Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 5002-5012.doi: 10.12307/2025.085
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different strategies to enhance mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of liver fibrosis: analysis of efficacy and potential risks
Xu Yan1, 2, Wang Xuesong1, 2, Zhou Lin1, 3, 4, 5, Zhou Xiaolei1, 2, Jin Yu2, Ye Junsong1, 3, 4, 5
- 1Subcenter for Stem Cell Clinical Translation, First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Ganzhou Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 4Key Laboratory for Tissue Engineering of Jiangxi Province, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 5Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Ministry of Education, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-20Accepted:2024-05-17Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-30 -
Contact:Ye Junsong, PhD, Associate professor, Subcenter for Stem Cell Clinical Translation, First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; Ganzhou Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; Key Laboratory for Tissue Engineering of Jiangxi Province, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Ministry of Education, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Xu Yan, Master candidate, Subcenter for Stem Cell Clinical Translation, First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32060232 (to YJS); Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, No. 20212BAB206057 (to YJS); Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Provincial Health Commission, No. 20191079 (to YJS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Yan, Wang Xuesong, Zhou Lin, Zhou Xiaolei, Jin Yu, Ye Junsong. Different strategies to enhance mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of liver fibrosis: analysis of efficacy and potential risks[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5002-5012.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
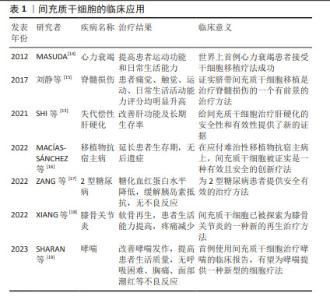
2.1 间充质干细胞的临床应用 间充质干细胞于1974年首次在骨髓中被分离出来,是人体中分布最广泛的细胞之一[11]。早在1995年,LAZARUS等[12]在《Bone Marrow Transplant》上首次报道了间充质干细胞的临床研究;2001年,德国STAUTER等首次用间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死患者获得成功;2005年,美国LAZARUS等用间充质干细胞与造血干细胞共移植治疗恶性血液病获得成功,提示共移植间充质干细胞会降低移植物抗宿主病的发生;国内王福生院士的最新研究成果显示,脐带间充质干细胞显著改善失代偿性患者的肝功能及长期生存率[13]。近年来,间充质干细胞在临床上应用广泛,见表1。"
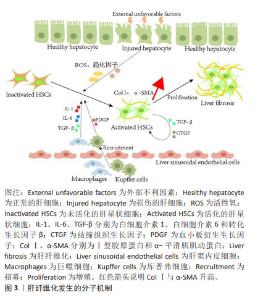
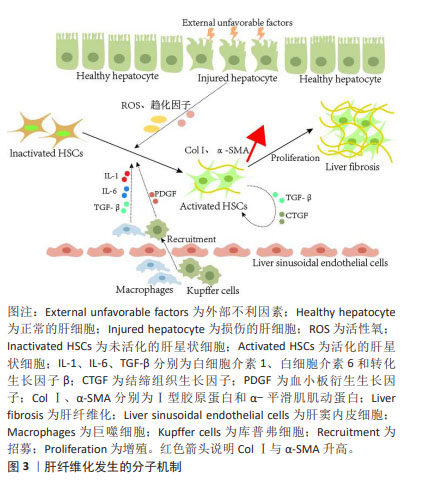
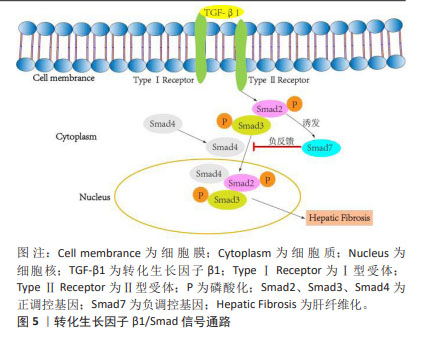
2.2 肝纤维化发生成因 肝脏主要由肝细胞组成,执行广泛的肝功能,例如解毒、胆汁酸合成和各种代谢过程。据报道,肝细胞是最先暴露于大多数类型肝损伤的细胞[20]。在物理、化学或生物因素等刺激对肝脏造成损伤时,受损的肝细胞会释放各种细胞因子、趋化因子和活性氧,将库普弗细胞募集到受损病变中产生炎症因子和生长因子,例如白细胞介素(白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6)和转化生长因子β[21-22];此外最新研究报道,巨噬细胞还可分泌血小板衍生生长因子[23],这些细胞因子是促进肝星状细胞激活的重要旁分泌信号[24]。激活的肝星状细胞通过分泌促纤维化因子转化生长因子β和结缔组织生长因子增强肝纤维化,同时以自分泌方式维持其激活状态[25]。活化的肝星状细胞还可以转分化为肌成纤维样细胞,这些细胞能够合成细胞外基质蛋白,例如Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、纤连蛋白和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白[26-28]。最终,细胞外基质蛋白过度沉积,损害肝脏的功能和结构,从而导致肝纤维化的发展。肝纤维化发生的分子机制见图3。"
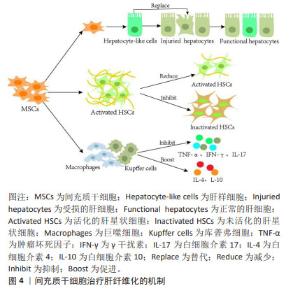
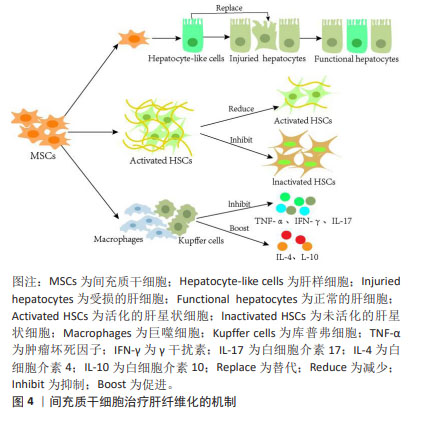
2.3 间充质干细胞改善肝纤维化的机制 研究表明,间充质干细胞有分化为肝样细胞以替代受损肝细胞的能力,并且通过抑制肝星状细胞的活化来修复受损的肝组织[29];此外,间充质干细胞可以分泌多种细胞因子与免疫细胞相互作用来调节免疫反应[30-31],因这些特有优势,在基础实验和临床研究中间充质干细胞治疗不同外界因素导致的肝纤维化成为热点。 2.3.1 间充质干细胞分化成肝样细胞 在多种原因引起的肝脏损伤过程中,肝细胞是最先受累的细胞。肝细胞损伤时,移植的间充质干细胞在受损肝脏的门静脉周围区域进行肝源性分化来替代垂死的肝细胞[32]。衍生的肝样细胞表达肝细胞标志物,并且具有糖原合成、低密度脂蛋白摄取、尿素产生和吲哚菁绿吸收等肝细胞功能[33-34],因此,分化的肝样细胞能够代替受损肝细胞并发挥作用。研究发现,在分化过程中间充质干细胞还会分泌多种细胞因子并抑制肝星状细胞活化,进而修复受损的肝脏[29]。此外,EWIDA等[35]也证实间充质干细胞来源的肝样细胞移植可有效改善大鼠肝纤维化,恢复受损的肝功能。鉴于肝纤维化最初是由肝细胞死亡引起的,因此替代受损的肝细胞可能是肝纤维化的根本治疗方法。 2.3.2 间充质干细胞抑制肝星状细胞活化 肝星状细胞活化是肝纤维化形成的重要因素[20,36]。研究证实,间充质干细胞通过抑制细胞增殖或刺激细胞凋亡来抑制肝星状细胞活化,从而发挥抗纤维化作用[37]。CHEN等[38]将骨髓间充质干细胞直接与肝星状细胞体外共培养时发现,骨髓间充质干细胞通过部分由Notch通路激活介导的细胞-细胞接触模式显著抑制肝星状细胞的增殖,并且PI3K/Akt通路参与Notch通路对肝星状细胞生长的抑制。 由于肝脏中有多种细胞类型,体外研究并不能完全模拟肝脏复杂情况,但动物模型可以作为体内的金标准。与体外实验结果一致,间充质干细胞移植通过抑制肝星状细胞增殖、促进肝星状细胞凋亡来改善大鼠肝纤维化水平[37]。据报道,核因子κB通路参与纤维化形成,活化的肝星状细胞会激活核因子κB通路,增强抗凋亡蛋白如Bcl-2基因的表达来抵抗肝星状细胞凋亡。研究人员发现,间充质干细胞可通过释放肝细胞生长因子抑制核因子κB通路,显著抑制肝星状细胞的增殖和活化,进而改善大鼠肝纤维化[39]。综上,经体内外研究证实,间充质干细胞可通过促进肝星状细胞的凋亡直接减少活化的肝星状细胞数量,抑制肝纤维化的发展。 2.3.3 间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用 间充质干细胞不仅具有分化为肝样细胞的能力,而且具有一定的免疫调节功能。研究表明,间充质干细胞通过分泌调节性细胞因子(如肝细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子和神经生长因子)抑制免疫细胞增生及牵移到肝脏,还可通过缓解肝脏炎症反应、减少肝细胞凋亡、刺激肝细胞再生发挥对纤维化的治疗作用[40]。间充质干细胞还通过抑制各种类型免疫细胞(包括T细胞、自然杀伤细胞、中性粒细胞和库普弗细胞)中肿瘤坏死因子α、γ干扰素和白细胞介素17等促炎细胞因子的合成,促进抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10的产生来发挥抗炎特性[41]。大鼠急性肝损伤研究也证实,间充质干细胞可抑制M1巨噬细胞活化,通过免疫调节显著降低肝脏炎症和胶原沉积[42]。间充质干细胞治疗肝纤维化的机制见图4。"

