Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3614-3623.doi: 10.12307/2025.637
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of central analgesia in rats with myofascial pain syndrome by intervention of “trigger points” with stagnant moving needles
Zhao Liping1, 2, Chen Yibo1, Wang Yaqian1, Li Zhitong1, Zhang Qi1, Gou Bo3, 4
- 1Graduate Department, 3Key Laboratory of Sports Technology Analysis and Skill Assessment of General Administration of Sport, 4School of Sports and Health Sciences, Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Brain Disease Hospital, Xi’an Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-11Accepted:2024-06-15Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-11-02 -
Contact:Gou Bo, Professor, Key Laboratory of Sports Technology Analysis and Skill Assessment of General Administration of Sport, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China; School of Sports and Health Sciences, Xi'an Physical Education University, Xi'an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhao Liping, MS, Rehabilitation Therapist, Graduate Department of Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China; Brain Disease Hospital, Xi’an Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Key Research & Development Project of Ministry of Science and Technology, No. YFC2006903 (to GB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Liping, Chen Yibo, Wang Yaqian, Li Zhitong, Zhang Qi, Gou Bo. Mechanism of central analgesia in rats with myofascial pain syndrome by intervention of “trigger points” with stagnant moving needles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3614-3623.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
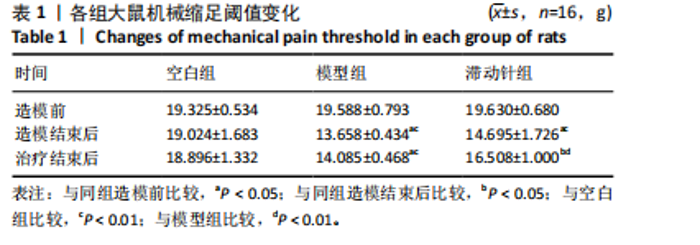
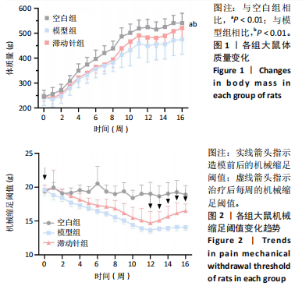
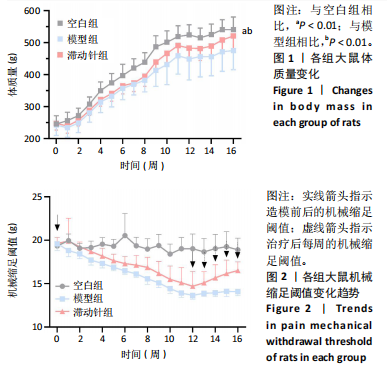
2.1 实验动物数量分析 48只SD大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 各组大鼠体质量变化 造模前,3组大鼠体质量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);造模后,与空白组比较,模型组与滞动针组大鼠体质量增长缓慢,可能与大鼠情绪、睡眠等问题有关;治疗结束后,模型组大鼠体质量低于空白组(P < 0.01),滞动针组大鼠体质量高于模型组(P < 0.01),见图1,说明滞动针可通过“神经-体液-内分泌”缓解肌筋膜疼痛综合征大鼠的疼痛,从而改善大鼠体质量。 2.3 各组大鼠机械缩足阈值比较 2.3.1 组内比较 空白组造模前、造模结束后及治疗结束后的大鼠机械缩足阈值无明显变化(P > 0.05);模型组大鼠造模结束后及治疗结束后的机械缩足阈值低于造模前(P < 0.05),造模结束后及治疗结束后的机械缩足阈值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);滞动针组大鼠造模结束后的机械缩足阈值低于造模前(P < 0.05),治疗结束后的机械缩足阈值高于造模结束后(P < 0.05),见表1。 2.3.2 组间比较 造模前,空白组、模型组和滞动针组大"
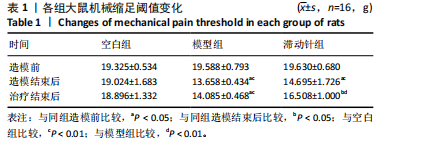
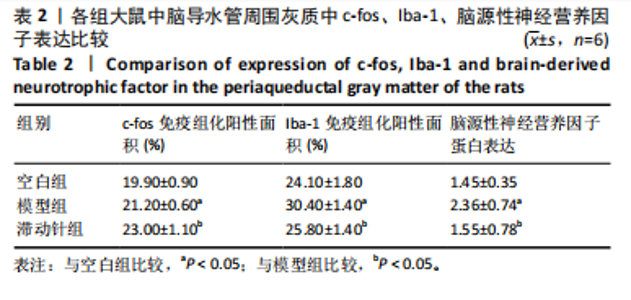
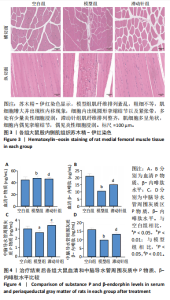
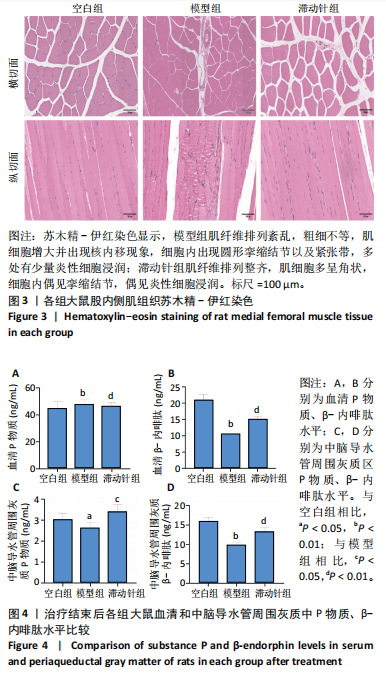
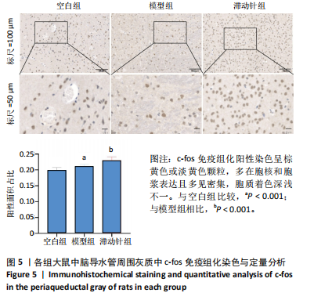
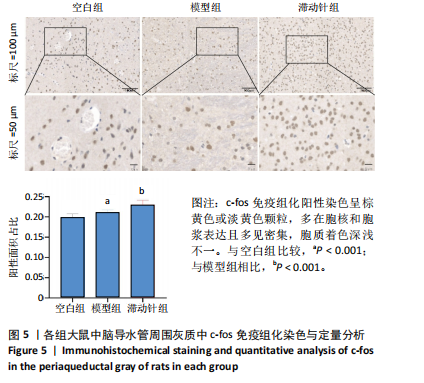
