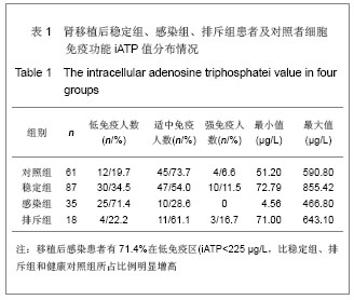
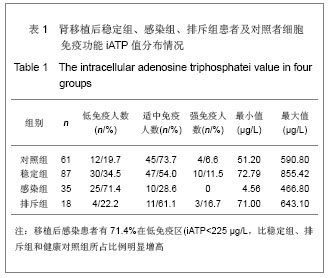
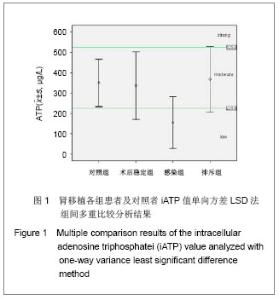
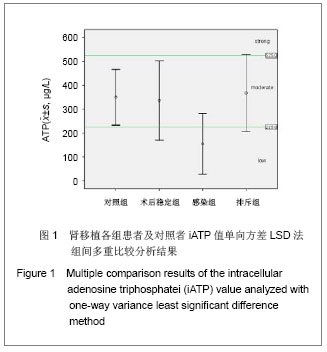
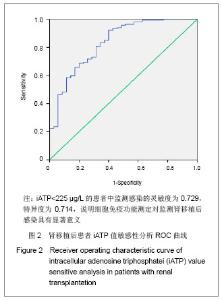
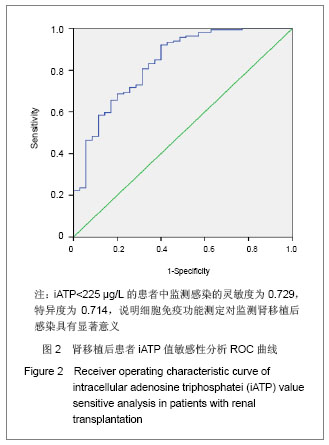
| [1] Cacciarelli TV, Reyes J, Jaffe R, et al. Primary tacrolimus (FK506) therapy and the long-term risk of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease in pediatric liver transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant. 2001;5(5):359-364.[2] Wang QH, Yuan XX, Wang J, et al.Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 2010;31(4):231-233王庆华,原欣翔,王瑾,等.细胞免疫能量测定在肾移植中的应用[J].中华器官移植杂志,2010,31(4):231-233.[3] Hooper E, Hawkins DM, Kowalski RJ, et al. Establishing pediatric immune response zones using the Cylex ImmuKnow assay. Clin Transplant. 2005;19(6):834-839.[4] Kowalski RJ, Post DR, Mannon RB, et al. Assessing relative risks of infection and rejection: a meta-analysis using an immune function assay. Transplantation.2006;82: 663-668[5] De Paolis P, Favarò A, Piola A, et al. "Immuknow" to measurement of cell-mediated immunity in renal transplant recipients undergoing short-term evaluation.Transplant Proc. 2011;43(4):1013-1016.[6] Bhorade SM, Janata K, Vigneswaran WT, et al. Cylex ImmuKnow assay levels are lower in lung transplant recipients with infection. J Heart Lung Transplant.2008;27(9): 990-994.[7] Hooper E, Hawkins DM, Kowalski RJ, et al. Establishing pediatric immune response zones using the Cylex ImmuKnow assay. Clin Transplant. 2005;19(6):834-839.[8] Kowalski R,Post D,Schneider MC, et al. Immune cell function testing:an adjunct to therapeutic drug monitoring in transplant patient management.Clin Transplant.2003; 17(2):77-88.[9] Cadillo-Chávez R, de Echegaray S, Santiago-Delpín EA, et al. Assessing the risk of infection and rejection in Hispanic renal transplant recipients by means of an adenosine triphosphate release assay.Transplant Proc. 2006;38(3):918-920.[10] Figuerres E, Olszewski M, Kletzel M. A flow cytometric technique using thiazole orange to detect platelet engraftment following pediatric stem-cell transplants.Cytotherapy. 2001; 3(4):277-283.[11] Moon HH, Kim TS, Roh YN, et al. Can immune function assay predict infection or recovery?Transplant Proc. 2012;44(4): 1048-1051.[12] Israeli M, Yussim A, Mor E, et al. Preceeding the rejection: in search for a comprehensive post-transplant immune monitoring platform.Transpl Immunol. 2007;18(1):7-12.[13] Halloran PF. T cell-mediated rejection of kidney transplants: a personal viewpoint. Am J Transplant. 2010 ;10(5):1126-1134.[14] Shearer GM,Clerici M. In vitro analysis of cell-mediated immunity:clinical relevance. Clin Chem.1994;40(11): 2162-2165. [15] Torío A, Fernández EJ, Montes-Ares O, et al. Lack of association of immune cell function test with rejection in kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc.2011;43(6): 2168-2170.