Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2113-2123.doi: 10.12307/2026.562
Previous Articles Next Articles
Electroactive materials applied in spinal surgery
Fu Lyupeng1, 2, Yu Peng3, Liang Guoyan2, Chang Yunbing1, 2
- 1School of Medicine, 3National Engineering Research Center of Human Tissue Function Reconstruction, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-25Accepted:2025-01-24Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-29 -
Contact:Chang Yunbing, PhD, Chief physician, School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Spine Surgery, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Fu Lyupeng, Master’s candidate, School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Spine Surgery, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, No. 2023B1515120078 (to CYB, LGY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fu Lyupeng, Yu Peng, Liang Guoyan, Chang Yunbing. Electroactive materials applied in spinal surgery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2113-2123.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
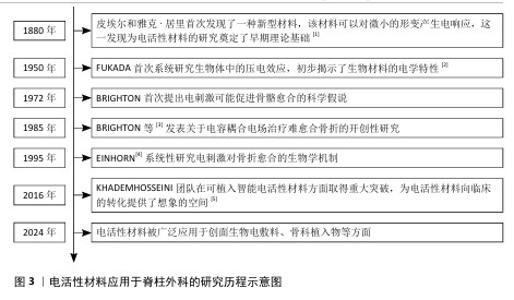
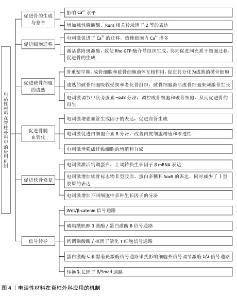
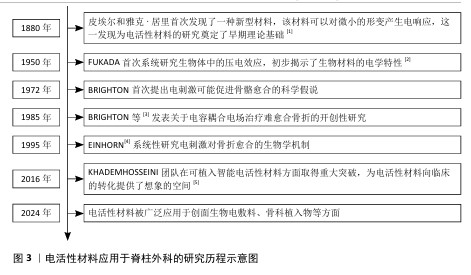
2.1 电活性材料应用于脊柱外科的研究历程 早在1880年,皮埃尔和雅克·居里首次发现了一种新型材料,该材料可以对微小的形变产生电响应,这为电活性材料的研究奠定了基础[1]。自1957年FUKADA等[2]发现骨骼中的压电效应以来,对骨骼中的机电效应及其在控制生长和重塑过程中的作用进行了广泛研究。1972年,BRIGHTON首次提出电刺激可能促进骨骼愈合的科学假说。1985年,BRIGHTON等[3]发表关于电容耦合电场治疗难愈合骨折的开创性研究,证实了电刺激对骨组织再生的积极作用。1995年,EINHORN[4]系统性研究电刺激对骨折愈合的生物学机制。进入21世纪,科学家们提出了“电活性生物材料”的概念,强调这些材料能够在电信号作用下改变其理化特性,或在外界刺激下产生电信号。这种新一代“智能”生物材料可以将电、电化学和力电信号直接传递给细胞和组织,在生物医学领域引起了广泛关注,科学家们更加注重提高电活性材料从实验室向临床应用的转化。2016年,KHADEMHOSSEINI团队在可植入智能电活性材料方面取得重大突破,为电活性材料向临床的转化提供了想象的空间[5]。直到2024年,电活性材料在脊柱外科领域中的研究迅速发展,在骨组织工程、神经修复等领域依旧展现出良好的临床应用潜力,并且比传统材料展现出了更好的机械性能和生物学特性。 电活性材料应用于脊柱外科的研究时间线见图3。电活性材料在脊柱外科应用的机制见图4。 "
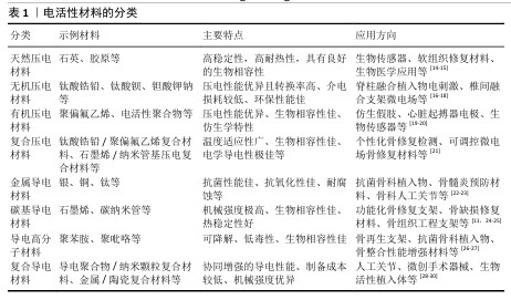
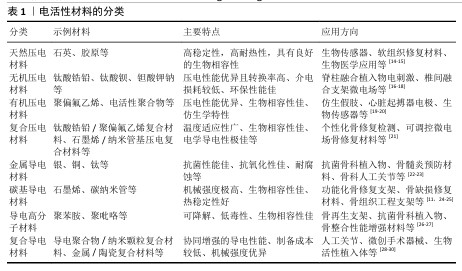
2.2 电活性材料简介 2.2.1 电活性材料的分类 压电材料:是一种智能新型电材料,可以对微小的形变产生电响应。早在1880年,皮埃尔和雅克·居里首次发现了这一现象:压电材料在形变过程中因离子或电荷的不对称位移导致电极化,从而产生电能。在各种生物材料中,压电生物陶瓷(如硝酸钠钾、BaTiO3[6]、铈酸锂钠钾等[7])在电活性假体应用方面显示出巨大的潜力。研究表明,活体组织中存在内源性电场,相关的离子及大分子运输在胚胎发育和创面愈合过程中扮演着重要角色[8]。上述现象为电活性材料应用于医学实际中提供了理论基础。 导电材料:导电材料主要有碳纳米管[9]、石墨烯[10]、碳纳米纤维等[11],本身具有出色的导电特性。研究发现,电刺激能够促进创面愈合并加快骨基质的生成,主要作用机制是通过提高骨密度来加速受损骨骼的愈合过程[12]。电刺激通过多种机制促进骨骼的修复和重建,包括加快新骨的生成与旧骨的重塑(成骨细胞途径)、调节离子通道的活性以改变细胞功能、增强骨细胞的功能活性,这些特点使得电刺激在骨修复领域展现出巨大的应用前景[13]。 电活性材料的分类见表1。 2.2.2 电活性材料的工作原理 电场促进骨再生:电场是一种生物物理技术,常用于调节细胞外基质的合成,并已在临床上应用于促进骨折和骨缺损的修复。AARON等[31]的临床前研究显示,电场可以调控软骨内骨化模型中的蛋白多糖和胶原合成,增强体内外骨形成、有效促进骨再生。 电场调控细胞行为:肌肉骨骼系统对物理和化学环境高度敏感。骨细胞和软骨细胞会对机械应力、流体流动、pH值和氧分压的变化作出反应,进而改变其表型,并通过表达一系列信号和结构分子,尤其是调控细胞外基质的组织构成及相关生物力学特性。通过将组织暴露于精确配置的电场,能够刺激骨骼和软骨修复所需的细胞外基质合成,潜在的作用机制包括通过细胞膜上的腺苷受体介导信号转导、激活骨诱导途径及促进骨骼细胞外基质的合成、调节结构和信号分子的表达。CADOSSI等[32]指出以上3种信号传导途径的协同作用有助于促进骨再生。 "

2.3 电活性的生物学效应 2.3.1 电刺激成骨 电刺激对细胞的直接影响是细胞内Ca2+水平,Ca2+介导了许多关键的细胞过程,如细胞凋亡、迁移、增殖和分化[33]。当细胞处于静止状态时,Ca2+浓度低至100 nmol/L,但当细胞受到电刺激时,细胞内Ca2+可以增加到500-1 000 nmol/L。对于大多数细胞来说,有两种主要来源的Ca2+,一个是通过嵌入浆膜中的离子通道,另一个是储存在内质网中的Ca2+,它们可以通过肌醇1,4,5-三磷酸受体和Ryanodine受体释放。 细胞质中的Ca2+与钙调蛋白结合。钙调蛋白可以作为钙传感器和信号传感器,结合和激活本身不能与钙结合的靶蛋白,从而参与细胞功能几乎所有方面的调节。钙调蛋白的激活可以进一步激活钙化,这是一种丝氨酸-苏氨酸磷酸酶,可以直接与核因子活化T细胞转录因子的核因子结合。核因子活化T细胞已被确定为介导Ca2+/钙调蛋白和钙化依赖性转录的转录因子,在休眠细胞中高度磷酸化并存在于细胞质中,与钙化的结合使其去磷酸化并转位到细胞核中,参与基因表达的调节。钙调蛋白激酶Ⅱ和肌球蛋白轻链激酶是Ca2+/钙调蛋白第二信使的其他靶点[34]。钙调蛋白激酶Ⅱ的激活是控制成骨细胞增殖和分化的关键调节剂。通过Ca2+流入介导的钙调蛋白/钙化/核因子活化T细胞信号通路促进成骨的机制被广泛认可[35]。 LIU等[36]通过实验发现,电刺激显著增加了成骨标志物和基因的表达,特别是碱性磷酸酶、胶原蛋白Ⅰ型mRNA和胶原蛋白Ⅰ型C端前肽的表达,诱导了α-Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、Runt相关转录因子2、富含半胱氨酸的分泌型酸性蛋白、骨含伽马羧酸蛋白和分泌型磷蛋白Ⅰ的mRNA转录,表明电刺激可以促进成骨细胞成熟、成骨细胞增殖和骨基质形成。 2.3.2 电场促进细胞迁移 间充质干细胞存在于其他组织和器官周围的结缔组织中,表现出分化为多种细胞类型的能力,包括成骨细胞、脂肪细胞、软骨细胞以及潜在的肌肉细胞、肌细胞、神经元和神经胶质细胞。ZHANG等[37]通过实验发现电场增加了细胞内Ca2+,细胞内Ca2+积累激活黏附斑激酶,最终导致细胞骨架的局灶性接触和Rho GTP酶介导组织的形成,协同促进了间充质干细胞迁移的增加,直接或间接促进了骨的修复再生。 2.3.3 电刺激促进破骨细胞的成熟 成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间的相互作用对于调节新骨的形成很重要。在骨重塑的早期阶段,成骨细胞通过分泌趋化因子(如核因子κB受体活化因子配体)与破骨细胞的前体细胞相互作用促进其分化为成熟的破骨细胞[38];破骨细胞通过核因子κB受体活化因子/核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素信号通路完成这一过程,成熟的破骨细胞负责吸收受损和老化的骨组织;随后,破骨细胞通过进一步激活成骨细胞来刺激新骨生长的过程。这些发现表明破骨细胞吸收和成骨细胞再生是骨愈合过程中的关键因素[39]。 在骨骼重塑的早期阶段,激活破骨细胞有利于去除和吸收受损的骨组织。针对骨缺损部位施加电刺激后,血液中甲状旁腺激素的浓度增加并激活破骨细胞,促进破骨细胞在受伤部位的自分泌功能,破骨细胞在4-8周时表达p38,这表明破骨细胞在骨缺陷周围进行骨吸收,因此,电刺激可以通过调节甲状旁腺激素-p38分泌机制的方式来控制破骨细胞数量的增加和早期的骨吸收;此外,破骨细胞亦可促进成骨细胞在中后期的成熟,以促进新的骨骼再生[40]。 2.3.4 电刺激促进软骨的修复 机械、电和电磁刺激在正常和病理条件下可能对调节透明软骨起到重要作用[41]。研究表明,电刺激可以促进成软骨分化和软骨成熟[42]。电刺激作用会影响细胞质膜的组织并诱导跨膜离子运输,从而增加细胞内Ca2+、激活钙调蛋白,上调转化生长因子β mRNA的表达[43]。电刺激还增加了软骨标志物Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白多糖和Sox9的表达,同时减少了Ⅰ型胶原的表达[44],这些调控作用诱导了间充质干细胞向透明软骨细胞的分化。