Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5907-5913.doi: 10.12307/2025.193
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism by which diabetes exacerbates intervertebral disc degeneration
Ma Jikun1, Wang Jianru1, Qi Junjie1, Liu Haifei2
- 1Shandong Second Medical University, Weifang 261000, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, Eastern District of Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-11Accepted:2024-06-21Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-07 -
Contact:Liu Haifei, MD, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Eastern District of Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Ma Jikun, Master candidate, Shandong Second Medical University, Weifang 261000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Jikun, Wang Jianru, Qi Junjie, Liu Haifei. Mechanism by which diabetes exacerbates intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5907-5913.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
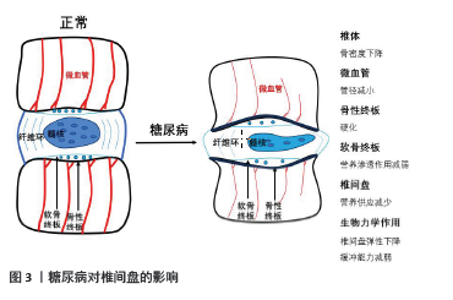
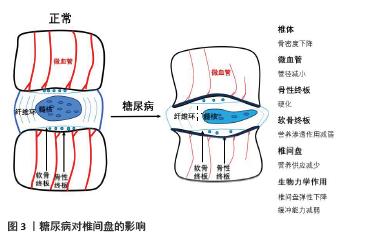
2.2 相关临床研究 KAISER等[19]通过测量377名参与者的L3椎体骨密度发现,随着年龄增大,骨密度降低,并且女性骨质流失量大于男性。骨质流失亦与椎间盘退变有关,椎体骨密度的改变会导致椎间盘相关生物力学作用重心变化。糖尿病则显著加速骨与软骨退变,致使椎体骨质流失加速,软骨终板退变加速,椎间盘生物力学作用受到影响。临床治疗中衡量椎间盘退变程度主要通过影像学检查(X射线片、CT、MRI)来实现,尤其在MRI检查普及的现代。影像学检查主要通过椎间高度、椎间盘信号及是否突出、软骨终板改变等进行评估,椎间高度是常用指标。椎间高度在评价椎间盘退变中占有重要位置,也是相对较早出现的影像学改变。一般来说随着年龄的增长,椎间盘出现退变,髓核含水量下降,体积减小,形变能力减弱,椎间高度也会降低。AGIUS等[20]对比100例2型糖尿病患者和86例非糖尿病患者(对照组),研究发现,糖尿病患者椎间高度较对照组明显降低,这表明糖尿病患者椎间盘退变相较对照组加快。PARK等[21]研究发现,2型糖尿病患者更容易发生退行性腰椎疾病,有更高的脊柱手术概率。SAKELLARIDIS[22]回顾分析102例行腰椎间盘突出症手术治疗的患者,对比同年龄段且无激素使用史、择期行非腰椎手术的患者,腰椎间盘突出症患者合并糖尿病比例(33/102)明显高于对照组(13/98)(P=0.001 3)。SAKELLARIDIS等[23]研究发现行颈椎间盘手术患者合并糖尿病比例(36/55)明显高于对照组(15/100),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001),作者分析这可能与糖尿病引起的微血管病变有关。糖尿病加速骨质流失、软骨退变、椎间高度下降,显著增加患者的脊柱手术概率,是椎间盘退变的危险因素。 2.3 糖尿病加剧椎间盘退变的途径 2.3.1 糖尿病对椎间盘组织血供的影响 椎间盘的营养途径主要是软骨终板途径,在椎间盘退变的发生机制中起到重要作用[24]。椎体内血管中营养物质经过软骨终板进入椎间盘,任何因素引起软骨终板及周围血管恶性改变,都会导致椎间盘血供减少。糖尿病微血管病变是其特发性并发症,是多器官损伤的病理学基础,主要的改变表现为微血管基底膜增厚、血管内皮细胞死亡及毛细血管数量减少。血管内皮细胞凋亡导致终板微血管密度降低,进而影响椎间盘血供[15],见图3。研究表明,软骨终板钙化、终板软骨细胞线粒体功能障碍及细胞外基质降解是软骨终板变性退变的主要原因[25]。软骨终板钙化及终板孔隙密度降低阻碍营养物质通过,改变了椎间盘细胞的生存环境,影响椎间盘细胞代谢[26]。QUAN等[27]在糖尿病大鼠模型中发现,糖尿病大鼠软骨终板明显变性退变,表现为软骨钙化、边界不清、血管侵犯、炎性细胞浸润及软骨细胞形态异常,类似于糖尿病对关节软骨的影响,这些改变被认为是软骨终板变性退变的标志。"
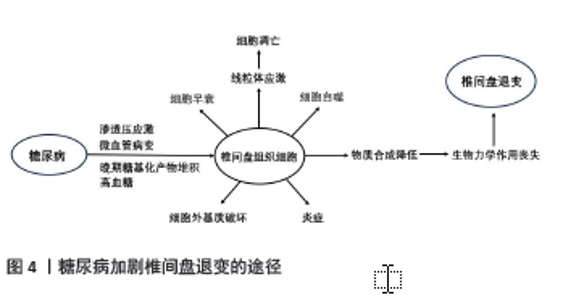
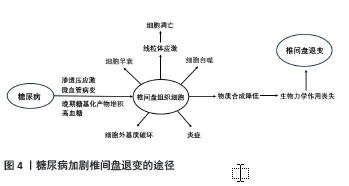
椎间盘是无血管组织,但是椎间盘退变伴有血管生长及软骨终板血管化[28]。研究证明,炎性细胞浸润髓核细胞并参与血管形成,加速椎间盘退变[29]。同时炎性细胞也会影响软骨细胞中的胶原蛋白[30]。CUI等[31]通过在电子显微镜下观察大鼠发现,炎症状态的椎间盘中胶原纤维分布不均且变的肥大,持续的炎症导致胶原蛋白结构破坏。炎症促进软骨终板钙化,阻碍椎间盘营养的转 运[32]。椎间盘细胞和细胞外基质营养物质减少是椎间盘退变的关键因素[26]。营养物质缺失导致细胞死亡、细胞外基质降解,导致椎间盘退变[33]。 2.3.2 糖尿病与椎间盘细胞衰老、凋亡和自噬的关系 细胞衰老是细胞功能退化及不可逆的停止分裂,而细胞过早的衰老也会由氧化应激、DNA结构损伤和有丝分裂应激诱导,这也是椎间盘细胞衰老的主要原因[34]。糖尿病可诱导髓核细胞过早衰老与凋亡引起椎间盘退变,糖尿病大鼠细胞衰老速度约是正常大鼠的2倍[35]。衰老细胞无法分裂新细胞,大量积累的衰老细胞无法承担新老细胞正常的更迭,拥有正常功能的细胞数量减少,组织的新陈代谢出现问题[36]。高血糖造成椎间盘组织细胞过早衰老和凋亡,细胞外基质降解,椎间盘细胞生存环境变差,椎间盘组织出现退变。退变的椎间盘组织各项功能减退,不能生产足量的新细胞及相关结构蛋白,同时大量细胞炎症因子释放和氧化应激进一步加快细胞过早衰老和凋亡[16]。 细胞凋亡是为维持内环境稳定、由基因决定的细胞程序性死亡。