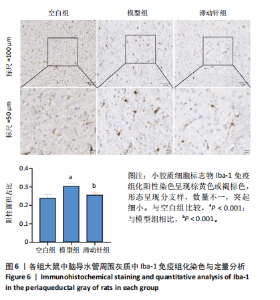
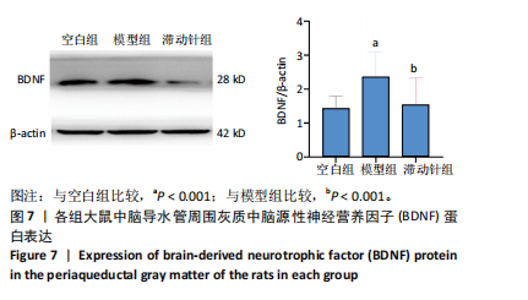
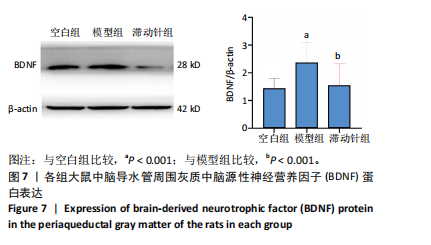
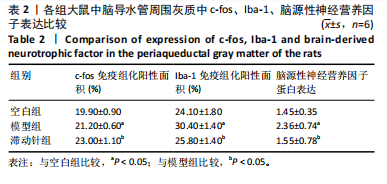
鼠机械缩足阈值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);造模结束后,模型组和滞动针组大鼠机械缩足阈值低于空白组(P < 0.01),模型组和滞动针组大鼠机械缩足阈值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);治疗结束后,与模型组相比,滞动针组机械缩足阈值明显升高(P < 0.01),见表1。各组大鼠机械缩足阈值变化趋势,见图2。 2.4 各组大鼠肌肉组织形态学观察结果 2.4.1 股内侧肌解剖观察 空白组大鼠股内侧肌腹弹性尚佳,颜色呈鲜红色,肌纤维未见粘连现象;模型组大鼠股内侧肌腹可触及挛缩的结节,肌纤维不同程度粘连,颜色呈暗红色;滞动针组大鼠股内侧肌腹平整,可偶见挛缩结节松解变小、硬度降低,紧绷带降低。 2.4.2 苏木精-伊红染色 空白组肌细胞形态大小相同,肌细胞间质紧密,纹理光滑,肌纤维排列整齐,可见典型明暗相间的横纹,未见炎性细胞浸润;模型组肌组织不规则、排列紊乱、断裂,肌纤维粗细不等,呈梭形聚集,肌细胞大小不一、间隙增宽,多处有少量炎性细胞浸润,出现核内移现象,肌细胞内出现圆形挛缩结节;滞动针组部分肌纤维排列整齐、间质减少,少量肌纤维断裂,胞核位于肌膜周边,偶见炎性细胞浸润,见图3。 2.5 各组大鼠血清中P物质、β-内啡肽水平 治疗结束后,模型组大鼠血清P物质水平高于空白组、滞动针组(P < 0.01),模型组大鼠血清β-内啡肽水平低于空白组、滞动针组(P < 0.01),见图4A,B。 2.6 各组大鼠中脑导水管周围灰质中P物质、β-内啡肽水平 治疗结束后,模型组大鼠中脑导水管周围灰质中P物质、β-内啡肽水平均低于空白组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),模型组大鼠中脑导水管周围灰质中P物质、β-内啡肽水平均低于滞动针组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),见图4C,D。 2.7 各组大鼠中脑导水管周围灰质中c-fos、Iba-1、脑源性神经营养因子表达 2.7.1 中脑导水管周围灰质中c-fos表达比较 c-fos免疫组化阳性染色呈棕黄色或淡黄色颗粒,多在胞核和胞浆表达且多见密集,胞质着色深浅不一。免疫组化染色结果显示,模型组c-fos阳性表达多于空白组(P < 0.001),滞动针组c-fos阳性表达多于模型组(P < 0.001),见表2、图5。 2.7.2 中脑导水管周围灰质中Iba-1表达比较 静息状态下,小胶质细胞标志物Iba-1免疫组化阳性染色呈现棕黄"
| [1] PROVENZANO DA, KAMAL KM, GIANNETTI V. Evaluation of Primary Care Physician Chronic Pain Management Practice Patterns. Pain Physician. 2018;21(6):E593-E602. [2] STRACCIOLINI A, CASCIANO R, LEVEY FRIEDMAN H, et al. Pediatric sports injuries: a comparison of males versus females. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(4):965-972. [3] SAXENA A, CHANSORIA M, TOMAR G, et al. Myofascial pain syndrome: an overview. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2015;29(1):16-21. [4] DUARTE FCK, WEST DWD, LINDE LD, et al. Re-Examining Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Toward Biomarker Development and Mechanism-Based Diagnostic Criteria. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(8):69. [5] CAO QW, PENG BG, WANG L, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of myofascial pain syndrome. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(9):2077-2089. [6] NIRAJ G. Pathophysiology and Management of Abdominal Myofascial Pain Syndrome (AMPS): A Three-Year Prospective Audit of a Management Pathway in 120 Patients. Pain Med. 2018;19(11):2256-2266. [7] 宋赣军.肌筋膜扳机点所致疼痛静息态脑血流与功能连接强度的耦合研究[D]. 遵义:遵义医科大学,2020. [8] NIDDAM DM, CHAN RC, LEE SH, et al. Central modulation of pain evoked from myofascial trigger point. Clin J Pain. 2007;23(5):440-118. [9] 李振全.滞动针刺疗法[C].中国针灸学会第九届全国中青年针灸推拿学术研讨会,中国上海,2010. [10] 王健,张卫华.