2.4 间充质干细胞联合不同策略改善肝纤维化 间充质干细胞因具有强大的分化潜能[43]、旁分泌作用和自动归巢能力[40,44],在抗炎及抗纤维化治疗中显示出了良好的应用前景。然而在体外分离和培养后,间充质干细胞面临营养、氧气和外部生长因子缺乏,以及间充质干细胞体内移植后面临着恶劣的微环境和炎症反应[45],导致间充质干细胞移植后肝脏定植率低、存活率低、作用时间短等问题。越来越多的研究表明,间充质干细胞通过联合药物[10]、基因修饰[46]、细胞因子等策略显著降低肝脏纤维化标志物基因(Ⅰ型胶原和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白)和蛋白质(α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、转化生长因子β1和磷酸化Smad3)的表达[47],疗效优于间充质干细胞单独治疗,这对提高间充质干细胞治疗肝纤维化疗效具有重要意义。 2.4.1 间充质干细胞联合药物 临床上肝纤维化的治疗方法主要包括消除病因、抑制炎症反应、抑制肝星状细胞活化、维持细胞外基质体内平衡等方面[48]。研究报道,中药凭借毒副作用小、不良反应少以及靶向调控与纤维化相关的转化生长因子β/Smad、Rho等信号通路等优势,被广泛应用于肝脏疾病的治疗[49],这为间充质干细胞单独治疗肝纤维化疗效不佳提供新思路。已有研究证实,间充质干细胞联合药物可显著改善肝纤维化。 联合药物提高间充质干细胞在肝脏中归巢率和存活率:间充质干细胞归巢是指在多种因素的作用下自体或外源性干细胞趋向性迁移,越过血管内皮细胞至靶向组织并定植存活的过程。间充质干细胞的归巢机制和淋巴细胞趋化至炎症损伤部位相似[50],然而间充质干细胞归巢效率低下,无法在靶组织中达到足够的归巢数量[7],这一缺点明显影响其治疗效果。研究发现,与未处理的骨髓间充质干细胞联合药物治疗相比,经褪黑激素预处理的骨髓间充质干细胞联合药物治疗增强了肝纤维化大鼠模型移植后骨髓间充质干细胞的归巢[51]。间充质干细胞联合中药改善肝纤维化也有多篇文献报道。骨髓间充质干细胞联合壮肝逐瘀煎可有效促进骨髓间充质干细胞向肝脏归巢,修复受损的肝组织[52]。柔肝化纤颗粒能动员骨髓间充质干细胞归巢于纤维化肝组织并修复受损肝组织,其机制可能与基质细胞衍生因子1/CXCR4轴有关[53]。人脐带间充质干细胞联合淫羊藿苷可促进人脐带间充质干细胞向受损肝组织的迁移,加速小鼠肝功能的恢复[54]。以上研究证实,间充质干细胞联合药物可促进间充质干细胞在受损的肝脏中定植,治疗肝纤维化得疗效明显优于间充质干细胞单独治疗。 联合药物抑制肝星状细胞活化:肝星状细胞活化可合成和分泌细胞外基质,在肝纤维化中起关键作用[55]。间充质干细胞联合药物不仅通过提高间充质干细胞在肝脏中定植,还可通过抑制肝星状细胞的活化,降低细胞外基质的合成和分泌,从而改善肝纤维化。据报道,阿魏酸在治疗肝纤维化方面非常有效,ZHANG等[56]采用骨髓间充质干细胞联合阿魏酸治疗大鼠纤维化时,证实其通过抑制细胞骨架重排并将miR-19b-3p递送至活化的肝星状细胞,使RhoA/ROCK信号失活来减弱肝星状细胞的活化,从而缓解肝纤维化,疗效优于单独阿魏酸或骨髓间充质干细胞治疗。骨髓间充质干细胞联合一贯煎通过调控RhoA/ROCK1通路抑制肝星状细胞活化,从而发挥抗纤维化的作用,二者联合的治疗效果优于各自单独作用[57]。NO可作为活化肝星状细胞的凋亡诱导剂[58],研究者将NO外源性供体硝普钠和间充质干细胞联合去治疗小鼠肝纤维化,结果显示间充质干细胞联合硝普钠使得肝星状细胞凋亡增加,进一步提高了间充质干细胞的抗纤维化效果[59]。 联合药物通过调节微环境改善肝纤维化:间充质干细胞特性和功能的变化离不开微环境的诱导[60],因此,维持肝脏微环境的稳态是保持细胞正常增殖、分化、代谢和功能活动的重要条件。在肝纤维化动物模型中,间充质干细胞联合姜黄素纳米纤维聚己内酯/聚乳酸羟基乙酸聚合物/胶原蛋白通过下调炎症递质和上调抗氧化因子显著改善肝纤维化[61]。在骨髓间充质干细胞联合白细胞介素18结合蛋白治疗肝纤维化的实验中,白细胞介素18结合蛋白能够通过相关分子机制影响肝脏微环境,促进间充质干细胞的增殖和分化,疗效优于骨髓间充质干细胞单独治疗[62]。在骨髓间充质干细胞协同氧化苦参碱治疗大鼠肝纤维化的实验中,联合治疗的效果也明显优于氧化苦参碱或骨髓间充质干细胞单独使用,但其并未增加骨髓间充质干细胞在肝脏的定植;值得注意的是,血清中白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10水平较骨髓间充质干细胞单独治疗明显升高,提示氧化苦参碱可能通过促进间充质干细胞分泌白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10改善肝纤维化[7]。还有研究表明,间充质干细胞联合硫化氢通过抗炎、抗氧化、抗凋亡和再生特性等机制减弱胆管结扎术诱导的肝纤维化[63]。综上所述,间充质干细胞联合药物通过下调炎症递质、上调抗氧化因子和炎症因子等机制调节微环境,有效改善肝纤维化。 联合药物通过调控信号通路改善肝纤维化:转化生长因子β/ Smad通路是肝纤维化相关的重要信号通路之一,其激活可加速肝脏炎症和纤维化的进展[64]。研究表明,丁香酚可通过调节大鼠转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路提高脂肪间充质干细胞抗纤维化活性。与脂肪间充质干细胞单独治疗相比,脂肪间充质干细胞联合丁香酚可显著改善血浆纤维蛋白原浓度、白细胞介素10水平和增殖细胞核抗原表达,降低肝脏纤维化标志物基因(Ⅰ型胶原和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白)和蛋白质(α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、转化生长因子β1和磷酸化Smad3)的表达[10]。间充质干细胞联合辛伐他汀可通过抑制转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路改善肝损伤,发挥强大的抗纤维化作用[65]。联合药物通过调控其他信号通路改善肝纤维化也有报道。在肝纤维化动物模型中,李汶航等[57]研究证实,骨髓间充质干细胞联合一贯煎可抑制Rho通路的关键分子RhoA、ROCK1的表达,从而抑制肝星状细胞活化,二者联合干预的疗效优于骨髓间充质干细胞单独使用。此外,血小板衍生生长因子信号通路在细胞外基质的积累中也起着重要作用,使用靶向血小板衍生生长因子受体的选择性酪氨酸激酶抑制剂伊马替尼可有效阻断血小板衍生生长因子受体信号传导,因此间充质干细胞联合伊马替尼治疗可能是限制肝纤维化发展和进展的有前途的方法[66]。文章总结了间充质干细胞联合药物通过调控信号通路进一步改善肝纤维化的机制,见表2。"

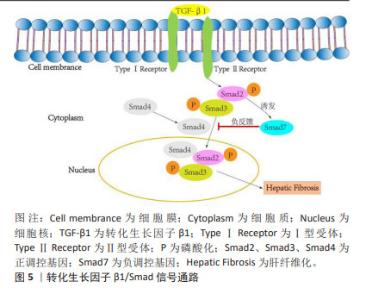
2.4.2 间充质干细胞联合基因修饰 基因修饰指在体外或体内通过病毒或非病毒载体将一系列具有生物学功能的基因导入宿主细胞,达到治疗某种疾病的目的[70]。越来越多的研究发现,可以通过腺病毒、慢病毒、反转录病毒等转染间充质干细胞使其过表达某种基因,从而提高间充质干细胞治疗肝纤维化的潜力[71]。此外,经过基因修饰的间充质干细胞也可以在体外传代培养后稳定表达某些外源基因,并且能够继续保持肝样细胞分化能力,发挥抗纤维化的作用。 基因修饰提高间充质干细胞在肝脏中归巢率:MA等[72]发现CXCR4修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞显著升高基质细胞衍生因子1α浓度并保持在相对稳定的水平,在肝脏中检测到强烈的标记骨髓间充质干细胞荧光信号,这表明CXCR4修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞大量准确地迁移至受损肝脏,基因修饰促进了间充质干细胞的归巢,进而改善肝功能。过表达纤维细胞生长因子4的骨髓间充质干细胞移植能够在早期促进骨髓间充质干细胞定位于肝脏,促进Jagged-1阳性干细胞增殖以及细胞核抗原和上皮黏附分子的表达,表明纤维细胞生长因子4转导的骨髓间充质干细胞可能通过移植的微环境促进肝脏再生[73]。研究表明,骨髓间充质干细胞过表达Bcl-2基因显示出更好的归巢率和存活率,并且增强了干细胞向肝样细胞的分化,促进肝硬化大鼠肝功能的恢复[74]。以上研究证实,基因修饰通过提高间充质干细胞归巢率增加间充质干细胞在肝脏中定植,从而更高效改善肝纤维化。 基因修饰抑制肝星状细胞的活化:研究发现,过表达肝细胞生长因子的间充质干细胞能够抑制肝星状细胞活化,改善肝功能。YIN等[75]的研究发现,肝细胞生长因子转染人脐带间充质干细胞可降低HSCs-T6细胞活力并抑制其活化,降低Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原、转化生长因子β1、Smad2和Smad3的表达,从而改善肝纤维化,疗效优于人脐带间充质干细胞单独治疗。研究人员将腺病毒介导的人尿激酶纤溶酶原激活剂(Ad-uPA)先转染到骨髓间充质干细胞上,再移植到肝纤维化大鼠体内,通过血清和肝组织进行生化、病理学分析,转染腺病毒后的干细胞组血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶、总胆红素、透明质酸、和Ⅲ型胶原水平显著降低,血清白蛋白水平升高,纤维化面积进一步减少,基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞比骨髓间充质干细胞单独治疗更显著抑制肝星状细胞的活化,从而改善肝纤维 化[46]。 基因修饰通过调控信号通路改善肝纤维化:Smad7作为转化生长因子β1/Smad 信号通路中必不可少的负调控基因,在抗纤维化过程中发挥着重要作用[76-78],见图5。"