同时,电刺激的存在还增加了不同细胞中多种生长因子的分泌,如胰岛素样生长因子1和2、转化生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白,在促进软骨修复方面有巨大的作用。 2.3.5 电刺激促进骨髓血管化 血管生成在骨愈合过程中至关重要,因为新生的血管网络可以为成骨提供充足的营养、氧气和生长因子。研究显示,电刺激能够通过促进血管生成因子的表达(如血管内皮生长因子和白细胞介素8)显著提升血管生成能力[45]。具体而言,直流电场能够引导人乳腺上皮细胞向阴极定向迁移,并诱导CXCR4和CXCR2受体的表达,这2个受体分别通过其配体基质细胞衍生因子1和白细胞介素8介导内皮祖细胞的募集与迁移[46]。 电刺激诱导的白细胞介素8分泌可提升内皮细胞的增殖能力和通透性,吸引淋巴细胞和中性粒细胞等免疫细胞聚集于血管周围区域[47]。其中,中性粒细胞的N2型极化进一步刺激基质细胞衍生因子1的分泌,从而形成基质细胞衍生因子1/CXCR4的正反馈回路,激活下游的磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B和β-catenin信号通路,这一机制有效促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移及成骨作用[48];此外,血管内皮生长因子与其受体的结合同样能够激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路,促进细胞骨架重组和内皮细胞迁移,从而加速血管生成过程[49]。综上所述,电刺激通过调控多种生物分子的表达和信号通路协同作用,为骨髓血管的修复及功能恢复提供了重要支持。 "

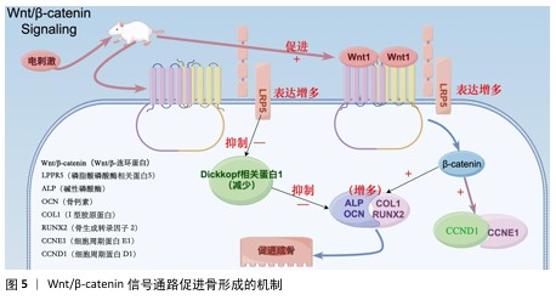
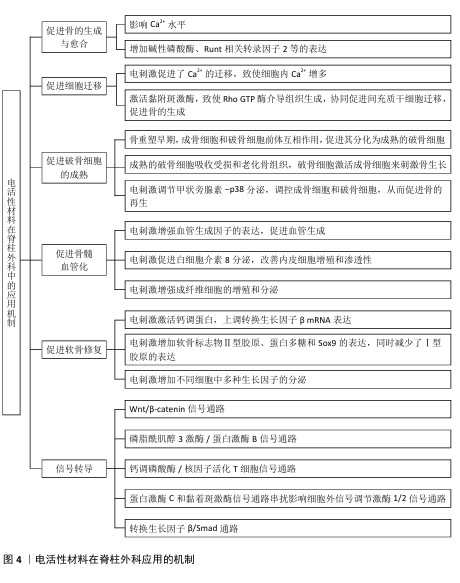
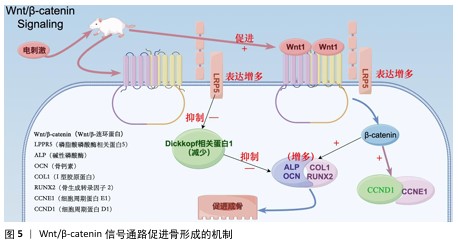
2.4 电活性材料的信号转导机制 骨组织工程中微电场材料促进骨的再生涉及多个信号转导机制,例如Wnt/β-catenin信号通路[50]、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路[51]、转化生长因子β/Smad通路[52]、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B通路[53]、Ca2+-核因子活化T细胞信号通路等[54]。通过体外施加的电磁场刺激机体内相关通路进而影响细胞对外部刺激(如激素、细胞因子等)的反应,以及生物介孔活性材料对成骨细胞的黏附等作用,从而促进成骨。 2.4.1 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 Wnt是一种分泌的脂质修饰蛋白,通过与细胞表面的多种不同受体结合激活经典Wnt信号通路,调控胚胎发育和成年期的多种生物过程,对人体的生长发育起着至关重要的作用[55]。其中,脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5和β-catenin是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的重要组成部分。ZHOU等[56]在对大鼠施加体外电刺激后,发现大鼠脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5和β-catenin mRNA表达显著增加。体外电刺激干预可减少Dickkopf相关蛋白 1的表达,Dickkopf相关蛋白 1通过与Wnt共受体脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5/6结合来负调控Wnt/β-catenin信号;此外,体外电刺激所增强的Wnt/β-catenin 蛋白信号显著增加了增殖阶段相关目标基因细胞周期蛋白D1基因和细胞周期蛋白E1基因以及分化阶段相关基因碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、Ⅰ型胶原和Runt相关转录因子2的表达,这些基因加速了成骨细胞的增殖、分化和矿化[57-60]。通过上述调节机制,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路显著促进了骨的形成(图5)。 2.4.2 磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路 磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路已被证明对成骨细胞分化、成熟和骨生长的所有阶段都至关重要,阻断磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路不仅会损害软骨细胞分化,还会抑制纵向骨生长[61]。NING 等[62]使用TiO2/Bi2O3异质结材料处理培养的骨髓间充质干细胞,发现细胞的磷脂酰肌醇3激酶基因表达显著增强,证实了异质结材料的电信号可以通过磷脂酰肌醇3激酶转导到细胞中,同时TiO2/Bi2O3异质结材料还显著上调成骨相关基因(Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶、骨形态发生蛋白2和骨钙素)的表达,以上结果都证实了TiO2/Bi2O3异质结材料可以通过机电生物信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和骨再生。 NING等[63]发现导电水凝胶可以显著增加细胞内Ca2+浓度,促进丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶/细胞外信号调节激酶信号通路和磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路途径中的蛋白质磷酸化,从而促进骨血管的生成,间接也促进骨组织再生。 2.4.3 钙调磷酸酶/核因子活化T细胞信号通路 WINSLOW等[64]发现电刺激作用于电压门控离子通道或连接蛋白43触发的离子将作为第二信使,激活钙调磷酸酶/核因子活化T细胞信号通路,而钙调磷酸酶/核因子活化T细胞信号转导是成骨分化的关键调节因子,从而促进成骨分化;同时,钙调磷酸酶/核因子活化T细胞信号通路的核心成分,如钙调蛋白、钙调磷酸酶和核因子活化T细胞在成骨谱系细胞中强烈表达,也印证了上述观点。WANG等[65]发现带负电荷的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸膜与氧化钡复合物可显著提高MC3T3-E1细胞中钙调磷酸酶、钙调蛋白和核因子活化T细胞的表达水平。核因子活化T细胞表达的上调促进其进入细胞核,从而激活各种成骨相关基因的转录,如Runt相关转录因子2[66]、骨桥蛋白[67]、Ⅰ型胶原[68],从而促进成骨分化。 2.4.4 蛋白激酶C和黏着斑激酶信号通路串扰影响细胞外信号调节激酶1/2信号通路 Ca2+的流入直接激活另一种由电刺激作用于电压门控离子通道触发的离子——蛋白激酶C信号通路[69]。SHEN等[70]设计了一种新型压电聚偏二氟乙烯-三氟乙烯层涂覆在氧化铟锡平面微电极上,电刺激能够通过钙介导的蛋白激酶C信号通路调节间充质干细胞的成骨分化,从而达到促进成骨的目的;聚偏二氟乙烯-三氟乙烯涂层的表面电荷可以很容易地通过预极化过程控制,从而触发整合素介导的黏着斑激酶信号通路,最终促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化;上游蛋白激酶C和黏着斑激酶信号通路之间的激活和随后的串扰导致下游细胞外信号调节激酶1/2信号通路的激活,促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化。 2.4.5 转化生长因子β/Smad通路 转化生长因子β在人体内调节多种细胞活动。转化生长因子β与其细胞表面受体的结合可以触发几个信号级联反应,转化生长因子β/Smad 通路就是其中之一。在骨形成过程中,转化生长因子β是骨骺生长板软骨细胞终末分化的有效抑制剂,这种抑制作用主要是由Smad分子介导[71]。VARANI等[72]发现转化生长因子β首先与自身 Ⅱ型受体结合,随之激活其Ⅰ型受体,激活的Ⅰ型受体导致 Smad 2或Smad 3在C端磷酸化,然后与Smad 4形成复合物并转位到细胞核中,通过MH1区域的发夹状结构与DNA上的SBE结合;同时,他们还发现Smad 2或Smad 3与Smad 4结合形成的复合物可上调靶基因连接蛋白43的表达,从而参与骨细胞的活动。而通过电刺激的参与,骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白Ⅰ型受体以及Smad 1/5/8的基因表达量提升,再次间接验证Smad蛋白对转化生长因子β通路中骨细胞有促进成骨作用[73]。 "

2.5 电活性材料在脊柱外科中的应用现状 2.5.1 促进骨骼组织的再生 人体产生的生物电场在创面愈合中起着举足轻重的作用,因为它具有稳定的直流电和电势,可驱动细胞迁移到损伤点,而电活性材料为各种形式的电刺激到达细胞提供了一种直接的方法。骨骼因具有压电性而对电刺激敏感,因此,可通过植入物将电刺激传递到细胞来调节成骨。导电聚合物是适合作为植入物的材料,因为它们对电信号有响应性[74]。因此,聚吡咯在骨组织再生方面也具有希望[21,75]。 2.5.2 新型抗菌平台 最近,随着生物医学工程的发展,生物医学植入物中的细菌黏附和感染都是日益严重的问题,导致植入物失败并增加翻修手术的概率。电刺激电活性抗菌材料可以破坏细菌生物膜的保护作用,以更清洁、更环保的策略有效杀死多重耐药细菌,避免滥用抗生素对公众健康和环境造成的潜在威胁[76]。鉴于活骨是一种典型的生物压电组织[77],SHUAI等[78]制备了聚偏二氟乙烯/Ag-聚多巴胺包被的BaTiO3支架,通过结合聚合物和陶瓷的压电柔韧性作为Ag纳米颗粒的导电和抗菌性能,证实该支架可促进MG-63细胞的增殖和分化、增强对大肠杆菌的抗菌活性,在脊柱骨修复中显示出巨大潜力。 2.5.3 导电支架 电刺激主要用作促进组织愈合和功能恢复的物理治疗方式[79]。FERRIGNO等[80]发现将导电聚合物与电刺激治疗结合使用可以更好地将电流传递到目标受损组织来提高电刺激效率,从而提高组织修复效率。 2.5.4 导电聚合物与生物分子相结合 在人体组织中,相同类型与不同类型的细胞之间,以及细胞与细胞外基质及其组分之间存在大量的生化和机械相互作用。