Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (28): 4447-4454.doi: 10.12307/2024.348
Previous Articles Next Articles
SRT1720, an activator of silent information regulator 1, alleviates acute traumatic brain injury in a rat model
Qian Longjie, Su Wenli, Zhu Wenxian, Wang Yixin
- Department of Emergency Surgery, Putuo Central Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 310000, China
-
Received:2023-04-09Accepted:2023-06-05Online:2024-10-08Published:2023-11-27 -
Contact:Wang Yixin, Chief physician, Department of Emergency Surgery, Putuo Central Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 310000, China -
About author:Qian Longjie, Master, Attending physician, Department of Emergency Surgery, Putuo Central Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 310000, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qian Longjie, Su Wenli, Zhu Wenxian, Wang Yixin. SRT1720, an activator of silent information regulator 1, alleviates acute traumatic brain injury in a rat model[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4447-4454.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
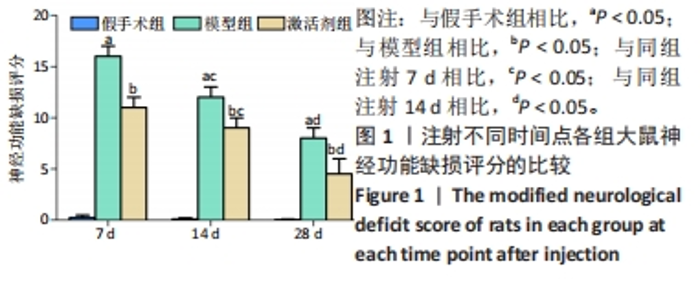
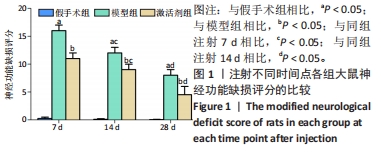
相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠神经功能缺损评分明显升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠神经功能缺损评分明显降低(P < 0.05)。假手术大鼠各时点的神经功能缺损评分比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠神经功能缺损评分降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠神经功能缺损评分降低(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠神经功能缺损评分降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠神经功能评分降低(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠神经功能缺损评分具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=126.331,P < 0.05)。 2.3 各组大鼠缺血侧脑组织含水量的比较 见图2。"
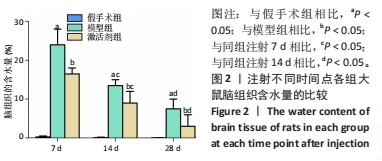
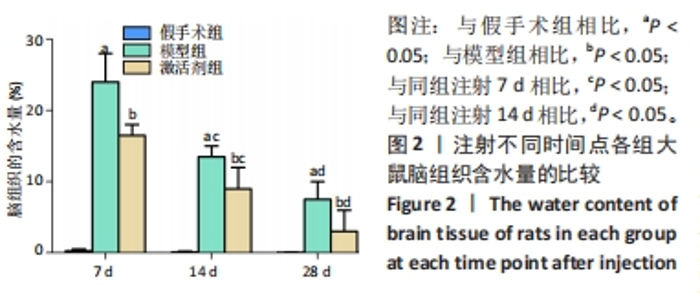
相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠缺血侧脑组织含水量升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠缺血侧脑组织含水量降低(P < 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠缺血侧脑组织含水量降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠缺血侧脑组织含水量降低(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠缺血侧脑组织含水量降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠缺血侧脑组织含水量降低(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠缺血侧脑组织含水量具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=176.194,P < 0.05)。 2.4 各组大鼠脑组织病理损伤观察结果 见图3。"
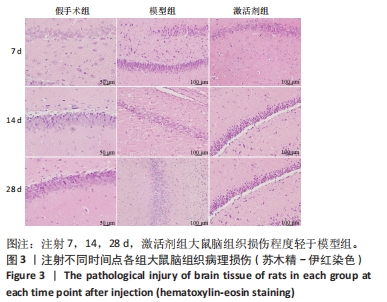
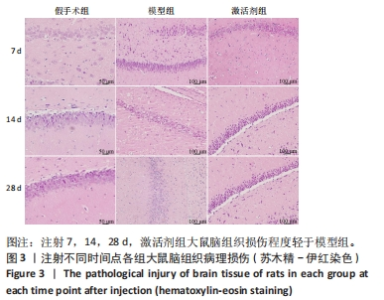
苏木精-伊红染色显示,假手术组大鼠脑组织结构清晰可辨,神经元细胞排列整齐,链接紧密,细胞染色较为均匀,核仁清晰,核质界限分明。模型组大鼠神经元细胞的胞膜丢失明显,排列松散,随着时间的延长,神经元细胞胞核染色逐渐变深,胞核变小明显,核质界限消失,核仁皱缩严重,至注射28 d时视野中出现大量的细胞碎片。激活剂组大鼠脑组织的病理损伤较模型组明显缓解,注射7 d时虽有部分神经元细胞固缩明显,但周边的神经元细胞的肿胀程度明显减轻;至注射14 d时神经元细胞的排列趋于正常,数量明显上升,胞膜及核膜趋于清晰;至注射28 d时,大鼠脑组织神经元形态趋于正常,偶见肿胀,脑组织病理损伤明显改善。 2.5 各组大鼠脑组织中神经细胞凋亡情况 见图4。"
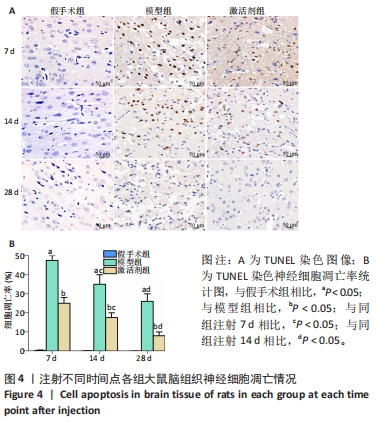
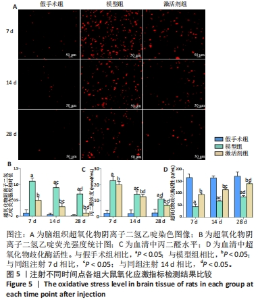
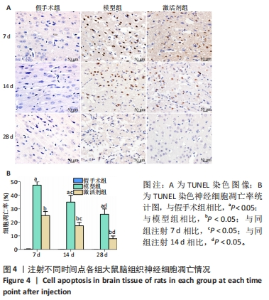
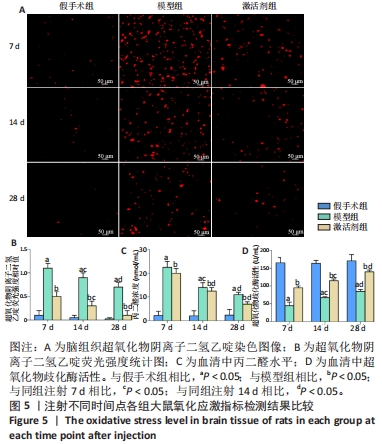
TUNEL染色定量分析结果显示,相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠脑组织神经细胞凋亡率升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠脑组织神经细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠脑组织神经细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠脑组织神经细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠脑组织神经细胞凋亡率降低P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的脑组织神经细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠脑组织神经细胞凋亡率具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=273.835,P < 0.05)。 