544.
[39] Reid IR,Brown JP,Burckhardt P,et al.Intravenous zoledronic acid in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med 2002;346(9):653-661.
[40] Iwamoto J,Sato Y, Uzawa M,et al. Comparison of Effects of Alendronate and Raloxifene on Lumbar Bone Mineral Density, Bone Turnover , and Lipid Metabolism in Elderly Women with Osteoporosi.Yonsei Med.2008;49(1):119-128.
[41] Luckey M, Kagan R,Greenspan S,et al.Once-weekly alendronate 70mg and raloxifene 60 mg daily in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.Menopause. 2004;11(4): 405-415.
[42] Muscoso E, Puglisi N, Mamazza C, et al. Antiresorption therapy and reduction in fracture susceptibility in the osteoporotfc elderly patient: open study.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2004;8:97-102.
[43] Recker R, Kendler D,Recknor CP, et al.Comparative effects of raloxifene and alendronate on fracture outcomes in postmenopausal women with low bone mass.Bone.2007; 40(4):843-851.
[44] Watts NB, Harris ST, Genant HK, et al.Intermittent cyclical etidronate treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.N Engl J Med.1990;323(2):73-79.
[45] Fujita T, Orimo H, Inoue T, et al. Clinical effect of bisphosphonate and vitamin D on osteoporosis:reappraisal of a multicenter double-blind clinical trial comparing etidronate and alfacalcidol.Bone Miner Metab.2007;25:130-137.
[46] Iwamoto J,Takeda T,Ichimura S. Effect of menatetrenone on bone mineral density and incidence of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: a comparison with the effect of etidronate.Orthop Sci.2001;6:487-492.
[47] Miller PD,Epstein S,Sedarati F, et al. Once-monthly oral ibandronate compared with weekly oral alendronate in postmenopausal osteoporosis: results from the head-to-head MOTION study.Curruent Reasrch and Opionion.2008;24(1): 207-213.
[48] Recknor C, Czerwinski,E, Bone HG,et al.Denosumab Compared With Ibandronate in Postmenopausal Women Previously Treated With Bisphosphonate Therapy.Obstet Gynecol.2013;121(6):1291-1299.
[49] McClung MR, Lewiecki EM, Cohen SB, et al. Denosumab in Postmenopausal Women with Low Bone Mineral Density.N Engl J Med.2006;354(8):821-831.
[50] Fukunaga M,Kushida K,Kishimoto H,et al.A comparison of the effect of risedronate and etidronate on lumbar bone mineral density in Japanese patients with osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial.Osteoporos Int.2002;13:971-979.
[51] 常晓芬,温广华.阿仑膦酸钠对绝经后妇女骨质疏松症治疗机骨折的预防作用[J].山西医科大学学报,2011,42(6):494-496.
[52] 张淑华,程佳芬,李文君,等.阿伦膦酸钠对绝经后妇女骨折的预防作用[J].同济大学学报:医学版,2010,31(2):51-54.
[53] 刘勇,樊继援,陈德才,等.利塞膦酸钠片防治绝经后骨质疏松症的有效应和完全性研究[C].广州:第十一次全国临床药理学学术大会,2008:284-286.
[54] 包丽华,林华,李建华, 等.二膦酸盐治疗对骨质疏松性骨痛、骨密度、骨强度的疗效及安全性[J].中华老年医学杂志,2003,22(11): 81-91.
[55] Kevin Grogan. EMA panel recommends pulling plug on Servier's Protelos.WORLD NEWS.2014,1.12.
[56] Jansen JP, Bergman GJ, Huels J, et al. The efficacy of bisphosphonates in the prevention of vertebral, hip, and nonvertebral-nonhip fractures in osteoporosis: a network meta-analysis.Semin Arthritis Rheum.2011;40(4): 275-284. e1-2.
[57] Freemantle N, Cooper C, Diez-Perez A, et al.Results of indirect and mixed treatment comparison of fracture efficacy for osteoporosis treatments:a meta-analysis.Osteoporos Int.2013;24(1):209-217.
