Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2909-2919.doi: 10.12307/2026.093
Previous Articles Next Articles
Insulin-like growth factors and ischemic stroke: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations
Zhou Xinying1, Sun Xinyue2, Zhu Wenhao2
- 1Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Zibo Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zibo 255399, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-05Accepted:2025-05-30Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-10 -
Contact:Zhu Wenhao, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Zibo Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zibo 255399, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Zhou Xinying, MS candidate, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:The Fifth Batch of National Training Program for Clinical Excellence in Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. [2022]1 (to ZWH); Science and Technology Co-construction Project of Science and Technology Department of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. GZY-KJS-SD-2023-008 (to ZWH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Xinying, Sun Xinyue, Zhu Wenhao. Insulin-like growth factors and ischemic stroke: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2909-2919.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
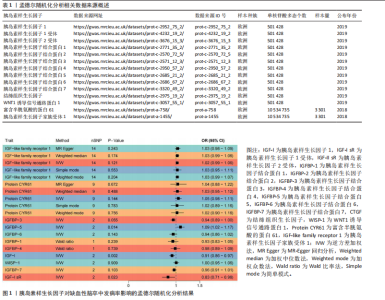
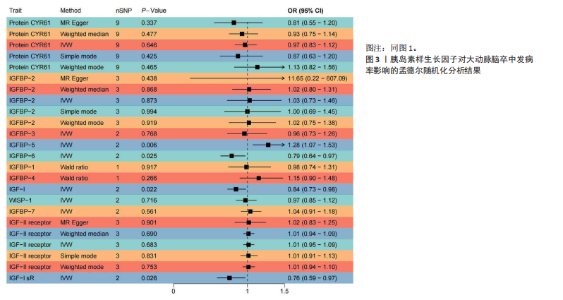
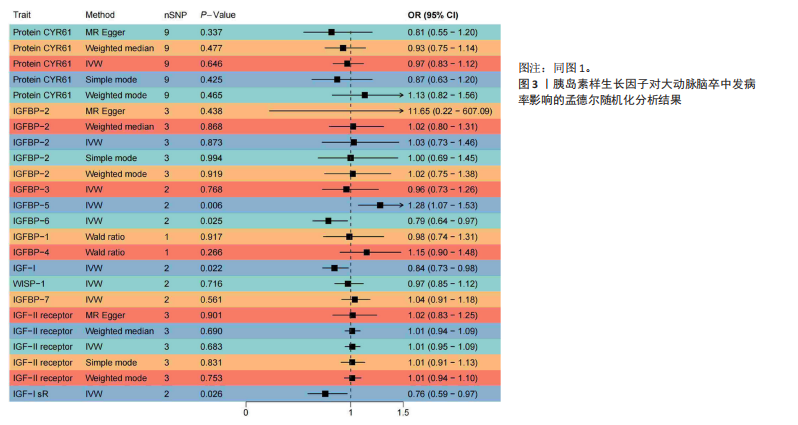
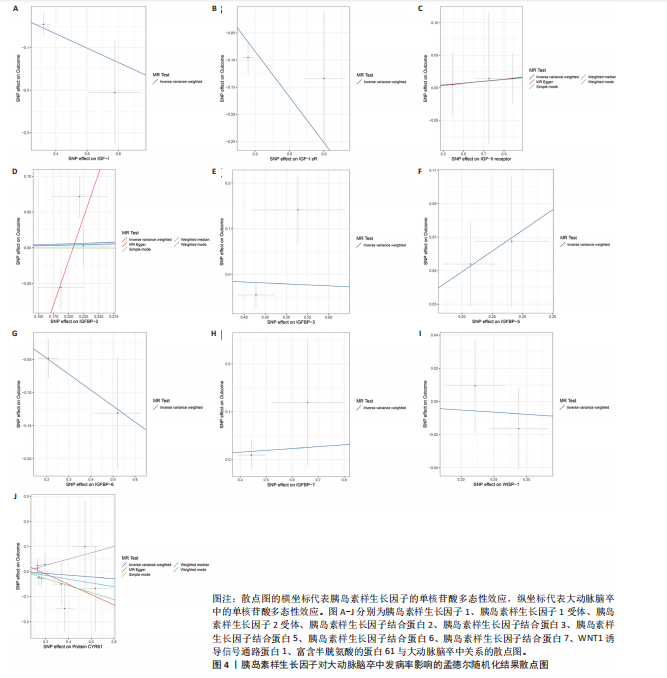
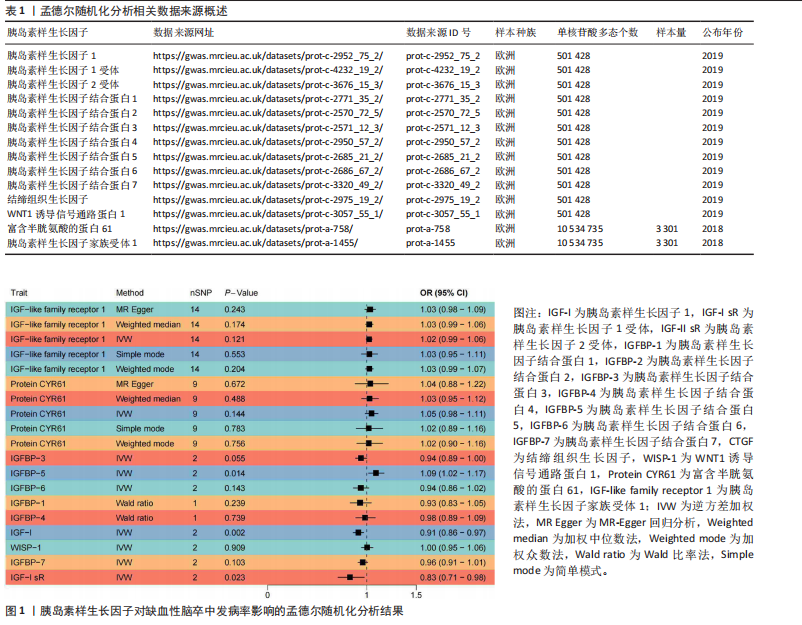
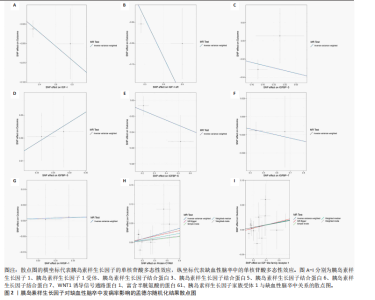
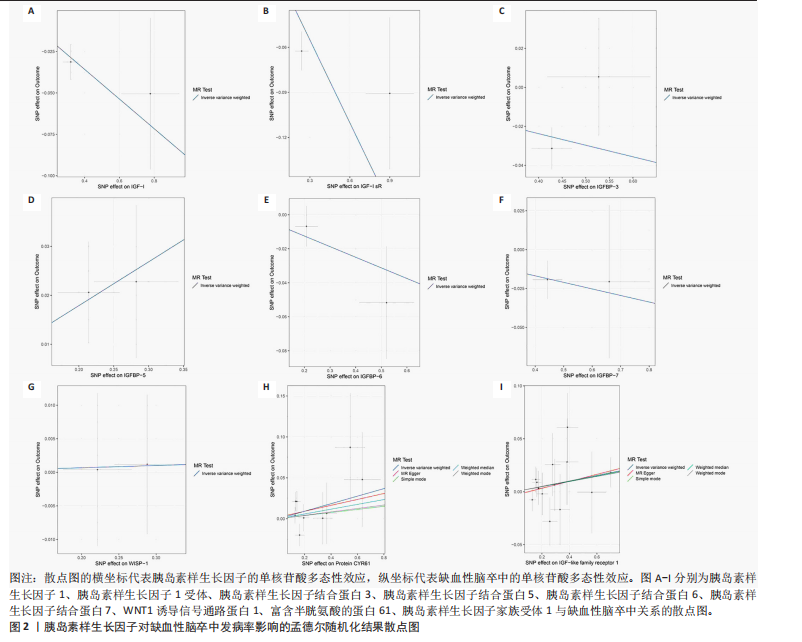
2.1 工具变量的选择 经过相关性和去除连锁不平衡筛选,合并整理并删除缺失项后最终得到54个单核苷酸多态性。 2.2 胰岛素样生长因子对缺血性脑卒中及其亚型发病率的影响 分析结果显示1种胰岛素样生长因子(胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白7)的遗传预测与心源性脑卒中的患病风险降低有关。 2.2.1 胰岛素样生长因子与缺血性脑卒中 分析结果显示各胰岛素样生长因子与缺血性脑卒中发病风险之间不存在显著的因果关联(P均> 0.05)。胰岛素样生长因子对缺血性脑卒中发病率影响的孟德尔随机化分析结果,见图1,2。 2.2.2 胰岛素样生长因子与大动脉脑卒中 分析结果显示各胰岛素样生长因子与大动脉脑卒中发病风险之间不存在显著的因果关联(P均> 0.05)。胰岛素样生长因子对大动脉脑卒中发病率影响的孟德尔随机化分析结果,见图3,4。 2.2.3 胰岛素样生长因子与心源性脑卒中 分析结果显示1种胰岛素样生长因子(胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白"
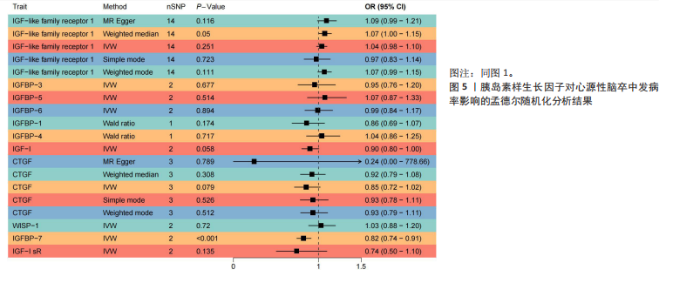
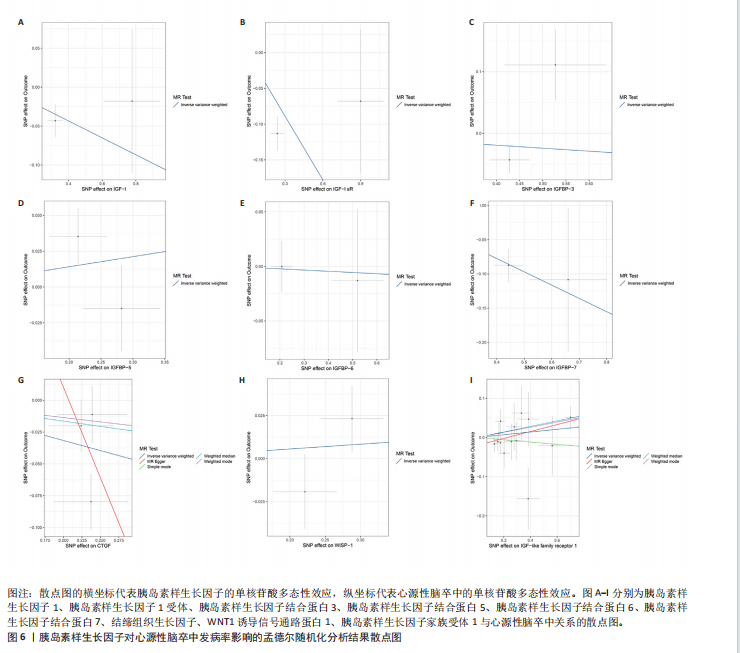
