Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (2): 269-278.doi: 10.12307/2025.274
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of different exercise interventions on carboxylesterase 1 and inflammatory factors in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats
Hu Shujuan1, 2, Cheng Ping3, Zhang Xiao3, Ding Yiting3, Liu Xuan1, Pu Rui1, Wang Xianwang3
- 1School of Education and Physical Education, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 423000, Hubei Province, China; 2College of Sports Science, Jishou University, Jishou 416000, Hunan Province, China; 3Department of Medicine, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 423000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-27Accepted:2024-03-06Online:2025-01-18Published:2024-05-24 -
Contact:Wang Xianwang, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 423000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Hu Shujuan, MD, Associate professor, School of Education and Physical Education, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 423000, Hubei Province, China; College of Sports Science, Jishou University, Jishou 416000, Hunan Province, China Cheng Ping, Master candidate, Department of Medicine, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 423000, Hubei Province, China Hu Shujuan and Cheng Ping contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81974115; Hubei Key Research and Development Program, No. 2021BGD010 (to WXW); Hubei Science and Technology Research Program, No. D20201306 (to WXW); Yangtze University College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Programs, Nos. Yz2022307, Yz2022164, and Yz2023165; Key Project of Social Science Foundation of Yangtze University, No. 2022csz07 (to HSJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Shujuan, Cheng Ping, Zhang Xiao, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Pu Rui, Wang Xianwang. Effects of different exercise interventions on carboxylesterase 1 and inflammatory factors in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 269-278.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
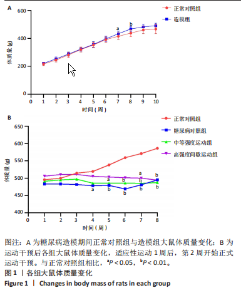
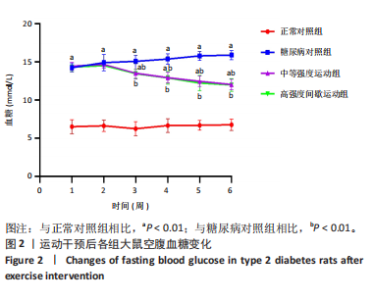
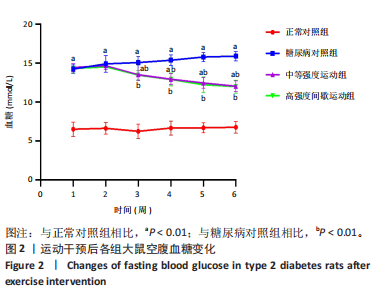
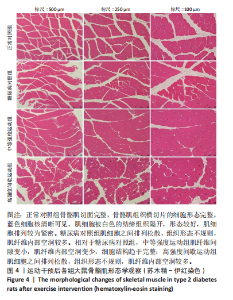
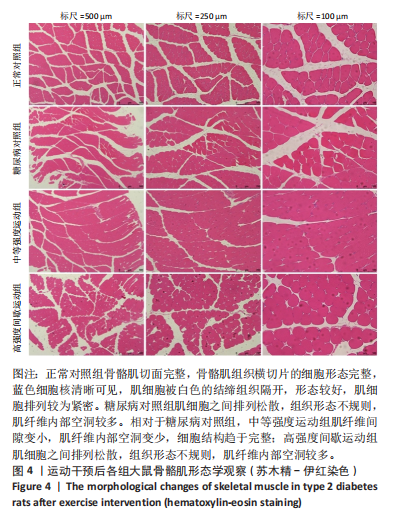
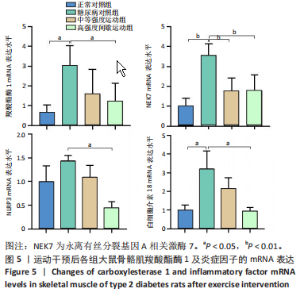
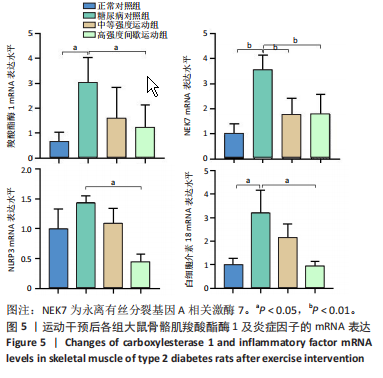
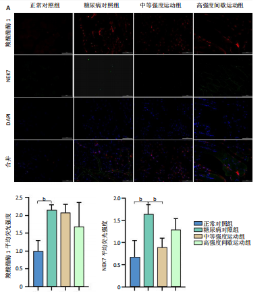
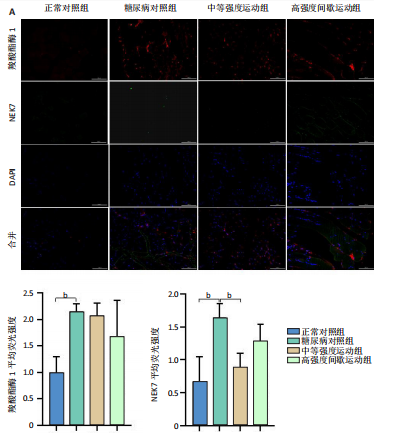
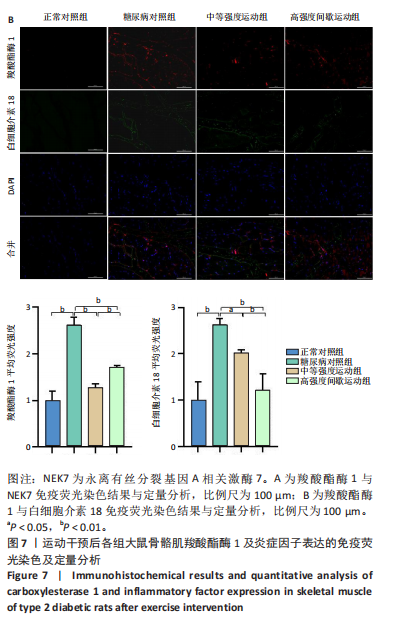
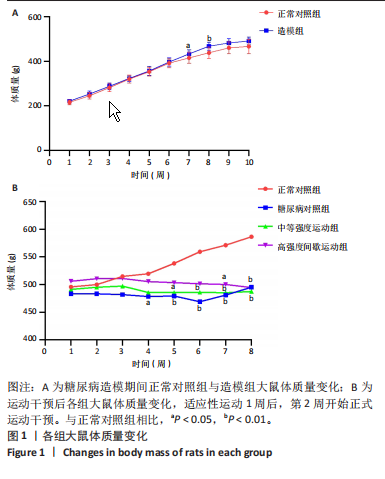
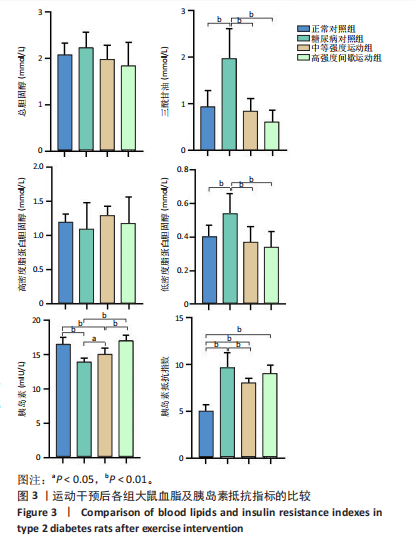