凋亡信号通路分为外源性通路和内源性通路,外源通路通过死亡配体及受体启动,内源性通路则由细胞应激触发[37]。正常机体的细胞凋亡受严格管控,但在糖尿病大鼠模型中,JIANG等[35]运用TUNEL检测发现糖尿病大鼠的髓核细胞凋亡增加,其激活外源性途径和内源性途径以加剧细胞凋亡。SHAN 等[38]发现,高糖可导致大鼠纤维环细胞JNK和p38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路活化和表达增高,导致细胞凋亡,这种调节呈现糖浓度依赖式。糖尿病大鼠脊索细胞过早凋亡,并向纤维软骨细胞转变,这些改变可增强基质金属蛋白酶和金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂的表达。基质金属蛋白酶的功能是降解细胞外基质,而金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂负责调控基质金属蛋白酶的活性,正常情况下二者维持微妙的平衡。变性的细胞外基质增加基质金属蛋白酶的表达,进而产生大量细胞外基质成分;细胞外基质过度破坏又会增加金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂的表达,二者都处于高表达状态,这形成了恶性循环[39]。在大鼠模型研究中发现糖尿病通过激活细胞凋亡信号通路以加剧细胞凋亡,导致细胞外基质大量破坏,蛋白酶调控失衡,使椎间盘退变进展加速。在人类髓核体外培养实验中,QI等[40]研究证实,高糖可导致人髓核间充质干细胞 p38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶磷酸化程度增高,蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原表达显著下降,细胞凋亡明显增加;应用p38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶抑制物可抑制高糖导致的磷酸化,并可改善蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原的表达,这为糖尿病患者椎间盘退变的治疗提供了思路。 自噬是细胞生存不可或缺的生理机制,通过溶酶体来降解细胞器来实现代谢与更新,但是过度的自噬会导致相关疾病的发生。自噬是多步骤过程,由自噬相关基因和轻链蛋白3调控。KONG等[41]运用体外髓核及纤维环细胞培养,分别将细胞置于体积分数10%胎牛血清、胎牛血清外加2种浓度的葡萄糖(0.1 mol/L和0.2 mol/L)中1 d和3 d,观察发现高糖可显著增加beclin-1、轻链蛋白3-Ⅱ、自噬相关基因3,5,7和12等自噬标记物的表达。自噬被认为是退行性疾病的一种保护机制,SHAO 等[42]通过体外髓核细胞培养发现,HuR(一种RNA结合蛋白)通过自噬相关基因7介导的自噬激活来抑制糖尿病椎间盘变性中的衰老。糖尿病大鼠的凋亡和衰老的椎间盘细胞自噬增加,这可能是椎间盘细胞面对应激的自我保护。 2.3.3 高糖对椎间盘细胞晚期糖基化产物表达和退变的影响 晚期糖基化产物的积累可能与糖尿病并发症和椎间盘退行性疾病的进展有关[43]。在高血糖的情况下,晚期糖基化产物是通过涉及还原糖的非酶促反应形成的,它们的形成导致蛋白质、核酸和脂质的氧化,其通过共价交联的方式影响细胞外基质蛋白的结构与功能,降低蛋白质的韧度和弹性,造成组织损伤[44]。糖基化产物受体存在于多种细胞,两者相结合引发炎症和自身免疫反应及细胞外基质降解,两者相互作用激活下游信号通路,产生过量促炎因子和氧自由基[43]。大量炎症因子及氧自由基的产生对椎间盘组织造成不可逆的损伤。聚集蛋白聚糖是椎间盘细胞外基质的主要蛋白多糖,人体和大鼠椎间盘细胞存在晚期糖基化产物和糖基化产物受体,而糖尿病椎间盘糖基化产物受体表达增强,聚集蛋白聚糖和胶原蛋白表达下调,这对椎间盘退变进展起到重要 作用[17]。 晚期糖基化产物的过量积累是椎间盘退变的重要因素,其加速细胞凋亡及阻碍细胞外基质正常代谢[45]。HU等[44]研究发现线粒体途径参与晚期糖基化产物诱导兔纤维环细胞细胞凋亡。在大鼠模型中,长期饮食暴露于晚期糖基化产物的大鼠椎间盘内胶原蛋白及糖胺聚糖含量明显减少,最终导致椎间盘组织硬化[46],而晚期糖基化产物抑制物吡哆胺可减轻2型糖尿病大鼠椎间盘变性[47]。进食富含复合碳水化合物、新鲜果蔬及适量肉类食物,避免食用高糖、高脂肪、油炸及烧烤的食物,能显著减少晚期糖基化产物的每日摄入[48]。对于糖尿病患者,尽可能减少富含晚期糖基化产物的食物摄入,对预防椎间盘退变有积极作用。 2.3.4 高糖诱导的渗透压改变对椎间盘退变的影响 健康状况下,人体椎间盘细胞外的渗透压在 430-496 mOsm/L间波动[49];退变椎间盘渗透压可下降至 300 mOsm/L(低渗透压)[50]。TAKEOKA等[51]认为高渗透压具有促进髓核细胞外基质合成以及维持细胞功能及表型的作用。WUERTZ等[50]研究发现,随着渗透压升高,人和牛髓核细胞聚蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原表达逐渐上升,Ⅰ型胶原表达受到抑制,渗透压降低可能是加快椎间盘退变的重要因素之一。NEIDLINGER-WILKE等[52]发现髓核细胞培养基渗透压从 300 mOsm/kg 提高到500 mOsm/kg 能增加聚蛋白聚糖的表达,而基质金属蛋白酶3的表达量下降。然而,近期也有研究证实,高渗透压诱发的氧化应激损伤可以加速体外培养髓核细胞的衰老和退变[53]。 渗透压增强结合蛋白在椎间盘细胞渗透压调节和退变中的作用受到关注,是哺乳动物体内唯一已知的能由高渗透压激活的转录因子,在髓核细胞渗透压调节的过程中发挥着重要作用[18]。髓核细胞中渗透压增强结合蛋白可被高渗透压激活,在核内转录水平对下游分子及基质表达进行调控,维持细胞内外渗透压平衡,调节椎间盘生物应力,保护细胞结构和功能,对髓核组织内环境稳态和生物学功能的维持具有重要意义,因此,渗透压增强结合蛋白可以认为是椎间盘退变的保护因素[54]。然而,渗透压增强结合蛋白的激活同时也可以提高促炎性因子的转录和表达,在椎间盘退变中起到作用[55]。促炎性因子在退变椎间盘中大量表达,其诱发的炎症反应是导致椎间盘退变的重要原因[56-57]。研究发现,在大鼠肾脏、肝脏和脑组织中,糖尿病可激活渗透压增强结合 蛋白并诱导炎性反应,导致组织损伤[58-59]。渗透压增强结合蛋白同时也被证实参与包括下丘脑、肾脏、血管、肝脏、关节等组织细胞的炎症反应,激活促炎性因子的表达[60]。 糖尿病微血管病变导致椎间盘血供减少,同时加速软骨终板变性退变,椎间盘组织所需营养物质减少,代谢废物不能及时排出,导致椎间盘组织氧分压、pH值及渗透压等理化环境改变。