Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Treatment strategies and biomechanical analysis for ulna coracoid process fractures
Liu Ren-hao1, Zhou Nan2, Bi Zheng-gang1
- 1First Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Land Reclamation Bureau General Hospital of Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150088, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2013-06-13Revised:2013-06-16Online:2013-10-22Published:2013-11-02 -
Contact:Bi Zheng-gang, First Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China bizhenggang@54dr.com -
About author:Liu Ren-hao★, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, First Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China liurenhao_1@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Ren-hao, Zhou Nan, Bi Zheng-gang . Treatment strategies and biomechanical analysis for ulna coracoid process fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
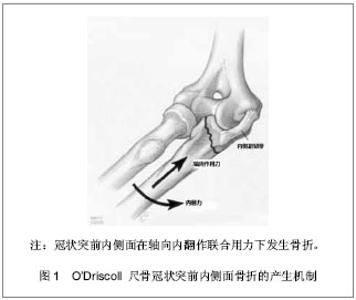
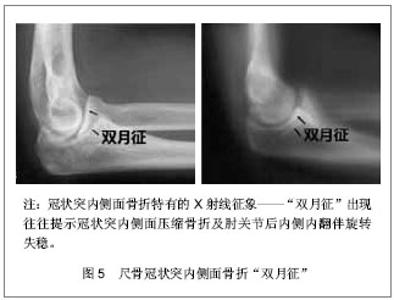
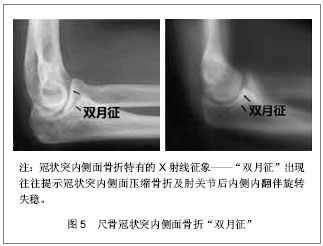
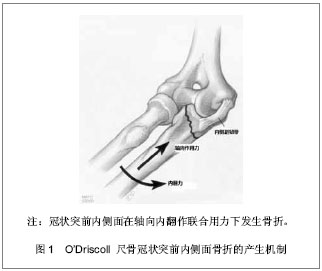
2.1 纳入研究基本概况 纳入的45篇文献包括尺骨冠状突骨折临床回顾性研究文章25篇,模拟冠状突骨折的试验性研究文章8篇,尺骨冠状突解剖学及生物力学研究性文章5篇,冠状突骨折治疗方法的对照性研究文章7篇。 2.2 解剖学及生物力学 尺骨冠状突是肘关节重要的骨性稳定结构,冠状突的解剖存在相当于肘关节前方支持扶璧,在肘关节屈伸运动中维持轴向稳定并防止发生脱位和内外翻失稳。 冠状突由尖部、体部、基底部组成,在体部和基底部内缘向内延伸出一骨性结构称为冠状突前内侧面,其上有内侧副韧带前束止点(高耸结节),具有重要的抗内翻作用。 前关节囊止点附丽在冠状突尖部远端约5.9 mm处,肱肌肌腱止点距冠状突尖部约12.1 mm[1]。 冠状突和附丽在其上的软组织结构一同在维持肘关节轴向稳定、后内侧、后外侧旋转稳定及防止肘内翻上发挥着重要作用。 2.3 损伤机制 冠状突骨折很少单独发生,常常合并前关节囊、韧带的撕裂和桡骨头、鹰嘴的骨折[2],多见于肘关节脱位的患者,文献报道在肘关节脱位的患者中有2%-15%合并有冠状突骨折[3-4]。最常见的损伤形式是当高处坠落或摔倒时上肢处于外展位手掌撑地,身体相对于上肢产生外翻力和后外侧旋转力,致使关节囊和韧带结构由外向内逐渐撕裂,继而肱骨远端与冠状突碰撞导致冠状突尖部或体部横行骨折,同时多伴有桡骨头的骨折[5]。由于冠状突前内侧面是一个相对独立无支撑的结构,当受到轴向内翻力时易于损伤,O’Driscoll等[6]提出上肢外展位摔倒时手掌撑地,由前臂向肘部传递的轴向力、内翻应力和肘部后内侧旋转作用力的联合作用导致外侧尺骨副韧带撕裂,致使肱骨远端同冠状突前内侧面发生撞击,导致前内侧面骨折[6],此种损伤多不合并内侧副韧带前束的损伤,见图1。"
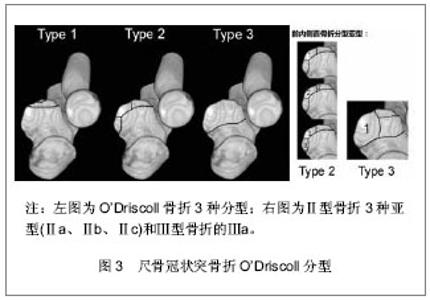
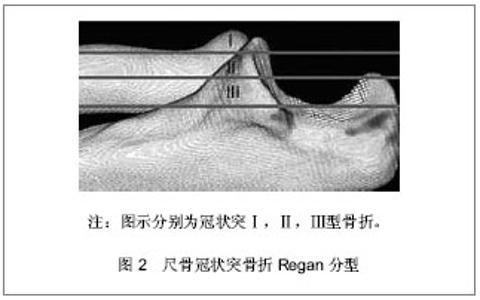
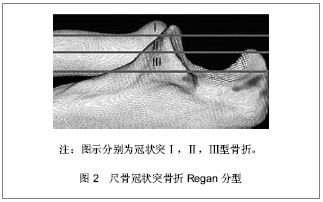
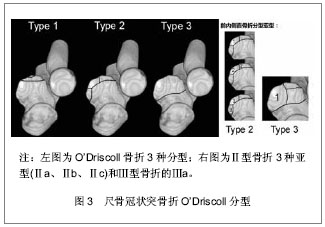
针对这一情况O’Driscoll等[6]依据骨折线的位置和骨折块大小提出了新的分型,强调了冠状突内侧面的重要性,并揭示了伴随软组织的损伤情况。O’Driscoll分型按骨折线的解剖位置将骨折分为3型,每一型又根据不同特点分为若干亚型,见图3。Ⅰ型:冠状突尖部骨折,骨折线位于冠状面,未延伸到高耸结节或冠状突体部,很少超过1/3冠状突高度。Ⅰa型冠状突尖部2 mm以内的骨折,Ⅰb型大于冠状突尖部2 mm的骨折,但未超过1/3冠状突高度且未延伸到内侧高耸结节及冠状突体部,该亚型常见于恐怖三联症。Ⅱ型:前内侧面骨折,Ⅱa型骨折线位于冠状突尖和高耸结节之间,内侧延伸至高耸结节前半部,外至冠状突尖部内侧;Ⅱb型骨折线在Ⅱa基础上延伸至冠状突尖部;Ⅱc骨折线在Ⅱb基础上延伸至整个高耸结节(内侧副韧带前束附丽处)。Ⅲ型:基底部骨折,骨折块超过冠状突高度50%的骨折,骨折线延伸至近端尺桡关节,常会造成近端尺桡关节的不稳定。Ⅲa型多为粉碎性骨折。Ⅲb型为伴有尺骨鹰嘴骨折,骨折线通过冠状突体部或基底部。"
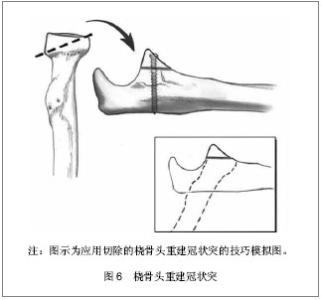