张卫华教授“滞动针疗法”治疗慢性躯体疼痛临床特色撷英[J].中医药导报,2022, 28(10):105-109. [11] 王雄将,唐宏亮,王开龙,等.基于枢经理论运用滞针术治疗腰臀肌筋膜疼痛综合征疗效观察[J].山西中医,2020,36(7):30-32. [12] 唐宏亮,王雄将,方芳,等.督脉滞针疗法治疗腰背肌筋膜疼痛综合征的随机对照研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2018,45(11):2409-2412. [13] 王晓琳.P物质参与小鼠中枢内源性下行抑制系统镇痛效应的形态学研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2007. [14] TAKEDA K, MURAMATSU M, CHIKUMA T, et al. Effect of memantine on the levels of neuropeptides and microglial cells in the brain regions of rats with neuropathic pain. J Mol Neurosci. 2009;39(3):380-390. [15] WEI F, GUO W, ZOU S, et al. Supraspinal glial-neuronal interactions contribute to descending pain facilitation. J Neurosci. 2008;28(42): 10482-10495. [16] DEUMENS R, STEYAERT A, FORGET P, et al. Prevention of chronic postoperative pain: cellular, molecular, and clinical insights for mechanism- based treatment approaches. Prog Neurobiol. 2013;104:1-37. [17] ZHAO H, ALAM A, CHEN Q, et al. The role of microglia in the pathobiology of neuropathic pain development: what do we know? Br J Anaesth. 2017;118(4):504-516. [18] LI L, HUANG Q, BARBERO M, et al. Proteins and Signaling Pathways Response to Dry Needling Combined with Static Stretching Treatment for Chronic Myofascial Pain in a RAT Model: An Explorative Proteomic Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):564. [19] LIU QG, LIU L, HUANG QM, et al. Decreased Spontaneous Electrical Activity and Acetylcholine at Myofascial Trigger Spots after Dry Needling Treatment: A Pilot Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017:2017:3938191. [20] ZHANG H, LÜ JJ, HUANG QM, et al. Histopathological nature of myofascial trigger points at different stages of recovery from injury in a rat model. Acupunct Med. 2017;35(6):445-451. [21] YALCIN I, BOHREN Y, WALTISPERGER E, et al. A time-dependent history of mood disorders in a murine model of neuropathic pain. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70(10):946-953. [22] HU ML, ZHOU FY, LIU JJ, et al. Electroacupuncture Inhibits the Activation of p38MAPK in the Central Descending Facilitatory Pathway in Rats with Inflammatory Pain. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7531060. [23] BIBER K, TSUDA M, TOZAKI-SAITOH H, et al. Neuronal CCL21 up-regulates microglia P2X4 expression and initiates neuropathic pain development. EMBO J. 2011;30(9):1864-1873. [24] WATSON C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates-The New Coronal Set. Academic press, 2004. [25] HSIEH YL, WU BT, YANG CC. Increased substance P-like immunoreactivities in parabrachial and amygdaloid nuclei in a rat model with masticatory myofascial pain. Exp Brain Res. 2020;238(12):2845-2855. [26] MARGALEF R, SISQUELLA M, BOSQUE M, et al. Experimental myofascial trigger point creation in rodents. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(1): 160-169. [27] HUANG QM, YE G, ZHAO ZY, et al. Myoelectrical activity and muscle morphology in a rat model of myofascial trigger points induced by blunt trauma to the vastus medialis. Acupunct Med. 2013;31(1):65-73. [28] JAFRI MS. Mechanisms of Myofascial Pain. Int Sch Res Notices. 2014; 2014:523924. [29] 陈晨,张义,郭长青,等.针刀干预对大鼠股内侧肌触发点肌组织内P物质和降钙素基因相关肽表达的影响 [J].针灸临床杂志, 2018,34(1):55-58,81. [30] HENRY JL. Future basic science directions into mechanisms of neuropathic pain. J Orofac Pain. 2004;18(4):306-310. [31] WU ZZ, GUAN BC, LI ZW, et al. Sustained potentiation by substance P of NMDA-activated current in rat primary sensory neurons. Brain Res. 2004;1010(1-2):117-126. [32] HSIEH YL, HONG CZ, CHOU LW, et al. Fluence-dependent effects of low-level laser therapy in myofascial trigger spots on modulation of biochemicals associated with pain in a rabbit model. Lasers Med Sci. 2015;30(1):209-216. [33] 李玉娥,邓晓燕,褚万琼.针刺滞针疗法加闪罐治疗背肌筋膜炎的疗效观察[J].湖北中医学院学报, 2007,9(3): 62. [34] 张广防,彭雄强,郭玲崧,等.浮针治疗颈肩部肌筋膜疼痛综合征应用效果、肌张力指标及超声弹性成像指标的研究[J].针灸临床杂志,2021,37(10):33-38. [35] HSIEH YL, HONG CZ, LIU SY, et al. Acupuncture at distant myofascial trigger spots enhances endogenous opioids in rabbits: a possible mechanism for managing myofascial pain. Acupunct Med. 2016;34(4): 302-309. [36] 李振全.滞动针疗法[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2016. [37] MENSE S. Pathophysiologic Basis of Muscle Pain Syndromes: An Update. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 1997;8(1):23-53. [38] CHU J, TAKEHARA I, LI TC, et al. Electrical twitch obtaining intramuscular stimulation (ETOIMS) for myofascial pain syndrome in a football player. Br J Sports Med. 2004;38(5):E25. [39] 徐安乐.肌筋膜触发点疼痛与脊髓中枢P物质和突触素关系探究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2019. [40] 谢尊艳.筋膜刀干预对肌筋膜疼痛触发点模型大鼠SP、5-HT、BK影响的研究[D].西安:西安体育学院,2022. [41] BAGLEY EE, INGRAM SL. Endogenous opioid peptides in the descending pain modulatory circuit. Neuropharmacology. 2020;173:108131. [42] KULLING P, SIEGFRIED B, FRISCHKNECHT HR, et al. Beta-endorphin-like immunoreactivity levels in the hypothalamus, the periaqueductal grey and the pituitary of the DBA mouse: determination by ELISA and relationship to nociception. Physiol Behav. 1989;46(1):25-28. [43] NAKAMURA T, TOMIDA M, YAMAMOTO T, et al. The endogenous opioids related with antinociceptive effects induced by electrical stimulation into the amygdala. Open Dent J. 2013;7:27-35. [44] 任晓暄,郭孟玮,赵雅芳,等.电针对大鼠类痛经痛反应、脊髓κ-受体表达及中脑导水管周围灰质脑啡肽和β-内啡肽含量的影响[J].