2.1 实验动物数量分析 正常对照组大鼠6只与造模成功的18只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 各组大鼠体质量的变化 如图1A所示,正常对照组和造模组于初始体质量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),从第2周开始喂养高脂饲料,结果显示第2-5周造模组和正常对照组大鼠体质量变化不太明显(P > 0.05),这可能与高脂饲料的脂肪含量不高有关;从第7周开始,与正常对照组相比,造模组大鼠体质量增加 (P < 0.05或P < 0.01);第8周开始注射链脲佐菌素,造模组大鼠体质量增加变缓,虽高于正常对照组但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 如图1B显示,运动干预前,正常对照组、中等强度运动组和高强度间歇运动组大鼠体质量略高于糖尿病对照组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);适应性运动1周后,第2周开始正式运动干预,从运动干预第4周开始,糖尿病对照组大鼠的体质量明显低于正常对照组(P < 0.05或 P < 0.01);从运动干预第5周开始,中等强度运动组大鼠的体质量低于正常对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);从运动干预第7周开始,高强度间歇运动组大鼠的体质量低于正常对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);中等强度运动组和高强度间歇运动组运动干预第7,8周的体质量相对于糖尿病对照组降低趋势明显,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),提示长期运动可能对降低2型糖尿病大鼠体质量有一定的效果,但运动干预6周时间未发现显著变化。 2.3 运动干预后各组大鼠空腹血糖变化 如图2显示,糖尿病对照组、中等强度运动组和高强度间歇运动组大鼠空腹血糖水平始终高于正常对照组(P < 0.01),从运动干预后的第3周开始,中等强度运动组和高强度间歇运动组大鼠空腹血糖水平明显低于糖尿病对照组(P < 0.01),提示运动可以降低2型糖尿病大鼠空腹血糖水平;中等强度运动组和高强度间歇运动组相比,高强度间歇运动组大鼠空腹血糖水平降低趋势更明显,但差异无显著性意义 (P > 0.05)。 2.4 运动干预后各组大鼠脂代谢及胰岛素抵抗情况比较 见图3。与正常对照组比较,糖尿病对照组大鼠血清三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平与胰岛素抵抗指数均升高 (P < 0.01),胰岛素活性降低(P < 0.01),总胆固醇、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平无明显变化(P > 0.05)。 6周运动干预后,与糖尿病对照组相比,中等强度运动组和高强度间歇运动组大鼠血清总胆固醇、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平无明显变化(P > 0.05),中等强度运动组和高强度间歇运动组大鼠血清三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平降低(P < 0.01),中等强度运动组和高强度间歇运动组大鼠血清胰岛素活性升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),中等强度运动组大鼠血清胰岛素抵抗指数降低(P < 0.01);高强度间歇运动组大鼠血清胰岛素活性高于中等强度运动组(P < 0.01),两组间其余血清指标检测值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.5 运动干预后各组大鼠骨骼肌形态学观察 各组大鼠骨骼肌苏木精-伊红染色结果,见图4。正常对照组骨骼肌切面完整,骨骼肌组织横切片的细胞形态完整,蓝色细胞核清晰可见,肌细胞被白色的结缔组织隔开,形态较好,肌细胞排列较为紧密。糖尿病对照组肌细胞之间排列松散,组织形态不规则,肌纤维内部空洞较多。相对于糖尿病对照组,中等强度运动组肌纤维间隙变小,肌纤维内部空洞变少,细胞结构趋于完整;高强度间歇运动组肌细胞之间排列松散,组织形态不规则,肌纤维内部空洞较多。提示中等强度的有氧运动可改善骨骼肌形态,而高强度间歇运动破坏了骨骼肌形态,对肌细胞造成损伤。 2.6 运动干预后各组大鼠骨骼肌羧酸酯酶1及炎症因子表达的比较 2.6.1 骨骼肌羧酸酯酶1及炎症因子mRNA表达 与正常对照组相比,糖尿病对照组大鼠骨骼肌羧酸酯酶1、NEK7、白细胞介素18 mRNA表达升高(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);与糖尿病对照组比较,中等强度运动组大鼠骨骼肌NEK7 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.01),高强度间歇运动组大鼠骨骼肌"
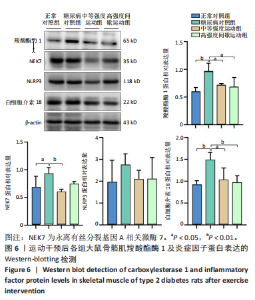
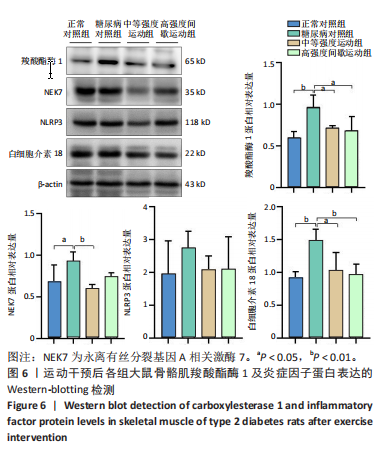
羧酸酯酶1、NEK7、NLRP3、白细胞介素18 mRNA均降低(P < 0.01或P < 0.05),见图5。 2.6.2 骨骼肌羧酸酯酶1及炎症因子的蛋白表达 Western-blotting检测结果显示,与正常对照组相比,糖尿病对照组大鼠骨骼肌羧酸酯酶1、NEK7、白细胞介素18的蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01或P < 0.05)。与糖尿病对照组比较,中等强度运动组大鼠骨骼肌羧酸酯酶1、NEK7、白细胞介素18的蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01或P < 0.05),高强度间歇运动组大鼠骨骼肌羧酸酯酶1、白细胞介素18蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);与中等强度运动组相比,高强度间歇运动组在羧酸酯酶1、NEK7、NLRP3、白细胞介素18蛋白的表达无明显变化(P > 0.05),见图6。"
