Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (34): 7269-7277.doi: 10.12307/2025.498
Previous Articles Next Articles
Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treatment of infected bone defects
Ren Bo1, Tang Yongliang1, Li Ni2, Liu Bangding1
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, 2Health Examination Center, Xi’an Central Hospital, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-06-20Accepted:2024-09-02Online:2025-12-08Published:2025-01-17 -
Contact:Liu Bangding, Associate chief physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Xi’an Central Hospital, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Ren Bo, Attending physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Xi’an Central Hospital, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ren Bo, Tang Yongliang, Li Ni, Liu Bangding. Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treatment of infected bone defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7269-7277.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
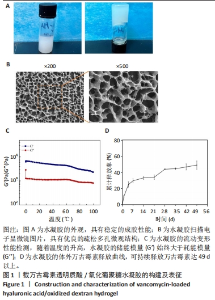
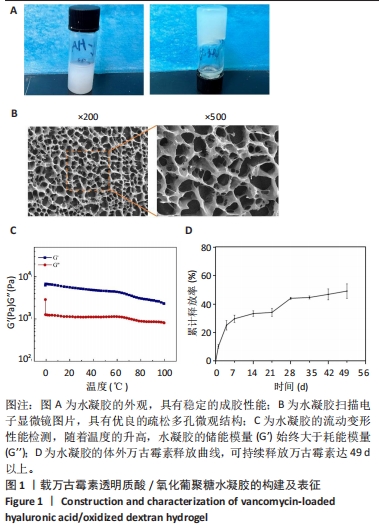
2.1 载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶的构建及表征 如图1A所示,载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶具有稳定的成胶性能;扫描电子显微镜下可见载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶具有良好的多孔结构,孔径在100-300 μm之间,见图1B。对载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶进行流变检测,发现随着温度的升高,水凝胶的储能模量(G’)始终大于耗能模量(G’’),见图1C,证实该水凝胶具有良好的力学性能。载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶的体外药物释放曲线显示,在最初的1周内万古霉素呈现快速释放,释放的药物量为(37.07±2.61)%,而后药物释放逐渐减缓,在第42天释放达到平衡,万古霉素的持续释放量为(58.54±3.94)%,见图1D。"
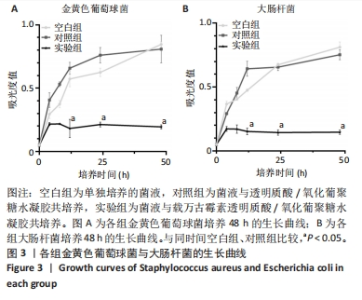
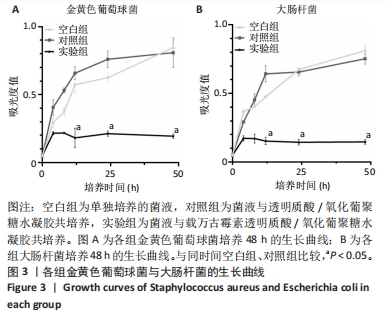
2.3 载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶的体外抗菌性能 大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌分别是革兰阴性菌和革兰阳性菌的代表性微生物[23-24]。随着培养时间的延长,空白组与对照组金黄色葡萄球菌吸光度值呈增加趋势,实验组金黄色葡萄球菌吸光度值呈稳定趋势,并且相同培养时间下实验组金黄色葡萄球菌吸光度值明显低于空白组、对照组(P < 0.05),见图3A。说明实验组中万古霉素在不断缓释发挥作用,而氧化葡聚糖和透明质酸并不具备抗菌性,这与先前的研究结果一致。 随着培养时间的延长,空白组与对照组大肠杆菌吸光度值呈增加趋势,实验组大肠杆菌吸光度值呈稳定趋势,并且相同培养时间下实验组大肠杆菌吸光度值明显低于空白组、对照组(P < 0.05),见图3B。说明实验组中万古霉素在不断缓释发挥作用,而氧化葡聚糖和透明质酸并不具备抗菌性。同时还可以看出,载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶对大肠杆菌的抑制作用要强于对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用。"

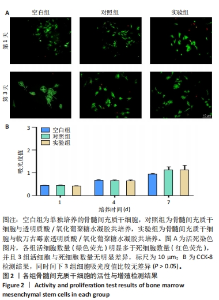
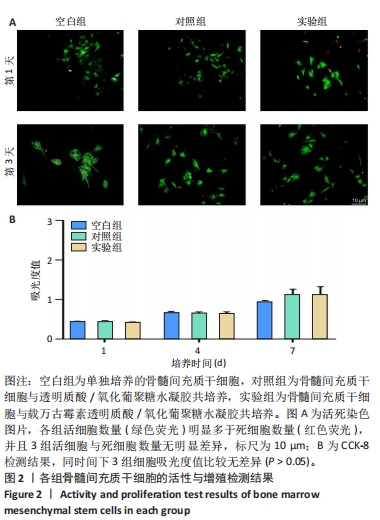
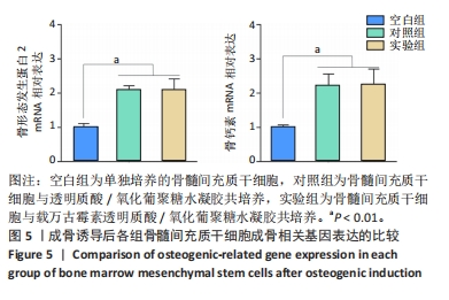
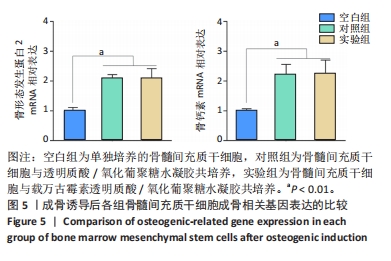
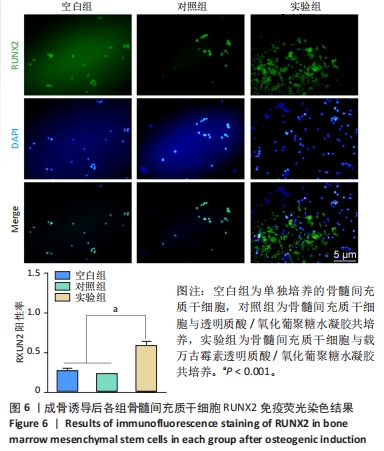
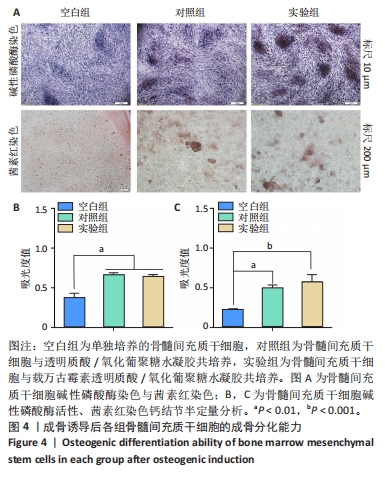
