Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (20): 3257-3262.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.20.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanism of osteoclast, bone resorption and fracture healing by V-ATPase a3 transport system
Song Min1, Dong Wan-tao2, Chen Bing-hu3, Chai Ju-tang1, Li Yan-long3, Wei Hong3, Chen Bing-xiong1, 3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730020, Gansu Province, China; 3People’s Hospital of Lintao County, Dingxi 730500, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2014-03-31Online:2014-05-14Published:2014-05-14 -
Contact:Chen Bing-xiong, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; People’s Hospital of Lintao County, Dingxi 730500, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Song Min, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81360554; Clinical Research Special Funds by Wu Jieping Medical Foundation, No. 320.6750.11061; Science and Technology Project for Youth of Gansu Province, No. 1208RJYA066
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Min, Dong Wan-tao, Chen Bing-hu, Chai Ju-tang, Li Yan-long, Wei Hong, Chen Bing-xiong. Molecular mechanism of osteoclast, bone resorption and fracture healing by V-ATPase a3 transport system[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(20): 3257-3262.
share this article

2.1 V-ATPase a3基因蛋白、破骨细胞的功能及生物学意义真核细胞中的阳离子转运ATPase有3种,其中V-ATPase存在于细胞质膜和细胞器膜上,位于细胞质膜上的V-ATPase参与正常生理及疾病的过程,如破骨细胞皱褶缘上V-ATPase参与骨吸收;位于细胞器膜上的V-ATPase维持细胞器的酸性环境,对于受体介导的内吞噬非常关键[1-2]。V-ATPase主要有2个结构域V0和V1,V0结构域是质子转运的通道,V1结构域主要是水解ATP供能[2]。ATPase a3基因产物为相对分子质量 116 000的蛋白(a3),是破骨细胞空泡型质子泵(空泡型氢离子三磷酸腺苷转运酶Vacuolar H+-translocatiing,ATP-ase,简称V-ATPase)跨膜部分之一,V-ATPase活化后将H+分泌到细胞外而完成骨吸收功能[3]。 ATPase a3基因编码的蛋白作为一种酶,能够水解ATP,并能利用ATP水解释放出的能量驱动物质跨膜运输,把H+转输到细胞外,破骨细胞在H+作用下完成骨的吸收(图1)。"

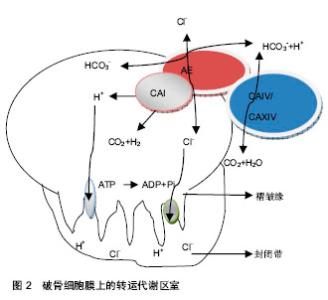
a3是V-ATPase的异构体,全部集中存在于破骨细胞皱褶缘上,是功能性破骨细胞的必需成分[4]。a3亚基的表达随破骨细胞核数的增加而增多,是V-ATPase的关键性亚基,由V-ATPase基因调控,是功能性破骨细胞的必需成分[3]。位于破骨细胞膜上的质子转运系统V-ATPase a3,水解ATP产生能量,逆浓度梯度转运H+跨膜转运的能量系统。为破骨细胞创造酸性环境,可见V-ATPase a3在破骨细胞骨吸收中不可或缺[5]。 破骨细胞起源于造血干细胞,是一种高度分化的多核巨细胞,也是在骨折愈合过程执行骨吸收的唯一细胞类型。在1,25(OH)2D3以及白细胞以及白细胞介素(白细胞介素1,3)等细胞因子的作用下,分化为成熟的破骨细胞[6]。其分化过程主要被基质/成骨细胞及来源于它们的巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(C-MSF)与核因子κB受体活化因子配体调控[7]。即RNAKL信号与破骨细胞前体细胞膜上的RANK结合,将信号传递与TRAF6,通过NIK和IKK活化核因子κB,活化核因子кB迅速与IKK分离进入细胞核,使c-Fos的高表达,c-Fos进一步与活化的T细胞核因子结合并相互作用,启动相应的靶基因的表达和转录,最终诱导成熟破骨细胞的形成。 在破骨细胞表面有许多标志性受体,如降钙素受体(CTR)、抗酒石酸磷酸酶(TRAP)、Ⅱ型碳酸酐酶、组织蛋白酶K及Vitornectin受体(CR)等[8]。破骨细胞膜上有质子泵,主要是空泡型质子泵。此外破骨细胞含有极其丰富的酸性磷酸酶、溶酶体酶、组织蛋白酶等,主要存在于粗面内质网、高尔基体中。 破骨细胞在骨吸收与骨的重建中起启动作用,附着于骨面形成骨吸收的微小环境,合成并释放水解酶和酸,终始骨矿溶解,骨胶原纤维的降解[9]。破骨细胞通过其质膜上的空泡型分泌分解骨结构中的矿物质,并通过分泌多种水解酶降解有机骨基质,通过各种细胞间的相互作用,以及多种细胞因子的调控,执行骨吸收。 破骨细胞细胞膜表面由许多不规则的绒毛状突起,可以增加与骨组织的接触面积,并且这些绒毛状的突起可以合成和释放酸与酶等多种生物活性物质,其在绒毛部位的空破区,是骨吸收的重要组成部分。其中碳酸酐酶在骨吸收中起极为重要的作用,释放的酸主要是通过Ⅱ型碳酸酐酶将CO2溶于水中形成H2CO3再次水解成H+和HCO3-。