2.6 各组大鼠氧化应激指标检测结果 超氧化物阴离子二氢乙啶免疫荧光染色显示,相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠脑组织中活性氧自由基含量升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠脑组织中活性氧自由基含量降低(P < 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠脑组织中活性氧自由基含量降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠脑组织中活性氧自由基含量降低(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠脑组织中活性氧自由基含量降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠脑组织中活性氧自由基含量降低(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠脑组织中活性氧自由基含量具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=86.571,P < 0.05),见图5A、B。 血清检测结果显示,相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠血清中丙二醛水平升高(P < 0.05),超氧化物歧化酶活性下降(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠血清中丙二醛水平下降(P < 0.05),超氧化物歧化酶活性升高(P < 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠血清丙二醛水平下降(P < 0.05)、超氧化物歧化酶活性升高(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠血清中丙二醛水平下降(P < 0.05)、超氧化物歧化酶活性升高(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠血清丙二醛水平下降(P < 0.05)、超氧化物歧化酶活性升高(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d的大鼠血清中丙二醛水平下降(P < 0.05)、超氧化物歧化酶活性升高(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠血清中丙二醛水平、超氧化物歧化酶活性具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=147.268,594.316,P < 0.05),见图5C、D。"
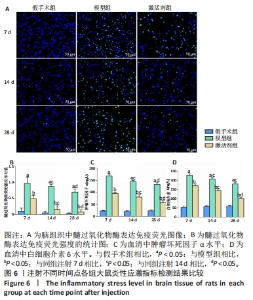
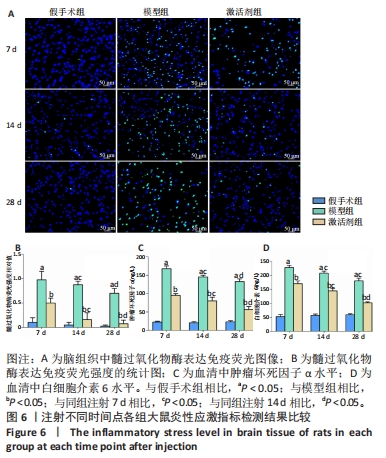
2.7 各组大鼠炎性应激指标检测结果 免疫荧光染色显示,相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠脑组织中髓过氧化物酶表达升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠脑组织中髓过氧化物酶表达降低(P < 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d大鼠脑组织中髓过氧化物酶表达降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d大鼠脑组织中髓过氧化物酶表达降低(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d大鼠脑组织中髓过氧化物酶表达降低(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d大鼠脑组织中髓过氧化物酶表达降低(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠脑组织中髓过氧化物酶表达具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=91.025,P < 0.05),见图6A、B。 血清检测结果显示,相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平下降(P < 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平下降(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d时大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平下降(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平下降(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d时大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平下降(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=226.354,649.157,P < 0.05),见图6C、D。"
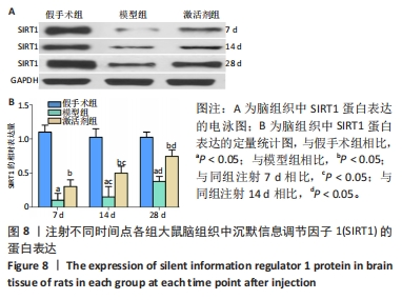
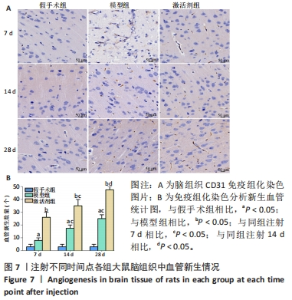
CD31免疫组化染色结果显示,相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠脑组织中新生血管数量增加(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠脑组织中新生血管数量增加(P < 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d大鼠脑组织中新生血管数量增加(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d大鼠脑组织中新生血管数量增加(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠脑组织中新生血管数量增加(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d大鼠脑组织中新生血管数量增加(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠脑组织中新生血管数量具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=158.309,P < 0.05)。 2.9 各组大鼠脑组织中SIRT1蛋白表达的比较 见图8。 "


Western blot检测结果显示,相同时间点下,与假手术组相比,模型组、激活剂组大鼠脑组织中SIRT1蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,激活剂组大鼠脑组织中SIRT1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05)。模型组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠脑组织中SIRT1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d大鼠脑组织中SIRT1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05)。激活剂组组内分析结果显示,与注射7 d相比,注射14,28 d的大鼠脑组织中SIRT1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与注射14 d相比,注射28 d大鼠脑组织中SIRT1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05)。各组大鼠脑组织中SIRT1蛋白表达具有明显的组别×时间交互作用(FInteraction=84.324,P < 0.05)。"