以上结果说明,载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶具有良好的体外广谱抗菌性。 2.4 载万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶的体外促成骨性能 各组骨髓间充质干细胞碱性磷酸酶染色与茜素红染色结果,见图4A。碱性磷酸酶染色结果显示,实验组与对照组可见大量明显聚集的碱性磷酸酶阳性染色,空白组碱性磷酸酶阳性染色少于对照组、空白组。茜素红染色结果显示,实验组钙结节数量最多,空白组钙结节数量最少。定量分析结果显示,实验组、对照组碱性磷酸酶活性、钙结节形成均高于空白组(P < 0.01或P < 0.001),实验组与对照组碱性磷酸酶活性、钙结节形成比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图4B,C。结果表明,两种水凝胶可以通过促进碱性磷酸酶表达及钙结节生成调节体外成骨活性。"
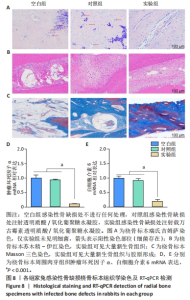
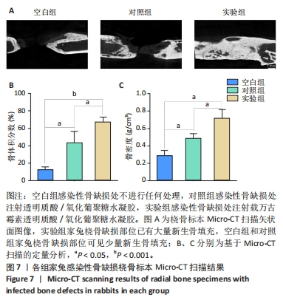
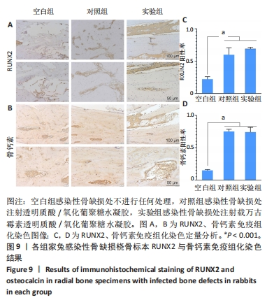
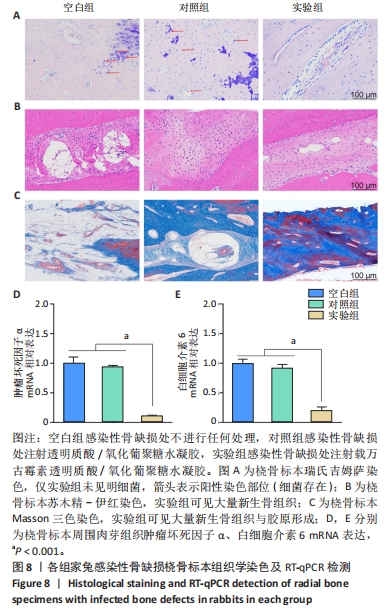
2.5.3 各组家兔桡骨标本组织形态观察 瑞氏吉姆萨染色结果显示,空白组和对照组桡骨标本中存在大量细菌,骨表面有明显侵蚀现象,表明感染没有得到控制;实验组桡骨标本中几乎没有细菌,见图8A。因此,透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶中万古霉素的持续释放可以有效地清除感染部位的细菌,为骨缺损部位提供适合骨再生的无菌的微环境。 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,空白组和对照组骨缺损部位有炎症细胞浸润,组织纤维排列紊乱,无明显新生骨小梁和骨组织形成;实验组骨缺损部位未见明显炎症细胞浸润,新生骨小梁排列整齐,见图8B。Masson结果染色显示,空白组骨缺损部位无新生骨和胶原;对照组可见少量新生骨,胶原排列紊乱;实验组骨缺损部位中有明显新骨与胶原形成,见图8C。 2.5.4 各组家兔桡骨标本周围肉芽组织炎症反应检测 RT-qPCR检测结果显示,实验组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6 mRNA表达均低于空白组、对照组(P < 0.001),空白组与对照组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6 mRNA表达比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图8D,E。结果表明,载有万古霉素透明质酸/氧化葡聚糖水凝胶能够通过下调炎症因子的表达抑制感染。 "
| [1] SHI M, ZHANG P, ZHAO Q, et al. Dual Functional Monocytes Modulate Bactericidal and Anti-Inflammation Process for Severe Osteomyelitis Treatment. Small. 2020;16(4):e1905185. [2] ZHENG S, ZHONG H, CHENG H, et al. Engineering Multifunctional Hydrogel With Osteogenic Capacity for Critical-Size Segmental Bone Defect Repair. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:899457. [3] 占华松,陈跃平,章晓云.骨组织工程技术治疗感染性骨缺损:优势与问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(30):4848-4854. [4] JIA WT, FU Q, HUANG WH, et al. Comparison of Borate Bioactive Glass and Calcium Sulfate as Implants for the Local Delivery of Teicoplanin in the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Osteomyelitis in a Rabbit Model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015; 59(12):7571-7580. [5] 文虹杰,陈仲,杨华刚,等.骨髓炎状态下成骨诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞转录组的测序分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(15): 2333-2338. [6] FANG B, QIU P, XIA C, et al. Extracellular matrix scaffold crosslinked with vancomycin for multifunctional antibacterial bone infection therapy. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120603. [7] MASTERS EA, TROMBETTA RP, DE MESY BENTLEY KL, et al. Evolving concepts in bone infection: redefining “biofilm”, “acute vs. chronic osteomyelitis”, “the immune proteome” and “local antibiotic therapy”. Bone Res. 2019;7:20. [8] 陈植,徐芳露,陈兵乾.自体富血小板血浆联合自体骨移植术治疗兔桡骨骨不连实验研究[J].交通医学,2024,38(1):6-10. [9] YUAN Q, LI L, PENG Y, et al. Biomimetic nanofibrous hybrid hydrogel membranes with sustained growth factor release for guided bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(4):1256-1271. [10] FAN YG, REN G, CUI Y, et al. Peptide-based hydrogel for enhanced bone repair. Mater Design. 