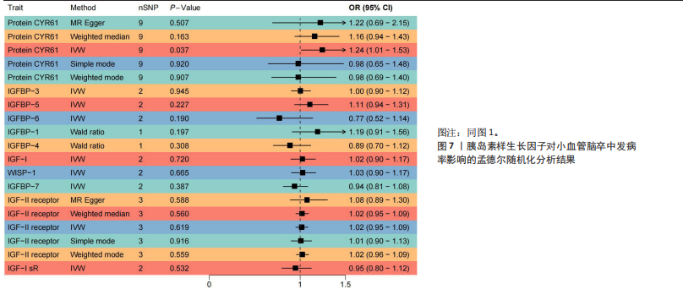
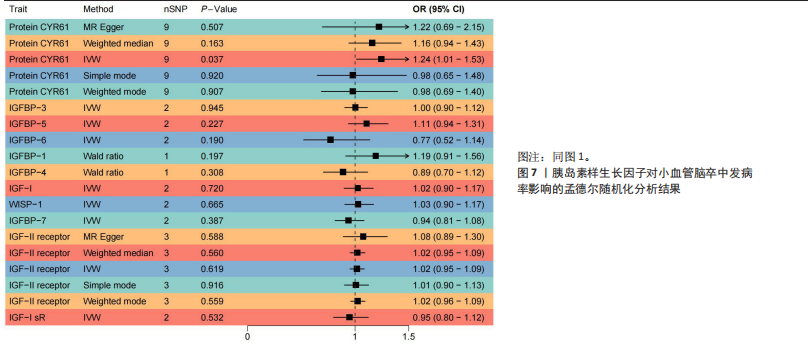
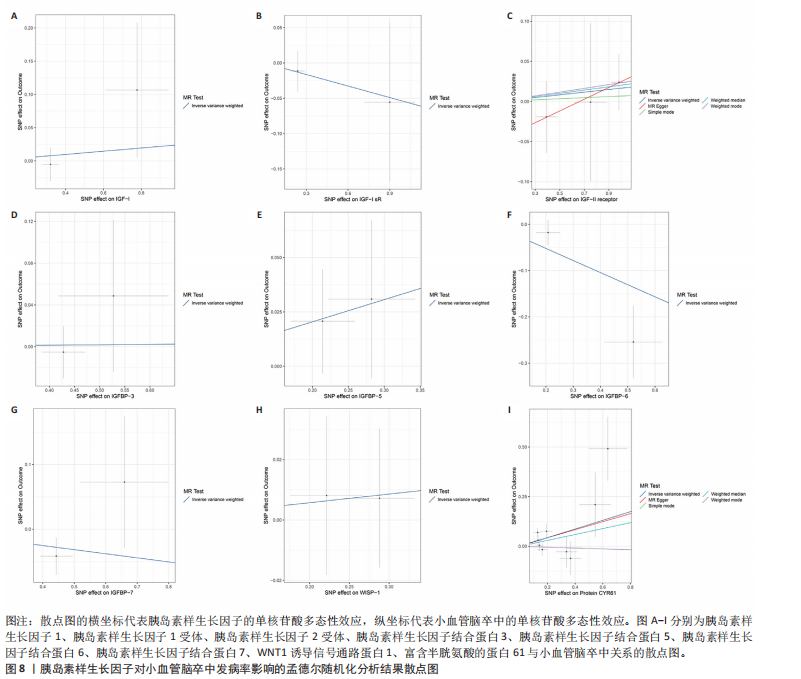
7)与心源性脑卒中发病风险之间存在显著的因果关联(P < 0.05),胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白7组患者心源性脑卒中发病风险显著降低(OR=0.82,95%CI=0.74-0.91,P=0.006)。胰岛素样生长因子对心源性脑卒中发病率影响的孟德尔随机化分析结果,见图5,6。 2.2.4 胰岛素样生长因子与小血管脑卒中 分析结果显示各胰岛素样生长因子与小血管脑卒中发病风险之间不存在显著的因果关联(P均> 0.05)。胰岛素样生长因子对小血管脑卒中发病率影响的孟德尔随机化分析结果,见图7,8。 2.3 缺血性脑卒中及其亚型对胰岛素样生长因子的影响 基于上述胰岛素样生长因子对缺血性脑卒中及其亚型发病率影响的结果,将缺血性脑卒中及其亚型作为暴露因素、胰岛素样生长因子作为结果变量进行反向孟德尔随机化分析,以深入了解其之间的因果关系。分析结果显示,缺血性脑卒中、大动脉脑卒中、心源性脑卒中、小血管脑卒中与胰岛素样生长因子均不存在反向因果关系。 2.4 可靠性评价 Cochran’s Q检验结果显示,在胰岛素样生长因子1受体和缺血性脑卒中(逆方差加权分析P=0.039)、富含半胱氨酸的蛋白61和小血管脑卒中(MR-Egger分析P=0.017)、富含半胱氨酸的蛋白61和小血管脑卒中(逆方差加权分析P=0.029)的分析中存在异质性(P < 0.05),但此次研究中其他胰岛素样生长因子与缺血性脑卒中及其亚型的分析均不存在异质性(P > 0.05)。MR-Egger回归分析显示,胰岛素样生长因子与缺血性脑卒中及其亚型的分析均不存在水平多效性(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] HERPICH F, RINCON F. Management of acute ischemic stroke. Crit Care Med. 2020; 48(11):1654-1663. [2] SHETH KN. Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(17): 1589-1596. [3] 《中国卒中中心报告2022》编写组,王陇德.《中国卒中中心报告2022》概要[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2024,21(8):565-576. [4] FEIGIN VL, ABATE MD, ABATE YH, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024;23(10):973-1003. [5] MALIK R, CHAUHAN G, TRAYLOR M, et al. Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nat Genet. 2018;50(4):524-537. [6] ALLARD JB, DUAN C. IGF-binding proteins: why do they exist and why are there so many? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018; 9:117. [7] LEROITH D, HOLLY JMP, FORBES BE. Insulin-like growth factors: Ligands, binding proteins, and receptors. Mol Metab. 2021; 52:101245. [8] AKKOÇ MF, KAPI E, BOZKURT M, et al. Investigation of the relationship of growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, and IGF-binding protein-3 levels with graft viability in autograft-transplanted pediatric patients with major burns. Transpl Immunol. 2022;73:101624. [9] 佘露.胰岛素样生长因子系统基因多态性与妊娠期糖尿病的关联研究[D].武汉:武汉科技大学,2024. [10] ANNUNZIATA M, GRANATA R, GHIGO E. The IGF system. Acta Diabetol. 2011;48:1-9. [11] BAXTER RC. Signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev. 2023;44(5):753-778. [12] 张静,潘燕.