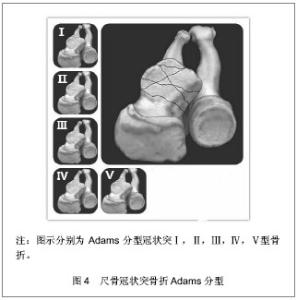
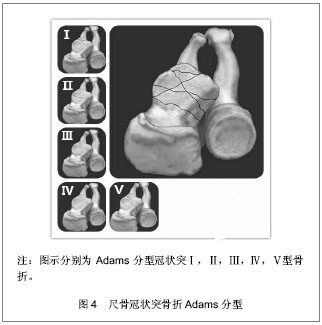
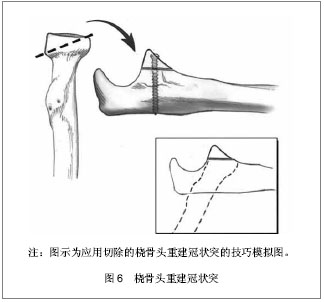
2.6 治疗方案 2.6.1 冠状突尖部骨折 Regan和/或O’DriscollⅠ型骨折。Ⅰ型冠状突骨折骨折块较小,大部分学者主张仅修复除冠状突外的其他损伤结构[10-14]。 Jeon等[13]通过最新实验研究发现单独ReganⅡ型冠状突骨折(已然包含Ⅰ型冠状突骨折)、单独前内侧面骨折、单独前外侧面骨折所造成的内翻外翻、内旋外旋角度变化均< 1°、位移< 1 mm,几乎不造成肘关节失稳,并提出在关节囊、韧带结构完好尤其是桡骨头完好时的情况下≤40%冠状突高度的冠状突骨折,肘关节仍可保持足够稳定性,可不需手术治疗。 Beingessner认为Ⅰ型冠状突骨折对肘关节运动力学和稳定性影响甚微,同完好肘关节相比在肘关节屈曲30°,90°,120°前臂分别置于旋前、旋后位时外翻角度仅有轻微改变,并且修复冠状突骨折亦并未纠正增长的外翻角度。因而建议在修复完成桡骨头和外侧尺骨副韧带后Ⅰ型冠状突骨折可不给予处理,若修复桡骨头和外侧尺骨副韧带后肘关节仍存在失稳可选择修复内侧副韧带,冠状突骨折不给予处理[10,12]。 但是一些学者认为冠状突尖部骨折的产生预示着肘部存在失稳,往往伴随着尺骨外侧副韧带、肘关节内侧副韧带、前关节囊的损伤,尤其是当冠状突尖部骨折块附着在前关节囊上时,修复该冠状突骨折具有重要意义[15-17]。 Ⅰ型冠状突骨折的修复多采用Hotchkiss正上方入路劈裂屈曲旋前肌群掀起肱肌及其前半部分进入冠状突,应用“套索式缝线”穿过近端尺骨钻孔或应用锚钉将骨折块及附着在其上的关节囊给以固定[18-22]。 Hausman等[23]则成功地应用关节镜技术对4例伴有Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型冠状突骨折和韧带损伤患者进行了手术,并取得了满意的结果。该学者指出关节镜技术仅支持小块冠状突骨折,技术要点:①首先明确尺神经位置,并避免损伤。②多选择2个入口,于肘关节近端前内侧面钝性创造观察窗口,然后在关节镜的观察下于肘关节前外侧面建立操作窗口,为便于观察可在前外侧面再建立一个窗口放置关节内牵开器必要时开阔视野。③在关节镜视野下找到骨折块和骨折基部,于近端尺骨背侧做1 cm切口由后向前插入导针,确保导针位于骨折基部中央,然后用关节镜抓手解剖复位骨折块并将导针穿过,必要时可用2枚导针。④由背侧沿导针插入空心螺钉,退出导针。⑤外侧副韧带的损伤需采取外侧切口单独处理。与传统切开复位内固定相比关节镜技术减少了对骨骼血运的破坏及软组织损伤[19,23]。 2.6.2 冠状突前内侧面骨折 O’DriscollⅡ型骨折。冠状突前内侧面自尺骨近侧干骺端向内延伸出约 7 mm,无支撑结构支持,该解剖特点使其在受到轴向内外应力时易于骨折[5,21]。冠状突前内侧面骨折多合并尺骨外侧副韧带撕裂,较少合并桡骨头骨折和内侧副韧带损伤[1,15]。如前所述Jeon等[13]认为单纯前内侧面冠状突骨折对肘关节稳定性影响甚小,无需修复。 Doornberg等[24]通过病例回顾分析发现冠状突前内侧面骨折行有限治疗(未手术、术中未处理、未达到稳固固定)的患者均有不同程度的肘关节失稳、半脱位和骨性关节炎等并发症,而行坚强稳固固定的患者均获得了优良结果。因而建议大多数冠状突前内侧面骨折行手术坚强固定治疗,并指出非手术治疗仅适用于非常小的骨折(Ⅱa)、不合并肘关节半脱位、侧位内翻应力下X射线片下肱桡关节间隙无变化[24-26]。 其他一些学者则认为Ⅱa和Ⅱb型在修复外侧尺骨副韧带后若肘关节稳定性良好则不需修复冠状突骨折[27]。Ⅱc型甚至个别Ⅱb型冠状突前内侧面骨折由于损伤了内侧副韧带前束,需手术治疗。修复冠状突前内侧面骨折的内侧入路选择有多种:①尺神经原始位置进入:先行尺神经前置,然后从尺侧腕屈肌两头的间隔进入,在分离解剖尺侧腕屈肌时应由远及近分离,防止损伤在高耸结节处附丽的内侧副韧带前束。②若骨折块较小可选择前述的Hotchkiss正上方入路[18],骨折块较大时也可将整个屈曲旋前肌群掀起,但需注意保护尺神经。 依据骨块大小及骨质情况选择固定方式:①恐怖三联征的小块骨折及前内侧面小块骨折可用“套索式缝线”穿过近端尺骨的钻孔或应用锚钉将骨折块连同附着在其上的前关节囊固定于肘关节屈曲位,缝线于尺骨干骺端背面系紧[28-29]。②大块前内侧面骨折可应用冠状突塑型钢板或T型钢板固定均可取得较好结果[18,20]。 2.6.3 冠状突体部或基底部非粉碎性骨折 Regan Ⅱ型或Ⅲ型骨折。大多数Ⅱ型或Ⅲ型冠状突骨折破坏了肱尺关节协调的关节结构及附丽在其上的软组织稳定结构,常导致肘关节失稳[3],往往需手术治疗。Ⅱ型或Ⅲ型非粉碎性骨折由于骨折块较大,在临床上易于诊断及手术固定,相对于冠状突尖部和前内侧面骨折处理起来反而简单且效果良好。 术中麻醉状态下行肘关节稳定性的影像学检查有助于判断韧带损伤情况及手术入路的选择,内侧副韧带检查采取肩部外展前臂旋前位肘关节外翻应力下X射线摄像,外侧副韧带检查取肩部外展前臂选后卫肘关节内翻应力下X射线摄像,据影像学关节间隙的变化判断有无韧带损伤[18]。手术多取内侧入路,合并外侧副韧带损伤时联合使用外侧入路;亦有学者提出前方入路治疗冠状突骨折的文献,认为前方入路更为直观,且固定牢固尤其是对于单独的 Regan Ⅲ型冠状突骨折效果较好[25-26];也可以选择后方正中切口,向上分别提拉起内外侧皮瓣行内外侧入路操作,该入路多应用于合并外侧副韧带损伤、鹰嘴骨折患者[30]。 大块非粉碎性骨折块可采用多种固定方法如冠状突钢板、空心拉力螺钉或实心螺钉。另据文献报道采用螺钉固定骨块时由后向前插入螺钉的固定方式生物力学效果较好[31]。