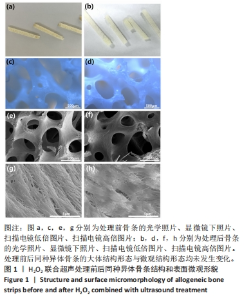
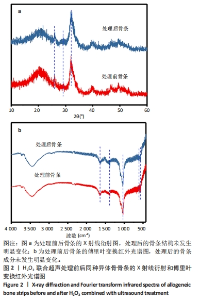
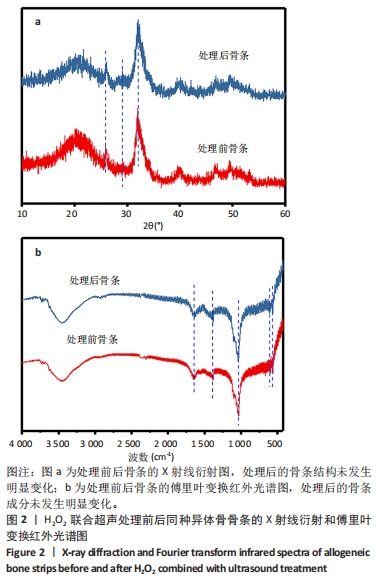
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (28): 5985-5993.doi: 10.12307/2025.471
Previous Articles Next Articles
Methods and effects on endotoxin removal in allogeneic bone
Hou Licun, Hu Kai, Shao Yiran
- Shanghai Gencong Biomedical Materials Research Center, Shanghai 201201, China
-
Received:2024-06-05Accepted:2024-07-27Online:2025-10-08Published:2024-12-07 -
About author:Hou Licun, Engineer, Shanghai Gencong Biomedical Materials Research Center, Shanghai 201201, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hou Licun, Hu Kai, Shao Yiran. Methods and effects on endotoxin removal in allogeneic bone[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5985-5993.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
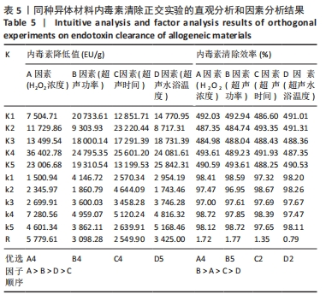
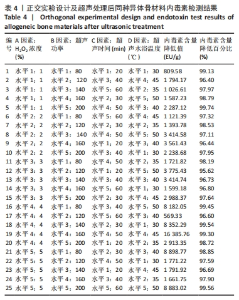
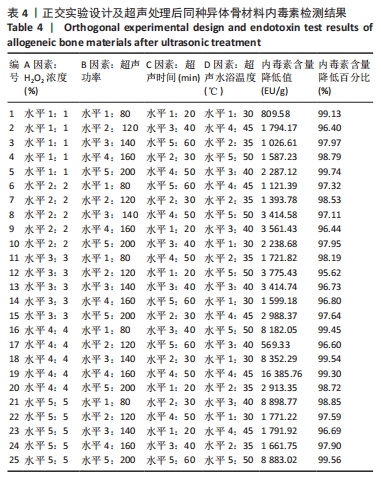
表5所示为正交实验的直观分析和因素分析结果,分析步骤如下:①分别对每次实验各因素的一水平的实验结果求和,即K1;再对每次实验结果各因素的二水平结果求和,即K2;对每次实验各因子三水平的结果求和,即K3;对每次实验各因子的四水平的结果求和,即K4;对每次实验各因子的五水平的结果求和,即K5;②再分别求出各因素个水平的平均值:即k1=K1/5,k2=K2/5,k3=K3/5,k4=K4/5,k5=K5/5;③分别求出各因素的平均值的差值也叫极差用R代表。此次实验中以平均值(k1-k5)中最大值与最小值之间的差值记为极差(R),其中极差愈大,所对应的因素越重要。由此可以确定出主、次要因素的排列顺序。根据各因素各水平所对应的指标结果的平均值大小,确定各因素取什么水平较好。"
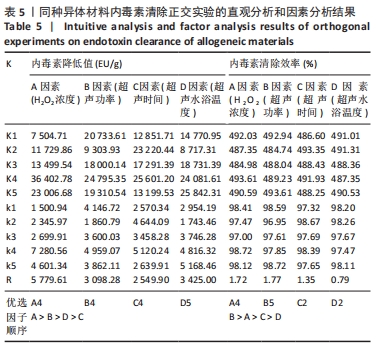
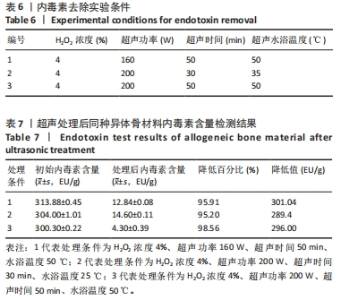
按照正交实验结果分析规则进行分析,并且分别按照内毒素含量降低值和内毒素清除效率来分析。如表5所示,以内毒素降低值来分析,在内毒素清除过程中H2O2浓度(A)对内毒素清除能力影响最大,其余依次是超声功率(B)、超声水浴温度(D)、超声时间(C)。提高同种异体骨材料内毒素清除能力的最优水平是A4B4C4D5,即为H2O2浓度4%、超声功率160 W、超声时间50 min、超声水浴温度50 ℃。以内毒素清除效率为分析条件进一步分析发现,影响内毒素清除效率的主次序为超声功率(B) > H2O2浓度(A) > 超声时间(C) > 水浴温度(D),最优水平为A4B5C2D2,即为H2O2浓度4%、超声功率200 W、超声时间30 min,超声水浴温度35 ℃。 综合分析2种分析方法,从去除内毒素机制考虑,功率越大、时间越长、温度越高,处理效果应该更佳。因此,对如下3种条件下(表6)内毒素去除效果进行验证,去除前后内毒素数值见表7所示,可以发现优选实验条件为H2O2浓度4%、超声功率200 W、超声时间50 min、超声水浴温度50 ℃时内毒素去除效率最高,进一步证明了该实验条件可有效去除同种异体骨材料的内毒素。"

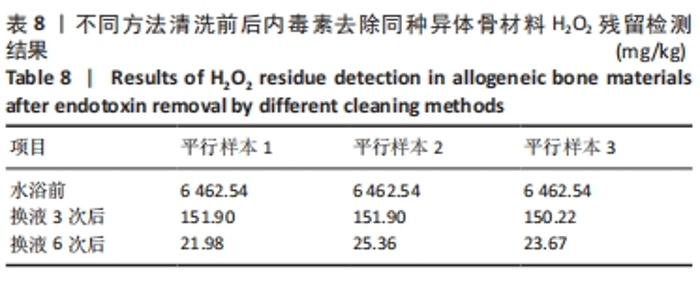
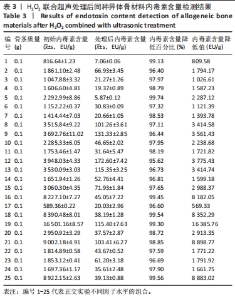
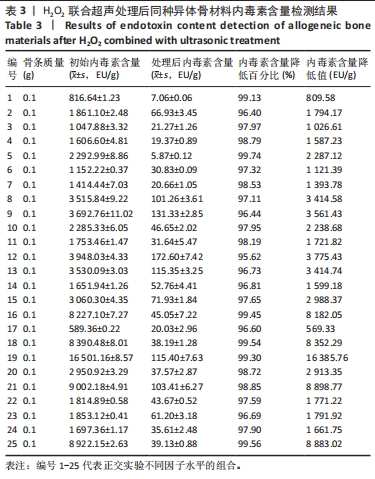
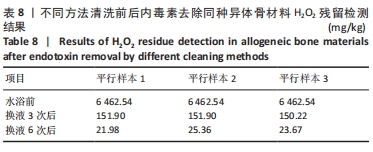