靶向胰岛素样生长因子系统抗肿瘤治疗的研究进展[J].中国合理用药探索,2024,21(3):20-28. [13] 熊思敏.精神分裂症患者血清IGF-2水平变化及其与临床特征的关系[J].中国医学创新,2025,22(7):126-129. [14] ARINAMI H, WATANABE Y, SUZUKI Y, et al. Serum cortisol and insulin-like growth factor 1 levels in major depressive disorder and schizophrenia. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1): 1148. [15] FANG Z, YANG S, ZHU L, et al. Association study of IGFBP1 and IGFBP3 polymorphisms with hypertension and cardio-cerebral vascular diseases in a Chinese Han population. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(44):77836. [16] LI Y, YANG W, LI J, et al. Relationship between serum insulin-like growth factor 1 levels and ischaemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022; 12(6):e045776. [17] YANG S, QIN C, CHEN M, et al. TREM2‐IGF1 Mediated Glucometabolic Enhancement Underlies Microglial Neuroprotective Properties During Ischemic Stroke. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(10):2305614. [18] JIANG Y, LIU Q, WANG C, et al. The interplay between cytokines and stroke: a bi-directional Mendelian randomization study. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):17657. [19] SON JW, PARK J, KIM YE, et al. Glia-like cells from late-passage human MSCs protect against ischemic stroke through IGFBP-4. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56:7617-7630. [20] SHIGETOMI E, SUZUKI H, HIRAYAMA YJ, et al. Disease-relevant upregulation of P2Y1 receptor in astrocytes enhances neuronal excitability via IGFBP2. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):6525. [21] GADD G, ÅBERG D, WALL A, et al. A Nonlinear Relation between Body Mass Index and Long-Term Poststroke Functional Outcome—The Importance of Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-1. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(9):4931. [22] BOEHM F J, ZHOU X. Statistical methods for Mendelian randomization in genome-wide association studies: a review. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20: 2338-2351. [23] LARSSON SC, BUTTERWORTH AS, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization for cardiovascular diseases: principles and applications. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(47): 4913-4924. [24] 朱凯,刘宛欣,罗昊冰,等.