电信号是神经系统中存在的主要特征物理刺激之一,脊髓损伤后,创伤部位以下的所有身体水平都可能受到影响,这可能导致神经功能丧失[81],生物医学没有直接支持脊髓损伤后轴突再生的治疗方法,治疗主要依靠稳定受伤部位以防止更多损伤、物理治疗和长期护理来改善患者的生活质量[82]。导电聚合物[如聚(3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩)]与生物分子之间的结合也可能是一种理想的材料[83]。MARQUES-ALMEIDA等[84]将用聚-1-赖氨酸、肝素、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和纤连蛋白功能化的聚(3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩)微纤维整合到脊髓损伤大鼠模型中,该导电系统在受伤部位呈现出良好的整合,微纤维促进了迁移细胞和生长轴突的纵向排列,并且用聚-1-赖氨酸/肝素/碱性成纤维细胞生长因子/纤连蛋白修饰被证明可以避免炎症和纤维化,并有助于组织愈合、增强血管形成和轴突再生。 2.5.5 生物活性创面敷料 人体皮肤还具有另一个关键特征,即完整皮肤的导电性[85],这在人类活动中起着至关重要的作用,一旦皮肤被破坏,就会产生40-200 mV/mm的内源性创面诱导电场,并立即启动创面愈合[86],这对于脊柱外科手术术后的恢复起着极大的作用。YU等[87]发现复杂导电性创面敷料显示出显著的促创面愈合能力,并在不同类型创面中表现出巨大潜力。导电创面敷料可以促进电刺激良好和均匀地传导到创面上,从而促进电疗的疗效。其次,它们可以单独用。另外,一些装有生物活性剂的导电创面敷料在外循环辅助下实现了可控的药物释放,实现了长期治疗,降低了初始爆裂和不良反应。 2.5.6 电活性螺钉系统 在脊柱外科手术中,螺钉植入是一种常用的技术,用于修复椎体并提供机械稳定性,同时,电刺激已被认为是一种有前景的非药物辅助手段,用于增强骨再生和融合。研究表明,正常骨组织表现出显著的负电性,骨损伤后电势可作为细胞信号促进骨细胞的迁移、增殖和分化[88-89]。直流电刺激已被证实可以加速腰椎的骨形成和愈合[90]。JAVEED等[91]设计了一种有机电活性的螺钉系统,对该螺钉系统施加电刺激后在脊柱骨缺损部位诱导的电场强度远超过了所需的治疗阈值,足以在目标椎间区域内实现成骨诱导。 2.5.7 压电聚合物水凝胶 脊髓损伤是一种严重的中枢神经系统疾病,常由机动车事故、摔伤等引发,已成为脊柱外科领域中日益常见的临床病症,对患者的运动、感觉及自主功能造成严重影响。随着人口老龄化的日渐加重,腰椎退行性病变患者也日渐增多,其压迫神经对患者预后生活质量影响较大。目前,电刺激因能够通过生物信号传导引导再生轴突跨越损伤间隙并与远端树突连接,同时增强细胞迁移和增殖,被广泛认为是修复脊髓损伤的重要治疗策略[92]。在保守、手术治疗的基础上,电刺激疗法也逐渐进入腰椎退行性病变的临床治疗。压电材料凭借其无需外部电源或植入电极即可将机械能转化为电刺激的独特能力,展现出在脊髓损伤和腰椎退行性病变修复中的巨大潜力[93]。ZHENG等[94]创新性地设计了一种含有50 g/L BaTiO3@PDA纳米颗粒的水凝胶材料,发现该材料不仅能够显著加速神经元生成,还能促进轴突再生和突触形成,通过增强再髓鞘化进一步改善神经功能恢复。这一发现为基于压电材料的水凝胶系统修复脊髓损伤提供了一种全新的、有效的治疗策略,具有广泛的应用前景。"

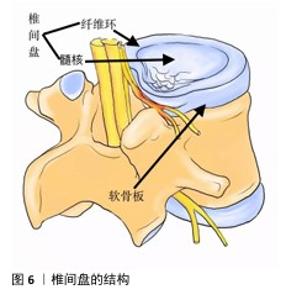
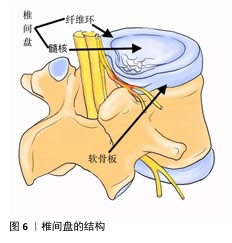
2.6 电活性材料的挑战 2.6.1 机械性能 导电聚合物本身非常脆,因此,很难使用高浓度的导电聚合物制造导电支架[95]。克服导电聚合物固有脆性的常见策略是将少量但足够数量的导电聚合物(刚好足以模拟天然组织的导电性)与非导电聚合物(例如聚乳酸、聚己内酯、壳聚糖等)或比导电聚合物脆性更低的水凝胶混合在一起作为基质,形成复合材料[96]。相反,导电聚合物的引入可以帮助提高非导电聚合物的适度机械强度和弹性模量[97]。对于薄膜和纤维基复合支架,可以通过调整导电聚合物与其聚合物基质之间的比例来调节支架的刚度[98]。 2.6.2 生物活性 现阶段临床使用的植入材料具有缺乏生物活性[99]、骨电传导性差[100]、难以在不影响机械性能的前提下调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞功能来促进骨折修复等缺点[101],并且不锈钢和钛基植入物进行CT和MRI等影像学检查时可能产生金属伪影[102],影响临床医生对病变的观察,因此,植入的骨组织支架材料不仅需要促进机体成骨,还应尽可能减少不良反应。例如,支架植入体内可能会被巨噬细胞等免疫细胞视为异物,从而产生排异反应引发炎症,因此,理想的新型生物材料应无细胞毒性,并最大限度上减轻机体的炎症反应[103]。 2.6.3 细胞学 骨再生是一个涉及到多种细胞、生长因子和生物材料综合作用的过程[104]。机体炎症环境、低氧张力、pH值等因素的影响在细胞层面也对骨修复提出了要求,目前主流的骨组织工程通常是处理间充质基质细胞。骨髓间充质干细胞是目前最常用于骨组织工程的干细胞,具有很高的成骨能力、抗炎、调节免疫的功能,在临床研究中发挥着重要的作用。研究表明,骨髓间充质干细胞还会向周围微环境释放旁分泌因子,包括转化生长因子β、成纤维细胞生长因子2、血管生成素2、血管内皮生长因子A等,通过募集巨噬细胞来促进骨折愈合[105]。然而,由于骨髓间充质干细胞从骨髓中获取困难及实验传代培养次数增加导致的长期多能性较差显著限制了其应用[106],因此,用于骨组织工程的理想干细胞应是易于获得且具有良好成骨潜力的细胞。 2.6.4 材料 椎间盘是由纤维软骨构成的结构,它位于相邻椎体之间,连接上椎体和下椎体(图6)。椎间盘包括软组织子结构,如髓核、纤维环等;除此之外,椎间盘还与位于椎体后方的滑膜关节共同组成脊柱的一个复杂结构,这些结构共同作用,提供运动、承重和灵活性,同时保护脊柱的神经解剖结构。髓核和纤维环是两种不同的黏弹性、依赖于水分的组织,主要由水、胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖组成[107]。蛋白聚糖的存在会在髓核中产生膨胀力,当髓核受到压缩时内部压力增大,从而在纤维环中产生箍缩应力,这种应力通过胶原纤维的拉伸来承载[108]。椎间盘退行性变化通常伴随蛋白聚糖的减少、细胞外基质的结构紊乱、纤维环撕裂以及椎间盘高度的降低,特别是蛋白聚糖的减少会导致水分的流失,进而改变各组成部分的特性,影响椎间盘整体的力学表现[109]。因此,理想的材料应该具备非常高的压缩、弯曲、扭转载荷水平。为防止材料植入后潜在的排异反应,材料应具有与天然骨相似的生物学特性,同时还需限制潜在的毒性缺陷[110]。单一材料通常很难模仿天然骨组织的组成,因此,需要使用几种不同的材料、涂层和复合材料,以便符合上述的生物学要求。其中,由聚合物、陶瓷、金属组成的支架主要用作骨组织工程支架的基础材料[111],虽然上述材料具有对骨组织的必要特性,但要找到一种理想的支架材料仍有许多工作要做。理想的支架材料必具有生物相容性[112]、可生物降解性[113]、高度多孔[114]、易于操作等特性,并最终能够促进成骨,同时在机械上适合承受相关负荷[115],目前符合上述要求的理想材料还未在实验室中合成,还需要进一步的基础研究以合成符合要求的复合材料。 "
| [1] UCHINO K. The development of piezoelectric materials and the new perspective//EDITOR F, editor. Advanced Piezoelectric Materials. Woodhead Publishing; 2017:1-92. [2] FUKADA E, YASUDA I. On the piezoelectric effect of bone. J Phys Soc Jpn. 1957;12(10): 1158-1162. [3] BRIGHTON CT, POLLACK SR. Treatment of recalcitrant non-union with a capacitively coupled electrical field. A preliminary report. JBJS. 1985;67(4):577-585. [4] EINHORN TA. Enhancement of fracture-healing. JBJS. 1995;77(6):940-956. [5] SHIN SR, FARZAD MR, TAMAYOL A, et al. A bioactive carbon nanotube-based ink for printing 2D and 3D flexible electronics. Adv Mater. 2016;28(17):3280. [6] PARK JB, KELLY BJ, KENNER GH, et al. Piezoelectric ceramic implants: in vivo results. J Biomed Mater Res. 1981;15(1): 103-110. [7] WANG Q, YANG J, ZHANG W, et al. Manufacture and cytotoxicity of a lead‐free piezoelectric ceramic as a bone substitute—consolidation of porous lithium sodium potassium niobate by cold isostatic pressing. Int J Oral Sci. 2009;1(2):99-104. [8] RAJABI AH, JAFFE M, ARINZEH TL. Piezoelectric materials for tissue regeneration: A review. Acta Biomater. 2015;24:12-23. [9] TANAKA M, AOKI K, HANIU H, et al. Applications of carbon nanotubes in bone regenerative medicine. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(4):659. [10] SHADJOU N, HASANZADEH M, KHALILZADEH B. Graphene based scaffolds on bone tissue engineering. Bioengineered. 