糖尿病导致最显著的体内内环境变化就是组织渗透压增高,内环境稳态对于髓核细胞维持正常结构和生理功能非常重要,而渗透压的改变可导致细胞内蛋白质和核酸的结构、功能发生改变,继而诱发细胞衰老、自噬甚至凋亡[18]。高血糖加速细胞衰老,衰老细胞分裂生产新细胞能力下降,不能进行正常的细胞更新换代,同时激活细胞凋亡信号通路,这使细胞过度凋亡,椎间盘细胞自噬增强。高血糖导致晚期糖基化产物的堆积,对细胞外基质造成损伤,蛋白多糖及胶原蛋白合成下降,椎间盘组织硬化,生物力学作用降低。糖尿病显著改变血浆渗透压,进而改变细胞渗透压并诱导椎间盘内炎症反应。高渗应激通过激发促炎因子的释放导致较强的炎性刺激,而细胞会通过各种方法来平衡渗透压[61]。髓核细胞通过改变基质生成来应对渗透压的变化[62]。细胞渗透压的改变对细胞的生存产生不良的影响,细胞内的水分因此减少,导致细胞收缩和功能改变。高渗透压导致DNA链损伤及蛋白质变性,最终出现细胞周期停滞和细胞凋亡[63]。糖尿病加剧椎间盘退变是一连串级联反应,高血糖使细胞结构功能损伤导致正常椎间盘细胞减少,细胞外基质破坏及结构蛋白含量减少致使椎间盘组织硬化丧失生物力学作用,椎间盘组织退变加速进而出现椎间盘突出。 2.3.5 糖尿病诱导椎间盘退变的其他途径 多元醇途径在糖尿病并发症的发展过程中起到重要作用[64]。KANG等[65]通过检测小鼠在高血糖情况下的氧化应激,发现葡萄糖代谢通过多元醇途径引起的氧化应激是糖尿病神经病变的主要原因,渗透压应激则是糖尿病视网膜病变的主要原因。多元醇途径可能通过p38激活介导细胞外基质降解加强,糖尿病大鼠模型中椎间盘细胞内醛糖还原酶、p38和金属蛋白酶水平升高,聚集蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白降解增加,金属蛋白酶抑制剂水平降低。醛糖还原酶是多元醇途径的关键酶,在细胞内高血糖的情况下会增加其表达,是引起糖尿病并发症的关键因素[64]。 肥胖与椎间盘退变有关[66]。肥胖显著增加椎间盘的机械负荷,使得椎间盘组织承担较大压力,所以肥胖人群在活动或外力作用下更容易出现椎间盘疾病。脂肪组织的增长和脂肪因子的改变有关,例如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、纤溶酶原激活物抑制剂1、脂肪组织中的脂联素,这些促炎因子状态改变与胰岛素抵抗及血管内皮细胞功能障碍相关,尤其是肥胖和糖尿病患者[67]。血浆中脂联素并不受糖尿病影响,其改变与肥胖有关。肥胖者血浆瘦素水平较高,椎间盘细胞存在瘦素受体,在肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等促炎细胞因子的存在下会增加参与椎间盘退行性变的蛋白酶表达[68]。2型糖尿病患者大多伴有肥胖,这加剧了椎间盘退变。糖尿病加剧椎间盘退变的不同途径总结见图4。 "

2.4 糖尿病患者椎间盘退变的药物治疗 如上述所总结糖尿病对椎间盘退变的不同影响途径,可针对不同影响途径行相关药物治疗。首先最为关键的是血糖的控制,糖尿病导致的细胞内高血糖状态是最早出现,也是最显著的改变,并发症的发生发展也以此为基础。临床上最为常见的是2型糖尿病,其治疗药物种类较多,应选择最为合适且安全有效的药物治疗,终身规律的药物治疗可控制血糖处于较为安全范围,良好的血糖控制是治疗糖尿病及其并发症的根本。 糖尿病的微血管病变直接导致椎间盘组织血供减少,而软骨终板途径是椎间盘营养物质来源,软骨终板变性退变导致营养物质渗透减少,椎间盘组织营养供应进一步减少发生退变。研究发现,姜黄素可通过上调自噬、抑制细胞凋亡、降低压力负荷诱导以预防软骨终板变性退变[28]。椎体骨质流失会出现椎间盘生物力学重心改变,加速椎间盘退变,这在老年女性中最为常见,而糖尿病可显著加速骨质流失及软骨退变。抗骨质疏松治疗、补充钙离子、促进钙吸收等药物联合使用,改善骨质疏松,对预防椎间盘退变有积极的作用。糖尿病诱导细胞早衰、凋亡及过度自噬。JIANG等[69]研究发现,白藜芦醇通过激活PI3K/Akt通路抑制白细胞介素1β介导的髓核细胞凋亡。GUO等[70]研究发现羽扇豆醇可增强线粒体的抗氧化应激能力,对抗高糖诱发的椎间盘细胞凋亡。二甲双胍除了能够降低血糖外,CHEN等[71]研究发现其可抑制髓核细胞的分解代谢基因表达,加强合成代谢基因的表达,通过刺激自噬来保护髓核细胞。细胞间铁过载参与髓核细胞铁死亡;DOU等[72]研究发现褪黑素可明显抑制髓核细胞铁死亡,是治疗椎间盘退变的新方法。此外晚期糖基化产物的过度累积会加速椎间盘退变,GLAESER等[47]研究发现晚期糖基化产物抑制剂吡哆胺可明显减轻糖尿病大鼠椎间盘退变。针对椎间盘退变的药物研究有巨大的研究价值及前景,这就需要进一步研究其退变机制,寻找有效的治疗靶点,见表2。"

| [1] ZHANG C, GULLBRAND SE, SCHAER TP, et al. Combined Hydrogel and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Moderate-Severity Disc Degeneration in Goats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(1-2):117-128. [2] FOURNIER DE, KISER PK, SHOEMAKER JK, et al. Vascularization of the human intervertebral disc: A scoping review. JOR Spine. 2020;3(4):e1123. [3] ERWIN WM, DESOUZA L, FUNABASHI M, et al. The biological basis of degenerative disc disease: proteomic and biomechanical analysis of the canine intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):240. [4] ALPANTAKI K, KAMPOUROGLOU A, KOUTSERIMPAS C, et al. Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for intervertebral disc degeneration: a critical review. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(9):2129-2144. [5] KUUSALO L, FELSON DT, WANG N, et al. Metabolic osteoarthritis - relation of diabetes and cardiovascular disease with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(2):230-234. [6] XIONG J, HU H, GUO R, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes as a New Strategy for the Treatment of Diabetes Complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:646233. [7] KING KB, ROSENTHAL AK. The adverse effects of diabetes on osteoarthritis: update on clinical evidence and molecular mechanisms. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(6):841-850. [8] AUFDERMAUR M, FEHR K, LESKER P, et al. Quantitative histochemical changes in intervertebral discs in diabetes. Exp Cell Biol. 1980;48(2): 89-94. [9] SILBERBERG R. The vertebral column of diabetic sand rats (Psammomys obesus). Exp Cell Biol. 1988;56(4):217-220. [10] ZIV I, MOSKOWITZ RW, KRAISE I, et al. Physicochemical properties of the aging and diabetic sand rat intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res. 1992; 10(2):205-210. [11] ROBINSON D, MIROVSKY Y, HALPERIN N, et al. Changes in proteoglycans of intervertebral disc in diabetic patients. A possible cause of increased back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(8):849-855; discussion 856. [12] MOBBS RJ, NEWCOMBE RL, CHANDRAN KN. Lumbar discectomy and the diabetic patient: incidence and outcome. J Clin Neurosci. 2001; 8(1):10-13. [13] TSURU M, NAGATA K, JIMI A, et al. Effect of AGEs on human disc herniation: intervertebral disc hernia is also effected by AGEs. Kurume Med J. 2002;49(1-2):7-13. [14] WON HY, PARK JB, PARK EY, et al. Effect of hyperglycemia on apoptosis of notochordal cells and intervertebral disc degeneration in diabetic rats. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(6):741-748. [15] XU HM, HU F, WANG XY, et al. Relationship Between Apoptosis of Endplate Microvasculature and Degeneration of the Intervertebral Disk. World Neurosurg. 2019;125:e392-e397. [16] FENG C, LIU H, YANG M, et al. Disc cell senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration: Causes and molecular pathways. Cell Cycle. 2016; 15(13):1674-1684. [17] MAHMOUD M, KOKOZIDOU M, GöGELE C, et al. Does Vitamin K2 Influence the Interplay between Diabetes Mellitus and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in a Rat Model? Nutrients. 2023;15(13):2872. [18] CHEUNG CY, KO BC. NFAT5 in cellular adaptation to hypertonic stress - regulations and functional significance. J Mol Signal. 2013;8(1):5. [19] KAISER J, ALLAIRE B, FEIN PM, et al. Correspondence between bone mineral density and intervertebral disc degeneration across age and sex. Arch Osteoporos. 2018;13(1):123. [20] AGIUS R, GALEA R, FAVA S. Bone mineral density and intervertebral disc height in type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30(4): 644-650. [21] PARK CH, MIN KB, MIN JY, et al. Strong association of type 2 diabetes with degenerative lumbar spine disorders. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):16472. [22] SAKELLARIDIS N. The influence of diabetes mellitus on lumbar intervertebral disk herniation. Surg Neurol. 