Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1114-1121.doi: 10.12307/2026.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Forskolin promotes C2C12 myoblast differentiation via regulating the ERK and Akt signaling pathways
Huang Liuyan, Zhang Wenxi, Chen Shuwen, Yu Shimei, Dai Zhong, Zuo Changqing
- School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523808, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-05Accepted:2025-01-13Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-23 -
Contact:Zuo Changqing, PhD, Associate professor, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523808, Guangdong Province, China Co-corresponding author: Dai Zhong, PhD, Associate professor, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523808, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Liuyan, Master candidate, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523808, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, No. 2023A1515140157 (to ZCQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Liuyan, Zhang Wenxi, Chen Shuwen, Yu Shimei, Dai Zhong, Zuo Changqing. Forskolin promotes C2C12 myoblast differentiation via regulating the ERK and Akt signaling pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1114-1121.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
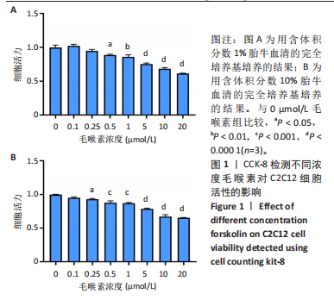
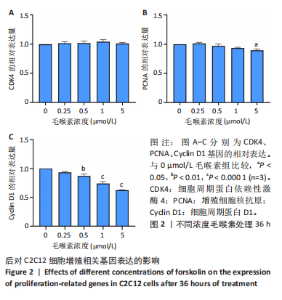
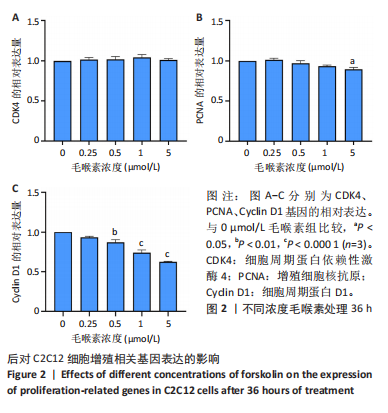
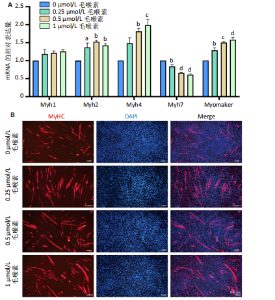
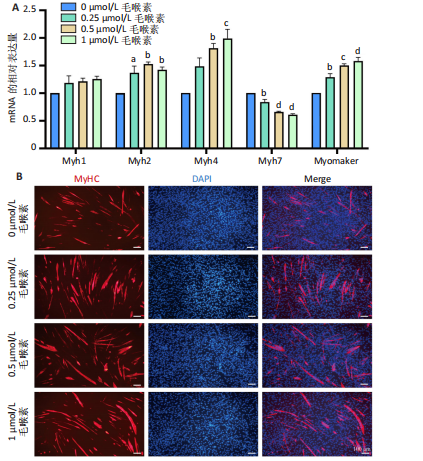
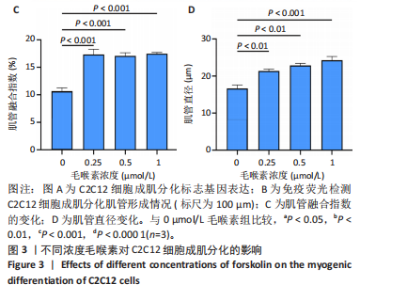
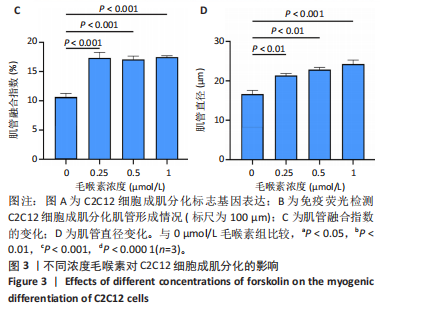
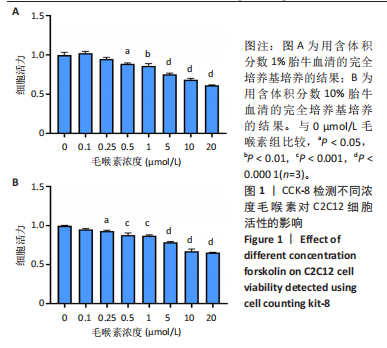
2.1 毛喉素对C2C12细胞活力的影响 首先,使用C2C12成肌细胞研究了不同浓度毛喉素处理的细胞毒性,将C2C12细胞分别与不同浓度的毛喉素(0-20 μmol/L)孵育48 h后进行CCK-8检测。结果显示,无论是在含体积分数1%胎牛血清或是在体积分数10%胎牛血清的培养基中培养,低浓度的毛喉素对C2C12成肌细胞的增殖过程无细胞毒性(图1A),但是当毛喉素浓度增加,细胞活力下降,并在毛喉素浓度> 1 μmol/L时活性下降20%左右(图1B)。这些数据表明,高剂量毛喉素处理会抑制C2C12细胞的活性。 2.2 毛喉素对C2C12细胞增殖相关基因的影响 为了进一步探讨毛喉素是否会影响C2C12细胞的增殖,在毛喉素处理C2C12细胞36 h后进行qRT-PCR检测。结果显示,CDK4表达水平在毛喉素处理的细胞和对照组细胞之间没有差异(图2A);PCNA表达水平在毛喉素处理浓度为5 μmol/L的时候下降(图2B);Cyclin D1表达水平在毛喉素处理浓度> 0.25 μmol/L时开始下降,毛喉素处理浓度为5 μmol/L时CyclinD1表达水平大幅下降(图2C)。以上结果说明高浓度毛喉素对C2C12细胞具有抗增殖作用。 2.3 毛喉素对C2C12细胞成肌分化的影响 2.3.1 qPCR分析 为了研究毛喉素对C2C12细胞成肌分化的影响,用不同浓度的毛喉素(0,0.25,0.5,1 μmol/L)孵育C2C12细胞,并在处理后进行qPCR分析,观察毛喉素对成肌分化标志基因mRNA表达的影响。在成肌分化4 d时,经毛喉素处理的细胞Myh2、Myh4基因表达水平较0 μmol/L毛喉素组增加(图3A),肌肉特异性膜蛋白Myomaker的表达水平也增加,而主要在Ⅰ型慢缩肌纤维中表达的Myh7"

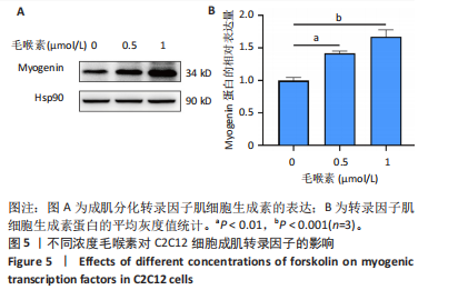
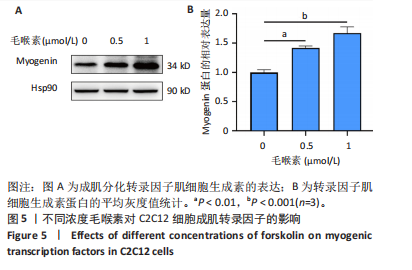
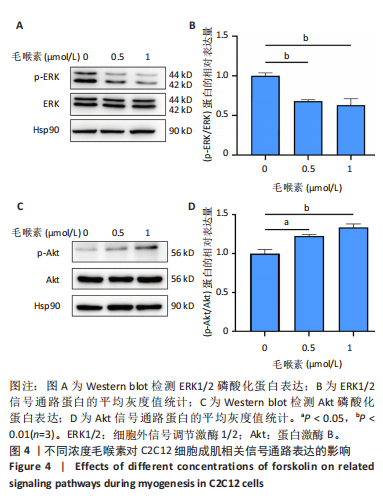
(图3B)。此外,定量分析数据显示:毛喉素处理后的C2C12细胞融合指数上升(图3C),与0 μmol/L毛喉素组相比,毛喉素处理各组肌管直径明显增加(图3D)。总之,与0 μmol/L毛喉素组相比,毛喉素处理各组MyHC阳性肌管的数量明显增多。以上结果表明,毛喉素能有效促进C2C12成肌细胞的分化。 2.4 毛喉素通过调控ERK1/2和Akt信号通路影响C2C12成肌细胞分化 先前研究表明,ERK1/2对哺乳动物骨骼肌生成至关重要 [15]。为了探讨毛喉素促进C2C12细胞分化的分子机制,采用Western blot法检测了毛喉素处理C2C12细胞分化2 d时ERK1/2磷酸化蛋白水平的变化(图4)。与对照组C2C12细胞相比,毛喉素处理2 d的C2C12细胞中磷酸化ERK1/2的蛋白表达显著减少,而总ERK1/2蛋白的水平保持不变(图4A),表明毛喉素的促肌生成作用依赖于ERK1/2信号通路的抑制。此外,在调节肌肉发育的信号通路中,Akt信号通路在肌肉生长中起着核心作用 [16],因此同时检测了Akt信号通路的变化,结果发现,成肌分化2 d时,毛喉素处理组磷酸化Akt的蛋白表达水平升高(图4C),表明毛喉素的促肌生成作用还依赖于Akt信号通路的激活。"