| [1] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版) [J].中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(4):315-409. [2] GALICIA-GARCIA U, BENITO-VICENTE A, JEBARI S, et al. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6275. [3] FRIEDRICHSEN M, POULSEN P, WOJTASZEWSKI J, et al. Carboxylesterase 1 gene duplication and mRNA expression in adipose tissue are linked to obesity and metabolic function. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56861. [4] JIN T, XU J, YIN L, et al. Hepatic Carboxylesterase 1 Is Induced by Glucose and Regulates Postprandial Glucose Levels. PLoS One. 2014; 9(10):e109663. [5] DOMINGUEZ E, GALMOZZI A, CHANG JW, et al. Integrated phenotypic and activity-based profiling links Ces3 to obesity and diabetes. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10 (2):113-121. [6] JERNAS M, OLSSON B, ARNER P, et al. Regulation of carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) in human adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;383(1):63-67. [7] NAGASHIMA S, YAGYU H, TAKAHASHI N, et al. Depot-specific expression of lipolytic genes in human adipose tissues--association among CES1 expression, triglyceride lipase activity and adiposity. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2011;18(3):190-199. [8] 童金英,易银沙,曹蓬荣,等.人羧酸酯酶1结构和功能的研究进展[J].生物工程学报,2012,28(12):1414-1422. [9] ESSER N, L’HOMME L, DE ROOVER A, et al. Obesity phenotype is related to NLRP3 inflammasome activity and immunological profile of visceral adipose tissue. Diabetologia. 2013;56(11):2487-2497. [10] LIU G, CHEN X, WANG Q, et al. NEK7: a potential therapy target for NLRP3-related diseases. Biosci Trends. 2020;14(2):74-82. [11] DING S, XU S, MA Y, et al. Modulatory Mechanisms of the NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Diabetes. Biomolecules. 2019;9(12):850. [12] CAI H, WANG P, ZHANG B, et al. Expression of the NEK7/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in patients with diabetic lower extremity arterial disease. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8(2):e001808. [13] LUO B, LI B, WANG W, et al. NLRP3 gene silencing ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy in a type 2 diabetes rat model. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104771. [14] ABOZAID YJ, AYADA I, VAN KLEEF LA, et al. Plasma proteomic signature of fatty liver disease: The Rotterdam Study. Hepatology. 2023;78(1): 284-294. [15] 甄为,罗俊生,霍晓川,等.羧酸酯酶1对大鼠颈动脉损伤后血管狭窄及炎性反应的影响[J].