2006; 66(2): 152-154. [23] SAKELLARIDIS N, ANDROULIS A. Influence of diabetes mellitus on cervical intervertebral disc herniation. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008; 110(8):810-812. [24] WU Y, LOAIZA J, BANERJI R, et al. Structure-function relationships of the human vertebral endplate. JOR Spine. 2021;4(3):e1170. [25] BELENGUER-VAREA Á, TARAZONA-SANTABALBINA FJ, AVELLANA-ZARAGOZA JA, et al. Oxidative stress and exceptional human longevity: Systematic review. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;149:51-63. [26] HABIB M, HUSSIEN S, JEON O, et al. Intradiscal treatment of the cartilage endplate for improving solute transport and disc nutrition. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1111356. [27] QUAN H, ZUO X, HUAN Y, et al. A systematic morphology study on the effect of high glucose on intervertebral disc endplate degeneration in mice. Heliyon. 2023;9(2):e13295. [28] XIAO L, DING B, GAO J, et al. Curcumin prevents tension-induced endplate cartilage degeneration by enhancing autophagy. Life Sci. 2020;258:118213. [29] LIN D, ALBERTON P, DELGADO CACERES M, et al. Loss of tenomodulin expression is a risk factor for age-related intervertebral disc degeneration. Aging Cell. 2020;19(3):e13091. [30] ZHAO J, DUAN L, WANG R, et al. Roflumilast prevents lymphotoxin α (TNF-β)-induced inflammation activation and degradation of type 2 collagen in chondrocytes. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(12):1191-1199. [31] CUI S J, FU Y, LIU Y, et al. Chronic inflammation deteriorates structure and function of collagen fibril in rat temporomandibular joint disc. Int J Oral Sci. 2019;11(1):2. [32] ZUO R, WANG Y, LI J, et al. Rapamycin Induced Autophagy Inhibits Inflammation-Mediated Endplate Degeneration by Enhancing Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling of Cartilage Endplate Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2019; 37(6):828-840. [33] MOHD ISA IL, TEOH SL, MOHD NOR NH, et al. Discogenic Low Back Pain: Anatomy, Pathophysiology and Treatments of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):208. [34] KONG JG, PARK JB, LEE D, et al. Effect of high glucose on stress-induced senescence of nucleus pulposus cells of adult rats. Asian Spine J. 2015; 9(2):155-161. [35] JIANG L, ZHANG X, ZHENG X, et al. Apoptosis, senescence, and autophagy in rat nucleus pulposus cells: Implications for diabetic intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(5):692-702. [36] DU J, XU M, KONG F, et al. CB2R Attenuates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Delaying Nucleus Pulposus Cell Senescence through AMPK/GSK3β Pathway. Aging Dis. 2022;13(2):552-567. [37] OHNISHI T, IWASAKI N, SUDO H. Causes of and Molecular Targets for the Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: A Review. Cells. 