另外,由于初始内毒素值偏低,处理后同种异体骨的内毒素降低值(即内毒素清除效率)较正交实验中数值低。 根据GBT 14233.2-2005《医用输液、输血、注射器具检验方法 第2部分:生物学试验方法》中规定每件植入物的内毒素水平应不超过20 EU,当包装量为1.0 g时,同种异体骨材料的内毒素限值为20 EU/g。依据该标准,采用H2O2联合超声在H2O2浓度4%、超声功率200 W、超声时间50 min、超声水浴温度50 ℃时内毒素去除效率最高,并且符合标准。 2.2 内毒素去除同种异体骨材料清洗前后H2O2残留检测结果 不同方法清洗前后,内毒素去除同种异体骨材料H2O2残留检测结果,见表8。 换液3次后H2O2残留量为(151.34±0.97) mg/kg,换液6次后H2O2残留量为(23.67±1.69) mg/kg,换液后H2O2残留量显著降低。从结果看,随着水浴加热的进行,样品中H2O2残留逐渐降低,在换液第6次后降低至26 mg/kg以下。"
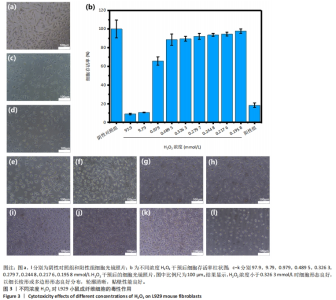
2.4 H2O2细胞毒性实验结果 如图3所示,随着H2O2浓度的降低,L929小鼠成纤维细胞存活率显著增高,在H2O2溶液稀释20 000倍(浓度为0.489 5 mmol/L)时细胞存活率为88.6%,稀释30 000倍(浓度为0.326 3 mmol/L)时细胞存活率约为90%,而在稀释35 000倍(浓度为0.279 7 mmol/L)时细胞存活率可达92%,显示H2O2浓度低于0.326 3 mmol/L(稀释30 000倍)时L929小鼠成纤维细胞存活率在90%以上,基本无细胞毒性;同时,细胞照片显示在H2O2浓度小于0.326 3 mmol/L时L929小鼠成纤维细胞形态良好,细胞以细长梭形或多边形形态良好分布,轮廓清晰,贴壁性能良好。"
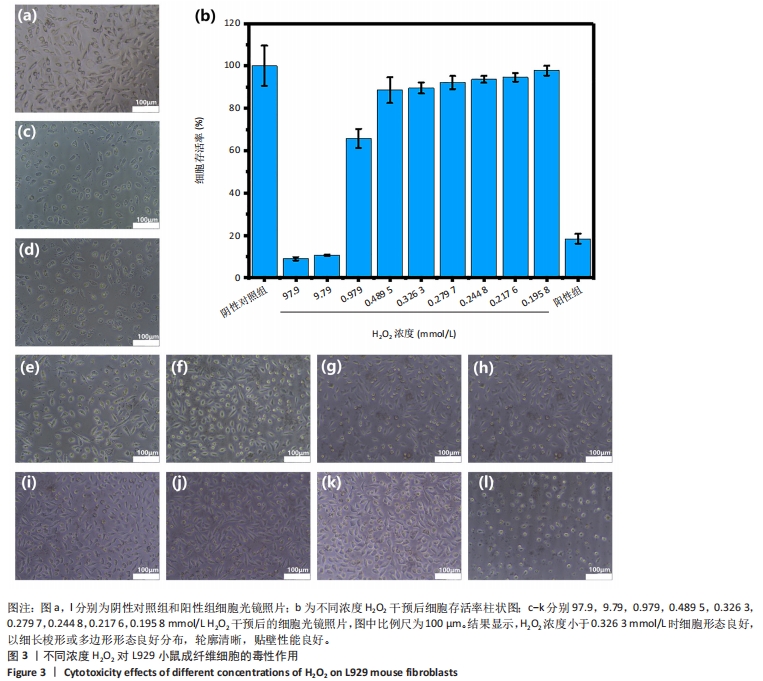
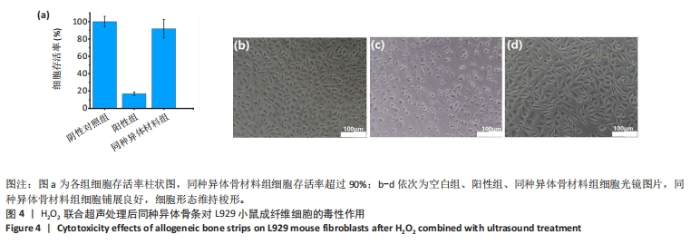
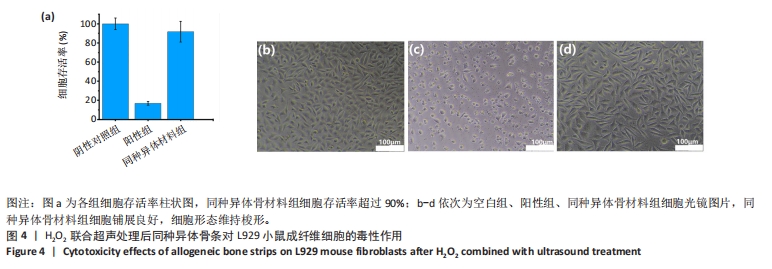
考虑到实验误差,此次实验设定细胞存活率超过90%才算是无潜在细胞毒性,因此,稀释倍数小于30 000-35 000倍之间存在H2O2毒性限值。稀释30 000倍(浓度为0.326 3 mmol/L)对应样品中H2O2残留值为55.471 mg/kg,稀释35 000倍(浓度为0.279 7 mmol/L)对应样品中H2O2残留值为47.551 mg/kg。从此次实验结果看,推荐样品中H2O2残留量限定值为47 mg/kg。 2.5 去除内毒素后同种异体骨材料中H2O2残留的细胞毒性检测结果 取60 ℃按照换液6次处理后的同种异体骨材料浸提液进行细胞毒性检测,结果显示同种异体骨材料浸提液干预后L929小鼠成纤维细胞存活率超过90%,同时结合细胞光学照片可见该组细胞铺展良好,贴壁效果良好,细胞形态维持梭形,见图4,说明该样品浸提液对L929小鼠成纤维细胞无明显细胞毒性。"
| [1] 高宏富,肖光夏,袁建成.抗内毒素研究进展[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2005,21(5):395-398. [2] HEINE H, RIETSCHEL ET, ULMER AJ. The biology of endotoxin. Mol Biotechnol. 2001;19(3):279-296. [3] WANG X, QUINN PJ. Endotoxins: lipopolysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria. Subcell Biochem. 2010;53:3-25. [4] 党京丹.细菌内毒素的研究及临床应用[J].山西医药杂志,2014, 43(7):771-773. [5] 李生军,张海霞,冯若飞.生物制品中内毒素的危害及其去除方法的研究进展[J].浙江农业科学,2021,62(9):1882-1885. [6] 张汉卿,马萍,于卓,等.去除玻璃仪器上内毒素方法的研究[J].中国消毒学杂志,2005,22(1):73-74. [7] 支兴蕾,李存玉,陈颖,等.超滤法去除生脉注射液中细菌内毒素的应用分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(23):21-24. [8] 刘艳,林峰,张海欣,等.超滤法去除食源性低聚肽中的细菌内毒素[J].食品科技,2014,39(12):340-343. [9] LI C, ZHAO C, MA Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted ultrafiltration process for removing bacterial endotoxin from diammonium glycyrrhizinate using response surface methodology. Ultrason Sonochem. 