若伴有鹰嘴骨折用与鹰嘴塑形的后位钢板,冠状突骨折则通过板孔使用螺钉牢固固定[18]。外侧副韧带损伤者均需修复,多于其肱骨外髁起点处撕脱,撕脱的外侧副韧带可用锚钉或者穿骨缝线固定到肱骨外髁处,修复的关键在于将其缝合到肘关节的旋转中心,即肱骨小头外侧中心处,以恢复其等距解剖结构保证外侧副韧带在肘关节运动过程中处于恒定紧张状态[32]。中间撕裂损伤应用1#或2#的不可吸收性缝合线缝合,较少应用肌腱移植。冠状突骨折和外侧副韧带修复完成后,若肘关节获得足够稳定性,内侧副韧带可不给予修复,治疗后前臂置于旋后位避免外翻力,内侧副韧带多可自行愈合[10]。若存在不稳定则可考虑修复内侧副韧带,也可考虑应用铰链式外固定支架。外固定支架既保证了肘关节的稳定性的维持也可允许早期肘关节活动,有利于治疗后功能的恢复[3]。 2.6.4 粉碎性冠状突骨折 粉碎性冠状突骨折为高能量损伤,临床处理困难,预后效果差,常伴有肘关节活动受限和骨性关节炎等并发症。 对于可修复的粉碎新冠状突骨折可选择较大的关节面骨折块给予复位固定,重建肱尺关节的解剖结构,恢复冠状突的前方支持扶璧作用防止肘关节后脱位或半脱位。 不可修复的粉碎性冠状突骨折,若同时伴有桡骨头骨折需要切除时,推荐应用切除的桡骨头重建冠状突[18,33-37],见图6;若单纯冠状突粉碎骨折可选择应用同侧鹰嘴尖部骨软骨自身移植重建冠状突,但当伴随鹰嘴骨折时不可采用鹰嘴截骨重建;亦可选择应用三面皮质骨髂骨移植重建冠状突[34-35],应用髂骨重建冠状突时髂骨移植物长2 cm,宽1 cm,高1 cm用 2.5 mm松质骨螺钉和垫圈将其固定并强调修复前关节囊和韧带结构以保证稳定性[35]。"

尽管有多种自体骨移植重建冠状突的方法,但是多位实施骨移植重建术的学者均认为自体骨移植重建可以作为一种治疗粉碎性骨折和肘部失稳的手术方法,但是该方法治疗后效果无法预知,随访结果亦好坏不一[35,37]。 针对这一弊端,Alolabi等[38]提出假体置换治疗不可修复的粉碎性冠状突骨折的研究。通过体外生物学试验发现当修复好损伤的韧带及关节囊时解剖型冠状突假体可恢复肘关节的稳定性,见图7A,当韧带受损伤不能充分发挥功能时,延长性冠状突假体较解剖型假体能更好的恢复肘关节稳定性,但仍不能达到完好肘关节的稳定水平,见图7B。 解剖型冠状突假体置换减少了肘关节脱位的概率但并未消除脱位的发生,而延长型假体则消除了再脱位的可能,即使在韧带损伤的情况下亦不脱位,但同完好肘关节相比并未完全恢复肘关节稳定性。粉碎性冠状突骨折患者若治疗后未取得足够稳定性,亦可安装铰链式外固定支架既可提供稳定性促进骨折和软组织愈合,又允许早期活动。"

| [1] Weber MF, Barbosa DM, Belentani C, et al. Coronoid process of the ulna: paleopathologic and anatomic study with imaging correlation. Emphasis on the anteromedial “facet”. Skeletal Radiol.2009;38:61-67. [2] Jason R. Hull, MD, John R, et al.Role of the coronoid process in varus osteoarticular stability of the elbow. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14:441-446. [3] Lee SK, Kim HY, Kim KJ, et al.Coronoid plate fixation of type II and III coronoid process fractures: outcome and prognostic factors.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012;22: 213-219. [4] Wells J, Ablove RH. Coronoid fractures of the elbow. Clin Med Res. 2008; 6(1):40-44. [5] Doornberg JN, de Jong IM, Lindenhovius AL, et al. The anteromedial facet of the coronoid process of the ulna.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16:667-670. [6] O’Driscoll SW, Jupiter JB, Cohen MS et al. Difficult elbow fractures: pearls and pitfalls. Instr Course Lect. 2003; 52: 113-134. [7] Regan W, Morrey B. Fractures of the coronoid process of the ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1989;71:1348-1354. [8] Adams JE, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Kallina CF 4th, et al. Fractures of the coronoid: morphology based upon computer tomography scanning. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2012;21: 782-788. [9] Sanchez-Sotelo J, O'Driscoll SW, Morrey BF. Medial oblique compression fracture of the coronoid process of the ulna.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14: 60-64. [10] Beingessner DM, Stacpoole RA, Dunning CE, et al. The effect of suture fixation of type I coronoid fractures on the kinematics and stability of the elbow with and without medial collateral ligament repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16: 213-217. [11] Samii A, Zellweger R. Fractures of the Coronoid Process of the Ulna:Which Ones to Fix and Which Ones to Leave Alone: A Review. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg.2008;34:113-119. [12] Beingessner DM, Dunning CE, Stacpoole RA ,et al. The effect of coronoid fractures on elbow kinematics and stability. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2007;22:183-190. [13] Jeon IH, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Zhao K, et al. The contribution of the coronoid and radial head to the stability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94-B:86-92. [14] Closkey RF, Goode JR, Kirschenbaum D, et al. The role of the coronoid process in elbow stability: a biomechanical analysis of axial loading. J Bone Joint Surg.2000;82A: 1749-1753. [15] Doornberg JN, Ring D. Coronoid fracture patterns. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31:45-52. [16] O’Driscoll SW, Jupiter JB, King GJW, et al. The unstable elbow. J Bone Jt Surg Am.2000; 82:724-738. [17] Chamseddine AH, Zein HK, Hamdan HR, et al. Unstable elbow dislocation with coronoid process fracture associated with distal radius fracture: a case report and review of the literature. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2010; 20:157-163. [18] Manidakis N, Sperelakis I, Hackney R, et al. Fractures of the ulnar coronoid process. Injury Int J Care Injured. 2012;43: 989-998. [19] Van Tongel A, Macdonald P, Van Riet R. Elbow arthroscopy in acute injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20(12):2542-2548. [20] Garrigues GE, Wray WH 3rd, Lindenhovius AL, et al. Fixation of the coronoid process in elbow fracture-dislocations.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(20):1873-1881. [21] Wang X, Chang SM, Yu GR. Anteromedial coronoid facet fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2013;23(3):251-255. [22] Budoff JE. Coronoid fractures. J Hand Surg Am.2012; 37(11):2418-2423. [23] Hausman MR, Klug RA, Qureshi S, et al.Arthroscopically Assisted Coronoid Fracture Fixation A Preliminary Report.