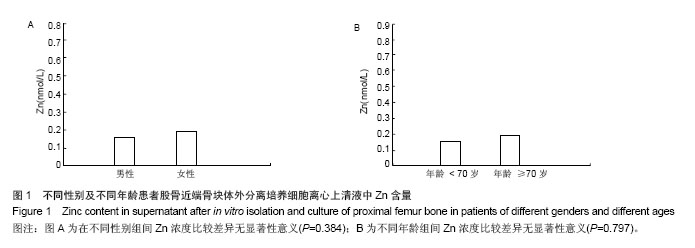
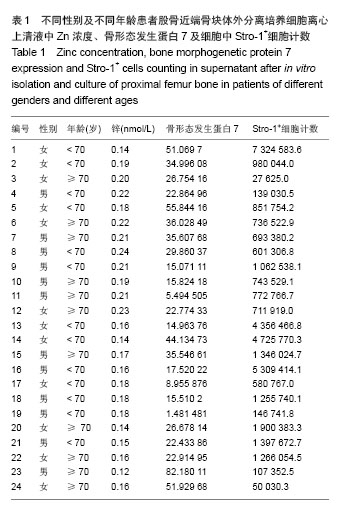
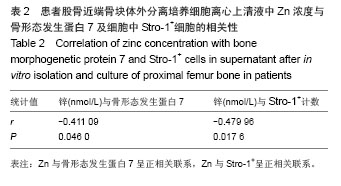
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (44): 7061-7065.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.44.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation of trace element zinc with bone morphogenetic protein 7 and Stro-1+ cells in proximal femur: predicting hip prosthesis life
Fu Xiao-dong, Wang Wei-li, Shen Yi, Li Xiao-miao
- Department of Orthopedics, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200127, China
-
Online:2014-10-22Published:2014-10-22 -
Contact:Wang Wei-li, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200127, China -
About author:Fu Xiao-dong, Master, Department of Orthopedics, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200127, China -
Supported by:the Health Science and Technology Project of Shanghai Pudong New District Health Bureau, No. PW2012D-2.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fu Xiao-dong, Wang Wei-li, Shen Yi, Li Xiao-miao. Correlation of trace element zinc with bone morphogenetic protein 7 and Stro-1+ cells in proximal femur: predicting hip prosthesis life[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(44): 7061-7065.
share this article
| [1]Caton JH, Prudhon JL,Ferreira A,et al. A comparative and retrospective study of three hundred and twenty primary Charnley type hip replacements with a minimum follow up of ten years to assess wether a dual mobility cup has a decreased dislocation risk.Int Orthop. 2014;38(6):1125-1129. [2]Berry DJ, Harmsen WS, Cabanela ME,et al.Twenty-five-year survivorship of two thousand consecutive primary Charnley total hip replacements: factors affecting survivorship of acetabular and femoral components.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(2):171-177. [3]Bidwell JP, Alvarez MB, Hood M Jr, et al.Functional impairment of bone formation in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis: the bone marrow regenerative competence. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2013;11(2):117-125. [4]Zhang L, Peng LP, Wu N, et al.Development of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell culture in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(9):1650-1655. [5]Persani L, Rossetti R, Di Pasquale E, et al.The fundamental role of bone morphogenetic protein 15 in ovarian function and its involvement in female fertility disorders. Hum Reprod Update. 2014 Jun 30. pii: dmu036. [6]商亚徽,赵宝红.锌对成骨细胞生物学作用研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2013,6(10):629-633. [7]Qiao Y, Zhang W, Tian P, et al.Stimulation of bone growth following zinc incorporation into biomaterials. 2014;35(25): 6882-6897. [8]Luo X, Barbieri D, Davison N, et al.Zinc in calcium phosphate mediates bone induction: in vitro and in vivo model.Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):477-485. [9]沈奕,李晓淼,傅晓东,等,股骨近端Stro-1+细胞与骨形态发生蛋白及其受体的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(45) : 8380-8384. [10]Vignon E, Valat JP, Rossignol M, et al. Osteoarthritis of the knee and hip and activity: a systematic international review and synthesis (OASIS).Joint Bone Spine. 2006;73(4): 442-455. [11]Caviglia HA1, Osorio PQ, Comando D.Classification and diagnosis of intracapsular fractures of the proximal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(399):17-27. [12]柳向东,柴冈,李东,等,成人骨髓间充值干细胞的体外培养和表型鉴定[J].上海第二医科大学学报,2004,4(24):300-301. [13]Mäkelä KT, Matilainen M, Pulkkinen P, et al. Countrywise results of total hip replacement. An analysis of 438,733 hips based on the Nordic ArthroplastyRegister Association database.Acta Orthop. 2014;85(2):107-116. [14]Lombardi AV Jr.Case studies in management of THA failure secondary to taper corrosion, modular junctions and metal-on-metal bearings.J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(4):663-667. [15]French TH, Russell N, Pillai A..The diagnostic accuracy of radionuclide arthrography for prosthetic loosening in hipand knee arthroplasty.