2018;9(1):38-47. [11] AOKI K, HANIU H, KIM YA, et al. The use of electrospun organic and carbon nanofibers in bone regeneration. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(3):562. [12] FERRIGNO B, BORDETT R, DURAISAMY N, et al. Bioactive polymeric materials and electrical stimulation strategies for musculoskeletal tissue repair and regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3):468-485. [13] LEPPIK L, OLIVEIRA KMC, BHAVSAR MB, et al. Electrical stimulation in bone tissue engineering treatments. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(2):231-244. [14] SAIGUSA Y. Quartz-based piezoelectric materials. In: Advanced Piezoelectric Materials. Woodhead Publishing; 2017:197-233. [15] BERA S, GUERIN S, YUAN H, et al. Molecular engineering of piezoelectricity in collagen-mimicking peptide assemblies. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2634. [16] FAHAD M, WAQAR A, KIM B. Effective-performance of inorganic and organic (barium zirconium titanate/polyvinylidene fluoride) piezoelectric composite for energy harvesting and self-powered smart IoT-based electronics. J Alloys Compd. 2024;985:174033. [17] KABRA H, DEORE HA, PATIL P. Review on advanced piezoelectric materials (BaTiO3, PZT). J Emerg Technol Innov Res. 2019;6(4):950. [18] CHEN W, YU Z, PANG J, et al. Fabrication of biocompatible potassium sodium niobate piezoelectric ceramic as an electroactive implant. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(4):345. [19] XIE L, WANG G, JIANG C, et al. Properties and applications of flexible poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based piezoelectric materials. Crystals. 2021;11(6):644. [20] NING C, ZHOU Z, TAN G, et al. Electroactive polymers for tissue regeneration: Developments and perspectives. Prog Polym Sci. 2018;81:144-162. [21] JAIN A, KJ P, SHARMA AK, et al. Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of PVDF/PZT composites: A review. Polym Eng Sci. 2015;55(7):1589-1616. [22] CHOI SR, KWON JW, SUK K, et al. The clinical use of osteobiologic and metallic biomaterials in orthopedic surgery: the present and the future. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(10):3633. [23] WANG N, DHEEN ST, FUH JYH, et al. Functions and applications of metallic and metallic oxide nanoparticles in orthopedic implants and scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(2):160-179. [24] ZHAO C, LU X, ZANDEN C, et al. The promising application of graphene oxide as coating materials in orthopedic implants: preparation, characterization and cell behavior. Biomed Mater. 2015; 10(1):015019. [25] LI M, XIONG P, YAN F, et al. An overview of graphene-based hydroxyapatite composites for orthopedic applications. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(1):1-18. [26] ARUMUGAM D, ADHIKARI S, BABU SSG, et al. Functionalized polyaniline nanofibrils on lamellar structured zirconium for effective bone mineralization. Appl Surf Sci. 2025;681:161566. [27] PERUMAL A, KANUMURI R, RAYALA SK, et al. Fabrication of bioactive corrosion-resistant polyaniline/TiO2 nanotubes nanocomposite and their application in orthopedics. J Mater Sci. 2020;55:15602-15620. [28] BORGES MH, NAGAY BE, COSTA RC, et al. Recent advances of polypyrrole conducting polymer film for biomedical application: Toward a viable platform for cell-microbial interactions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023; 314:102860. [29] DUBEY KA, CHAUDHARI CV, BHARDWAJ YK, et al. Polymers, blends and nanocomposites for implants, scaffolds and controlled drug release applications. Adv Biomater Biomed Appl. 2017:1-44. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-3328-5_1 [30] SHANMUGANANTHA L, BAHARUDIN A, SULONG AB, et al. Prospect of metal ceramic (Titanium-Wollastonite) composite as permanent bone implants: A narrative review. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(2):277. [31] AARON RK, CIOMBOR DMK, SIMON BJ, et al. Treatment of nonunions with electric and electromagnetic fields. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;419:21-29. [32] CADOSSI R, MASSARI L, RACINE-AVILA J, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation of bone healing and joint preservation: Cellular mechanisms of skeletal response. JAAOS Glob Res Rev. 2020;4(5):e19. [33] KATOH K. Effects of electrical stimulation of the cell: wound healing, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and signal transduction. Med Sci. 2023;11(1):11. [34] VILLALOBO A, BERCHTOLD MW. The role of calmodulin in tumor cell migration, invasiveness, and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):765. [35] ZHANG X, WANG T, ZHANG Z, et al. Electrical stimulation system based on electroactive biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Mater Today. 