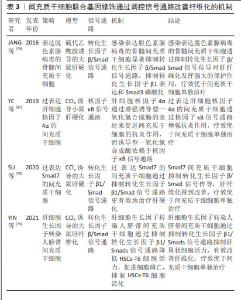
SU等[78]将过表达Smad7基因的间充质干细胞注射到大鼠纤维化模型中,通过定量PCR、Western blotting和ELISA染色法发现,Smad7-间充质干细胞处理后大鼠血清胶原Ⅰ、Ⅲ、胶原酶Ⅰ、Ⅲ水平显著降低,转化生长因子β1、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂1 mRNA水平降低,从而证明Smad7-间充质干细胞抑制转化生长因子β/Smad 信号传导使肝纤维化得到改善。JANG等[79]采用感染表达decorin腺病毒的骨髓间充质干细胞治疗硫代乙酰胺诱导的大鼠肝纤维化,与骨髓间充质干细胞单独治疗相比,感染表达脱色素腺病毒的骨髓间充质干细胞更强烈地抑制转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路,证实骨髓间充质干细胞联合基因修饰治疗肝纤维化的效果更佳。研究人员还发现,肝细胞生长因子转染的人脐带间充质干细胞可降低HSCs-T6细胞活力,可能也与抑制转化生长因子β1/Smad信号通路的激活有关[75]。 基因修饰除作用于转化生长因子β1/Smad信号通路外,还可以作用于其他信号通路。Wnt通路由高度保守的分泌糖蛋白组成,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路传导抑制可导致肝星状细胞激活下调,进而改善肝纤维化。研究发现,胎盘间充质干细胞可通过上调C-反应蛋白促进肝硬化大鼠模型的血管生成,通过Wnt信号通路促进肝脏再生[80]。MA等[46]也证实,基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞也可通过下调Wnt信号传导相关分子mRNA和蛋白的表达改善纤维化。研究发现,过表达肝细胞核因子4α的间充质干细胞通过核因子κB信号通路增强抗炎作用,对小鼠肝硬化的治疗效果优于间充质干细胞单独治疗[81],见表3。"
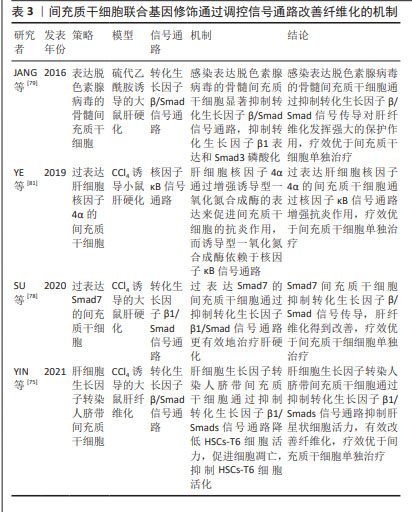
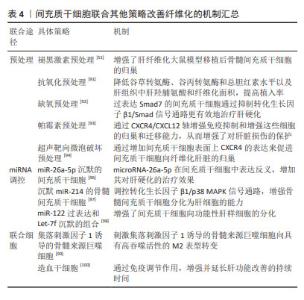
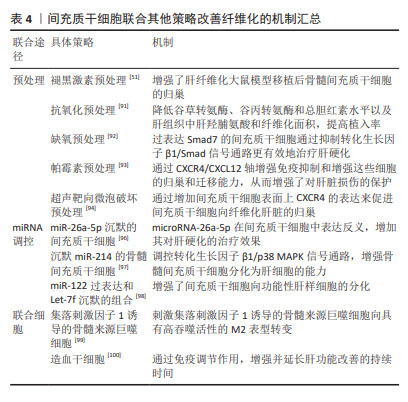
大量动物模型实验证实,基因修饰的间充质干细胞在治疗肝纤维化方面表现出巨大优势[79,81-82]。病毒介导的基因转入技术因高转染效率被广泛应用于转入细胞体内,通过构建稳定表达或瞬时表达某种外源基因的细胞系去治疗某些疾病。然而,基因转染技术存在免疫原性反应、细胞毒性、插入突变等生物安全问题,同时也存在技术难度较高、费用较高、过程也较为复杂等弊端[83]。 2.4.3 间充质干细胞联合细胞因子 上文提到,间充质干细胞在体内外都可向肝样细胞分化来代替受损肝细胞,对肝纤维化病程有逆转作用。研究发现,许多细胞因子可以促进间充质干细胞的分化。成纤维细胞生长因子2可以诱导骨髓间充质干细胞加速分化,并分泌基质金属蛋白酶降解胶原沉积,从而改善纤维化[84]。血管内皮生长因子可以增加间充质干细胞移植的数量并提高干细胞移植治疗肝纤维化的疗效,促进肝脏再生,有效改善肝功能,这可能与肝窦内皮通透性增加和血管细胞黏附分子1表达增加有关[85]。肝细胞生长因子作为一种重要的肝脏生长因子,可通过其受体激活刺激肝细胞增殖,抑制肝细胞凋亡,进而促进肝脏再生。研究发现,肝细胞生长因子能够诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞分化,分化得到的肝细胞能够表达肝脏特异性标志物白蛋白、角蛋白18,行使肝细胞糖原储存、尿素产生、低密度脂蛋白摄取等功能[86]。ZHANG等[87]将过表达肝细胞生长因子的骨髓间充质干细胞通过静脉移植到肝硬化模型大鼠体内,采用血清学、生化学和组织学方法证实肝细胞生长因子-骨髓间充质干细胞相较于骨髓间充质干细胞单独治疗可有效改善大鼠肝硬化。 除了成纤维细胞生长因子2、血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子外,经过炎性因子预处理的间充质干细胞也可有效改善肝纤维化。NASIR等[88]用白细胞介素6预处理纤维化肝脏可改善肝脏微环境,为间充质干细胞移植做好准备,从而减少纤维化后肝损伤,白细胞介素6和间充质干细胞的协同作用似乎是减轻肝纤维化并改善肝功能的首选治疗选择。此外,肿瘤坏死因子α/白细胞介素1β预处理的脂肪间充质干细胞可通过环氧化酶2/前列腺素E2通路减轻小鼠胆汁淤积性肝损伤和纤维化[89]。 据报道,卵泡抑素样1是一种转化生长因子β诱导的基质细胞蛋白,被认为是间充质干细胞增殖和分化的内在调节因子。ZHENG等[90]实验表明,卵泡抑素样1促进了间充质干细胞对巨噬细胞的免疫抑制,保证了间充质干细胞在肝纤维化中的抗纤维化作用。因此,间充质干细胞联合细胞因子在临床中治疗肝纤维化展现出巨大潜力,但还需要大规模和精心设计的随机试验,进而去分析其作用机制和治疗效果。 2.4.4 间充质干细胞联合其他策略 间充质干细胞除了可以联合药物、基因修饰、细胞因子提高肝纤维化的疗效外,还可以通过预处理、miRNA调控及与其他细胞联合等治疗策略,使间充质干细胞在减轻肝纤维化方面表现出更好的肝源性分化、归巢和存活功能。 LIAO等[91]研究表明,抗氧化预处理的脂肪间充质干细胞可通过降低谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶和总胆红素水平以及肝组织中肝羟脯氨酸和纤维化面积,来增强脂肪间充质干细胞对肝纤维化的治疗效果,特别是通过抑制氧化损伤来提高肝纤维化模型中脂肪间充质干细胞的肝脏植入效率,有效提高脂肪间充质干细胞移植对肝纤维化的治疗效果。KOJIMA等[92]的研究也证实,与正常氧气条件下培养的间充质干细胞相比,缺氧条件下培养的间充质干细胞对肝硬化小鼠的治疗效果更大。有研究采用雷帕霉素对人脐带间充质干细胞进行预处理,通过CXCR4/CXCL12轴增强免疫抑制和增强干细胞的归巢和迁移能力,从而增强了对肝脏损伤的保护[93]。还有研究通过尾静脉移植超声靶向微泡破坏预处理的间充质干细胞治疗小鼠肝纤维化,发现归巢至纤维化肝脏的间充质干细胞数量明显多于未经预处理的间充质干细胞数量,结果表明超声靶向微泡破坏可以通过增加间充质干细胞表面上CXCR4的表达来促进间充质干细胞向纤维化肝脏的归巢[94]。 miRNA在间充质干细胞的增殖、分化、迁移及细胞因子旁分泌等过程中起关键作用,参与调控间充质干细胞修复组织损伤的过程[95]。CHEN等[96]将miR-26a-5p沉默的间充质干细胞移植到大鼠肝硬化模型中发现,与间充质干细胞单独治疗相比,miRNA调控的间充质干细胞治疗效果增强,结果表明抑制间充质干细胞中miR-26a-5p可能通过增加肝细胞生长因子的产生进一步改善肝纤维化的严重程度。吴振兴等[97]最新研究证实,移植沉默miR-214的骨髓间充质干细胞可保护肝纤维化大鼠的肝功能,减轻肝纤维化程度,由此推测沉默miR-214可增强骨髓间充质干细胞分化为肝细胞的能力,从而抑制肝纤维化的进展,其机制可能与调控转化生长因子β1/p38 MAPK信号通路有关。此外,miR-122过表达和Let-7f沉默的组合也增强了间充质干细胞向功能性肝样细胞的分化[98]。 WATANABE等[99]将间充质干细胞和集落刺激因子1诱导的骨髓来源巨噬细胞联合治疗肝硬化时发现,在细胞共培养中,间充质干细胞诱导骨髓来源巨噬细胞向具有高吞噬活性的M2表型转变;在小鼠肝硬化体内模型中,联合治疗可减少肝纤维化、降低血液中肝酶水平,相较于间充质干细胞或集落刺激因子1诱导的骨髓来源巨噬细胞单一疗法更有效。研究发现,造血干细胞输注对慢性肝病患者的肝功能有短期改善,例如:SHARMA等[100]将自体间充质干细胞联合造血干细胞治疗失代偿性肝硬化患者时,发现具有免疫调节作用的间充质干细胞与造血干细胞结合增强了治疗效果,并且延长肝功能改善的持续时间;间充质干细胞和造血干细胞共培养结果表明,间充质干细胞支持造血干细胞的增殖和自我更新能力,该研究还解决了两种细胞类型在共培养过程中的冲突问题。文章对间充质干细胞联合其他策略治疗纤维化的机制进行汇总,见表4。"