再通过H+离子泵转运出细胞[10]。H+离子泵主要为泡状型H+-ATP酶(ATPase),将该酶活化将H+离子源源不断的转运出细胞[11]。 破骨细胞皱褶缘上存在V-ATPase转运系统可以创造酸性环境,这种酸性环境可以使羟磷灰石降解并激活cathepsin K消化胶原的酶,从而促进骨吸收,阻止V-ATPase转运系统的功能可以抑制骨吸收,以V-ATPase转运系统作为靶点,为代谢性骨病的防治提供新思路[12]。 破骨细胞拥有独特的高度特化的质子产生机制及协同转运装置,还能分泌胶原酶和其他在骨基质蛋白降解中有活性的水解酶来快速溶解矿物质。为成骨细胞、软骨细胞、内皮细胞等参与骨骼的重建细胞体系提供一种微环境。在正常状态下维系骨骼的动态平衡,在骨折时参与骨折的重塑,恢复骨骼的生物力学结构。 2.2 V-ATPase a3转运系统在骨吸收的作用 创伤骨折伴随在人们的生活中,治疗技术正在日新月异的完善,但是骨折愈合与重建机制仍需要研究阐明。骨折愈合重建机制包括启动过程,参与的细胞,重建的参与细胞,修复中参与的细胞因子,修复过程的终止原理[13-14]。人体即使没有发生骨折,也时时刻刻发生着骨结构的改造和重建。而发生骨折中改建机制也非常重要,在这中改建机制破骨细胞扮演着非常重要的角色。 V-ATPase a3基因蛋白在破骨细胞发生破骨与改建机制中起主要作用。其包括大量的破骨细胞活化,募集在骨折端,合成水解酶与酸,进行骨吸收,在骨吸收后连接成骨细胞完成修复过程。破骨细胞在骨吸收过程必须依赖酸性环境,V-ATPase a3基因蛋白水解ATP产生能量,质子泵在这种能量的驱使下,将H+转运到细胞外,破骨细胞和水解酶在酸性环境下进行骨吸收。在研究中制备编码V-ATPase a3转运系统缺失的小鼠,小鼠的破骨细胞数目正常,在骨吸收过程中不能形成陷窝,破骨细胞不能形成细胞外的酸化环境,不能形成酸化腔,也不能降解骨结构中矿物质,从而是小鼠出现骨质硬化[15]。V-ATPase a3转运系统在破骨细胞执行骨吸收中不可或缺,该基因发生突变或缺失是婴儿骨硬化并发生以及胚胎死亡的主要原因[16]。 破骨细胞在骨吸收过程中,包括骨矿物质的溶解,与其细胞膜上的质子泵—空泡型H+离子三磷酸腺苷酸酶(V-ATPase)密切相关,其功能是分泌酸,创造酸性环境中,使其矿物质溶解[17]。空泡型H+离子三磷酸腺苷酸酶中的编码跨膜通道116kDa亚基的基因,水解ATP产生能量,将H+转运出细胞外,对破骨细胞的功能的发挥在骨吸收中具有决定性意义[18]。 吴承亮等[16]在实验中发现地塞米松+右归饮血清组与生路盐水和地塞米松+对照血清组有显著差异,从而得出右归饮具有阻止V-ATPase a3转运系统,起到抑制破骨细胞的作用。破骨细胞皱褶缘上V-ATPase a3转运系统在局部富集,分泌H+到细胞外形成酸性环境。酸性代谢产物和溶酶体酶的释放有利于酸性环境的维持[19]。 破骨细胞是骨吸收主要执行细胞,在骨重建中也起关键作用。在正常的生理状态下,维持骨骼的动态平衡。骨折后在骨折愈合在重塑期,破骨细胞分泌大量的偶联因子(鞘氨醇1磷酸、肝细胞生长因子等)分泌[20-21],促使成骨细胞和破骨细胞聚集在骨折端,从而使骨折端形成的新骨通过成骨细胞和破骨细胞偶联完成骨折的重塑,骨的重建都按着数学法则,使骨的内部结构和外表形态适应其载荷环境的变化。 2.3 V-ATPase a3转运系统在骨折愈合中的作用 在骨折愈合后期,原始骨痂形成后,内外骨痂及桥梁骨痂得进一步改建,骨折端的死骨经过爬行营代过程,新生血管伴成骨细胞和破骨细胞的侵入,死骨被清除,排列再乱的骨小梁趋于规律,以及哈佛系统的重建,幼稚的交织骨变成熟的板层骨,使骨质更加坚固。在这骨痂的改建过程中,破骨细胞在担当着非常重要的作用。 当组织细胞受到外界刺激时细胞因子产生,刺激活化破骨细胞,使大量的破骨细胞聚集、趋化及附着于改建的的骨表面。破骨细胞的细胞膜皱褶缘与骨基质共同形成一个密闭的骨吸收的微环境,完成骨吸收及骨细胞性骨溶解[20-21]。 破骨细胞主要功能是骨吸收,在维持骨折后骨痂的改建、正常的骨骼动态平衡中是必需的。从破骨细胞的活化开始,随之细胞骨架结构发生重组、细胞极性的改变以及出现特定的骨吸收膜区域[22]。在骨吸收过程中,破骨细胞褶皱缘形成一个特殊的环状密封区域,存在于褶皱缘上的V-ATPase a3转运系统,将胞内H+转运到密闭腔隙,提供酸性环境,促使无机物移动,并为水解酶提供酸性环境,完成骨骼的重建。 在骨痂的塑型期,破骨细胞与成骨细胞在骨外表面上是骨的吸收或者沉积,在内部结构上是改变骨组织的体积密度,加强或再吸收骨组织的内部结构。以优化的形态和结构完成自身的重建,无论其在几何形态还是内部结构上都与承载环境充分适应。 V-ATPase a3转运系统的主要功能是将H+转运出细胞外,处于静止状态破骨细胞的V-ATPase a3转运系统位于胞浆的空泡膜系统,当破骨细胞活化时黏附于骨表面,致使其结构骨架发生改变,空泡膜系统向附近的细胞膜表面移行并与之融合[23],募集在破骨细胞表面的皱褶缘上,将Ⅱ型碳酸酐酶水解成H+和HCO3-在V-ATPase a3转运系统的作用下,转运出细胞生成酸性环境,有利于无机质和胶原纤维的降解。V-ATPase a3转运系统营造酸化的环境,是骨中无机物移动,暴露出有机成分(Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型胶原纤维),随后被组织蛋白酶K降解[13-14];分布于破骨细胞皱褶缘上V- ATPase a3转运系统将H+转运到微环境中,再通过非能量依赖性交换机制分泌Cl-维持细胞内外的电荷平衡,使破骨细胞处于酸性的微环境中[24](图2)。破骨细胞膜上的高表达IV型碳酸酐酶、XIV型碳酸酐酶,支持破骨细胞膜上的AE蛋白、碳酸酐酶形成转运代谢区室。 矿物质在酸性微环境中被溶解,有机成分在水解酶的作用下降解,降解后的产物被破骨细胞吞噬排泄后,破骨细胞从骨表面脱离后重新转移到新的位点[25]。破骨细胞分解无机骨基质与H+有关。H+的产生由Ⅱ型碳酸酐酶催化产生,由V- ATPase a3转运系统转运。H+通过以下反应溶解无极骨基质,Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2+ 8H+→6HPO42-+10Ca2++2H2O所形成的Ca2+和磷酸经细胞外液进入血液[26]。"