2023;68:177-203. [36] LIU H, ZHANG C, XIONG W, et al. Advances in electroactive biomaterials: through the lens of electrical stimulation promoting bone regeneration strategy. J Orthop Transl. 2024;47:191-206. [37] ZHANG Y, YAN J, XU H, et al. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields promote mesenchymal stem cell migration by increasing intracellular Ca2+ and activating the FAK/Rho GTPases signaling pathways in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9:1-10. [38] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast–osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107. [39] DETSCH R, BOCCACCINI AR. The role of osteoclasts in bone tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(10): 1133-1149. [40] SUN J, XIE W, WU Y, et al. Accelerated bone healing via electrical stimulation. Adv Sci. 2024:2404190. doi:10.1002/advs.202404190. [41] XU J, WANG W, CLARK CC, et al. Signal transduction in electrically stimulated articular chondrocytes involves translocation of extracellular calcium through voltage-gated channels. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(3): 397-405. [42] KRUEGER S, RIESS A, JONITZ-HEINCKE A, et al. Establishment of a new device for electrical stimulation of non-degenerative cartilage cells in vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(1):394. [43] MATTA C, MOBASHERI A. Regulation of chondrogenesis by protein kinase C: emerging new roles in calcium signalling. Cell Signal. 2014;26(5):979-1000. [44] KWON HJ, CHUN H, LEE GS, et al. Electrical stimulation drives chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells in the absence of exogenous growth factors. Sci Rep. 2016; 6(1):39302. [45] WANG YT, MENG XT. A review of the evidence to support electrical stimulation-induced vascularization in engineered tissue. Regen Ther. 2023;24:237-244. [46] CUNHA F, RAJNICEK AM, MCCAIG CD, et al. Electrical stimulation directs migration, enhances and orients cell division and upregulates the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR2 in endothelial cells. J Vasc Res. 2019;56(1):39-53. [47] KATOH K. Effects of electrical stimulation of the cell: wound healing, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and signal transduction. Med Sci. 2023;11(1):11. [48] CAI B, LIN D, LI Y, et al. N2-polarized neutrophils guide bone mesenchymal stem cell recruitment and initiate bone regeneration: A missing piece of the bone regeneration puzzle. Adv Sci. 2021; 8(19):2100584. [49] SIMONS M, GORDON E, CLAESSON-WELSH L, et al. Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(10):611-625. [50] MACDONALD BT, TAMAI K, HE X. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009; 17(1):9-26. [51] LIU SL, ZHOU YM, CHEN J, et al. LGR6 promotes osteogenesis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;519(1):1-7. [52] YU C, YING X, SHAHBAZI MA, et al. A nano-conductive osteogenic hydrogel to locally promote calcium influx for electro-inspired bone defect regeneration. Biomaterials. 2023;301:122266. [53] JIANG Z, DENG L, LI M, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 modulates PI3K/AKT pathway for enhanced osteogenesis via GPER. Phytomedicine. 2024;124:155284. [54] KANG JY, KANG N, YANG YM, et al. The role of Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling and its modulation on osteoclastogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(10):3646. [55] HU L, CHEN W, QIAN A, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Components and Mechanisms in Bone Formation, Homeostasis, and Disease. Bone Res. 2024;12(1):39. [56] ZHOU J, LI X, LIAO Y, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Inhibit Bone Loss in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats. Endocrine. 2015;49:258-266. [57] SUN LY, HSIEH DK, LIN PC, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Accelerate Proliferation and Osteogenic Gene Expression in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells During Osteogenic Differentiation. Bioelectromagnetics. 2010; 31(3):209-219. [58] CLARK CC, WANG W, BRIGHTON CT. Up‐regulation of Expression of Selected Genes in Human Bone Cells with Specific Capacitively Coupled Electric Fields. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(7):894-903. [59] ZHAI M, JING D, TONG S, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Promote in Vitro Osteoblastogenesis Through a Wnt/β‐catenin Signaling‐associated Mechanism. Bioelectromagnetics. 