解放军医学院学报,2014,35(3):261-265. [16] ZHANG T, TIAN J, FAN J, et al. Exercise training-attenuated insulin resistance and liver injury in elderly pre-diabetic patients correlates with NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1082050. [17] COLBERG SR, SIGAL RJ, YARDLEY JE, et al. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(11):2065-2079. [18] HU S, HU Y, LONG P, et al. The effect of tai chi intervention on NLRP3 and its related antiviral inflammatory factors in the serum of patients with pre-diabetes. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1026509. [19] KHAKROO ABKENAR I, RAHMANI-NIA F, LOMBARDI G. The Effects of Acute and Chronic Aerobic Activity on the Signaling Pathway of the Inflammasome NLRP3 Complex in Young Men. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania). 2019;55(4):105. [20] 黎妮.不同运动对糖尿病大鼠心肌NLRP3炎症小体及IL-1β的影响[D].成都:成都体育学院,2018. [21] 余臣祖,张朝宁,刘国安.实验性2型糖尿病动物模型研究进展[J].医学综述,2006,12(1):41-42. [22] 任曙光,吴建华,巨英超.天麦消渴片对糖尿病模型大鼠血糖的影响[J].中医杂志,2011,52(19):1679-1681. [23] 李娣,陈锐,陈嘉勤,等.有氧运动与黑枸黄酮干预酒精性肝损伤模型小鼠炎性因子的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(32): 5197-5202. [24] 崔新雯,张一民,汪赞,等.自噬介导的高强度间歇运动对中年大鼠骨骼肌质量和有氧运动能力随时间变化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(8):1196-1204. [25] HANSEN M, PALSØE MK, HELGE JW, et al. The effect of metformin on glucose homeostasis during moderate exercise. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(2):293-301. [26] JADHAV RA, HAZARI A, MONTERIO A, et al. Effect of Physical Activity Intervention in Prediabetes: A Systematic Review With Meta-analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2017;14(9):745-755. [27] LIAN J, NELSON R, LEHNER R. Carboxylesterases in lipid metabolism: from mouse to human. Protein Cell. 2018;9(2):178-195. [28] XU J, LI Y, CHEN WD, et al. Hepatic carboxylesterase 1 is essential for both normal and farnesoid X receptor-controlled lipid homeostasis. Hepatology. 2014;59(5):1761-1771. [29] ELLINGHAUS P, SEEDORF U, ASSMANN G. Cloning and sequencing of a novel murine liver carboxylesterase cDNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1397(2):175-179. [30] GHOSH S. Cholesteryl ester hydrolase in human monocyte/macrophage: cloning, sequencing, and expression of full-length cDNA. Physiol Genomics. 2000;2(1):1-8. [31] SANGHANI SP, SANGHANI PC, SCHIEL MA, et al. Human carboxylesterases: an update on CES1, CES2 and CES3. Protein Pept Lett. 2009;16(10):1207-1214. [32] YAO H, BAI R, REN T, et al. Enhanced Platelet Response to Clopidogrel in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats due to Impaired Clopidogrel Inactivation by Carboxylesterase 1 and Increased Exposure to Active Metabolite. Drug Metab Dispos. 