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:3147-3152. [24] Doornberg JN, Ring DC. Fracture of the anteromedial facet of the coronoid process. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88A(10): 2216-2224. [25] Reichel LM, Milam GS, Reitman CA. Anterior approach for operative fixation of coronoid fractures in complex elbow instability.Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg.2012;16(2):98-104. [26] Han SH, Yoon HK, Rhee SY. Anterior approach for fixation of isolated type III coronoid process fracture. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2013 ;23(4):395-405. [27] Pollock JW, Brownhill J, Ferreira L, et al. The effect of anteromedial facet fractures of the coronoid and lateral collateral ligament injury on elbow stability and kinematics. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91(6):1448-1458. [28] Ring D, Doornberg JN. Fracture of the anteromedial facet of the coronoid process surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(Suppl 2 Pt. 2:):267-283. [29] Ring D. Fractures of the coronoid process of the ulna. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31(10):1679-1689. [30] Kloen P, Buijze GA. Treatment of proximal ulna and olecranon fractures by dorsal plating. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2009; 21(6):571-585. [31] Moon JG, Zobitz ME, An KN, et al. Optimal screw orientation for fixation of coronoid fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23(4):277-280. [32] McKee MD, Pugh DM, Wild LM, et al. Standard surgical protocol to treat elbow dislocations with radial head and coronoid fractures. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;Suppl 1(Pt 1):22-32. [33] van Riet RP, Morrey BF, O’Driscoll SW. Use of osteochondral bone graft in coronoid fractures. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2005; 14(5):519-523. [34] Kohls-Gatzoulis J, Tsiridis E, Schizas C. Reconstruction of the coronoid process with iliac crest bone graft. J Shoulder Elbow Surg .2004; 13:217-220. [35] Chung CH, Wang SJ, Chang YC, et al. Reconstruction of the coronoid process with iliac crest bone graft in complex fracture-dislocation of elbow. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007; 127:33-37. [36] Wu H, Liao Q, Zhu Y. Surgical reconstruction of comminuted coronoid fracture in terrible triad injury of the elbow. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012; 22:667-671. [37] van Riet RP, Morrey BF, O'Driscoll SW. Use of osteochondral bone graft in coronoid fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14:519-523. [38] Alolabi B, Gray A, Ferreira LM, et al. Reconstruction of the coronoid using an extended prosthesis: an in vitro biomechanical study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2012; 21: 969-976. [39] Fern SE, Owen JR, Ordyna NJ, et al. Complex varus elbow instability: a terrible triad model. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2009; 18(2):269-274. [40] Turker M, Derincek A, Canar M. Coronoid fractures and elbow instability, general review and clinical presentation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2010;20:353-358. [41] Rodriguez Martin J, Pretell-Mazzini J, Andres-Esteban EM, et al. Outcomes after terrible triads of the elbow treated with the current surgical protocols. A review.Int Orthop. 2011;35(6): 851-860. [42] Foruria AM, Augustin S, Morrey BF, et al. Heterotopic ossification after surgery for fractures and fracture-dislocations involving the proximal aspect of the radius or ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(10):e661-667. [43] Zeiders GJ, Patel MK.Management of unstable elbows following complex fracture dislocations the "terrible triad" injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 4:75-84. [44] Egol KA, Immerman I, Paksima N, et al. Fracture-dislocation of the elbow functional outcome following treatment with a standardized protocol. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007;65(4): 263-270. [45] Ring D, Guss D, Jupiter JB. Reconstruction of the coronoid process using a fragment of discarded radial head. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(3):570-574. |
| [1] |
Wen Yangning, Han Xiaoqiang, Feng Chao, Sun Haibiao.
Meta-analysis of open reduction and internal fixation versus total elbow arthroplasty for distal humeral fracture in the
elderly |
| [2] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [3] | Yang Xiao, Mei Wei, Zhang Wei. Absorbable rod or titanium alloy screws for Mason type II radial head fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4328-4332. |
| [4] |
Li Ningxin, Yang Zhaohui.
In-depth discussion on the treatment of terrible triad of the elbow |
| [5] | Fu Jiaxin, Xiao Lianping, Wang Shusen, Li Xiaodong, Han Liqiang, Wang Tonghao. Therapeutic effects of paraspinal approach combined with internal fixation through pedicle of fractured vertebra versus traditional AF screw-rod system for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1177-1181. |