2016;37(3):152-162. [60] FATHI E, FARAHZADI R. Enhancement of Osteogenic Differentiation of Rat Adipose Tissue-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Zinc Sulphate Under Electromagnetic Field via the PKA, ERK1/2, and Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathways. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0173877. [61] YE C, ZHANG W, HUANG K, et al. Extracellular IL-37 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Activation of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(10):753. [62] NING C, YU P, WANG Z, et al. 0D/1D Heterojunction Implant with Electro-Mechanobiological Coupling Cues Promotes Osteogenesis. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(50):2106249. [63] NING C, XIAO C, GUAN P, et al. Extracellular Matrix‐based Conductive Interpenetrating Network Hydrogels with Enhanced Neurovascular Regeneration Properties for Diabetic Wounds Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(1):2101556. [64] WINSLOW MM, STARBUCK M, CRABTREE GR, et al. Calcineurin/NFAT Signaling in Osteoblasts Regulates Bone Mass. Dev Cell. 2006;10(6):771-782. [65] WANG P, HAO L, ZHANG P, et al. Gadolinium-doped BTO-functionalized Nanocomposites with Enhanced MRI and X-ray Dual Imaging to Simulate the Electrical Properties of Bone. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020; 12(44):49464-49479. [66] XU J, LI Z, HOU Y, et al. Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Runx2-induced Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(12):2527. [67] WANG Y, QU X, YANG Y, et al. AMPK Promotes Osteogenesis and Inhibits Adipogenesis Through AMPK-Gfi1-OPN Axis. Cell Signal. 2016;28(9):1270-1282. [68] DONG M, JIAO G, LIU H, et al. Biological Silicon Stimulates Collagen Type 1 and Osteocalcin Synthesis in Human Osteoblast-like Cells Through the BMP-2/Smad/RUNX2 Signaling Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;173:306-315. [69] GUTIÉRREZ A, CONTRERAS C, PRIETO D, et al. Role of Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase (MAPK), and Protein Kinase C (PKC) in Calcium Signaling Pathways Linked to the α1-adrenoceptor in Resistance Arteries. Front Physiol. 2019;10:55. [70] SHEN S, HE X, WENG W, et al. Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on P(VDF‐TrFE) Layer Coated Microelectrodes. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(12):2227-2236. [71] LI T, CHEN D, O’KEEFE RJ, et al. TGF-β Signaling in Chondrocytes. Front Biosci. 2005;10:681. [72] VARANI K, PASQUINI S, FENG L, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Stimulation in Osteogenesis and Chondrogenesis: Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):809. [73] ZOU M, CHEN Z, FENG L, et al. The Smad-dependent TGF-β and BMP Signaling Pathway in Bone Remodeling and Therapies. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:593310. [74] ARAMBULA-MALDONADO R, MEQUANINT K. Carbon-based Electrically Conductive Materials for Bone Repair and Regeneration. Mater Adv. 2022;3(13):5186-5206. [75] ZANJANIZADEH EZAZI N, SHAHBAZI MA, SHATALIN YV, et al. Conductive Vancomycin-loaded Mesoporous Silica Polypyrrole-based Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Int J Pharm. 2018;536(1):241-250. [76] LI J, FENG Y, CHEN W, et al. Electroactive Materials: Innovative Antibacterial Platforms for Biomedical Applications. Prog Mater Sci. 2023;132:101045. [77] SAMADI A, SALATI MA, SAFARI A, et al. Comparative Review of Piezoelectric Biomaterials Approach for Bone Tissue Engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022;33(12):1555-1594. [78] SHUAI C, LIU G, QI F, et al. A Strawberry-like Ag-decorated Barium Titanate Enhances Piezoelectric and Antibacterial Activities of Polymer Scaffold. Nano Energy. 2020;74:104825. [79] MENG S, ROUABHIA M, ZHANG Z. Electrical Stimulation in Tissue Regeneration. Appl Biomed Eng. 2011:37-62. doi:10.5772/18874 [80] FERRIGNO B, DURAISAMY N, MOSKOW J, et al. Bioactive Polymeric Materials and Electrical Stimulation Strategies for Musculoskeletal Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3): 468-485. [81] SILVA NA, REIS RL, REIS RL, et al. From Basics to Clinical: A Comprehensive Review on Spinal Cord Injury. Prog Neurobiol. 2014; 114:25-57. [82] KARSY M, HAWRYLUK G. Modern Medical Management of Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19:1-7. [83] GREEN R, ABIDIAN MR. Conducting Polymers for Neural Prosthetic and Neural Interface Applications. Adv Mater. 