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:693436. [16]Prokopetz JJ, Losina E, Bliss RL, et al.Risk factors for revision of primary total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:251. [17]Ruetze M, Richter W.Adipose-derived stromal cells for osteoarticular repair: trophic function versus stem cell activity.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2014;16:e9. [18]Bianco P, Kuznetsov SA, Riminucci M, et al. Postnatal skeletal stem cells. Methods Enzymol 2006; 419:117-148. [19]Kim IS, Song YM, Cho TH, et al. In vitro response of primary human bone marrow stromal cells to recombinant human bone morphogenic protein-2 in the early and late stages of osteoblast differentiation. Dev Growth Differ 2008; 50: 553-564. [20]Boden SD.The ABCs of BMPs. Orthop Nurs. 2005;24(1): 49-52; quiz 53-4. [21]Otto WR, Rao J.Tomorrow's skeleton staff: mesenchymal stem cells and the repair of bone and cartilage. Cell Prolif. 2004;37(1):97-110. [22]Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR.Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors. 2004;22(4):233-241. [23]Wan M, Cao X.BMP signaling in skeletal development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(3):651-657. [24]Lee JT, Jung JW, Choi JY, et al.Enhanced bone morphogenic protein adenoviral gene delivery to bone marrow stromal cells using magnetic nanoparticle.J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;39(3):112-119. [25]Glynn ER, Londono AS, Zinn SA, et al.Culture conditions for equine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expression of key transcription factors during their differentiation into osteoblasts.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2013;4(1):40. [26]Kaigler D, Krebsbach PH, West ER, et al.Endothelial cell modulation of bone marrow stromal cell osteogenicpotential. FASEB J. 2005;19(6):665-667. [27]Wang C, Wang X, Xu XL, et al.Bone microstructure and regional distribution of osteoblast and osteoclast activity in the osteonecrotic femoral head.PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96361. [28]Nam J, Perera P, Rath B, et al.Dynamic regulation of bone morphogenetic proteins in engineered osteochondral constructs by biomechanical stimulation.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(5-6):783-792. [29]Alam N, St-Arnaud R, Lauzier D, et al.Are endogenous BMPs necessary for bone healing during distraction osteogenesis? Clin Orthop Relat es.2009;467(12):3190-3198. [30]Friedlaender GE, Perry CR, Cole JD, et al.Osteogenic protein-1 (bone morphogenetic protein-7) in the treatment of tibialnonunions.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83-A Suppl 1 S151-S158. [31]Nishi Y.Zinc and growth.J Am CollNutr. 1996;15(4):340-344. [32]Yamaguchi M, Uchiyama S. Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand-stimulated osteoclastogenesis in mouse marrow culture is suppressed by zinc in vitro.IntJ Mol Med. 2004;(1): 81-85. [33]Yamaguchi M, Uchiyama S.Combination of beta-cryptoxanthin and zinc has potent effects on apoptotic cell death and suppression of bone resorption-related gene expression in osteoclasticcells.Int J Mol Med. 2008;22(2): 221-228. |
| [1] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [2] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [3] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [4] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [5] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [6] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [7] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [8] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [9] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [10] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [11] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [12] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [15] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||