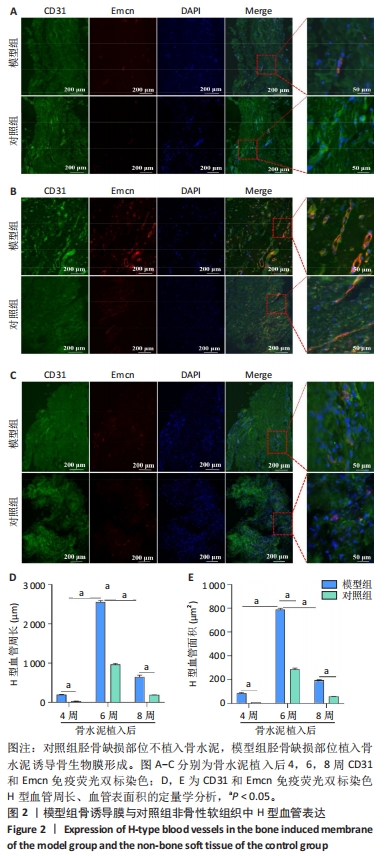
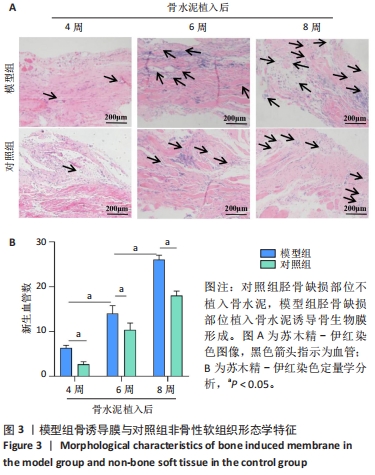
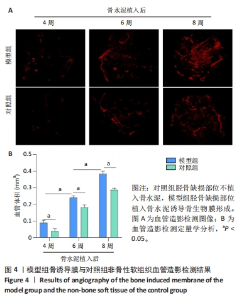
[1] RUDER JA, LI K, MATUSZEWSKI PE, et al. Promoting bone formation and healing in segmental defects through ectopic induced membrane. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2022;31(3):161-165.
[2] 邢浩,张永红,王栋.长骨大段骨缺损修复方法的优势与不足[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(3):426-430.
[3] MASQUELET AC, FITOUSSI F, BEGUE T, et al. Reconstruction of the long bones by the induced membrane and spongy autograft. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2000;45(3):346-353.
[4] MASQUELET AC, KANAKARIS NK, OBERT L, et al. Bone repair using the Masquelet technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101:1024-1036.
[5] MASQUELET AC. Muscle reconstruction in reconstructive surgery:soft tissue repair and long bone reconstruction. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2003; 388(5):344-346.
[6] 李卓伟,高峻青,王朝辉,等.诱导膜技术联合双钢板治疗胫骨骨干大段骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(8):737-740.
[7] 文虹杰,陈仲,杨华刚,等.基于PRISMA原则的对比Masquelet技术与骨搬运修复下肢大段骨缺损疗效的meta分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2021,39(4):484-491.
[8] 甄相周,陈鹏,凌建生,等.Masquelet技术治疗长骨干骨缺损的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(2):207-209.
[9] EL-HADIDI TT, SOLIMAN HM, FAROUK HA, et al. Staged bone grafting for the management of segmental long bone defects caused by trauma or infection using induced-membrane technique. Acta Orthop Belg. 2018;84(4):384-396.
[10] 吴斗,刘强.Masquelet技术修复骨缺损的实验研究现状和展望[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2020,37(11):1983-1987.
[11] ALFORD AI, NICOLAOU D, HAKE M, et al. Masquelet’s induced membrane technique: Review of current concepts and future directions. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(4):707-718.
[12] KLEIN C, MONET M, BARBIER V, et al. The Masquelet technique: Current concepts, animal models, and perspectives. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020; 14(9):1349-1359.
[13] RAMASAMY SK. Structure and Functions of Blood Vessels and Vascular Niches in Bone. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:5046953.
[14] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):323-328.
[15] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, WANG L. Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):376-380.
[16] WANG Q, ZHOU J, WANG X, et al. Coupling induction of osteogenesis and type H vessels by pulsed electromagnetic fields in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in mice. Bone. 2022;154:116211.
[17] XU R, YALLOWITZ A, QIN A, et al. Targeting skeletal endothelium to ameliorate bone loss. Nat Med. 2018;24(6):823-833.
[18] LU J, ZHANG H, CAI D, et al. Positive-Feedback Regulation of Subchondral H-Type Vessel Formation by Chondrocyte Promotes Osteoarthritis Development in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):909-920.
[19] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insigh. 2020;5(8):e135446.
[20] SHEN Z, CHEN Z, LI Z, et al. Total Flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae Enhances Angiogenic-Osteogenic Coupling During Distraction Osteogenesis by Promoting Type H Vessel Formation Through PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β Instead of HIF-1α/ VEGF Axis. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:503524.
[21] DANIEL M, SHEPPARD N, CARLOS G, et al. H Vessel Formation as a Marker for Enhanced Bone Healing in Irradiated Distraction Osteogenesis. Semin Plast Surg. 2024;38(1):31-38.
[22] 马金辉,任岩松,王佰亮,等.H亚型血管在股骨头坏死中的作用机制研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(11):1486-1491.
[23] SHAO W, WANG P, LV X, et al. Unraveling the Role of Endothelial Dysfunction in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Pathway to New Therapies. Biomedicines. 2024;12(3):664.