| [1] Progress in heterologous biosynthesis of forskolin. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021;48(1-2):kuab009. [2] ROSHNI PT, REKHA PD. Biotechnological interventions for the production of forskolin, an active compound from the medicinal plant, Coleus forskohlii. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2024;30(2):213-226. [3] SAPIO L, GALLO M, ILLIANO M, et al. The Natural cAMP Elevating Compound Forskolin in Cancer Therapy: Is It Time? J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(5):922-927. [4] BANGAY G, BRAUNING FZ, ROSATELLA A, et al. Anticancer diterpenes of African natural products: Mechanistic pathways and preclinical developments. Phytomedicine. 2024;129:155634. [5] SALZILLO A, RAGONE A, SPINA A, et al. Forskolin affects proliferation, migration and Paclitaxel-mediated cytotoxicity in non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines via adenylyl cyclase/cAMP axis. Eur J Cell Biol. 2023;102(2):151292. [6] WU J, YUE B. Regulation of myogenic cell proliferation and differentiation during mammalian skeletal myogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;174:116563. [7] 吴玲玲, 张小玉, 李晓,等. miR-196b-5p促进成肌细胞增殖分化[J]. 遗传, 2023,45(5):435-446. [8] CHEN JY, PENG SY, CHENG YH, et al. Effect of Forskolin on Body Weight, Glucose Metabolism and Adipocyte Size of Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Animals (Basel). 2021;11(3):645. [9] AWALE GM, BARAJAA MA, KAN HM, et al. Regenerative engineering of long bones using the small molecule forskolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(22):e2219756120. [10] XU C, TABEBORDBAR M, IOVINO S, et al. A zebrafish embryo culture system defines factors that promote vertebrate myogenesis across species. Cell. 2013,155(4):909-921. [11] ZHANG Y, ZHU Y, LI Y, et al. Long-term engraftment of myogenic progenitors from adipose-derived stem cells and muscle regeneration in dystrophic mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(21):6029-6040. [12] JEONG J, CHOI KH, KIM SH, et al.Combination of cell signaling molecules can facilitate MYOD1-mediated myogenic transdifferentiation of pig fibroblasts. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021;12(1):64. [13] CHEN AE, GINTY DD, FAN CM. Protein kinase A signalling via CREB controls myogenesis induced by Wnt proteins. Nature. 2005; 433(7023):317-322. [14] TAGLIETTI V, KEFI K, RIVERA L, et al. Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor signaling restores skeletal muscle stem cell regeneration in rats with muscular dystrophy. Sci Transl Med. 2023;15(685):eadd5275. [15] KNIGHT JD, KOTHARY R. The myogenic kinome: protein kinases critical to mammalian skeletal myogenesis. Skelet Muscle. 