2019;47(8):794-801. [33] MARRADES MP, GONZALEZ-MUNIESA P, MARTINEZ JA, et al. A dysregulation in CES1, APOE and other lipid metabolism-related genes is associated to cardiovascular risk factors linked to obesity. Obes Facts. 2010;3(5):312-318. [34] VANDANMAGSAR B, YOUM YH, RAVUSSIN A, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011;17(2):179-188. [35] HE Y, ZENG MY, YANG D, et al. NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature. 2016; 530(7590):354-357. [36] XU J, LU L, LI L. NEK7: a novel promising therapy target for NLRP3-related inflammatory diseases. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016;48(10):966-968. [37] KONG X, LU AL, YAO XM, et al. Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Advanced Glycation End Products Promotes Pancreatic Islet Damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:9692546. [38] YANG W, LIU L, WEI Y, et al. Exercise suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice with diet-induced NASH: a plausible role of adropin. Lab Invest. 2021;101(3):369-380. [39] MARDARE C, KRUGER K, LIEBISCH G, et al. Endurance and Resistance Training Affect High Fat Diet-Induced Increase of Ceramides, Inflammasome Expression, and Systemic Inflammation in Mice. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:4536470. [40] LIANG F, HUANG T, LI B, et al. High-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training alleviate beta-amyloid deposition by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Neuroreport. 2020;31(5):425-432. [41] 卞学鹏,姬瑞方,刘蓓蓓,等.有氧运动降低胰岛素抵抗小鼠海马细胞焦亡相关蛋白及炎症因子的表达[J].生理学报,2020,72(4): 455-462. [42] 何天雄.有氧运动对APP/PS1小鼠NEK7/Caspase-1/IL-1β表达及学习记忆能力的影响[D].成都:成都体育学院,2021. [43] PHILLIPS ME, ADEKANYE O, BORAZJANI A, et al. CES1 Releases Oxylipins from Oxidized Triacylglycerol (oxTAG) and Regulates Macrophage oxTAG/TAG Accumulation and PGE(2)/IL-1beta Production. ACS Chem Biol. 2023;18 (7):1564-1581. [44] SMOLAK P, NGUYEN M, DIAMOND C, et al. Target cell activation of a structurally novel NLRP3 inhibitor NT-0796 enhances potency. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024;388(3):798-812. [45] BIE J, ZHAO B, SONG J, et al. Improved insulin sensitivity in high fat- and high cholesterol-fed Ldlr-/- mice with macrophage-specific transgenic expression of cholesteryl ester hydrolase: role of macrophage inflammation and infiltration into adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285(18):13630-13637. |
| [1] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Su Xiaoyang, Chen Wenting, Fu Yidan, Zhao Yan, Lan Danfeng, Yang Qiuping. Correlation between Mer receptor tyrosine kinase and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1593-1599. |