针刺研究,2012,37(1):1-7. [45] WANG SJ, ZHANG YP, CANDIOTTI KA. Effects of electroacupuncture on pain sensation in a rat model of hyperalgesia with nicotine dependence. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(4):905-910. [46] 周倩文.针刺对偏头痛CGRP、β-EP、5-HT、c-fos含量影响及相关机制研究[D].镇江:江苏大学,2018. [47] WU X, ZHANG M, HUANG H. Effect of qilongtoutong granule on calcitonin gene-related peptide, beta-endorphin, serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenalin in migraine model rats and mice. J Tradit Chin Med. 2014;34(2):188-193. [48] CRUZ-MENDOZA F, JAUREGUI-HUERTA F, AGUILAR-DELGADILLO A, et al. Immediate Early Gene c-fos in the Brain: Focus on Glial Cells. Brain Sci. 2022;12(6):687. [49] VALVERDE-NAVARRO AA, OLUCHA FE, GARCIA-VERDUGO JM, et al. Distribution of basal-expressed c-fos-like immunoreactive cells of the periaqueductal grey matter of the rat. Neuroreport. 1996;7(15-17): 2749-2752. [50] LI H, ZHANG X, CHEN M, et al. Dexmedetomidine inhibits inflammation in microglia cells under stimulation of LPS and ATP by c-Fos/NLRP3/caspase-1 cascades. EXCLI J. 2018;17: 302-311. [51] 郁晓燕,倪衡建,高永静.外周炎症性疼痛刺激诱导大鼠中脑导水管周围灰质胶质细胞激活及细胞因子的表达[J].解剖学报, 2008,39(4):460-465. [52] 王列.针刺“激痛点”对肌筋膜疼痛综合征大鼠疼痛敏化调控的机制研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2020. [53] 马俊杰.针刺、艾灸对肌筋膜疼痛综合征大鼠IL-8、PGE2及脊髓OX-42、BDNF表达影响的对比研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2022. [54] 肖蕾,潘洁,高育龙,等.基于“肌骨调衡”学术思想行滞动针疗法治疗风寒痹阻型神经根型颈椎病 [J].颈腰痛杂志,2024,45(1):145149. [55] 肖蕾,潘洁,高育龙,等.滞针动态施治疗法治疗神经根型颈椎病风寒痹阻证的随机对照试验[J]. 中医药导报,2023,29(10):50-55,59. [56] 吴丹卉,陈晓琴.滞动针法的相关文献研究与思考[J].江西中医药, 2023,54(5):62-64. [57] LANGEVIN HM, CHURCHILL DL, WUJ, et al. Evidence of connective tissue involvement in acupuncture. FASEB J. 2002;16(8):872-874. |
| [1] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [2] | Lei Senlin, Chen Xiaoan, Chen Ping, Wang Zhaofeng. Exercise prevention and treatment of Parkinson’ s disease mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor: role and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5454-5468. |
| [3] | Cao Zhengpei, Lu Shengsheng, Zhang Jiahuan, Wang Xiaoying. Effects of silver needle comprehensive therapy on the ultrasonographic morphology of multifidus muscles in patients with lumbar disc herniation: an ultrasound morphologic assessment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2261-2267. |
| [4] | Liu Xinxin, Geng Zhizhong, Chen Jian. Effects of high-intensity interval training with different intervention durations on cognitive function in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2282-2289. |
