Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 2444-2449.doi: 10.12307/2025.386
Previous Articles Next Articles
Constructing a Nomogram model of vulnerable carotid plaques in patients at high risk of stroke based on clinical baseline characteristics and carotid ultrasound parameters
Qin Jie1, Li Yujuan1, Wang Bili1, Lai Zefei2, Ma Yueming2
- 1First People’s Hospital of Fuzhou, Fuzhou 344000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Jiangxi Combined Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital, Nanchang 330000, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-26Accepted:2024-05-14Online:2025-04-28Published:2024-09-09 -
About author:Qin Jie, Associate chief physician, First People’s Hospital of Fuzhou, Fuzhou 344000, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Program of Jiangxi Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2022B223 (to LZF); Science and Technology Program of Jiangxi Provincial Health and Wellness Commission, No. 202311244 (to MYM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qin Jie, Li Yujuan, Wang Bili, Lai Zefei, Ma Yueming. Constructing a Nomogram model of vulnerable carotid plaques in patients at high risk of stroke based on clinical baseline characteristics and carotid ultrasound parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2444-2449.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
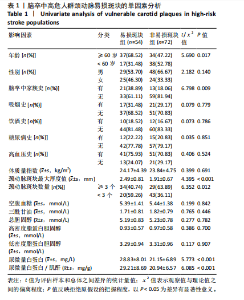
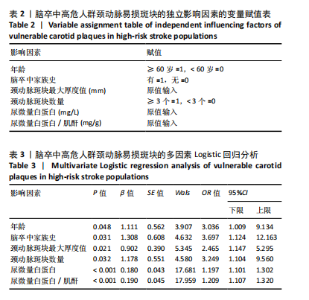
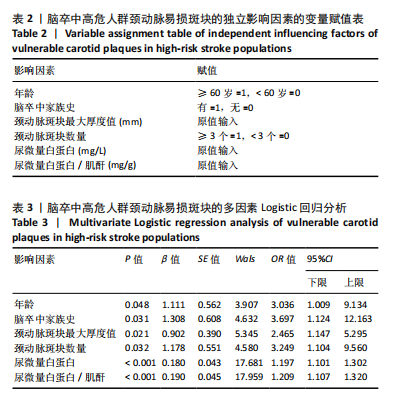
2.1 参与者数量分析 纳入的180例患者资料信息完整,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块的检出情况 结果显示,180例脑卒中高危人群检出颈动脉易损斑块共有77例(42.8%),其中建模集126例中检出颈动脉易损斑块有54例(42.9%),验证集54例中检出颈动脉易损斑块有23例(42.6%)。 2.3 影响脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块的单因素分析 结果显示,具有统计学意义的因素共6个,包括年龄、脑卒中家族史、颈动脉斑块最大厚度值、颈动脉斑块数量、尿微量白蛋白和尿微量白蛋白/肌酐(P < 0.05),见表1。 2.4 影响脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块的多因素 Logistic回归分析 将单因素分析中有统计学意义的影响因素纳入多因素Logistic回归分析,自变量赋值见表2。结果显示,年龄、脑卒中家族史、颈动脉斑块最大厚度值、颈动脉斑块数量、尿微量白蛋白和尿微量白蛋白/肌酐均是脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块的独立影响因素(P < 0.05),见表3。将上述6个独立影响因素进行共线性诊断,方差膨胀因子分别为1.0,1.1,1.2,1.1,1.1,1.1,均< 10,表示上述6个独立影响因素之间不存在多重共线性问题。 2.5 脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块的风险Nomogram模型构建 基于多因素Logistic回归分析算法,将脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块的形成概率设为P,Logit(p)= -13.072+1.111×(年龄)+1.308×(脑卒中家族史)+0.902×(斑块厚度)+1.178×(斑块数量)+0.180×(尿微量白蛋"

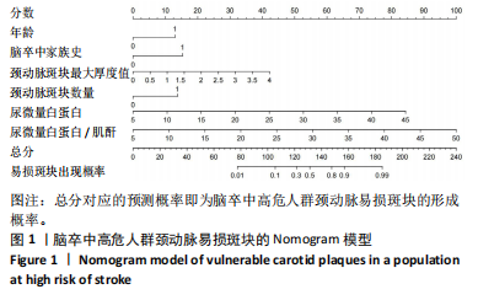
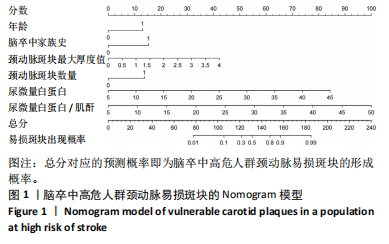
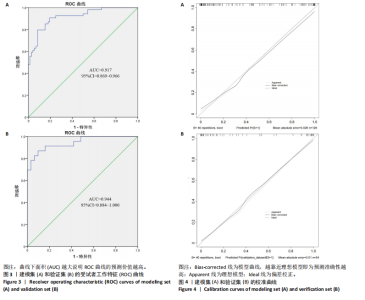