2011;1:29. [16] HO PT, PARK E, LUONG QXT, et al. Amelioration of Cancer Cachexia by Dalbergia odorifera Extract Through AKT Signaling Pathway Regulation. Nutrients. 2024;16(21):3671. [17] LAURENZA A, SUTKOWSKI EM, SEAMON KB. Forskolin: a specific stimulator of adenylyl cyclase or a diterpene with multiple sites of action? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989;10(11):442-447. [18] ZHANG H, LIU Y, LIU J, et al. cAMP-PKA/EPAC signaling and cancer: the interplay in tumor microenvironment. J Hematol Oncol. 2024;17(1):5. [19] LAUTHERBACH N, GONCALVES DAP, SILVEIRA WA, et al. Urocortin 2 promotes hypertrophy and enhances skeletal muscle function through cAMP and insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathways. Mol Metab. 2022; 60:101492. [20] ASLAM M, LADILOV Y. Emerging Role of cAMP/AMPK Signaling. Cells. 2022;11(2):308. [21] TCHAKARSKA G, SOLA B. The double dealing of cyclin D1. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(2):163-178. [22] DIECKMAN LM, FREUDENTHAL BD, WASHINGTON MT. PCNA structure and function: insights from structures of PCNA complexes and post-translationally modified PCNA. Subcell Biochem. 2012;62:281-299. [23] DE LA SERNA IL, ROY K, CARLSON KA, et al. MyoD can induce cell cycle arrest but not muscle differentiation in the presence of dominant negative SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling enzymes. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276(44):41486-41491. [24] DOS SANTOS M, BACKER S, AURADE F, et al. A fast Myosin super enhancer dictates muscle fiber phenotype through competitive interactions with Myosin genes. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1039. [25] MO M, ZHANG Z, WANG X, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying the impact of muscle fiber types on meat quality in livestock and poultry. Front Vet Sci. 2023;10:1284551. [26] MILLAY DP, O’ROURKE JR, SUTHERLAND LB, et al. Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation. Nature. 2013;499(7458):301-305. [27] KILANOWSKA A, ZIOLKOWSKA A, STASIAK P, et al. cAMP-Dependent Signaling and Ovarian Cancer. Cells. 2022;11(23):3835. [28] PARK HB, BAEK KH. E3 ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes regulating the MAPK signaling pathway in cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022;1877(3):188736. [29] LAKE D, CORREA SA, MULLER J. Negative feedback regulation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(23):4397-4413. [30] 刘波, 黄晓帆, 李冬寒, 等. Forskolin激活cAMP信号通路调控小鼠心肌成纤维细胞结缔组织生长因子的表达[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2015,44(1):1-9. [31] CRISTOBAL I, RINCON R, MANSO R, et al. Hyperphosphorylation of PP2A in colorectal cancer and the potential therapeutic value showed by its forskolin-induced dephosphorylation and activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842(9):1823-1829. [32] XIAO D, CALDOW M, KIM HJ, et al. Time-resolved phosphoproteome and proteome analysis reveals kinase signaling on master transcription factors during myogenesis. iScience. 