| [1] KISSELEVA T, BRENNER D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(3): 151-66. [2] YANG X, LI Q, LIU W, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells in hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis: from pathogenesis to treatment. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023;20(6):583-599. [3] CALIGIURI A, GENTILINI A, PASTORE M, et al. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Liver Fibrosis Regression. Cells. 2021;10(10): 2759. [4] OLSON JC, SUBRAMANIAN R, KARVELLAS CJ. Intensive care management of liver transplant recipients. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2022; 28(6):709-714. [5] ZHANG L, XIANG J, ZHANG F, et al. MSCs can be a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1047907. [6] LIU P, QIAN Y, LIU X, et al. Immunomodulatory role of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in liver fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1096402. [7] 柴宁莉,徐世平,万军,等.氧化苦参碱协同骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠肝纤维化的实验研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2013,33(6): 840-844. [8] DI BONZO LV, FERRERO I, CRAVANZOLA C, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells as a two-edged sword in hepatic regenerative medicine: engraftment and hepatocyte differentiation versus profibrogenic potential. Gut. 2008;57(2): 223-231. [9] 向俊西,刘鹏,杨丽斐,等.生长因子诱导骨髓间充质干细胞肝向分化抑制慢性肝纤维化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(33): 5286-5291. [10] FATHY M, OKABE M, SAAD ELDIEN HM, et al. AT-MSCs Antifibrotic Activity is Improved by Eugenol through Modulation of TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway in Rats. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;25(2):348. [11] LAN T, LUO M, WEI X. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):195. [12] LAZARUS HM, HAYNESWORTH SE, GERSON SL, et al. Ex vivo expansion and subsequent infusion of human bone marrow-derived stromal progenitor cells (mesenchymal progenitor cells): implications for therapeutic use. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;16(4):557-564. [13] SHI M, LI Y Y, XU RN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in decompensated liver cirrhosis: a long-term follow-up analysis of the randomized controlled clinical trial. Hepatol Int. 2021;15(6):1431-1441. [14] MASUDA S. Cardiac stem cells in patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Lancet (London, England). 2012;379(9819): 891. [15] 刘静,韩冬梅,薛梅,等.脐带间充质干细胞鞘内注射治疗脊髓损伤的长期临床观察[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2017,13(6): 313-317. [16] MACÍAS-SÁNCHEZ MDM, MORATA-TARIFA C, CUENDE N, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Treating Steroid-Resistant Acute and Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease: A Multicenter Compassionate Use Experience. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022;11(4):343-355. [17] ZANG L, LI Y, HAO H, et al. Efficacy and safety of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes: a single-center, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled phase II trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):180. [18] XIANG XN, ZHU SY, HE HC, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapy for cartilage regeneration in knee osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):14. [19] SHARAN J, BARMADA A, BAND N, et al. First Report in a Human of Successful Treatment of Asthma with Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Case Report with Review of Literature. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(7): 1026-1029. [20] HAMMERICH L, TACKE F. Hepatic inflammatory responses in liver fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;20(10):633-646. [21] KOYAMA Y, BRENNER DA. Liver inflammation and fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(1):55-64. [22] LI X, WANG Y, WANG H, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is the crossroads of autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis signaling pathways and participates in liver fibrosis. Inflamm Res. 2015;64(1): 1-7. [23] DAMANIK FFR, VERKOELEN N, VAN BLITTERSWIJK C, et al. Control Delivery of Multiple Growth Factors to Actively Steer Differentiation and Extracellular Matrix Protein Production. Adv Biol. 2021;5(4): e2000205. [24] SÁNCHEZ-VALLE V, CHÁVEZ-TAPIA NC, URIBE M, et al. Role of oxidative stress and molecular changes in liver fibrosis: a review. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(28): 4850-4860. [25] ABOU-SHADY M, FRIESS H, ZIMMERMANN A, et al. Connective tissue growth factor in human liver cirrhosis. Liver. 2000;20(4): 296-304. [26] ROEHLEN N, CROUCHET E, BAUMERT TF. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells. 2020;9(4):875. [27] PAROLA M, PINZANI M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;65:37-55. [28] NESHAT SY, QUIROZ VM, WANG Y, et al. Liver Disease: Induction, Progression, Immunological Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Interventions. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6777. [29] JIN Y, SHI R, QI T, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells show hepatic differentiation potential and therapeutic effect in rats with acute liver failure. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2023;55(4):601-612. [30] KANG SH, KIM MY, EOM YW, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Liver Disease: Present and Perspectives. Gut liver. 2020; 14(3):306-315. [31] LEE EJ, HWANG I, LEE JY, et al. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Improves the Therapeutic Efficacy of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via RAD51. Mol Ther. 2018;26(3):845-859. [32] SUN H, SHI C, YE Z, et al. The role of mesenchymal stem cells in liver injury. Cell Biol Int. 2022;46(4):501-511. [33] YAO L, HU X, DAI K, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells: promising treatment for liver cirrhosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):308. [34] LI QY, CHEN J, LUO YH, et al. Sodium Butyrate Pre-Treatment Enhance Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BM-MSCs) into Hepatocytes and Improve Liver Injury. Curr Mol Med. 2022;22(7): 663-674. [35] EWIDA SF, ABDOU AG, EL-RASOL ELHOSARY AA, et al. Hepatocyte-like Versus Mesenchymal Stem Cells in CCl4-induced Liver Fibrosis. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017;25(10):736-745. [36] WANG S, LI K, PICKHOLZ E, et al. An autocrine signaling circuit in hepatic stellate cells underlies advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci Transl Med. 2023;15(677):eadd3949. [37] LEE C, KIM M, HAN J, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Influence Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells, and Constitute a Promising Therapy for Liver Fibrosis. Biomedicines. 2021;9(11):1598. [38] CHEN S, XU L, LIN N, et al. Activation of Notch1 signaling by marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through cell-cell contact inhibits proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci. 2011;89(25-26): 975-981. [39] WANG PP, XIE DY, LIANG XJ, et al. HGF and direct mesenchymal stem cells contact synergize to inhibit hepatic stellate cells activation through TLR4/NF-kB pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43408. [40] ZHENG W, YANG Y, SEQUEIRA RC, et al. Effects of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells on Liver Diseases . Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(5):442-452. [41] GAZDIC M, ARSENIJEVIC A, MARKOVIC BS, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Dependent Modulation of Liver Diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13(9): 1109-1117. [42] CAO Y, JI C, LU L. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(8):562. [43] KHUU D N, NYABI O, MAERCKX C, et al. Adult human liver mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells participate in mouse liver regeneration after hepatectomy. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(8):1369-1380. [44] YUAN M, HU X, YAO L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell homing to improve therapeutic efficacy in liver disease. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1): 179. [45] HU C, WU Z, LI L. Pre-treatments enhance the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in liver diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1): 40-49. [46] MA ZG, LV XD, ZHAN LL, et al. Human urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene-modified bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate liver fibrosis in rats by down-regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(6):2092-2103. [47] KIM MD, KIM SS, CHA HY, et al. Therapeutic effect of hepatocyte growth factor-secreting mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of liver fibrosis. Exp Mol Med. 2014;46(8):e110. [48] LIU H, WANG X, DENG H, et al. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolomics to Reveal the Mechanism of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Treating Liver Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(22):16086. [49] 王河,陈少锋,谭蓓蓓.中药治疗肝纤维化研究进展[J].内蒙古中医药,2023,42(2):128-131. [50] 朱杰,易发现.间充质干细胞归巢机制及影响因素研究进展[J].中国医药科学,2023,13(6):25-29. [51] MORTEZAEE K, PASBAKHSH P, RAGERDI KASHANI I, et al. Melatonin Pretreatment Enhances the Homing of Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Following Transplantation in a Rat Model of Liver Fibrosis. Iran Biomed J. 2016;20(4):207-216. [52] 罗艺徽,吴姗姗,王振常,等.壮方壮肝逐瘀煎联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对CCl4大鼠肝纤维化的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报, 2023,43(3):443-449. [53] 吕艳杭,吴姗姗,温智稀,等.柔肝化纤颗粒动员骨髓间充质干细胞归巢治疗肝纤维化大鼠的机制研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2021, 39(10):146-149,278-279. [54] CUI H, LIU Z, WANG L, et al. Icariin-treated human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells decrease chronic liver injury in mice. Cytotechnology. 2017;69(1):19-29. [55] TONG G, CHEN X, LEE J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 18 attenuates liver fibrosis and HSCs activation via the SMO-LATS1-YAP pathway. Pharmacol Res. 2022;178:106139. [56] ZHANG R, LI W, JIANG X, et al. Ferulic Acid Combined With Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuates the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Alleviates Liver Fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 863797. [57] 李汶航,张睿,崔欣怡,等.一贯煎联合骨髓间充质干细胞调控RhoA/ROCK1通路抑制大鼠肝纤维化的实验研究[J].世界中医药, 2022,17(18):2563-2568. [58] LEUNG TM, FUNG ML, LIONG EC, et al. Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of fibrogenic factors in experimental liver fibrosis in mice. Histol Histopathol. 2011;26(2):201-211. [59] ALI G, MOHSIN S, KHAN M, et al. Nitric oxide augments mesenchymal stem cell ability to repair liver fibrosis. J Transl Med. 2012;10:75. [60] TAN L, LIU X, DOU H, et al. Characteristics and regulation of mesenchymal stem cell plasticity by the microenvironment - specific factors involved in the regulation of MSC plasticity. Genes Dis. 2022; 9(2):296-309. [61] TAWFEEK GA, KASEM HA, ELSHOALA SE. Curcumin Nanofiber PCL/PLGA/Collagen Enhanced the Therapeutic Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells against Liver Fibrosis in Animal Model and Prevented its Recurrence. Nanotheranostics. 2023;7(3):299-315. [62] 石磊,范荣,聂为民,等.白细胞介素-18结合蛋白联合骨髓来源间充质干细胞治疗肝纤维化的实验研究[J].感染、炎症、修复, 2010,11(1):33-36. [63] MOHAMMED RA, SHAWKY HM, RASHED LA, et al. Combined effect of hydrogen sulfide and mesenchymal stem cells on mitigating liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation: Role of anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-fibrotic biomarkers. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021;24(12):1753-1762. [64] SONG Y, WEI J, LI R, et al. Tyrosine kinase receptor B attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β/SMAD signaling. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md). 2023;78(5):1433-1447. [65] JANG YO, KIM SH, CHO MY, et al. Synergistic effects of simvastatin and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on hepatic fibrosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(1):264-271. [66] MAZHARI S, GITIARA A, BAGHAEI K, et al. Therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and imatinib in a rat model of liver fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;882:173263. [67] 温智稀,王振常,黄晶晶,等.Notch信号系统对骨髓间充质干细胞定向分化的影响及鳖甲煎丸的干预作用[J].时珍国医国药,2017, 28(12):2847-2849. [68] 乔天阳.基于FGF2-DLK1信号通路研究一贯煎促进骨髓MSCs逆转肝纤维化的作用机制[D].北京:首都医科大学,2017. [69] 黄晶晶,黄鸿娜,王振常,等.鳖甲煎丸干预SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路对骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗肝纤维化的影响研究[J].