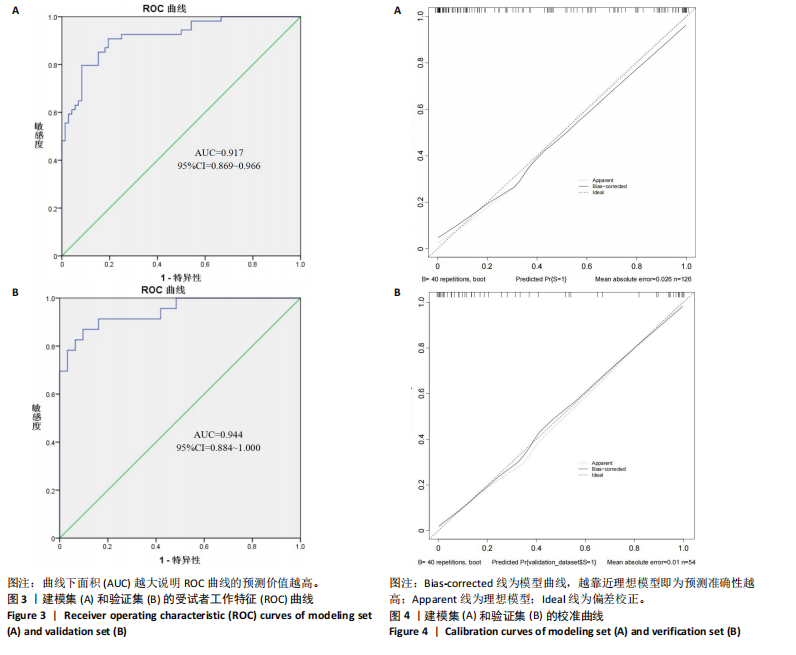
2.6 Nomogram模型的临床可用性评价 如图2所示,建模集和验证集的决策曲线显示,Nomogram模型在脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块的风险范围内表现为正的净效益,表明该模型的潜在临床获益可观,可用性较高。其中“All”线表示所有脑卒中高危人群均形成颈动脉易损斑块,且经模型干预后所获得的效益;“None”线表示所有脑卒中高危人群均未形成颈动脉易损斑块,且未经干预获得的效益(即为0);“Nomogram model”红色线表示采用该预警模型将脑卒中高危人群分为易损斑块组和非易损斑块组所获得的临床效益。 2.7 风险预警模型预测效能验证 受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)曲线结果显示,建模集的曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)为0.917,Youden指数0.713,灵敏度和特异度分别为79.6%和91.7%,提示模型具有较好的区分度,见图3A。校准曲线结果显示,平均绝对误差为0.026,提示模型预测概率与实际发生的概率之间差异不大,具备较好的预测准确性,见图4A。验证集的AUC为0.944,Youden指数为0.773,灵敏度和特异度分别为87.0%和90.3%,校准曲线的平均绝对误差为0.010,提示模型具备较好的外部预测性能,见图3B,图4B。"

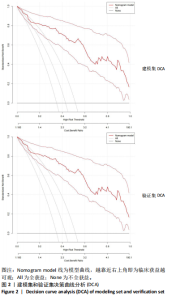
| [1] 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组.常用脑影像技术在脑卒中诊断中的应用指南[J].中华神经科杂志,2024,57(3): 206-224. [2] XIAOYAN X, ZHIJUAN P, MEIHUI L , et al. Impact of extended nursing model after multi-disciplinary treatment on young patient with post-stroke. World J Clin Cases. 2023;11(14):3148-3157. [3] 童亭亭,尤敏,王婷,等.脑卒中患者疾病复发恐惧研究进展[J].老年医学研究,2024,5(2):56-60. [4] 胡盛寿,王增武.《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022》概述[J].中国心血管病研究,2023,21(7):577-600. [5] WANG YJ, LI ZX, GU HQ, et al. China Stroke Statistics: an update on the 2019 report from the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in Neurological Diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, the Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and Institute for Global Neuroscience and Stroke Collaborations. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2022;7(5):415-450. [6] ERLINGE D, MAEHARA A, BEN-YEHUDA O, et al. Identification of vulnerable plaques and patients by intracoronary near-infrared spectroscopy and ultrasound (PROSPECT II): a prospective natural history study. Lancet. 2021;397(10278): 985-995. [7] LI J, WU H, Hang H, et al. Carotid vulnerable plaque coexisting with cerebral small vessel disease and acute ischemic stroke: a Chinese Atherosclerosis Risk Evaluation study. Eur Radiol. 2022;32(9):6080-6089. [8] HJELMGREN O, JOHANSSON L, PRAHL U, et al. Inverse association between size of the lipid-rich necrotic core and vascularization in human carotid plaques. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2018;38(2):326-331. [9] YING Z, JING C, JINGYI Z, et al. Plaque Elasticity and Intraplaque Neovascularisation on Carotid Artery Ultrasound: A Comparative Histological Study. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021;62(3):358-366. [10] SHIYAO G, LUNI Z, JING C, et al. Associations of plaque morphology and location with Intraplaque neovascularization in the carotid artery by contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1097070. [11] 谭杰.动脉粥样硬化脑梗死患者颈动脉超声造影参数与神经损害、斑块性质变化的相关性[J].海南医学院学报,2018,24(19):1770-1773+1778. [12] 刘滢滢,康松,梅雪,等.超声造影评估易损颈动脉斑块的研究进展[J].血管与腔内血管外科杂志,2023,9(7):836-840+845. [13] 胡斌彬,罗成宏,陆伟恒,等.脑卒中高危人群无症状颈动脉斑块易损性与实验室指标的关系及对脑血管缺血事件发生的影响[J].中国当代医药, 2022,29(8):25-28. [14] WU J, ZHANG H, LI L, et al. A nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with low-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma: A population-based analysis. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020;40(7):301-312. [15] 王震,陈林云,王琳,等.结直肠癌术后发生肠梗阻的影响因素分析及预测模型的构建[J].结直肠肛门外科,2024,30(1):64-71. [16] 高永祥,张晋昕.Logistic回归分析的样本量确定[J].循证医学,2018,18(2): 122-124. [17] 国家卫生计生委脑卒中筛查与防治工程委员会.脑卒中筛查与防治技术规范[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2013,5(9):44-50. [18] 戴全,邱海英,孙伟薇,等.实时三维超声血管斑块定量分析技术检测颈动脉斑块特征的临床价值[J].临床超声医学杂志,2019,21(8):589-592. [19] 张强,孟书静,成帅,等.老年脑卒中患者自我感知老化状况及影响因素[J].中医药临床杂志,2023,35(3):545-549. [20] 张伟伟,秦绪成,李伟伟,等.2014-2020年连云港市脑卒中发病趋势分析[J].预防医学,2022,34(9):932-936+950. [21] 范丽军.Orem自我护理模式对卒中后抑郁患者心理健康状态和自护能力的影响探究[J].中国医学创新,2021,18(8):100-103. [22] HARPAZ D, SEET RCS, MARKS RS, et al. Blood-Based Biomarkers Are Associated with Different Ischemic Stroke Mechanisms and Enable Rapid Classification between Cardioembolic and Atherosclerosis Etiologies. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(10):804. [23] ZHAO JJ, LU Y, CUI JY, et al. Characteristics of symptomatic plaque on high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging and its relationship with the occurrence and recurrence of ischemic stroke. Neurol Sci. 2021;42(9):3605-3613. [24] CHITI A. Atherosclerotic plaque healing. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):293-294. [25] 张红珍,杨少玲,赫兰,等.五种机器学习模型预测颈动脉粥样硬化患者发生缺血性脑卒中的效能比较[J].右江医学,2023,51(11):972-979. [26] 崔永芬.颈动脉超声筛查脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块与尿微量蛋白/肌酐尿微量白蛋白的关系研究[J].实用医学影像杂志,2022,23(6):642-645. [27] 何燕,盛灿,韩秋荣,等. 缺血性脑卒中患者颈动脉斑块易损性危险因素分析及预测模型构建[J]. 中华现代护理杂志,2023,29(21):2873-2879. [28] 林陆韬,林宇,蓝璧高,等.血清Hcy、hs-CRP水平及血管内皮功能与冠心病患者冠状动脉狭窄程度的相关性[J].中国医药科学,2023,13(18):145-148. [29] 辛爱华,于曰彬,马瑞.氯吡格雷联合磺酰脲类降糖药治疗缺血性脑卒中并糖尿病的价值[J].糖尿病新世界,2023,26(8):98-101. [30] 赵智芳,邓菲菲,刘顺芳.2型糖尿病患者颈动脉斑块形成的危险因素分析[J].临床医学研究与实践,2024,9(3):17-20. [31] YI X, ZHU L, SUI G, et al. Inflammation and Endothelial Function Relevant Genetic Polymorphisms and Carotid Plaque in Chinese Population. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2020;27(9):978-994. [32] 祝琳,白海威,米小昆,等.