| [1] Niilura K.Vacuolar ATPase as a drug discovery.Drug News Perspect.2006;19(3):139-144. [2] 游海燕,邓云,覃文新.V-ATPases 的功能及其抑制剂研究进展[J].生命科学,2009,21(4): 499-504. [3] 杜文喜,肖鲁伟,吴承亮,等.两种不同培养方法对破骨细胞ATPase a3基因表达和骨吸收活性的影响[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2009,33(1):29-31. [4] 吴鹰,沈志强.破骨细胞空泡型质子泵及其抑制剂的研究进展[J].国外医学:药学分册,2005,32(3):188-191. [5] Cipriano DJ,Wang Y,Bond S,et al.Structure and regulation of the vacuolar ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1777(7-8): 599-604. [6] 孟祥阁.破骨细胞分化的信号转导系统[J].科协论坛,2009,1: 75-76. [7] Lacey DL,Timms E,Tan HL,et al.Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell.2008;93(2):165-176. [8] 赵晴潇,何爱民.破骨细胞分化发育中的信号转导及转录因子研究进展[J].山东医药,2009, 49(19):111-113. [9] 黄怡,李玉冲.破骨细胞功能与形成相关调节因子研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2009,30(1):51-53. [10] 陈建庭,张忠民,金大地,等.血小板衍生生长因子-AA对破骨细胞功能的影响[J].中华外科杂志,2010,38(6):465-467. [11] Nordstron T,Shrode LD,Rotstein OD,et al.Chronic extracellular acidosis induces plasmalemmal vacuolar type H+ ATPase activity in osteoclasts.J Biol Chem.2007;272: 6354-6360. [12] Beutler JA,McKee TC.Novel marine and microbial natural product inhibitors of vacuolar ATPase.Curr Med Chem. 2003; 10(9):787-796. [13] Zhao Q,Shao J,Chen W,et al.Osteoclast differentiation and gene regulation.Front Biosci.2007;12:2519-2529 [14] 刘振东,马梦然.骨折愈合理论研究现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2010,18(16):1402-1405. [15] Li YP,Chen W,Liang Y,et al. Atp6i deficient mice exhibit severe osteopetrosis due to loss of osteoclast-me-diated extracellular acidification.Nat genet.2009; 23(4):447-451. [16] Xu J,Cheng T,Feng HT,et al.Structure and function of V-ATPases in osteoclasts: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of osteolysis.Histol Histopathol. 2007,22(4): 443-445. [17] 吴承亮,李陶冶,吴俊生,等.右归饮对体外培养破骨细胞分化与功能的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2010,28(2):304-307. [18] Rousselle AV,Heymann D.Osteoclastic acidification pathways during bone resorption.Bone.2007;30:533-540. [19] 高建军,王洪复.破骨细胞成熟和活化以及骨吸收机制[J].国外医学:内分泌学分册, 2007;18(2):57-61. [20] Ryu J,Kim HJ,Chang EJ,et al.Kim Sphingosine 1-phosphate as a regulast differentiation and osteoclast-osteoblast coupling. EMBO J.2006;25(24):5840-5851. [21] 苏佳灿,许硕贵,张春才.骨重建中细胞因子的作用及机制[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008, 8(6):593-595. [22] 狄升蒙,田宗成,高翔,等.破骨细胞研究进展[J].细胞生物学杂志, 2009,31(6):792-798. [23] 扈英伟,于世凤.破骨细胞质子泵调控的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,7(1): 88-90. [24] Schlesinger PH,Blair HC,Teitelbaum SL,et al.Characterization of the Osteoclast Ruffled Border Channel and Its Role in Bone Resorption.J Biol Chem.2007;272(6): 18636-18643. [25] 刘继中,胡藴玉.破骨细胞骨吸收机制的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,9(4): 401-402. [26] 文剑明,郑铭豪.