2020;68:105215. [10] 韦群.干热条件与内毒素灭活关系的研究[J].中国药事,2004, 18(11):710-712. [11] NOLAN JP, MCDEVITT JJ, GOLDMANN GS, et al. Endotoxin binding by charged and uncharged resins. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975;149(3): 766-770. [12] HEIMESAAT MM, SCHABBEL N, LANGFELD LQ, et al. Prophylactic Oral Application of Activated Charcoal Mitigates Acute Campylobacteriosis in Human Gut Microbiota-Associated IL-10-/- Mice. Biomolecules. 2024;3;14(2):141. [13] BARBOSA GD, DACH E, LIU X, et al. Computational and experimental study of different brines in temperature swing solvent extraction desalination with amine solvents. Desalination. 2022;537:115863. [14] 吴中华.Triton X-114用于去除内毒素的研究[J].安徽医药,2016, 20(5):848-851. [15] CHRIS-OLAIYA A, KAPOOR A, RICCI KS, et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange in liver failure. World J Hepatol. 2021;13(8):904-915. [16] PETSCH D, RANTZE E, ANSPACH FB. Selective adsorption of endotoxin inside a polycationic network of flat-sheet microfiltration membranes. J Mol Recognit. 2015;11(1-6):222-230. [17] TAPOUK FA, NABIZADEH R, NASSERI S, et al. Embedding of L–Arginine into graphene oxide (GO) for endotoxin removal from water: modeling and optimization approach. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2020;607:125491. [18] ZHANG Y, YANG H, ZHOU K, et al. Synthesis of an affinity adsorbent based on silica gel and its application in endotoxin removal. React Funct Polym. 2007;67(8):728-736. [19] SCHNEIER M, RAZDAN S, MILLER AM, et al. Current technologies to endotoxin detection and removal for biopharmaceutical purification. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020;117(8):2588-2609. [20] CAMPBELL DH, CHERKIN A. The destruction of pyrogens by hydrogen peroxide. Science. 1945;102(2656):535-536. [21] ROMANO KP, HUNG DT. Targeting LPS biosynthesis and transport in gram-negative bacteria in the era of multi-drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2023;1870(3):119407. [22] 李颜颜,史锋,李烨,等.