2023;229:111862. [11] 陈品叡,裴锡波,薛轶元.磁响应水凝胶在骨组织工程中的作用与优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(3):452-457. [12] LI Y, LIU X, LI B, et al. Near-Infrared Light Triggered Phototherapy and Immunotherapy for Elimination of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Infection on Bone Implant. ACS Nano. 2020;14(7):8157-8170. [13] WANG S, ZHANG J, LI W, et al. Hyaluronic acid-guided assembly of ceria nanozymes as plaque-targeting ROS scavengers for anti-atherosclerotic therapy. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;296:119940. [14] CHANG CY, JOHNSON HC, BABB O, et al. Biomimetic stiffening of cell-laden hydrogels via sequential thiol-ene and hydrazone click reactions. Acta Biomater. 2021;130:161-171. [15] 刘晖,刘爱峰,张宇,等.透明质酸支架在软骨修复工程中的优势和应用策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(34):5518-5524. [16] PRONINA EV, VOROTNIKOV YA, POZMOGOVA TN, et al. No Catalyst Added Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation of Dextran: An Environmentally Friendly Route to Multifunctional Polymers. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2020;8(13):5371-5379. [17] WEI P, JING W, YUAN Z, et al. Vancomycin- and Strontium-Loaded Microspheres with Multifunctional Activities against Bacteria, in Angiogenesis, and in Osteogenesis for Enhancing Infected Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(34):30596-30609. [18] KARAKEÇILI A, TOPUZ B, KORPAYEV S, et al. Metal-organic frameworks for on-demand pH controlled delivery of vancomycin from chitosan scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;105:110098. [19] CROES M, BAKHSHANDEH S, VAN HENGEL IAJ, et al. Antibacterial and immunogenic behavior of silver coatings on additively manufactured porous titanium. Acta Biomater. 2018;81:315-327. [20] HUANG F, CHEN T, CHANG J, et al. A conductive dual-network hydrogel composed of oxidized dextran and hyaluronic-hydrazide as BDNF delivery systems for potential spinal cord injury repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;167:434-445. [21] HASSANI BESHELI N, MOTTAGHITALAB F, ESLAMI M, et al. Sustainable Release of Vancomycin from Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles for Treating Severe Bone Infection in Rat Tibia Osteomyelitis Model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(6):5128-5138. [22] CUI Y, WANG Z, LI Z, et al. Functionalized anti-osteoporosis drug delivery system enhances osseointegration of an inorganic-organic bioactive interface in osteoporotic microenvironment. Mater Design. 