| [5] | Li Jingxuan, Shi Dai, Wu Guofeng. Regulatory effects of cAMP response element-binding protein on hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor level in a rat model of drug-resistant epilepsy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5659-5664. |
| [6] | Ma Ruixin, Liu Pan, Zhang Qiong, Zeng Gaofeng, Zong Shaohui. Molecular mechanism of total flavonoids of hawthorn leaves regulating astrocytes to repair spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5327-5333. |
| [7] | Yang Yazhu, Du Juan, Qu Haifeng, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on learning and memory ability of brain aging mice induced by D-galactose [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4487-4493. |
| [8] | An Hepeng, Liu Zhenteng, Li Lixin, Xu Yafang, Fan Guofeng. Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on neuronal activity, pain, and related cytokines in rats with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4120-4125. |
| [9] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Mingjuan, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng. Effects of aerobic and resistance exercise on antioxidant stress index and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the hippocampus of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 264-269. |
| [10] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng . Effects of aerobic and resistance exercises on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nuclear factor-kappa B and inflammatory cytokines in skeletal muscle of type II diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 669-675. |
| [11] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [12] | Wang Yuxiang, Cui Chuanju, Li Yanling, Li Aifan. Effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor modified human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2045-2049. |
| [13] | Lu Yi, Deng Wenchong. Regulation and difference of different exercise styles on brain structure and cognitive function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3252-3258. |
| [14] | Shi Zhengliang, Zhang Hua, Fan Zhiyong, Ma Wei, Yuan He, Yang Bing. Nerve conduits of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol with brain-derived neurotrophic factor microspheres for peripheral nerve defects in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1555-1559. |
| [15] | Zhang Jian, Chen Miao, Li Weixin, Ye Yichao, Xu Huiyou, Ma Ke, Chen Xuyi, Sun Hongtao, Zhang Sai. Collagen/heparin sulfate scaffolds loaded with brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote neurological and locomotor function recovery in rats after traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5538-5544. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||