颈动脉易损斑块:影像学评价和缺血性卒中风险预测[J].国际脑血管病杂志,2020(2):140-144. [33] 彭佩燕,张泽鑫,吴壮雄.颈动脉斑块最大厚度值和Lp-PLA2水平与颈动脉易损斑块的相关性[J].中国超声医学杂志,2024,40(1):16-19. [34] 陈大伟,石进.颈动脉狭窄的脑卒中风险评估现状和思考[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2022,24(6):561-563. [35] JOHRI AM, NAMBI V, NAQVI TZ, et al. Recommendations for the Assessment of Carotid Arterial Plaque by Ultrasound for the Characterization of Atherosclerosis and Evaluation of Cardiovascular Risk: From the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2020;33(8):917-933. [36] 邓旭,庄文龙,薛慧,等.中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值、纤维蛋白原与2型糖尿病患者颈动脉内中膜厚度的关系[J].检验医学,2023,38(4):368-372. [37] 张晓燕,宋晶,吴晓明,等.颈动脉超声筛查脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块与ACR、ALBU的相关性研究[J].影像科学与光化学,2021,39(4):544-549. [38] 崔永芬.颈动脉超声筛查脑卒中高危人群颈动脉易损斑块与尿微量蛋白/肌酐尿微量白蛋白的关系研究[J].实用医学影像杂志,2022,23(6):642-645. [39] 李肖楠,孙威,王越晖.尿微量白蛋白在心脑血管疾病诊治中的研究进展[J].中国实验诊断学,2019,23(1):162-165. [40] 卢静,易兴阳,李洁,等.炎症和内皮功能相关基因多态性与颈动脉斑块相关性研究[J].中华神经科杂志,2020,53(10):763-771. [41] YANG D, JI Y, WANG D, et al. Comparison of carotid atherosclerotic plaques between subjects in Northern and Southern China: a Chinese atherosclerosis risk evaluation study. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020;5(2):138-145. [42] 徐驲,黄浪浪,李毅然,等.健脾化浊调脂颗粒调节肠道菌群紊乱治疗动脉粥样硬化的研究[J].光明中医,2023,38(9):1623-1626. [43] 陈纪烨,李晓雅,张晓囡,等.基于“血脉微癥”理论探讨动脉粥样硬化斑块防治思路[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2023,43(11):1366-1370. |
| [1] | Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Central anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of tea polyphenols in exercise fatigue model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6474-6481. |
| [2] | Bu Nan, Yang Yicheng, , Song Beibei, Bai Kaixiang, Du Yunyun, . Evaluating the compensatory function of intelligent assistive devices for the blind in China based on the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3650-3656. |
| [3] | Liao Qing, Zeng Jing, Chen Jun, Yuan Lixia, Liu Gang. Moxibustion alleviates cartilage lesions in rats with knee osteoarthritis through regulating the circPan3/miR-667-5p/Ghrelin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2475-2483. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiaojun, Tian Wengrong, Bu Panpan, Qi Yusong, Ma Zhiwei, Li Peipei, Ma Shaolin. Expression and regulation of miR-192-5p in hypertrophic scar tissue and fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2500-2506. |
