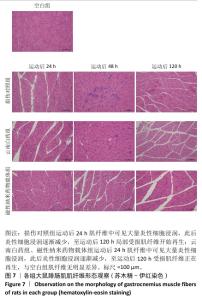
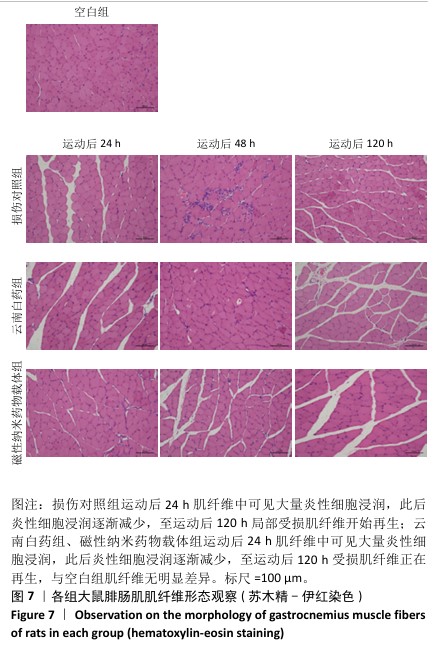
[1] PARK H, OTTE A, PARK K. Evolution of drug delivery systems: From 1950 to 2020 and beyond. J Control Release. 2022;342:53-65.
[2] TAY ZW, CHANDRASEKHARAN P, FELLOWS BD, et al.Magnetic Particle Imaging: An Emerging Modality with Prospects in Diagnosis, Targeting and Therapy of Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(21):5285.
[3] 唐倩倩,吴荣谦,樊海明,等.基于磁性纳米材料的靶向治疗研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2022,49(12):2266-2277.
[4] 周静,苏丹柯.超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子诊断与治疗乳腺癌的研究进展[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2023,30(9):836-841.
[5] HALDER J, PRADHAN D, BISWASROY P, et al. Trends in iron oxide nanoparticles: a nano-platform for theranostic application in breast cancer. J Drug Target. 2022;30(10):1055-1075.
[6] 李骁君.利用bFGF包裹的纳米磁性颗粒对大鼠急性骨骼肌钝挫伤恢复过程中收缩应力及MHC-Ⅱb表达影响研究[J].天津体育学院学报,2011,26(1):34-36,41.
[7] 董超,陈乐琴.运动性肌肉损伤的治疗方法现状与展望[C]//中国体育科学学会.第十三届全国体育科学大会论文摘要集:专题报告(运动医学分会).山西师范大学,2023:3. doi:10.26914/c.cnkihy.2023.063245.
[8] MA Z, ZHANG B, FAN Y, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine combined with hepatic targeted drug delivery systems: A new strategy for the treatment of liver diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;117:109128.
[9] 张红波.植物源性芥子酸对运动性骨骼肌损伤大鼠骨骼肌氧化应激和线粒体功能的影响[J].分子植物育种,2023,21(24):8227-8233.
[10] 吴丽君,王佳怡,毕翔宇.虾青素通过mTOR-ULK1自噬通路对大鼠运动性骨骼肌损伤影响的研究[J].山东体育学院学报,2024, 40(3):114-126.
[11] 刘东彪.胡椒活性物质胡椒碱通过调节PI3K/AKT改善大鼠运动性骨骼肌损伤[J].分子植物育种,2024,22(5):1654-1662.
[12] 武堂晓,杨曦,尹紫依,等.沙漠干热环境下大鼠运动骨骼肌损伤评价指标的筛选[J].陆军军医大学学报,2024,46(8):894-900.
[13] 雷珊,王黎安,林福星,等.具有双重治疗机制的磁性纳米无定型氧化铁基药物递送系统(英文)[J].化学物理学报,2020,33(3): 376-389.
[14] MOHABBAT M, ARAZI H. Effect of resistance training plus enriched probiotic supplement on sestrin2, oxidative stress, and mitophagy markers in elderly male Wistar rats. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):7744.
[15] ARMSTRONG RB, OGILVIE RW, SCHWANE JA. Eccentric exercise-induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983;54(1):80-93.
[16] 田野,杨锡让,倪东海,等.运动性骨骼肌结构、机能变化的机制研究—Ⅰ力竭运动对骨骼肌纤维超微结构的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,1992,11(4):202-204.
[17] 徐叔云.药理实验方法学[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2002.
[18] 肖钰雪,刘宏岩,史晓梅,等.三七总皂苷对心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠心肌ZO-1、Occludin、Cx43蛋白表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2023,42(3):239-243,260.
[19] 郑亚萍,刘春杰.白芍总苷对心肌缺血再灌注大鼠心肌细胞焦亡及NLRP3炎症小体表达的影响[J].中药新药与临床药理,2019, 30(8):910-914.
[20] 潘胜莲,郑士立,周夏慧,等.针刺联合颈痛颗粒治疗神经根型颈椎病及对患者IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β和血液流变学指标的影响[J].中国针灸,2019,39(12):1274-1278.
[21] 郑荣发,莫伟彬,黄鹏,等.电针对运动大鼠腓肠肌组织代谢酶及自噬基因表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(6): 1127-1136.
[22] 刘冰洋,刘雪菲,房磊.鹿茸菇多糖的提取工艺优化及其对大鼠运动性骨骼肌损伤影响的研究[J].中国食品添加剂,2024,35(2): 137-144.
[23] 卢嘉茵,姚志超,郝晓静,等.N6-甲基腺苷甲基化相关因子在小鼠骨骼肌损伤修复中的表达及机制[J].解剖学报,2024,55(3): 285-294.