细菌类脂A结构与功能研究进展[J].微生物学报,2008,48(6):844-849. [23] 周巾煜,李倩倩,黄纯翠,等.细菌脂多糖及其寡糖链结构分析技术研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2017,44(1):49-57. [24] ZIEMBOWICZ S, KIDA M, KOSZELNIK P. The impact of selected parameters on the formation of hydrogen peroxide by sonochemical process. Sep Purif Technol. 2018;204:149-153. [25] JAWALE RH, GOGATE PR. Combined treatment approaches based on ultrasound for removal of triazophos from wastewater. Ultrason Sonochem. 2018;40(Pt B):89-96. [26] LIM M, SON Y, KHIM J. The effects of hydrogen peroxide on the sonochemical degradation of phenol and bisphenol A. Ultrason Sonochem. 2014;21(6):1976-1981. [27] 王林,高嵩涛,张俊娟,等.瘤段骨灭活回植与同种异体骨移植治疗四肢恶性骨肿瘤的对比研究[J].实用器官移植电子杂志,2019, 7(4):262-266. [28] 裴宇盛,蔡彤,陈晨,等.细菌内毒素重组C因子检测方法的验证[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2020,33(1):76-79. [29] 王犇,马翔,张淑娟,等.过氧化氢危险性分析[J].无机盐工业, 2013,45(3):15-18. [30] JAYASURIYA AC, SHAH C, EBRAHEIM NA, et al. Acceleration of biomimetic mineralization to apply in bone regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2008;3(1):015003. [31] 华堃池,胡永成.梯度乙醇脱脂对异体松质骨脱脂效果及力学性能的评估[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(34):5502-5507. [32] 罗楚文,孔超颖,汤朝晖.超声化学在生物医学中应用的研究进展[J].化学学报,2023,81(7):836-842. [33] SONG W, DE LA CRUZ AA, REIN K, et al. Ultrasonically induced degradation of microcystin-LR and-RR: Identification of products, effect of pH, formation and destruction of peroxides. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40(12):3941-3946. [34] 古昌红,傅敏,丁培道,等.超声波降解吡啶溶液[J].化学研究与应用,2003,15(3):387-389. [35] 张锋.微波-Fenton试剂协同降解甲基橙废水研究[J].化学工程师, 2017(4):30-33. [36] LIN JG, CHANG CN, WU JR. Decomposition of 2-chlorophenol in aqueous solution by ultrasound/H2O2 process. Water Sci Technol. 1996; 33(6):75-81. [37] 贲永光,钟红茂,孔繁晟,等.超声协同H2O2降解模拟废水中苯酚的影响因素试验研究[J].土木建筑与环境工程,2012,34(1):96-101 [38] RAHDAR S, IGWEGBE CA, GHASEMI M, et al. Degradation of aniline by the combined process of ultrasound and hydrogen peroxide (US/H2O2). MethodsX. 2019;6:492-499. [39] 张贝利,张伟滨,邓廉夫.同种异体骨移植研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2005,26(3):164-167. [40] 赵丹.