破骨细胞的形成、功能及细胞因子的调节[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,1998, 4(1):64-67. [27] Manolson MF,Yu H,Chen W,en al.The a3 isoform of the 100kDa V-ATPase a3 subunit is highly but differentially expressed in large(≥10nuclei) and small (≤5nuclei) osteoclasts.J Biol Chen.2008;278(49):49271-49278. [28] Ramanan R,Kannan K,Sivanesan SD,et al.Bio-sequestration of carbon dioxide using carbonic anhydrase enzyme purified from Citrobacter freundii.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009; 25(6):981-987. [29] Xu J,Feng HT,Wang C,et al.Effects of bafilomycin A1:aninhibitor of vacuolar H+-ATPases on endocytosis and apoptosis in RAW cells and RAW cell-derived osteoclasts.J Cell Biochem.2003;88(6):1256-1264. [30] Zhao C,Irie N,Takada Y,et al. Bidirectional ephrinB2-EphB4 signaling controls bone homeostasis.Cell Metabolism. 2006; 4(2):111-121. [31] Matsumoto N, Daido S, Sun-Wada GH,et al.Diversity of proton pumps in osteoclasts: V-ATPase with a3 and d2 isoforms is a major form in osteoclasts.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1837(6):744-749. [32] Ochotny N, Voronov I, Owen C,et al.The R740S mutation in the V-ATPase a3 subunit results in osteoclast apoptosis and defective early-stage autophagy.J Cell Biochem. 2013;114 (12): 2823-2833. [33] Crasto GJ, Kartner N, Yao Y, et al.Luteolin inhibition of V-ATPase a3-d2 interaction decreases osteoclast resorptive activity.J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(4):929-941. [34] Voronov I, Ochotny N, Jaumouillé V, et al.The R740S mutation in the V-ATPase a3 subunit increases lysosomal pH, impairs NFATc1 translocation, and decreases in vitro osteoclastogenesis.J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(1):108-118. [35] Thudium CS, Jensen VK, Karsdal MA, et al.Disruption of the V-ATPase functionality as a way to uncouple bone formation and resorption - a novel target for treatment of osteoporosis. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012;13(2):141-151. [36] Ochotny N, Flenniken AM, Owen C, et al.The V-ATPase a3 subunit mutation R740S is dominant negative and results in osteopetrosis in mice.J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(7):1484- 1493. [37] Nyman JK, Väänänen HK.A rationale for osteoclast selectivity of inhibiting the lysosomal V-ATPase a3 isoform.Calcif Tissue Int. 2010;87(3):273-283. [38] Ochotny N, Van Vliet A, Chan N, et al.Effects of human a3 and a4 mutations that result in osteopetrosis and distal renal tubular acidosis on yeast V-ATPase expression and activity.J Biol Chem. 2006;281(36):26102-26111. [39] Bhargava A, Voronov I, Wang Y,et al.Osteopetrosis mutation R444L causes endoplasmic reticulum retention and misprocessing of vacuolar H+-ATPase a3 subunit.J Biol Chem. 2012;287(32):26829-26839. [40] Kartner N, Yao Y, Li K,et al.Inhibition of osteoclast bone resorption by disrupting vacuolar H+-ATPase a3-B2 subunit interaction.J Biol Chem. 2010;285(48):37476-37490. [41] Serrano EM, Ricofort RD, Zuo J,et al.Regulation of vacuolar H(+)-ATPase in microglia by RANKL.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;389(1):193-197. [42] Xu J, Cheng T, Feng HT,et al.Structure and function of V-ATPases in osteoclasts: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of osteolysis.Histol Histopathol. 2007;22(4):443- 454. |