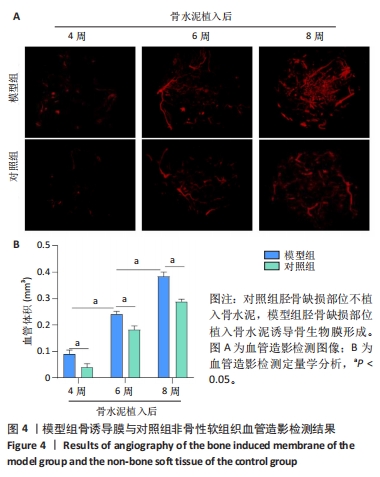
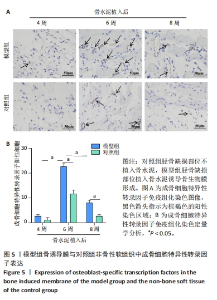
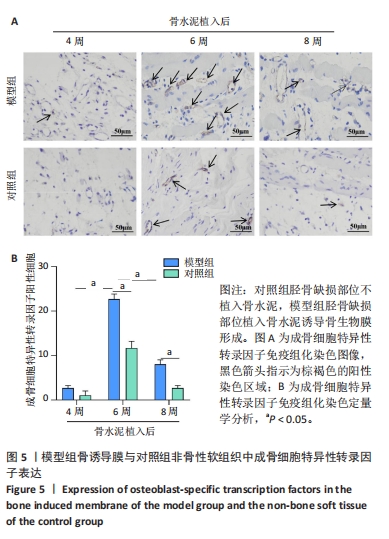
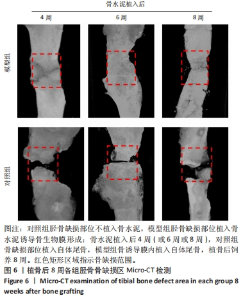
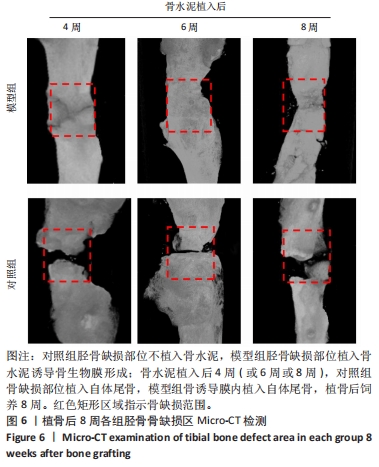
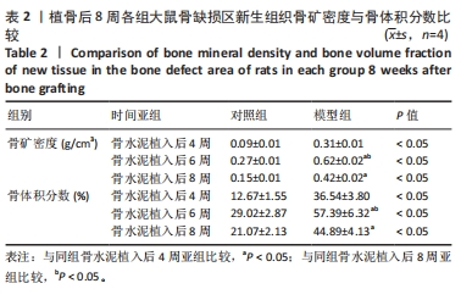
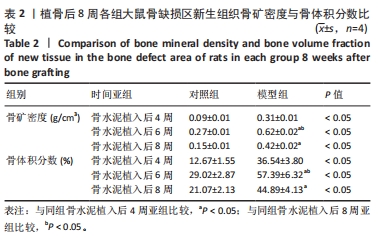
[24] 申震,姜自伟,李定,等.基于Masquelet诱导膜技术比较不同固定方式构建的胫骨大段骨缺损模型[J].中国实验动物学报,2018,26(6):673-680.
[25] SHEN Z, CHEN Z, SHI X, et al. Comparison between Tonifying Kidney Yang and Yin in Treating Segmental Bone Defects Based on the Induced Membrane Technique: An Experimental Study in a Rat Model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:6575127.
[26] SHEN Z, LIN H, CHEN G, et al. Comparison between the induced membrane technique and distraction osteogenesis in treating segmental bone defects: An experimental study in a rat model. PLoS One. 2019;14(12):e0226839.
[27] 赵常红,关彩萍.H型血管在骨构建和重塑中的作用机制[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2023,16(4):404-412.
[28] 刘晓南,余斌.H型血管在骨发育及骨疾病中作用研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(5):751-757.
[29] 张志秀,刘静,曾佩芸,等.H型血管在骨质疏松症中的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(4):575-579.
[30] 王亮,盛茂,袁晔,等.骨内H型血管在去势骨质疏松症模型中的变化[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(13):873-879.
[31] LANGEN UH, PITULESCU ME, KIM JM, et al. Cell-matrix signals specify bone endothelial cells during developmental osteogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(3):189-201.
[32] 田炯义,陈芊凝,陈骥,等.骨血管及其微环境调控造血和骨稳态的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2023,43(8):736-741.
[33] 陈培生,林小凤,林凤飞,等.H型血管耦联成血管-成骨机制在骨微环境重构机制的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2021,37(11):1048-1054.
[34] 曾志奎,熊伟,梁卫东,等.骨碎补总黄酮调控H型血管影响大鼠股骨Masquelet诱导膜模型的骨重建[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(32): 5130-5135.
[35] NAKASHIMA K, ZHOU X, KUNKEL G, et al. The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 2002;108(1):17-29.
[36] 李紫玲,李经堂.转录因子Sp7/Osterix的研究进展[J].南昌大学学报(医学版),2020,60(6):76-81.
[37] SHEN Z, DONG W, CHEN Z, et al. Total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae enhances CD31hiEmcnhi vessel formation and subsequent bone regeneration in rat models of distraction osteogenesis by activating PDGFBB/VEGF/RUNX2/OSX signaling axis. Int J Mol Med. 2022;50(3):112.
[38] 申震,陈泽华,郭英,等.骨碎补总黄酮对牵张成骨模型大鼠中H血管及成血管-成骨耦联的作用[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(3):1352-1356.
|