| [6] | Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan. Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1188-1195. |
| [7] | Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang . Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1196-1202. |
| [8] | Fan Zhirong, Peng Jiajie, Zhong Degui, Zhou Lin, Su Haitao, Huang Yongquan, Wu Jianglin, Liang Yihao. Suture anchor combined with open reduction and internal fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for ankle fracture combined with deltoid ligament injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1307-1312. |
| [9] | Zhou Yu, Liu Yuehong, Liu Shuping, Chen Xi, Qin Wei, Li Qifeng. Spinal stability of intervertebral grafting reinforced by five or six augmenting screws versus transvertebral grafting reinforced by four augmenting screws for thoracolumbar vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 505-511. |
| [10] | Dong Haichao, Xu Xin, Li Peinan, Chen Changjian, Zheng Lianjie. Mini-plate, Herbert screw and absorbable rod in the internal fixation of Mason type II radial head fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 518-524. |
| [11] | Li Xianzhou, Wang Qian, Zhang Cunxin . Lumbar spondylolisthesis: status and prospects of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 621-627. |
| [12] | Yin Hao, Zhou Enchang, Pan Zhengjun, Chen Guang, Jiang Hua. Finite element analysis of the four and three cannulated screws combined with buttress plate fixation for the treatment of Pauwels III femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5133-5137. |
| [13] |
Song Chao, Ding Zhihong, Yin Tao, Li Zhenshi, Wu Liang, Zhou Wenchao, Xu Bo, Liu Yue, Kong Dece, Yang Tieyi, Zhang Yan .
Finite element evaluation of the stability of the elbow joint in the “terrible triad injury” by two surgical methods
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3834-3839.
|
| [14] |
Wang Lei, Li Zilong, Yuan Binbin, Wu Qingwei, Tang Fengming.
Clinical effect of locking plate versus anterograde intramedullary nail in the treatment of adult humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3924-3930.
|
| [15] | Hao Liang, Zhang Zhonglin, Wang Baodong, Bi Zhenggang. Intertrochanteric fracture of the femur: improvement of internal fixation device, surgical changes and related disputes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2927-2935. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||