同种异体骨移植的研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报,2013, 48(5):577-580. [41] 冯仕明,高顺红,焦成.同种异体骨移植的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(21):1797-1799. [42] 游永刚,唐辉,陈克久,等.同种异体骨的骨诱导活性研究现状[J].西南国防医药,2008,18(3):449-452. [43] GARDNER EM, VONDERHEIDE N, FISHER R, et al. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on human tendon allograft. Cell Tissue Bank. 2013;14(4):667-671. |
| [1] | Wang Xuanqiang, Zhang Wenyang, Li Yang, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Wang Le, Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi. Effects of chronic exposure to low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields on contractility and morphology of the quadriceps muscle in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [2] | Ren Bo, Tang Yongliang, Li Ni, Liu Bangding. Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treatment of infected bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7269-7277. |
| [3] | Sheng Wenbo, Liu Bingli, Li Sibo, Ao Rongguang, Yu Baoqing. Cement-augmented short-segment percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for the stage II Kümmell’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7286-7292. |
| [4] | Zeng Yu, Xie Chengwei, Hong Yuanqi, Su Shenghui, Dong Xieping. In vitro angiogenesis and osteogenesis properties of copper-doped mesoporous bioactive glass [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5941-5949. |
| [5] | Shen Zhen, Huang Ziyue, He Zhijuan, Wang Yiting, Chen Qigang, Geng Chunmei, Huang Yajing, Wu Zugui. Dynamic expression of H-type vessels coupled with bone repair effect in bone induced membrane for massive bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5950-5956. |
| [6] | Gang Fangli, Dang Zhongxiu, Li Ruiyun, Li Xiao, Sun Xiaoyang. Techniques and performance of biominerals for fabricating bone tissue engineering scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5957-5967. |