[58] Ellis AG, Reginster JY, Luo X, et al. Indirect comparison of bazedoxifene vs oral bisphosphonates for the prevention of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal osteoporotic women. Curr Med Res Opin.2014;30(8):1617-1626.
[59] Ellis AG, Reginster JY, Luo X, et al. Bazedoxifene versus oral bisphosphonates for the prevention of nonvertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at higher risk of fracture: a network meta-analysis.Value Health.2014; 17(4): 424-432.
[60] 全会标,高勇义.利塞膦酸钠临床研究进展[J].医学综述,2007, 13(1):66-68. |
| [1] | Wang Ling, Zhao Hong-xia, Hua Qiang. Percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous kyphoplasty and expansive pedicle screw fixation for repairing primary osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 350-355. |
| [2] | Song Quan-sheng, Tang Fu-bo, Wang Xiao-hu, Zhang Jia-li, Li Zhi-fei, Rao Yuan-sen, Wu Liang, Tai Zhi-hong, Qin Hai-biao, Xu Jian-wen. Relationship between the lumbar quantitative computed tomography values and contrast agent dispersion in osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3051-3056. |
| [3] | Ren Rong, Li Ling-wei, Guo Qi-fa. Feasibility of implantation of a cemented femoral stem in the treatment of osteoporotic femoral neck fracture in elderly patients: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7261-7266. |
| [4] | Xu Can, Li Ming-qing, Wang Cheng-gong, Li Kang-hua, Liu Hua. Research progress of bone microarchitecture and microdamage detection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6673-6681. |
| [5] | Zhang Yan, Yang Qiu-ping, Zhao Yan, Zhao Yu-mei, Tan Hong, Du Si-cheng. Establishing a rat model of type 2 diabetes: its bone metabolism level [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6041-6047. |
| [6] | Wei Jun-qiang, Liu Li-rui, Wang Xin-yu, Yan Shi, Jin Yu, Feng Zhen. Proximal femoral nail antirotation fixation for osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly: characteristics of deep venous thrombosis of lower extremity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5224-5230. |
| [7] | Zhang Yi-long, Ren Lei, Sun Zhi-jie, Wang Ya-hui, Sun He. New vertebral compression fractures after vertebroplasty: association with osteoporosis and spinal sagittal imbalances [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5263-5269. |
| [8] | Li Shi-hong, Liu Yang. Measurement of bone metabolism markers and changes of bone mineral density in patients with bone and joint disease and fractures in perioperative period [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5290-5295. |
| [9] | Wu Jian-jun. Biocompatibility of Sextant minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation for osteoporotic vertebral fractures in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4603-1609. |
| [10] | Ning Xu, Zhuang Yong, Liu Miao, Zhang Hao, Huang Ming-zhi. Biomechanical properties of lower anterior vertebral pedicle screw system and its effects on osteoporotic vertebral stability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4665-4670. |
| [11] | Liu Yang, Liu Dan, Xiao Yun-xiang, Chen Hai-dan, Zhao Hong-wei. Biomechanical properties of a novel pourable cement pedicle screw and its application to osteoporotic lumbar degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4671-4676. |
| [12] | Yu Hai-ming, Li Yi-zhong, Yao Xue-dong, Lin Jin-kuang, Pan Yuan-cheng, Zhuang Hua-feng,Wang Pei-wen. Percutaneous vertebroplasty or percutaneous kyphoplasty for Kummell’s disease with vertebral posterior wall collapse: how to treat individually? [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(26): 3856-3862. |
| [13] | Ren Zhi-shuai, Cheng Zhao-jun, Sun He-jun, Sun Zhen-hui, Cui Zi-jian, Zhang Li-long, Lin Yong-zhi, Zhang Ren-zan, Peng Bing, Zhang Xue-li. Osteoporosis-related factors in patients with knee osteoarthritis before total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3212-3218. |
| [14] | Huang Cheng-long, Xiao Jin-gang. Osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells on a composite scaffold in the repair of osteoporotic bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6696-6702. |
| [15] | Liang Jing, Zhou Qi, Wei Li, Hu Fang-qiong, Wang Jun. Specific gene expression of osteoclasts under different oxygen tension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(29): 4695-4700. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||