2022;25(6):104489. [33] JIANG X, JI S, CUI S, et al. Apol9a regulates myogenic differentiation via the ERK1/2 pathway in C2C12 cells. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:942061. [34] CHENG C, ZHANG S, GONG Y, et al. Cordycepin inhibits myogenesis via activating the ERK1/2 MAPK signalling pathway in C2C12 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023,165:115163. [35] FU X, MATSUI T, FUNABA M. Enhancement of vitamin C-induced myogenesis by inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;612:57-62. [36] TORTORELLA LL, MILASINCIC DJ, PILCH PF. Critical proliferation-independent window for basic fibroblast growth factor repression of myogenesis via the p42/p44 MAPK signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2001;276(17):13709-13717. [37] ENDO T. Postnatal skeletal muscle myogenesis governed by signal transduction networks: MAPKs and PI3K-Akt control multiple steps. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;682:223-243. [38] EIGLER T, ZARFATI G, AMZALLAG E, et al. ERK1/2 inhibition promotes robust myotube growth via CaMKII activation resulting in myoblast-to-myotube fusion. Dev Cell. 2021;56(24):3349-3363. [39] SCHIAFFINO S, DYAR KA, CICILIOT S, et al. Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J. 2013;280(17):4294-4314. [40] NAMKOONG S, KIM CK, CHO YL, et al. Forskolin increases angiogenesis through the coordinated cross-talk of PKA-dependent VEGF expression and Epac-mediated PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling. Cell Signal. 2009;21(6):906-915. [41] GHORBANI A, JEDDI-TEHRANI M, SAIDPOUR A, et al. PI3K/AKT and Mdm2 activation are associated with inhibitory effect of cAMP increasing agents on DNA damage-induced cell death in human pre-B NALM-6 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015;566:58-66. [42] CHEN YJ, BASKARAN R, CHANG CF, et al. Decapeptide from Potato Hydrolysate Induces Myogenic Differentiation and Ameliorates High Glucose-Associated Modulations in Protein Synthesis and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in C2C12 Cells. Biomolecules. 2022;12(4):565. [43] QUAN-JUN Y, YAN H, YONG-LONG H, et al. Selumetinib Attenuates Skeletal Muscle Wasting in Murine Cachexia Model through ERK Inhibition and AKT Activation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16(2):334-343. [44] LI H, GUAN K, WANG R, et al. Synergistic effects of MFG-E8 and whey protein on mitigating d-galactose-induced sarcopenia through PI3K/AKT/PGC-1alpha and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways. J Dairy Sci. 2024; 107(1):9-23. |