| [7] | Wu Yonghao, Zhu Shuaiqi, Li Yuqiao, Zhang Chenfei, Xia Weiwei, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng. Correction effect of local kyphosis of the spine after percutaneous kyphoplasty in super-aging patients with vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5854-5861. |
| [8] | Chen Can, Zhao Yu, Hu Binhan, Du Mengfan, Liu Junning, Niu Susheng, Zhang Yan. Effect of ultrasound-guided needle-knife release of the ligamentum flavum on the expression of integrin alpha5 and beta1 in degenerative rabbit lumbar intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 331-338. |
| [9] | Gao Simiao, Han Xue, Wu Xiaoguang, Zheng Jinyu, Gao Fangwen, Li Kuihua, Peng Yong, Liu Lanxiang. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with low-frequency transcranial ultrasound stimulation on the electroencephalographic signals of rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 402-408. |
| [10] | Hu Binhan, Chen Can, Huang Maochang, Zhao Yu, Liu Junning, Niu Susheng, Zhang Yan. Effect of ultrasound-guided needle-knife on matrix homeostasis of rabbit cartilaginous endplate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3758-3766. |
| [11] | Zhang Jiahao, Li Jiacheng, Wen Mingtao, Guo Yanbo, Luo Di, Li Gang. Astragaloside IV alleviates oxidative stress injury and promotes osteogenesis in MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3529-3536. |
| [12] | Zhu Weiwei, Fan Zhengchao, Xu Ying, Xia Jizhu, Zhao Xiangzhi. Dual-modality imaging bionic nanoparticles for sonodynamic therapy on medullary thyroid carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3410-3419. |
| [13] | Qin Jie, Li Yujuan, Wang Bili, Lai Zefei, Ma Yueming. Constructing a Nomogram model of vulnerable carotid plaques in patients at high risk of stroke based on clinical baseline characteristics and carotid ultrasound parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2444-2449. |
| [14] | Li Xiaoqiang, Chen Wei, Li Mingyue, Shan Tianchi, Shen Wen. Value of preoperative quantitative ultrasound analysis of quadriceps femoris in predicting chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1388-1393. |
| [15] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||