| [1] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [2] | Cheng Shigao, , Wang Wanchun, Jiang Dong, Li Tengfei, Li Xun, Ren Lian. Comparison of the standard and long-stem bone cement prosthesis replacement in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 362-367. |
| [3] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [4] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [5] | Jiang Shengyuan, Li Dan, Jiang Jianhao, Shang-you Yang, Yang Shuye. Biological response of Co2+ to preosteoblasts during aseptic loosening of the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [6] | Mao Guoshu, Zhou Min, Li Xiaoming, Zhou Zihong, Yin Qudong. Effect of the third fragment on the healing of femoral shaft fractures after intramedullary nailing fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2405-2409. |
| [7] | Wu Yukun, Han Jie, Wen Shuaibo. Mechanism of Runx2 gene in fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2274-2279. |
| [8] | Wu Shengxiang, Liu Yuan, Lu Shuai. Mini-locking titanium plate system fixation in the treatment of carpal scaphoid fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1874-1878. |
| [9] | Xu Nuo, Cao Zhen, Li Xiaojie, Shi Chun. MicroRNA-21 regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoclasts in periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1225-1230. |
| [10] | Xu Shaoce, Wang Shiyao, Zhou Jianwei, Pan Yixin, Wang Yuliang. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 regulation and mechanism in callus formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1083-1088. |
| [11] | Liu Zhendong, Qin Sihe. Four-dimensional space events of fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 903-910. |
| [12] | Ge Juncheng, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Sun Wei, Wang Weiguo, Guo Wanshou, Li Zirong. Application of bisphosphonates in avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 753-759. |
| [13] | Zhang Yanan, Yan Xia, Meng Zengdong. Zn and Mg increase the bioactivity and osteogenic induction of hydroxyapatite biomaterial in bone repair: clinical application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 606-611. |
| [14] | Zhang Chao, Li Xingyong, Ma Guifu, Pu Xingyu, Luo Wenyuan. Hoxa9 silencing promotes tibial fracture healing by regulating osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5600-5606. |
| [15] | Li Yanqiang, Pan Deyue, Nan Feng, Han Xin. Treatment of senile osteoporotic patella fractures with double tension band [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5338-5342. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||