[24] 郭冰冰.不同运动负荷大鼠骨骼肌损伤及修复过程中血液肌酸激酶和乳酸脱氢酶变化的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2012.
[25] 屈红林,王家磊.复方中药与延迟性肌肉损伤血清学指标的变化:随机对照实验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(37): 7346-7349.
[26] TAGUCHI K, OGAKI S, MAEDA H, et al. Carbon Monoxide Alleviates Post-ischemia-reperfusion Skeletal Muscle Injury and Systemic Inflammation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2024;47(4):868-871.
[27] NANAVATI K, RUTHERFURD-MARKWICK K, LEE SJ, et al. Effect of curcumin supplementation on exercise-induced muscle damage: a narrative review. Eur J Nutr. 2022;61(8):3835-3855.
[28] 贾前生,左锋.植物乳杆菌L15对过度运动引起大鼠骨骼肌损伤的改善作用[J].食品科学,2023,44(13):79-87.
[29] JESPERSEN GJ, NEDERGAARD A, REITELSEDER S, et al. Activated protein synthesis and suppressed protein breakdown signaling in skeletal muscle of critically ill patients. PLoS One. 2017;6(3):e18090.
[30] 廖苾芝,王屿萌,周达岸.基于PI3K-AKT信号通路探讨体外冲击波治疗大鼠慢性骨骼肌损伤的作用机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2023, 43(10):2475-2480.
[31] 张六妹,刘菁菁,林晓烨,等.高强度间歇运动改善骨骼肌损伤和提高大鼠运动能力的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(35): 5603-5609.
[32] 王冠锦,赵暘.黄芪甲苷对力竭运动致大鼠骨骼肌损伤及细胞凋亡的影响[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2023,38(1):80-86.
[33] 张帅军,唐月梅,张大鼎,等.刺梨果粉缓解过度训练大鼠骨骼肌氧化应激损伤效果的研究[J].食品工业科技,2022,43(12): 338-346.
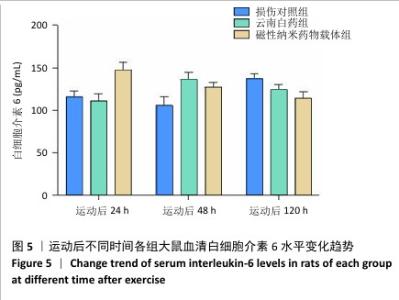
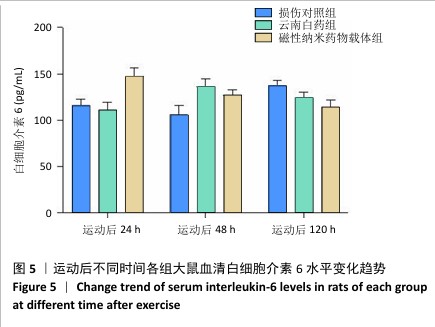
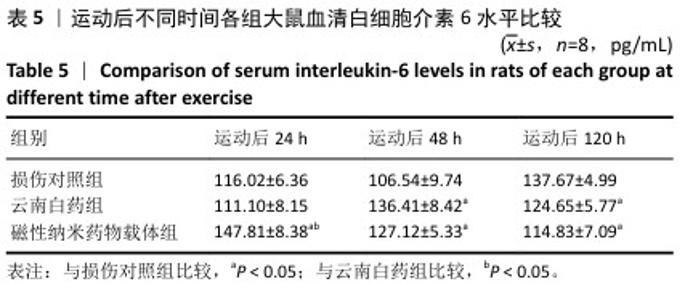
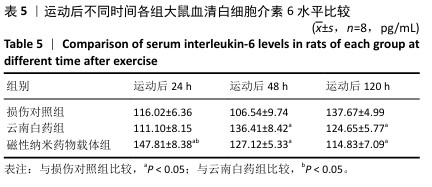
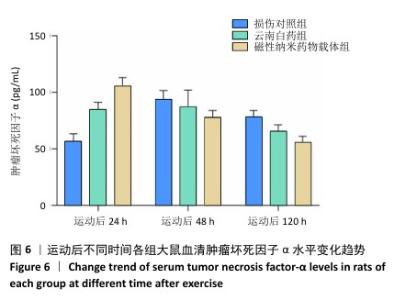
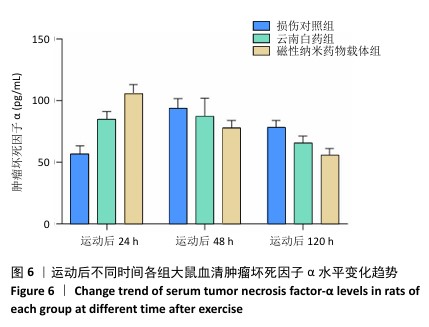
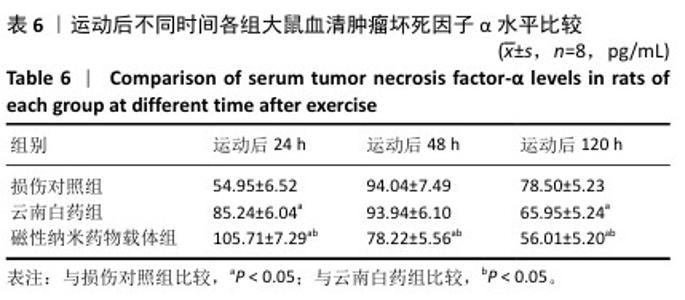
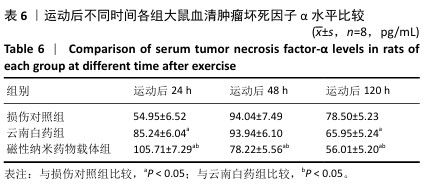
|