| [1] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [2] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [3] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [4] | Wang Xuanqiang, Zhang Wenyang, Li Yang, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Wang Le, Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi. Effects of chronic exposure to low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields on contractility and morphology of the quadriceps muscle in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [5] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [6] | Zhang Wenhua, Li Xun, Zhang Weichao, Li Xinying, Ma Guoao, Wang Xiaoqiang . Promoting myogenesis based on the SphK1/S1P/S1PR2 signaling pathway: a new perspective on improving skeletal muscle health through exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1265-1275. |
| [7] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [8] | Wen Zixing, Xu Xin, Zhu Shengqun. Correlations between gastrocnemius morphology parameters and physical activity capacity in elderly females under high-frequency ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1058-1063. |
| [9] | Li Tingyue, Guo Qian, He Wenxi, Wu Jiayuan. Long noncoding RNA TP53TG1 promotes odontogenic and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7776-7782. |
| [10] | Cai Zhixing, Xia Qiufang, Chen Lili, Zhu Danyang, Zhu Huiwen, Sun Yanan, Liang Wenyu, Zhao Heqian. Effect of Roujishuncuiyin on the improvement of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7537-7543. |
| [11] |
Li Yunzhe, Niu Zefan, Wang Zirou, Ai Chongyi, Chen Gang, Wang Xinxing.
Asperosaponin VI promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells under hypoxia environment #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7481-7489.
|
| [12] | Liu Chenchen, Liu Ruize, Bao Mengmeng, Fang Li, Cao Liquan, Wu Jiangbo. Blood flow restriction training intervention in the elderly with sarcopenic obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6963-6970. |
| [13] | Wang Jiaqian, , Jiang Changjun, Peng Yi, Ma Mi, Li Junhan. Study on the role of aerobic exercise in regulating the CNPY2-mediated AKT/GSK3β pathway for improving non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6441-6448. |
| [14] | Hu Shujuan, Liu Dang, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang. Ameliorative effect of walnut oil and peanut oil on atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6482-6488. |
| [15] | Zhang Zihan¹, Wang Jiaxin¹, Yang Wenyi², Zhu Lei¹. Regulatory mechanism of exercise promoting mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6499-6508. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||