时珍国医国药,2018,29(7):1565-1567. [70] SUN Y, XUE C, WU H, et al. Genetically Modified Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Cartilage Regeneration. Stem Cells Dev. 2023;32(13-14): 365-378. [71] VARKOUHI AK, MONTEIRO APT, TSOPORIS JN, et al. Genetically Modified Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: Application in Critical Illness. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(5):812-827. [72] MA HC, SHI XL, REN H Z, et al. Targeted migration of mesenchymal stem cells modified with CXCR4 to acute failing liver improves liver regeneration. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(40):14884-14894. [73] WANG J, XU L, CHEN Q, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing FGF4 contribute to liver regeneration in an animal model of liver cirrhosis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8):12774-12782. [74] JIN S, LI H, HAN M, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Enhanced Bcl-2 Expression Promote Liver Recovery in a Rat Model of Hepatic Cirrhosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(5):1117-1128. [75] YIN F, MAO LC, CAI QQ, et al. Effect of Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Transfected Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Hepatic Stellate Cells by Regulating Transforming Growth Factor-β1/Smads Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2021;30(21):1070-1081. [76] LEE H, YU DM, BAHN MS, et al. Hepatocyte-specific Prominin-1 protects against liver injury-induced fibrosis by stabilizing SMAD7. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(8): 1277-1289. [77] XU X, GUO Y, LUO X, et al. Hydronidone ameliorates liver fibrosis by inhibiting activation of hepatic stellate cells via Smad7-mediated degradation of TGFβRI. Liver Int. 2023; 43(11):2523-2537. [78] SU DN, WU SP, XU SZ. Mesenchymal stem cell-based Smad7 gene therapy for experimental liver cirrhosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1): 395. [79] JANG YO, CHO MY, YUN CO, et al. Effect of Function-Enhanced Mesenchymal Stem Cells Infected With Decorin-Expressing Adenovirus on Hepatic Fibrosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(9):1247-1256. [80] JUN J H, JUNG J, KIM J Y, et al. Upregulation of C-Reactive Protein by Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Angiogenesis in A Rat Model with Cirrhotic Liver. Int J Stem Cells. 2020;13(3):404-413. [81] YE Z, LU W, LIANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha alleviate liver injury by modulating anti-inflammatory functions in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1): 149. [82] HU C, ZHAO L, LI L. Genetic modification by overexpression of target gene in mesenchymal stromal cell for treating liver diseases. J Mol Med. 2021;99(2):179-192. [83] HASSANZADEH A, SHAMLOU S, YOUSEFI N, et al. Genetically-modified Stem Cell in Regenerative Medicine and Cancer Therapy; A New Era. Curr Gene Ther. 2022;22(1):23-39. [84] 韩宁,严丽波,唐红.《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2022年版)》更新要点解读[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2023,31(4):385-388. [85] YUAN K, LAI C, WEI L, et al. The Effect of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor on Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Engraftment in Rat Fibrotic Liver upon Transplantation. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019: 5310202. [86] SNYKERS S, VANHAECKE T, PAPELEU P, et al. Sequential exposure to cytokines reflecting embryogenesis: the key for in vitro differentiation of adult bone marrow stem cells into functional hepatocyte-like cells. Toxicol Sci. 2006;94(2):330-341; discussion 235-9. [87] ZHANG Y, LI R, RONG W, et al. Therapeutic effect of hepatocyte growth factor-overexpressing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on CCl(4)-induced hepatocirrhosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(12):1186. [88] NASIR GA, MOHSIN S, KHAN M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and Interleukin-6 attenuate liver fibrosis in mice. J Transl Med. 2013;11: 78. [89] LUAN X, CHEN P, LI Y, et al. TNF-α/IL-1β-licensed hADSCs alleviate cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis in mice via COX-2/PGE2 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1): 100. [90] ZHENG X, ZHOU X, MA G, et al. Endogenous Follistatin-like 1 guarantees the immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells during liver fibrotic therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):403. [91] LIAO N, SHI Y, WANG Y, et al. Antioxidant preconditioning improves therapeutic outcomes of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells through enhancing intrahepatic engraftment efficiency in a mouse liver fibrosis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):237. [92] KOJIMA Y, TSUCHIYA A, OGAWA M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells cultured under hypoxic conditions had a greater therapeutic effect on mice with liver cirrhosis compared to those cultured under normal oxygen conditions. Regen Ther. 2019;11:269-281. [93] ZHENG J, LI H, HE L, et al. Preconditioning of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells by rapamycin increases cell migration and ameliorates liver ischaemia/reperfusion injury in mice via the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12546. [94] 许何明.超声微泡增效间充质干细胞归巢治疗小鼠肝纤维化的机制初探[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2020. [95] CETIN Z, SAYGILI EI, GÖRGISEN G, et al. Preclinical Experimental Applications of miRNA Loaded BMSC Extracellular Vesicles. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(2):471-501. [96] CHEN L, ZENG W, YANG B, et al. Expression of antisense of microRNA-26a-5p in mesenchymal stem cells increases their therapeutic effects against cirrhosis. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(3):1500-1508. [97] 吴振兴,夏青青.移植沉默miR-214的骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠肝纤维化的影响[J].国际消化病杂志,2022,42(5):329-334. [98] DAVOODIAN N, LOTFI AS, SOLEIMANI M, et al. The combination of miR-122 overexpression and Let-7f silencing induces hepatic differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Cell Biol Int. 2017;41(10):1083-1092. [99] WATANABE Y, TSUCHIYA A, SEINO S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Induced Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages Synergistically Improve Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(3):271-284. [100] SHARMA M, PONDUGALA PK, JAGGAIHGARI S, et al. Safety Assessment of Autologous Stem Cell Combination Therapy in Patients With Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis: A Pilot Study. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022; 12(1):80-88. [101] CHIABOTTO G, PASQUINO C, CAMUSSI G, et al. Molecular Pathways Modulated by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles in Experimental Models of Liver Fibrosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:594794. [102] 丁翼,罗晓敏,杨斌,等.骨髓间充质干细胞改善肝纤维化机制的研究进展[J].药学学报,2022,57(4):863-874. [103] HU C, ZHAO L, DUAN J, et al. Strategies to improve the efficiency of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for reversal of liver fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(3):1657-1670. [104] LOPATINA T, GAI C, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Cross Talk between Cancer and Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Extracellular Vesicles Carrying Nucleic Acids. Front Oncol. 2016;6:125. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [3] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [4] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [5] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [6] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [7] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [8] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [9] | Weng Zongqin, Zhao Hailong. Mechanism of exosomal miRNA involved in tumor chemotherapy resistance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1504-1511. |
| [10] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [11] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [12] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [13] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [14] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [15] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||