2021;206. doi:10.1016/J.MATDES.2021.109753 [23] YANG Y, YANG S, WANG Y, et al. Anti-infective efficacy, cytocompatibility and biocompatibility of a 3D-printed osteoconductive composite scaffold functionalized with quaternized chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2016;46:112-128. [24] ZHAO X, LI P, GUO B, et al. Antibacterial and conductive injectable hydrogels based on quaternized chitosan-graft-polyaniline/oxidized dextran for tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2015;26:236-248. [25] PEISELER M, KUBES P. More friend than foe: the emerging role of neutrophils in tissue repair. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(7):2629-2639. [26] SAINT-PASTOU TERRIER C, GASQUE P. Bone responses in health and infectious diseases: A focus on osteoblasts. J Infect. 2017;75(4):281-292. [27] GARCÍA-GONZÁLEZ CA, BARROS J, REY-RICO A, et al. Antimicrobial Properties and Osteogenicity of Vancomycin-Loaded Synthetic Scaffolds Obtained by Supercritical Foaming. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10(4):3349-3360. [28] MOHD ZAFFARIN AS, NG SF, NG MH, et al. Nano-Hydroxyapatite as a Delivery System for Promoting Bone Regeneration In Vivo: A Systematic Review. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(10):2569. [29] HE R, SUI J, WANG G, et al. Polydopamine and hyaluronic acid immobilisation on vancomycin-loaded titanium nanotube for prophylaxis of implant infections. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022; 216:112582. [30] GUPTA A, BRIFFA SM, SWINGLER S, et al. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Curcumin-Cyclodextrins Loaded into Bacterial Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing Applications. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(5):1802-1811. [31] TAO J, ZHANG Y, SHEN A, et al. Injectable Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel/Nanoparticle-Loaded System for Local Delivery of Vancomycin in the Treatment of Osteomyelitis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:5855-5871. [32] MAKAROV C, COHEN V, RAZ-PASTEUR A, et al. In vitro elution of vancomycin from biodegradable osteoconductive calcium phosphate-polycaprolactone composite beads for treatment of osteomyelitis. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014;62:49-56. [33] YANG Y, CHU L, YANG S, et al. Dual-functional 3D-printed composite scaffold for inhibiting bacterial infection and promoting bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2018;79: 265-275. [34] CUI Y, LIU H, TIAN Y, et al. Dual-functional composite scaffolds for inhibiting infection and promoting bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022;16:100409. [35] LI B, CAI Q, WANG Z, et al. D-arginine Enhances the Effect of Alpha-Amylase on Disassembling Actinomyces viscosus Biofilm. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:864012. [36] LI D, QIU Y, ZHANG S, et al. A Multifunctional Antibacterial and Osteogenic Nanomedicine: QAS-Modified Core-Shell Mesoporous Silica Containing Ag Nanoparticles. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:4567049. [37] HU Y, CHEN X, WANG S, et al. Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):20. [38] SULTANKULOV B, BERILLO D, SULTANKULOVA K, et al. Progress in the Development of Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Biomolecules. 2019;9(9):470. |
| [1] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [2] | Zhou Hongli, Wang Xiaolong, Guo Rui, Yao Xuanxuan, Guo Ru, Zhou Xiongtao, He Xiangyi. Fabrication and characterization of nanohydroxyapatite/sodium alginate/polycaprolactone/alendronate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [3] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [4] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [5] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [6] | Liu Yang, Liu Donghui , Xu Lei, Zhan Xu, Sun Haobo, Kang Kai. Role and trend of stimuli-responsive injectable hydrogels in precise myocardial infarction therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [7] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [8] | Guo Yuchao, Ni Qianwei, Yin Chen, Jigeer·Saiyilihan, Gao Zhan . Quaternized chitosan hemostatic materials: synthesis, mechanism, and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [9] | Fu Lyupeng, Yu Peng, Liang Guoyan, Chang Yunbing. Electroactive materials applied in spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2113-2123. |
| [10] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [11] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [12] | Zhou Shibo, Yu Xing, Chen Hailong, Xiong Yang. Nanocrystalline collagen-based bone combined with Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction repairs bone defects in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 354-361. |
| [13] | Yan Qiquan, Yang Libin, Li Mengjun, Ni Yazhuo, Chen Keying, Xu Bo, Li Yaoyang, Ma Shiqing, Li Rui, Li Jianwen. Preparation and antibacterial properties of porcine small intestinal submucosal composite nanohydroxyapatite bioscaffold loaded with antimicrobial peptide KR-12-a5 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 384-394. |
| [14] | Liu Xiaohong, Zhao Tian, Mu Yunping, Feng Wenjin, Lyu Cunsheng, Zhang Zhiyong, Zhao Zijian, Li Fanghong. Acellular dermal matrix hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [15] | Yuan Qian, Zhang Hao, Pang Jie. Characterization and biological properties of naringin-loaded chitosan/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||