| [5] | Liu Jianxiang, Feng Xingxing, Wang Shuxia, Zhou Rong, Lyu Mengxing, Qu Kexuan. Effects of different activators on platelet-rich plasma growth factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2067-2073. |
| [6] | Ba Yanhong, Gao Minghong, Chen Yingxin. Impact of graft thickness on corneal endothelial decompensation following simple Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1199-1207. |
| [7] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [8] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [9] | Niu Yongkang, Feng Zhiwei, Wang Yaobin, Liu Zhongcheng, Xiang Dejian, Liang Xiaoyuan, Yi Zhi, Zhan Hongwei, Geng Bin, Xia Yayi. Resveratrol activates extracellular-regulated protein kinase 5 signaling protein to promote proliferation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 908-916. |
| [10] | Zhao Yuxin, Liang Liang, Jin Feng, Xu Yangyang, Kang Zhijie, Fang Yuan, He Yujie, Wang Xing, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe. Establishment and stress analysis of a finite element model for adolescent cervical disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 448-454. |
| [11] | Zheng Xiang, Zhang Mingxing, Huang Ya, Shan Sharui. Improvement of lower limb walking function in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain by biofeedback assisted electrical stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 547-553. |
| [12] | Zhu Bochao, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Zhao Nannan, Liu Haoyuan, Xu Zhenhua, Wang Yupu. Jiawei Chunze Decoction treats urinary retention after spinal cord injury in rats based on the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 371-378. |
| [13] | Zhang Qiming, Liao Di, Zhong Zhiliang, Lin Lihua, Zheng Xiang, Li Qiong, Shan Sharui. Effect of deep muscle stimulation combined with electromyographic biofeedback on the spasms of the triceps surae and gait changes after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 385-392. |
| [14] | Li Ke, Cao Shuai, Zhang Qiongchi, He Xijing, Li Haopeng, Li Jie. Finite element analysis of biomechanical effect of lumbar range of motion on the implants after lumbar fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5747-5752. |
| [15] | Zhang Dezhou, Wang Chaoqun, Shi Jun, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Ma Yuan, Hou Erfei, Zhao Danyang, Hao Yunteng, Wang Simin, Li Xiaohe, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Wang Xing. Characteristics and significance of age-related changes in cervical uncinate process-related angle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5766-5772. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||