| [1] STEVENS AR, HADIS M, MILWARD M, et al. Photobiomodulation in Acute Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Neurotrauma. 2023;40(3-4):210-227. [2] ZHAO Q, SUN X, ZHENG C, et al. The evolutionarily conserved hif-1/bnip3 pathway promotes mitophagy and mitochondrial fission in crustacean testes during hypoxia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2023;324(1):128-142. [3] JURCAU A, JURCAU CM. Mitochondria in Huntington’s disease: implications in pathogenesis and mitochondrial-targeted therapeutic strategies. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(7):1472-1477. [4] OKA N, DOAN VTH, MATSUBARA H, et al. Protective effects of alpha-mangostin encapsulated in cyclodextrin-nanoparticle on cerebral ischemia. J Control Release. 2023;353(1):216-228. [5] WANG Y, JIA Y, XU Q, et al. Association between myeloperoxidase and the risks of ischemic stroke, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation: A Mendelian randomization study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023;33(1):210-218. [6] LIU Y, LI F, SHANG S, et al. Functional-structural large-scale brain networks are correlated with neurocognitive impairment in acute mild traumatic brain injury. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023;13(2):631-644. [7] CHEN YX, DU L, WANG LN, et al. Effects of Dexmedetomidine on Systemic Inflammation and Postoperative Complications in Laparoscopic Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Double-blind Randomized Controlled Trial. World J Surg. 2023;47(2):500-509. [8] SONG H, DING Z, CHEN J, et al. The AMPK-SIRT1-FoxO1-NF-κB signaling pathway participates in hesperetin-mediated neuroprotective effects against traumatic brain injury via the NLRP3 inflammasome. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(6):970-983. [9] FRANKOT MA, O’HEARN CM, BLANCKE AM, et al. Acute gut microbiome changes after traumatic brain injury are associated with chronic deficits in decision-making and impulsivity in male rats. Behav Neurosci. 2023;137(1):15-28. [10] KANGUSSU LM, ALMEIDA-SANTOS AF, FERNANDES LF, et al. Transgenic rat with overproduction of ubiquitous angiotensin-(1-7) presents neuroprotection in a model of ischemia and reperfusion. Brain Res Bull. 2023;192(1):184-191. [11] ZHU XY, MA TT, LI Y, et al. Fingolimod protects against neurovascular unit injury in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(4):869-874. [12] CHEN X, LI P, HUANG R, et al. Ulinastatin affects focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via SOCS1-mediated JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023;50(1):107-116. [13] KODALI M, MADHU LN, REGER RL, et al. Intranasally administered human MSC-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit NLRP3-p38/MAPK signaling after TBI and prevent chronic brain dysfunction. Brain Behav Immun. 2023;108(2):118-134. [14] GILFARB R, TAPP Z, LEMANSKI E, et al. Multiparity Differentially Affects Specific Aspects of the Acute Neuroinflammatory Response to Traumatic Brain Injury in Female Mice. Neuroscience. 2023;511(2):86-99. [15] JOHNSON NH, KERR NA, DE RIVERO VACCARI JP, et al. Genetic predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease alters inflammasome activity after traumatic brain injury. Transl Res. 2023;257(1):66-77. [16] CHEN F, LIU J, LI FQ, et al. β2-Microglobulin exacerbates neuroinflammation, brain damage, and cognitive impairment after stroke in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(3):603-608. [17] LIU C, YANG ZX, ZHOU SQ, et al. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor enhances the neuroprotective effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(6):1286-1292. [18] JIN J, WANG F, TIAN J, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to coagulopathy after traumatic brain injury. JCI Insight. 2023;8(6):e141110. [19] ZHU ZH, JIA F, AHMED W, et al. Neural stem cell-derived exosome as a nano-sized carrier for BDNF delivery to a rat model of ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2023;8(2):404-409. [20] TARAN S, CHO SM, STEVENS RD. Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: Is it so Different? Neurocrit Care. 2023;38(1):178-191. [21] KOYAMA R, SHICHITA T. Glial roles in sterile inflammation after ischemic stroke. Neurosci Res. 2023;187(2):67-71. [22] 张健,陈淼,李伟鑫,等.负载脑源性神经营养因子胶原/肝素硫酸支架促进颅脑创伤大鼠神经运动功能的恢复[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(34): 5538-5544. [23] ZHAO P, WEI Y, SUN G, et al. Fetuin-A alleviates neuroinflammation against traumatic brain injury-induced microglial necroptosis by regulating Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):269. [24] GIORDANO KR, SABER M, GREEN TRF, et al. Colony-Stimulating Factor-1 Receptor Inhibition Transiently Attenuated the Peripheral Immune Response to Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurotrauma Rep. 2023;4(1):284-296. [25] LIU N, LI Y, JIANG Y, et al. Establishment and Application of a Novel In Vitro Model of Microglial Activation in Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurosci. 2023;43(2):319-332. [26] CHEN X, MI L, GU G, et al. Dysfunctional Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondrion Coupling Is Associated with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Neurological Deficits in a Rodent Model of Severe Head Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2022;39(7-8):560-576. [27] CHENG S, CHEN C, WANG L. Gelsemine Exerts Neuroprotective Effects on Neonatal Mice with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury by Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(5): 1305-1319. [28] 孙建平,李筱雨,谷晓玉,等.硫化氢对创伤性颅脑损伤大鼠行为及脑水肿的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2021,38(11):2171-2174. [29] QARYOUTI D, GREENE-CHANDOS D. Neurocritical Care Aspects of Ischemic Stroke Management. Crit Care Clin. 2023;39(1):55-70. [30] 郑粲,王革生,王文鑫,等.经耳迷走神经刺激对急性创伤性颅脑损伤大鼠神经功能的改善作用及其机制[J].山东医药,2022,62(8):42-46. [31] SEZER C, ZıRH S, GOKTEN M, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Milrinone on Acute Traumatic Brain Injury. World Neurosurg. 2023;170(1):558-567. [32] PRABHAKAR NK, KHAN H, GREWAL AK, et al. Intervention of neuroinflammation in the traumatic brain injury trajectory: In vivo and clinical approaches. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;108(1):108902. [33] WANG JP, LI C, DING WC, et al. Research Progress on the Inflammatory Effects of Long Non-coding RNA in Traumatic Brain Injury. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022; 15(3):835012. [34] SHARMA R, CHU E, DILL LK, et al. Ccr2 Gene Ablation Does Not Influence Seizure Susceptibility, Tissue Damage, or Cellular Inflammation after Murine Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2023;40(3-4):365-382. [35] GHORBANI DEHBALAEI M, SAHEBKAR A, SAFARIAN M, et al. Study protocol for a pilot randomised controlled trial evaluating the effectiveness of oral trehalose on inflammatory factors, oxidative stress, nutritional and clinical status in traumatic head injury patients receiving enteral nutrition. BMJ Open. 2022;12(9):e060605. [36] ZHANG Y, JIA P, WANG K, et al. Lactate modulates microglial inflammatory responses after oxygen-glucose deprivation through HIF-1α-mediated inhibition of NF-κB. Brain Res Bull. 2023;195(2):1-13. [37] ZHAO P, Wei Y, Sun G, et al. Fetuin-A alleviates neuroinflammation against traumatic brain injury-induced microglial necroptosis by regulating Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):269. [38] YAN M, JIN H, PAN C, et al. Chronic Microcystin-LR-Induced α-Synuclein Promotes Neuroinflammation Through Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Microglia. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(2):884-900. [39] CHENG L, LIU Z, XIA J. New insights into circRNA and its mechanisms in angiogenesis regulation in ischemic stroke: a biomarker and therapeutic target. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(1):829-840. [40] TAÏLÉ J, BRINGART M, PLANESSE C, et al. Antioxidant Polyphenols of Antirhea borbonica Medicinal Plant and Caffeic Acid Reduce Cerebrovascular, Inflammatory and Metabolic Disorders Aggravated by High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in a Mouse Model of Stroke. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(5):858-884. [41] YANG J, GUO Q, WANG L, et al. POU Domain Class 2 Transcription Factor 2 Inhibits Ferroptosis in Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Activating Sestrin2. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(2):658-670. [42] HSIEH CT, YEN TL, CHEN YH, et al. Aging-Associated Thyroid Dysfunction Contributes to Oxidative Stress and Worsened Functional Outcomes Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(2):217. [43] CHEN Q, MIN J, ZHU M, et al. Protective role of PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway in chronic renal failure induced injury of rat hippocampal neurons. Int J Neurosci. 2023;133(2):123-132. [44] ROSHAN MILANI S, POURHEYDAR B, DANESHFAR S, et al. Decreased Cardiac NOX4 and SIRT-1 Protein Levels Contribute to Decreased Angiogenesis in the Heart of Diabetic Rats: Rescue Effects of IGF-1 and Exercise. Adv Pharm Bull. 2023;13(1):202-209. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [3] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [4] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [5] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [6] | Chen Zepeng, Hou Yonghui, Chen Shudong, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treats spinal cord injury by reducing apoptosis of spinal cord neurons under glucose and oxygen deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [7] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 380-386. |
| [8] | Jiang Yu, Xu Lin, Zhao Yalin, Liu Gang, Zhang Yaqi, Bai Huizhong, Ren Jingpei, Zeng Jie, Mu Xiaohong. Effects of Shujin Jiannao Prescription on cell apoptosis in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4477-4483. |
| [9] | Zhou Minghan, Zhang Hui, Zheng Xianbo, Xu Wuji. Significance of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway expression in nucleus pulposus cells at different oxygen concentrations in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4491-4497. |
| [10] | Chen Chen, Zheng Runquan, Zhang Guichun. Effects of emodin on the proliferation, apoptosis and oxidative stress of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4528-4534. |
| [11] | Ma Jianglei, Zhang Huijie, Zhang Chenfang, Yang Xitong, Cheng Jianjie, Wang Guangming. Neuroprotective mechanism by which fenofibrate regulates superoxide dismutase 2 expression in transgenic C57BL/6J mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4547-4552. |
| [12] | Chu Kai, Sun Jianhua. Effects of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00707 on chondrocyte injury and inflammatory factor secretion in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4565-4571. |
| [13] | Duan Yanzhe, Hua Jianlin, Ding Zhibin, Jiang Nan, Song Lijuan, Yan Yuqing, Ma Cungen. Visual analysis of the effect of apoptosis on ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4145-4150. |
| [14] | Tao Jingwei, Zhou Jingya, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong, Fan Xiao. Effect and mechanism of tetramethylpyrazine regulating ferroptosis in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4158-4163. |
| [15] | Luo Shanchao, Tang Jiren. Effect of hesperetin on inflammatory degeneration of chondrocytes by inhibiting oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4184-4188. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||