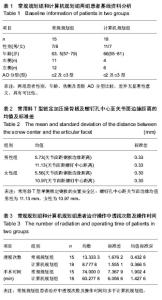
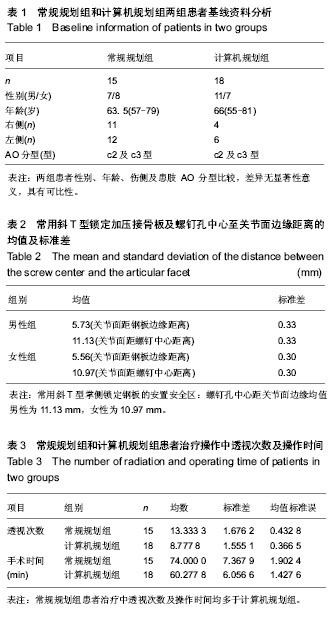
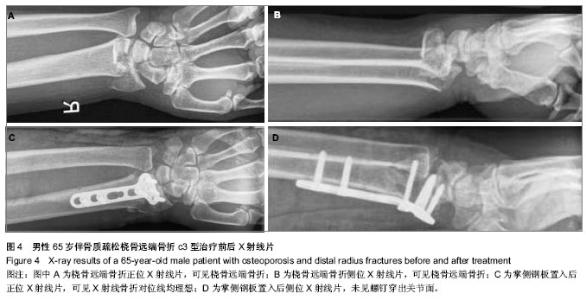
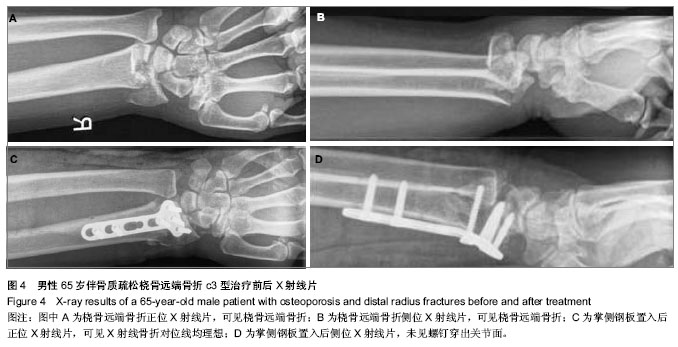
| [1] Handl DP, Jones MD, Tremble TE. Treatment of Complex Fracture Wrist Fractures. Orthop Clin of North Am. 2002; 33(1):35-38.[2] 张殿英,姜保国,傅中国,等.斜T型锁定加压接骨板治疗桡骨远端骨折的临床研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2004,20(11):24-26.[3] 姜保国,张殿英,付中国,等.桡骨远端骨折的治疗建议[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12:1053-1056.[4] Wong KK, Chan KW, Kwok TK, et al.Volar fixation of dorasally displaced distal radial frcture using locking compression plate. J orthop Surg.2005;13:155-157.[5] 郝光亮,郝永强,晏焕青,等.老年髋部骨折的住院治疗费用分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2008,14(3):200-203.[6] 胡明,冯孟明,黄凤山,等.椎体成形联合椎弓根钉棒系统治疗中老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(10): 899-902.[7] 钱增杰,张长虹,陈庚,等.椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折15例体会[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(3):230-231.[8] 赵强.掌侧角钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端骨折的影像学分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012, 27(3):270-271.[9] 雷荣福,洪华,董凯.桡骨远端掌侧锁定钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012,27(7):648-648.[10] 熊湘彦.普通钢板与锁定钢板治疗老年桡骨远端粉碎骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012, 27(1):69-70.[11] Lozano-Calderón SA, Souer S, Mudgal C, et al. Wrist Mobilization Following Volar Plate Fixiation of Fractures of the Distal Part of the Radius, J of Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:1297-1304.[12] 陈国辉,土井一辉,顾立强,等.桡骨远端关节内骨折的分类与关节镜下复位固定[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(10):1168-1170.[13] 陆建华,王志刚,黄莉.应用数字骨科技术获取腰椎双皮质椎弓根螺钉的置入参数[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(52):9732- 9736.[14] 冯飞,李七渝,米俊达.腕关节的三维可视化研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2006,14(17):1331-1333.[15] 颜冰珊,尹望平,聂文忠.正常下尺桡关节三维有限元模型的建立及验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(17): 3135-3138.[16] 董俊文,李锐,张为众,等.应用三维建模有限元方法定位分析腕舟骨肿物及切除后的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2006,10(16):73-75.[17] 黄若昆,谢鸣,余嘉,等.虚拟现实技术应用于髋部骨折手术仿真的建立[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(13):2383-2389.[18] 宫福良,李杰,范钦波,等.三种不同方法治疗桡骨远端不稳定骨折的功能对比研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,9,842-843.[19] Wilcke MK, Abbaszadegan H, Adolphson PY. Wrist function recovers more rapidly after volar locked plating than after external fixation but the outcomes are similar after 1 year. Acta Orthop.2011;82(1):76-81.[20] Neal C Chen, Jesse B Jupiter. Managements of Distal Radial Fractures. J of Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:2051-2062.[21] Thomas W, Mary B. Functional outcome of unstable distal radius fracture: ORIF with a volar fixed-angle Tine late versus external fixation. J Hand Surg (Am). 2005;30:289-290.[22] Jupiter JB, Marent-Huber M,LCP Study Group.Operative Management of Distal Radial Fractures with 2.4-Millimeter Locking plates: A Multicenter Prospective Case Series: Surgical Technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010; 92:96-106.[23] Mallee W, Doornberg JN, Ring D, et al. Comparison of CT and MRI for Diagnosis of Suspected Scaphoid Fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:20-28.[24] 杜玉勇,尹芸生,薛晓峰,等.构建并验证儿童肱骨髁上骨折三维有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(22):4265-4269.[25] 王光达,张柞福,齐晓军,等.膝关节三维有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(52):9702-9705. |