[16] Gautam A, Fischer SA, Yango AF, et al. Cell mediated immunity (CMI) and post transplant viral infections--role of a functional immune assay to titrate immunosuppression. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006;6(13-14):2023-2026.[17] Rodrigo E, López-Hoyos M, Corral M, et al.ImmuKnow(®) as a diagnostic tool for predicting infection and acute rejection in adult liver transplant recipients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Transpl. 2012. in press.[18] Te HS, Dasgupta KA, Cao D, et al. Use of immune function test in monitoring immunosuppression in liver transplant recipients. Clin Transplant. 2012.[19] Zhou T,Xue F,Han LZ,et al.Invasive fungal infection after liver transplantation: risk factors and significance of immune cell function monitoring. J Dig Dis. 2011;12(6):467-475.[20] Zhou H,Wu Z,Ma L,et al.Assessing immunologic function through CD4 T-lymphocyte ahenosine triphosphate levels by ImmuKnow assay in Chinese patients following renal transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2011;43(7): 2574-2578.[21] Hwang S, Kim KH, Song GW, et al. Peritransplant monitoring of immune cell function in adult living donor liver transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2010;42(7):2567-2571.[22] Kobashigawa JA, Kiyosaki KK, Patel JK, et al. Benefit of immune monitoring in heart transplant patients using ATP production in activated lymphocytes.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010;29(5):504-508.[23] Israeli M, Ben-Gal T, Yaari V, et al.Individualized immune monitoring of cardiac transplant recipients by noninvasive longitudinal cellular immunity tests. Transplantation. 2010; 89(8):968-976.[24] Xue F, Zhang J, Han L, et al. Immune cell functional assay in monitoring of adult liver transplantation recipients with infection. Transplantation. 2010;89(5):620-626.[25] Husain S, Raza K, Pilewski JM, et al. Experience with immune monitoring in lung transplant recipients: correlation of low immune function with infection.Transplantation. 2009; 87(12):1852-1857.[26] Israeli M, Klein T, Sredni B, et al.ImmuKnow: a new parameter in immune monitoring of pediatric liver transplantation recipients. Liver Transpl. 2008;14(6):893-898.[27] Mandras SA,Crespo J,Patel HM.Innovative application of immunologic principles in heart transplantation. Ochsner J. 2010;10(4):231-235.[28] Ling X, Xiong J, Liang W, et al. Can immune cell function assay identify patients at risk of infection or rejection?A meta-analysis. Transplantation. 2012;93(7):737-743.[29] Huskey J, Gralla J, Wiseman AC. Single time point immune function assay (ImmuKnow) testing does not aid in the prediction of future opportunistic infections or acute rejection.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(2):423-429.[30] Gesundheit B, Budowski E, Israeli M, et al. Assessment of CD4 T-lymphocyte reactivity by the Cylex ImmuKnow assay in patients following allogeneic hematopoietic SCT.Bone Marrow Transplant.2010;45(3):527-533. |