血浆蛋白与骨质疏松症的关系及潜在治疗靶点:基于国际UK Biobank数据库信息[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(18):3948-3960. [25] BRACUN V, VAN ESSEN B, VOORS AA, et al. Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7), a link between heart failure and senescence. ESC Heart Fail. 2022;9(6): 4167-4176. [26] FERREIRA JP, PACKER M, SATTAR N, et al. Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐7 concentrations in chronic heart failure: Results from the EMPEROR programme. Eur J Heart Fail. 2024;26(4):806-816. [27] ZHANG L, SMYTH D, AL-KHALAF M, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 (IGFBP7) links senescence to heart failure. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022;1(12):1195-1214. [28] 曹庆泽.IGFBP7在创伤性脑损伤中作用机制的研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2024. [29] WYPYCH M, DOMITRZ I, KOCHANOWSKI J. Insulin-like growth factor 1 and its prognostic value in the course of acute ischemic cerebrovascular events. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2023;8:e146. [30] ABUDUXUKUER R, NIU PP, GUO ZN, et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor 1 levels and migraine risk: a Mendelian randomization study. Neurol Ther. 2022; 11(4):1677-1689. [31] HUANG R, SHI J, WEI R, et al. Challenges of insulin-like growth factor-1 testing. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2024;61(5):388-403. [32] HAYES CA, MORGAN NI, THOMAS KC, et al. Neuronal and astrocyte insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling differentially modulates ischemic stroke damage. bioRxiv. 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.04.02.535245. [33] SABER H, HIMALI JJ, BEISER AS, et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor 1 and the risk of ischemic stroke: the Framingham study. Stroke. 2017;48(7):1760-1765. [34] CHEN G, LIN T, WU M, et al. Causal association of cytokines and growth factors with stroke and its subtypes: A Mendelian randomization study. Mol Neurobiol. 2024; 61(6):3212-3222. [35] CAO Z, MIN J, TAN Q, et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 and brain health: Evidence from 369,711 participants in the UK Biobank. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023;15(1):140. [36] SERHAN A, BODDEKE E, KOOIJMAN R. Insulin-like growth factor-1 is neuroprotective in aged rats with ischemic stroke. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019;11:349. [37] BAKE S, OKOREEH A, KHOSRAVIAN H, et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-1 treatment stabilizes the microvascular cytoskeleton under ischemic conditions. Exp Neurol. 2019;311:162-172. [38] HAYES CA, ASHMORE BG, VIJAYASANKAR A, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 differentially modulates glutamate-induced toxicity and stress in cells of the neurogliovascular unit. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:751304. [39] 许向明,范玉华.胰岛素样生长因子1在脑小血管病诊治中研究进展[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2023,49(4):242-247. [40] MACHADO FJDM, MARTA-ENGUITA J, GÓMEZ SU, et al. Transcriptomic Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles in the Search for Novel Plasma and Thrombus Biomarkers of Ischemic Stroke Etiologies. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(8):4379. [41] PRENTICE R L, ZHAO S, JOHNSON M, et al. Proteomic risk markers for coronary heart disease and stroke: validation and mediation of randomized trial hormone therapy effects on these diseases. Genome Med. 2013;5:1-15. [42] 冀伟,郭倩,郑广涛,等.GPER抑制IGF2R表达介导缺血性脑卒中的抗炎作用[J].陕西医学杂志,2023,52(4):369-375. [43] ÅBERG D, GADD G, JOOD K, et al. Serum IGFBP-1 Concentration as a Predictor of Outcome after Ischemic Stroke—A Prospective Observational Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(11):9120. [44] 张翠,吴孟海,多云妍.胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白3在脑梗死模型的表达及Smad信号通路的参与机制[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2024,26(3):331-335. [45] 王品砚.外泌体miR-140-5p靶向IGFBP5可激活PI3K/AKT信号通路,减轻TDP-43包涵体对神经元的损害[D].长沙:中南大学,2023. [46] WANG P, XUE Y, ZUO Y, et al. Exosome-encapsulated microRNA-140-5p alleviates neuronal injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage by regulating IGFBP5-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(12):7212-7228. [47] CUI Y, WANG XH, ZHAO Y, et al. Association of serum biomarkers with early neurologic improvement after intravenous thrombolysis in ischemic stroke. PloS One. 2022;17(10):e0277020. [48] LIU Y, HUAN W, WU J, et al. IGFBP6 is downregulated in unstable carotid atherosclerotic plaques according to an integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2020;27(10):1068-1085. [49] 李玉岩,梁莹莹,周洁信,等.IGFBP6在不稳定颈动脉斑块中的作用:生物信息学分析与实验验证[J].