2022;11(3):394. [38] SHAN L, YANG D, ZHU D, et al. High glucose promotes annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis through activating the JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(7):BSR20190853. [39] ZHOU X, HONG Y, ZHAN Y. Karacoline, identified by network pharmacology, reduces degradation of the extracellular matrix in intervertebral disc degeneration via the NF-κB signaling pathway. J Pharm Anal. 2020;10(1):13-22. [40] QI L, WANG R, SHI Q, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium restored the expression of collagen II and aggrecan in nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells exposed to high glucose. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(3):455-466. [41] KONG CG, PARK JB, KIM MS, et al. High glucose accelerates autophagy in adult rat intervertebral disc cells. Asian Spine J. 2014; 8(5):543-548. [42] SHAO Y, SUN L, YANG G, et al. Icariin protects vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and degeneration via activating Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:937502. [43] TSAI TT, HO NY, LIN YT, et al. Advanced glycation end products in degenerative nucleus pulposus with diabetes. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(2): 238-244. [44] HU Y, SHAO Z, CAI X, et al. Mitochondrial Pathway Is Involved in Advanced Glycation End Products-Induced Apoptosis of Rabbit Annulus Fibrosus Cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(10): E585-E595. [45] LUO R, SONG Y, LIAO Z, et al. Impaired calcium homeostasis via advanced glycation end products promotes apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress in human nucleus pulposus cells and exacerbates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. FEBS J. 2019; 286(21):4356-4373. [46] KRISHNAMOORTHY D, HOY RC, NATELSON DM, et al. Dietary advanced glycation end-product consumption leads to mechanical stiffening of murine intervertebral discs. Dis Model Mech. 2018;11(12):dmm036012. [47] GLAESER JD, JU D, TAWACKOLI W, et al. Advanced Glycation End Product Inhibitor Pyridoxamine Attenuates IVD Degeneration in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9709. [48] PRASAD C, IMRHAN V, MAROTTA F, et al. Lifestyle and Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) Burden: Its Relevance to Healthy Aging. Aging Dis. 2014;5(3):212-217. [49] YANG Y, WANG X, LIU Z, et al. Osteogenic protein-1 attenuates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in a hyperosmotic culture. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(6):BSR20181708. [50] WUERTZ K, URBAN JP, KLASEN J, et al. Influence of extracellular osmolarity and mechanical stimulation on gene expression of intervertebral disc cells. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(11):1513-1522. [51] TAKEOKA Y, KANG JD, MIZUNO S. In vitro nucleus pulposus tissue model with physicochemical stresses. JOR Spine. 2020;3(3):e1105. [52] NEIDLINGER-WILKE C, MIETSCH A, RINKLER C, et al. Interactions of environmental conditions and mechanical loads have influence on matrix turnover by nucleus pulposus cells. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(1): 112-121. [53] XU J, LI H, YANG K, et al. Hyper-osmolarity environment-induced oxidative stress injury promotes nucleus pulposus cell senescence in vitro. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(9):BSR20191711. [54] JOHNSON ZI, SHAPIRO IM, RISBUD MV. Extracellular osmolarity regulates matrix homeostasis in the intervertebral disc and articular cartilage: evolving role of TonEBP. Matrix Biol. 2014;40:10-16. [55] SADOWSKA A, KAMEDA T, KRUPKOVA O, et al. Osmosensing, osmosignalling and inflammation: how intervertebral disc cells respond to altered osmolarity. Eur Cell Mater, 2018;36:231-250. [56] MOLINOS M, ALMEIDA CR, CALDEIRA J, et al. Inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration and regeneration. J R Soc Interface. 2015;12(108):20150429. [57] DE GEER CM. Cytokine Involvement in Biological Inflammation Related to Degenerative Disorders of the Intervertebral Disk: A Narrative Review. J Chiropr Med., 2018;17(1):54-62. [58] CHOI SY, LIM SW, SALIMI S, et al. Tonicity-Responsive Enhancer-Binding Protein Mediates Hyperglycemia-Induced Inflammation and Vascular and Renal Injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(2):492-504. [59] LEE JY, JEONG EA, KIM KE, et al. TonEBP/NFAT5 haploinsufficiency attenuates hippocampal inflammation in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7837. [60] CHOI SY, LEE-KWON W, KWON HM. The evolving role of TonEBP as an immunometabolic stress protein. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(6):352-364. [61] BROCKER C, THOMPSON DC, VASILIOU V. The role of hyperosmotic stress in inflammation and disease. Biomol Concepts. 2012;3(4):345-364. [62] LUO Z, WEI Z, ZHANG G, et al. Achilles’ Heel-The Significance of Maintaining Microenvironmental Homeostasis in the Nucleus Pulposus for Intervertebral Discs. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(23):16592. [63] THIEMICKE A, NEUERT G. Kinetics of osmotic stress regulate a cell fate switch of cell survival. Sci Adv. 2021;7(8):eabe1122. [64] NIIMI N, YAKO H, TAKAKU S, et al. Aldose Reductase and the Polyol Pathway in Schwann Cells: Old and New Problems. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(3):1031. [65] KANG Q, YANG C. Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenetic role and therapeutic implications. Redox Biol. 2020;37:101799. [66] KERR GJ, TO B, WHITE I, et al. Diet-induced obesity leads to behavioral indicators of pain preceding structural joint damage in wild-type mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):93. [67] LI S, HUANG C, XIAO J, et al. The Potential Role of Cytokines in Diabetic Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Aging Dis. 2022;13(5): 1323-1335. [68] ZHANG QH, CUI XY, WANG D, et al. Anti-obesity effect of escin: a study on high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022; 26(21):7797-812. [69] JIANG Y, XIE Z, YU J, et al. Resveratrol inhibits IL-1β-mediated nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(3):BSR20190043. [70] GUO MB, WANG DC, LIU HF, et al. Lupeol against high-glucose-induced apoptosis via enhancing the anti-oxidative stress in rabbit nucleus pulposus cells. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(10):2609-2620. [71] CHEN D, XIA D, PAN Z, et al. Metformin protects against apoptosis and senescence in nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates disc degeneration in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(10):e2441. [72] DOU X, MA Y, LUO Q, et al. Therapeutic potential of melatonin in the intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibiting the ferroptosis of nucleus pulpous cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2023;27(16):2340-2353. [73] PARK CH, MIN KB, MIN JY, et al. Strong association of type 2 diabetes with degenerative lumbar spine disorders. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):16472. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [3] | Wan Lingling, Wu Mengying, Zhang Yujiao, Luo Qingqing. Inflammatory factor interferon-gamma affects migration and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells through pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [4] | Liu Zhezhe, Yu Meiqing, Wang Tingting, Zhang Min, Li Baiyan. Troxerutin modulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway to inhibit brain injury and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1137-1143. |
| [5] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [6] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [7] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [8] | Xu Fei, Yan Jinqiang, Chai Shoudong. Mechanical stress regulates apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1064-1072. |
| [9] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [10] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [11] | Ding Zhili, Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Liu Jiang, Ding Yu. Constructing rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration models by different methods under X-ray guidance: a comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 995-1002. |
| [12] | Zhang Fei, Zuo Jun. Inhibition of hypertrophic scar in rats by beta-sitosterol-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7301-7309. |
| [13] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [14] | Kang Linzhi, Liu Zhenshuai, Wei Jiaxu, Chang Na, Zhu Dacheng. Inhibitory effects of sinomenine hydrochloride in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia CEM cells and transcriptomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6674-6680. |
| [15] | Su Qin, Jia Siwei, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Li Yanbing, Mu Bingtao, Song Lijuan, Ma Cungen, Yu Jiezhong. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide intervenes in SH-SY5Y cell injury induced by beta-amyloid protein 1-42: protective effect of mitochondrial autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6688-6696. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||