2015;27(46):7620-7637. [84] MARQUES-ALMEIDA T, LANCEROS-MENDEZ S, RIBEIRO C. State of the Art and Current Challenges on Electroactive Biomaterials and Strategies for Neural Tissue Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(1):2301494. [85] KUBISZ L, HOJAN-JEZIERSKA D, SZEWCZYK M, et al. In Vivo Electrical Impedance Measurement in Human Skin Assessment. Pure Appl Chem. 2019;91(9):1481-1491. [86] REID B, ZHAO M. The Electrical Response to Injury: Molecular Mechanisms and Wound Healing. Adv Wound Care. 2014;3(2):184-201. [87] YU R, ZHANG H, GUO B. Conductive Biomaterials as Bioactive Wound Dressing for Wound Healing and Skin Tissue Engineering. Nanomicro Lett. 2022;14:1-46. [88] EISCHEN-LOGES M, OLIVEIRA KMC, BHAVSAR MB, et al. Pretreating Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Electrical Stimulation Causes Sustained Long-lasting Pro-osteogenic Effects. PeerJ. 2018;6:e4959. [89] YUAN X, ARKONAC DE, CHAO PH, et al. Electrical Stimulation Enhances Cell Migration and Integrative Repair in the Meniscus. Sci Rep. 2014;4(1):3674. [90] KHALIFEH JM, ZOHNY Z, MACEWAN M, et al. Electrical Stimulation and Bone Healing: A Review of Current Technology and Clinical Applications. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2018;11:217-232. [91] JAVEED S, ZHANG JK, GREENBERG JK, et al. Electroactive Spinal Instrumentation for Targeted Osteogenesis and Spine Fusion: A Computational Study. Int J Spine Surg. 2023;17(1):95-102. [92] CHENG Y, XU Y, QIAN Y, et al. 3D Structured Self-Powered PVDF/PCL Scaffolds for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Nano Energy. 2020;69:104411. [93] KAPAT K, SHUBHRA QT, ZHOU M, et al. Piezoelectric Nano‐Biomaterials for Biomedicine and Tissue Regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(44):1909045. [94] ZHENG Z, LI G, WANG X, et al. Piezoelectric Composite Hydrogel with Wireless Electrical Stimulation Enhances Motor Functional Recovery of Spinal Cord Injury. J Mater Sci Technol. 2024;172:228-239. [95] KAUR G, ADHIKARI R, CASS P, et al. Electrically Conductive Polymers and Composites for Biomedical Applications. RSC Adv. 2015;5(47):37553-37567. [96] LIU D, HUYAN C, WANG Z, et al. Conductive Polymer-Based Hydrogels and Their Application in Wearable Sensors: A Review. Mater Horiz. 2023;10(8):2800-2823. [97] GUO X, LI J, WANG F,et al. Application of Conductive Polymer Hydrogels in Flexible Electronics. J Polym Sci. 2022;60(18): 2635-2662. [98] MARSUDI MA, ARISKI RT, WIBOWO A, et al. Conductive Polymeric-Based Electroactive Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: Current Progress and Challenges from Biomaterials and Manufacturing Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11543. [99] DING C, LV H, HUANG S, et al. The Application Progress of Nonthermal Plasma Technology in the Modification of Bone Implant Materials. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024;10(10):5893-5914. [100] TRISI P, LAZZARA R, RAO W, et al. Bone-Implant Contact and Bone Quality: Evaluation of Expected and Actual Bone Contact on Machined and Osseotite Implant Surfaces. Int J Periodontics Restor Dent. 2002;22(6):535-545. [101] LI J, QIN L, YANG K, et al. Materials Evolution of Bone Plates for Internal Fixation of Bone Fractures: A Review. J Mater Sci Technol. 2020;36:190-208. [102] ESPIRITU J, BERANGI M, YIANNAKOU C, et al. Evaluating Metallic Artefact of Biodegradable Magnesium-Based Implants in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Bioact Mater. 2022;15:382-391. [103] PRZEKORA A. The Summary of the Most Important Cell-Biomaterial Interactions That Need to Be Considered During in Vitro Biocompatibility Testing of Bone Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;97:1036-1051. [104] ASL SH, HOSSEINPOOR H, PARIVAR K, et al. Physical Stimulation and Scaffold Composition Efficiently Support Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Tissue Cell. 2018;50:1-7. [105] ONGARO A, PELLATI A, BAGHERI L, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Stimulate Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Bone Marrow and Adipose Tissue Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2014;35(6):426-436. [106] ZHONG S, HE X, LI Y, et al. Conditioned Medium Enhances Osteogenic Differentiation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;16:141-150. [107] NIKKHOO M, WANG JL, ABDOLLAHI M, et al. A Regenerative Approach Towards Recovering the Mechanical Properties of Degenerated Intervertebral Discs: Genipin and Platelet-rich Plasma Therapies. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231(2):127-137. [108] NEWELL N, LITTLE JP, CHRISTOU A, et al. Biomechanics of the Human Intervertebral Disc: A Review of Testing Techniques and Results. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017; 69:420-434. [109] VAN DER VEEN AJ, EMANUEL KS, EMANUEL KS, et al. The Poro-elastic Behaviour of the Intervertebral Disc: A New Perspective on Diurnal Fluid Flow. J Biomech. 2016;49(6): 857-863. [110] ABBASIAN M, MASSOUMI B, MOHAMMAD-REZAEI R, et al. Scaffolding Polymeric Biomaterials: Are Naturally Occurring Biological Macromolecules More Appropriate for Tissue Engineering? Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;134:673-694. [111] QU H, FU H, HAN Z, et al. Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: A Review. RSC Adv. 2019;9(45):26252-26262. [112] KUMAR A, NUNE KC, MURR LE, et al. Biocompatibility and Mechanical Behaviour of Three-Dimensional Scaffolds for Biomedical Devices: Process–Structure–Property Paradigm. Int Mater Rev. 2016;61(1):20-45. [113] ZHANG F, KING MW. Biodegradable Polymers as the Pivotal Player in the Design of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(13):1901358. [114] SLATER AG, COOPER AI. Function-Led Design of New Porous Materials. Science. 2015;348(6238):aaa8075. [115] FROST BA, CAMARERO-ESPINOSA S, FOSTER EJ. Materials for the Spine: Anatomy, Problems, and Solutions. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(2):253. [116] BOEHLER C, AQRAWE Z, ASPLUND M. Applications of PEDOT in Bioelectronic Medicine. Bioelectron Med. 2019;2(2):89-99. [117] ZHAO H, LIU C, LIU Y, et al. Harnessing Electromagnetic Fields to Assist Bone Tissue Engineering. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023; 14(1):7. [118] NAGA SM, MAHMOUD EM, EL-MAGHRABY HF, et al. Porous Scaffolds Based on Biogenic Poly (ε-Caprolactone)/Hydroxyapatite Composites: In Vivo Study. Adv Nat Sci: Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;9(4):045004. [119] TOTH JM, WANG M, ESTES BT, et al. Polyetheretherketone as a Biomaterial for Spinal Applications. Biomaterials. 2006; 27(3):324-334. [120] PARSONS AJ, AHMED I, WARRIOR NA, et al. Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone (PEEK) Biomaterials and Composites: Challenges, Progress, and Opportunities. Polym Rev. 2024:1-39. doi:10.1080/15583724.2024.2406965 [121] Ei H, CUI J, LIN K, et al. Recent Advances in Smart Stimuli-Responsive Biomaterials for Bone Therapeutics and Regeneration. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):17. [122] PEREZ JR, KOUROUPIS D, LI DJ, et al. Tissue Engineering and Cell-Based Therapies for Fractures and Bone Defects. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018;6:105. |
| [1] | Tan Jing, Li Li, Wang Liangliang, Qin Xiangyu. Bionic functional coating improves the integration of titanium implants and skin tissue interface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2014-2022. |
| [2] | Liu Huan, Zeng Shaopeng, Chen Jun, He Linqian, Yang Ying, Zhang Jing. Aging-related dysregulation of glucose metabolism: crossroads of cancer and neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1527-1538. |
| [3] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [4] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [5] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [6] | Zhang Zhaowei, Chen Ouzile, Bai Mingru, Wang Chenglin. Therapeutic potential of bioactive substances secreted by dental mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 163-174. |
| [7] | Luo Wenbin, Li Ruoyun, Pan Chaofan, Luo Changjiang. Engineered exosomes for repairing tissue damage: application potential, excellent biological stability, and targeting specificity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 204-217. |
| [8] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [9] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [10] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [11] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [12] | Chen Yilin, Jiang Xiaobo, Qu Honglin, Liu Ruilian. General pattern of GSK3/Nrf2-regulated biological rhythms in organismal aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1257-1264. |
| [13] | Wang Rongrong, Huang Yushan, Li Xiangmiao, Bai Jinzhu. Prostaglandin E1 regulates vascular-related factors and protects microcirculatory function during the acute phase of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 958-967. |
| [14] | Zhang Yu, Xu Ruian, Fang Lei, Li Longfei, Liu Shuyan, Ding Lingxue, Wang Yuexi, Guo Ziyan, Tian Feng, Xue Jiajia. Gradient artificial bone repair scaffold regulates skeletal system tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| [15] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||