| [3] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [4] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [5] | Wang Rongrong, Huang Yushan, Li Xiangmiao, Bai Jinzhu. Prostaglandin E1 regulates vascular-related factors and protects microcirculatory function during the acute phase of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 958-967. |
| [6] | Zhao Zengbo, Li Chenxi, Dou Chenlei, Ma Na, Zhou Guanjun. Anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects of chitosan/sodium glycerophosphate/sodium alginate/leonurine hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 678-685. |
| [7] | Cai Zhixing, Xia Qiufang, Chen Lili, Zhu Danyang, Zhu Huiwen, Sun Yanan, Liang Wenyu, Zhao Heqian. Effect of Roujishuncuiyin on the improvement of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7537-7543. |
| [8] | Wang Tong, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Yang Hu, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Action mechanism of Gegenmaqi prescription in treatment of periarthritis of shoulder combined with type 2 diabetes based on TCMSP database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7669-7678. |
| [9] | Xu Biao, Dong Yuzhen, Lu Tan. Effect of dihydroquercetin on the expression of inflammatory response markers in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6843-6850. |
| [10] | Hu Shujuan, Liu Dang, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang. Ameliorative effect of walnut oil and peanut oil on atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6482-6488. |
| [11] | Sun Yahui, Wang Yufeng, Guo Chao, Yao Junjie, Ji Yuanyuan, Li Zhongxu, Lou Huijuan, Jiang Jinglei, Sun Yiping, Xu Jing, Cong Deyu. Effect of massage on extracellular matrix collagen deposition in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5549-5555. |
| [12] | Geng Longyu, Sheng Li, Bai Shuo, Gao Beiyao, Ge Ruidong, Jiang Shan . Role and molecular mechanism of pyroptosis in motor system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5695-5703. |
| [13] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: data analysis of serum metabolite and inflammatory factor in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5263-5271. |
| [14] | Chen Chunlan, Ye Meiyi, Pan Yuwei, Yuan Jia, Zhou Pengjun. Immunomodulatory effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5031-5040. |
| [15] | Yu Hanglin, Tian Haodong, Wen Shiyuan, Huang Li, Liu Haowei, Li Hansen, Wang Peisong, Peng Li. Changes in glucose metabolism and intestinal flora in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after high-intensity intermittent exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 286-293. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||