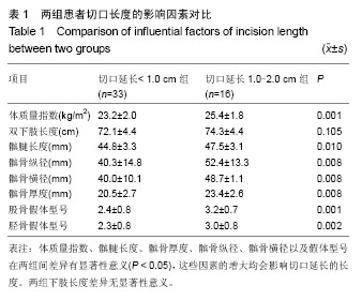
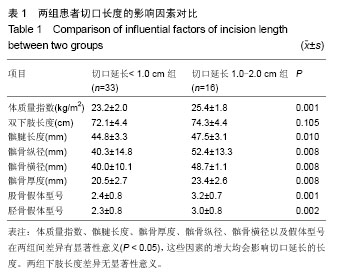
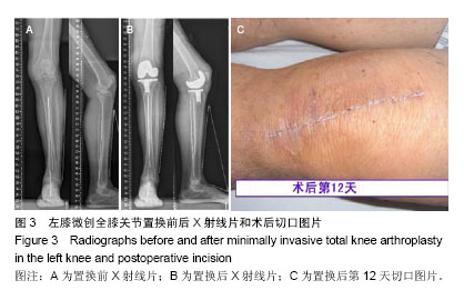
| [1] Robertsson O, Scott G, Freeman MA. Ten-year survival of the cemented Freeman-Samuelson primary knee arthroplasty. Data from the Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register and the Royal London Hospital. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(4): 506-507.
[2] Nilsdotter AK, Toksvig-Larsen S, Roos EM. Knee arthroplasty: are patients' expectations fulfilled? A prospective study of pain and function in 102 patients with 5-year follow-up. Acta Orthop. 2009;80(1):55-61.
[3] Noble PC, Conditt MA, Cook KF, et al. The John Insall Award: Patient expectations affect satisfaction with total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;452:35-43.
[4] Tria AJ Jr. Exploring the depths of minimally invasive quadriceps-sparing total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2006; 29(3):214-215.
[5] Fisher DA, Watts M, Davis KE. Implant position in knee surgery: a comparison of minimally invasive, open unicompartmental, and total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(7 Suppl 1): 2-8.
[6] Fuchs S, Rolauffs B, Plaumann T, et al. Clinical and functional results after the rehabilitation period in minimally-invasive unicondylar knee arthroplasty patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2005;13(3):179-186.
[7] Goble EM, Justin DF. Minimally invasive total knee replacement: principles and technique. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004;35(2): 235-245.
[8] Costa CR, Johnson AJ, Harwin SF, et al. Critical review of minimally invasive approaches in knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2013;26(1):41-50.
[9] 高英健,王伟力.微创膝关节置换的临床应用现状[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(39):6985-6990.
[10] 张勇,陈建民,王黎明,等.微创全膝关节置换术治疗膝骨性关节炎的早期临床疗效研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,28(10): 963-965.
[11] Cho KY, Kim KI, Umrani S, et al. Better quadriceps recovery after minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(8):1759-1764.
[12] Kim JG, Lee SW, Ha JK, et al. The effectiveness of minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty to preserve quadriceps strength: a randomized controlled trial. Knee.2011; 18(6): 443-447.
[13] Berger RA, Sanders S, Gerlinger T, et al. Outpatient total knee arthroplasty with a minimally invasive technique. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(7 Suppl 3):33-38.
[14] Haas SB, Cook S, Beksac B. Minimally invasive total knee replacement through a mini midvastus approach: a comparative study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(428): 68-73.
[15] Tashiro Y, Miura H, Matsuda S, et al. Minimally invasive versus standard approach in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;463:144-150.
[16] Wegrzyn J, Parratte S, Coleman-Wood K, et al. The John Insall award: no benefit of minimally invasive TKA on gait and strength outcomes: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):46-55.
[17] Dalury DF, Dennis DA. Mini-incision total knee arthroplasty can increase risk of component malalignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;440:77-81.
[18] Deirmengian CA, Lonner JH. What's new in adult reconstructive knee surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(2):182-188.
[19] Deirmengian CA, Lonner JH. What's new in adult reconstructive knee surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92(16):2753-2764.
[20] He P, Zhu Q, Zhang Z, et al. Relationship between the tibial mechanical axis and bony anatomical landmarks of the calf and foot as measured on radiographs obtained with a new laser-calibrated position. J Xray Sci Technol. 2013;21(4): 497-506.
[21] 朱琦,徐栋梁,何沛恒,等.正常中国南方汉族青年第2跖骨干轴线与踝关节中心的关系:激光瞄准定位可重复标准体位下肢X射线照片分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(22):4062-4066.
[22] Guy SP, Farndon MA, Conroy JL, et al. A prospective randomised study of minimally invasive midvastus total knee arthroplasty compared with standard total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2012;19(6):866-871.
[23] Costa CR, Johnson AJ, Harwin SF, et al. Critical review of minimally invasive approaches in knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2013;26(1):41-50.
[24] 王志强,黄伟,梁熙,等.微创与传统入路对全膝关节置换术后早期股四头肌肌力的影响[J].中华骨科杂志, 2013,33(12): 1204-1211.
[25] 王志强,黄伟,梁熙,等. 微创与传统膝关节置换术失血量比较[J].中华创伤杂志, 2013,29(1):38-42.
[26] 李灿锋,曾羿,沈彬,等. Quadriceps-Sparing入路与传统入路全膝关节置换术临床疗效的Meta分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2013,7(6):844-851.
[27] Granchi D, Cenni E, Giunti A, et al. Metal hypersensitivity testing in patients undergoing joint replacement: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(8):1126-1134.
[28] Yin ZG, Zhang JB, Kan SL, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of imaging modalities for suspected scaphoid fractures: meta-analysis combined with latent class analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(8):1077-1085.
[29] Tria AJ Jr. Minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty: the importance of instrumentation. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004; 35(2):227-234.
[30] Tria AJ Jr. Minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty: past, present, and future. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2007;36 (9 Suppl):6-7.
[31] Pongcharoen B, Yakampor T, Charoencholvanish K. Patellar tracking and anterior knee pain are similar after medial parapatellar and midvastus approaches in minimally invasive TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(5):1654-1660.
[32] Martin A, Sheinkop MB, Langhenry MM, et al. Comparison of two minimally invasive implantation instrument-sets for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(3):359-366.
[33] Rodriguez HA. Mini-incision total knee arthroplasty can increase risk of component malalignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;449:320; author reply 320.
[34] Niki Y. Comparison of two minimally invasive implantation instrument-sets for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(9):1608-1609; author reply 1610-1611.
[35] Adams J, Ryall C, Pandyan A, et al. Proximal interphalangeal joint replacement in patients with arthritis of the hand: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(10): 1305-1312.
[36] Roue J, de Thomasson E, Carlier AM, et al. [Influence of body mass index on outcome of total hip arthroplasty via a minimally invasive anterior approach]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2007;93(2):165-170.
[37] Laskin RS. Minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty: the results justify its use. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;440:54-59. |