解放军医学杂志, 2024,49(6):701-710. [50] YI X, WU C, WANG H, et al. Effect of connective tissue growth factor and inflammatory factors on the condition and prognosis of patie nts undergoing reperfusion for acute ischemic stroke. Am J Transl Res. 2024;16(11):7155. [51] LEEUWIS JW, NGUYEN TQ, THEUNISSEN MGJ, et al. Connective tissue growth factor is associated with a stable atherosclerotic plaque phenotype and is involved in plaque stabilization after stroke. Stroke. 2010;41(12):2979-2981. [52] GUO K, LUO J, FENG D, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing with combined use of bulk RNA sequencing to reveal cell heterogeneity and molecular changes at acute stage of ischemic stroke in mouse cortex penumbra area. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:624711. |
| [1] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [2] | Tao Daiju, Su Haiyu, Wang Yuqi, Shen Zhiqiang, He Bo . Construction and identification of stable PC12 cell lines with high/low expression of miR-122-5p [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1790-1799. |
| [3] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [4] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [5] | Cao Xinyan, Yu Zifu, Leng Xiaoxuan, Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Liu Xihua. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation on motor function and gait in children with cerebral palsy: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1539-1548. |
| [6] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [7] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [8] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [9] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [10] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [11] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [12] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [13] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [14] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [15] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||