Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (9): 1464-1469.doi: 10.12307/2024.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury
Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian
- Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-01-17Accepted:2023-02-24Online:2024-03-28Published:2023-07-26 -
Contact:Huang Jian, MD, Chief physician, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yang Yifeng, Master, Attending physician, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Young People's Program of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2022QN034 (to YYF); 2022 Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Health Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 202201352 (to HJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 抗氧化应激相关信号通路 在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中观察到氧化应激和抗氧化机制之间的失衡,这与再灌注激活的活性氧的过度生成有关,最终导致心脏细胞死亡和细胞凋亡。Nrf2是细胞调节抗氧化应激反应的重要转录因子,虽然Nrf2自身无抗氧化作用,但Nrf2可以启动下游抗氧化因子而达到器官保护的作用[4]。LI等[5]对心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠研究发现,Dex组大鼠血清肌酸激酶同工酶和心肌肌钙蛋白Ⅰ浓度较低,梗死面积较小,室速、室颤发生次数明显减少,Dex组心肌相关蛋白Nrf2、血红素加氧酶1、醌氧化还原酶 1表达显著升高,心肌氧化应激标记物超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶水平明显降低;相反,使用Kelch样本相关蛋白1-Nrf2/抗氧化反应元件(Kelch sample related protein-1-Nrf2/antioxidant response element,Keap1-Nrf2/ARE)通路抑制剂全反式维甲酸,Dex的保护作用减弱。结果表明Dex可以通过激活Keap1-Nrf2/ARE信号转导通路施加抗氧化应激来预防心肌缺血再灌注损伤。其具体过程为,当心肌组织发生氧化应激时,Keap1-Nrf2/ARE信号转导通路被激活,Nrf2从Keap1解离;然后Nrf2易位到细胞核中并以快速顺序与ARE结合,以刺激下游抗氧化基因的表达。在探讨Nrf2/ARE通路在Dex骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤预处理中的作用中发现,Dex组湿/干质量比、丙二醛、乳酸脱氢酶、肌酸激酶水平降低,超氧化物歧化酶和Nrf2/血红素加氧酶1水平明显增高,Dex可通过α-肾上腺素能受体促进Nrf2在细胞核中的表达,而Nrf2的下游产物具有抗氧化作用[6]。 Nrf2及其下游蛋白sulfiredoxin1同样可能参与了氧化应激损伤。实验中,Dex改善肺静态顺应性,减少肺组织细胞凋亡,检测发现Nrf2和 sulfiredoxin1蛋白表达水平升高。Dex治疗可以通过Nrf2-sulfiredoxin1途径减少氧化应激损伤来减轻肺缺血再灌注损伤[7]。Dex还可以通过 miR-205-5P/高迁移率族蛋白B1(high mobility group protein B1,HMGB1)通路提升Nrf2及其下游蛋白血红素加氧酶1表达,减少过氧化物水平并增加抗氧化酶水平,抗氧化应激,从而减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤[8]。 最近的研究表明,线粒体形态的功能障碍是肺损伤发生和发展的重要标志[9]。SIRT3是一种高度保守的烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸依赖性脱乙酰酶,主要在线粒体中表达。新出现的证据表明,SIRT3通过去乙酰化调节氧化应激、脂肪酸氧化和抗氧化反应系统的线粒体蛋白功能[10]。WANG等[11]研究发现Dex可以减轻肢体缺血再灌注损伤诱导的肺损伤,减轻肺泡结构破坏和炎性细胞浸润,抑制活性氧和丙二醛水平并恢复抗氧化酶(超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶)活性,Dex可以深度促进Nrf2核转位并增强Nrf2和血红素加氧酶1的表达,促进SIRT3的表达。通过激活Nrf2/血红素加氧酶1/SIRT3轴,进而减少炎症,减轻氧化应激,促进线粒体功能,抑制细胞凋亡。还有研究发现,Dex可以通过活化T 细胞核因子5/沉默信息调节因子2相关酶1/Nrf2信号通路促进Nrf2核转位增加,降低丙二醛、活性氧水平[12]。 硫氧还蛋白1是保护心脏免受缺血再灌注损伤和活性氧损伤的关键分子,硫氧还蛋白1在缺氧、氧化应激时表达增加。WU等[13]发现Dex通过改善心脏功能、减少心肌细胞凋亡和氧化应激来修复心肌缺血再灌注损伤,研究发现Dex组硫氧还蛋白1的水平得以保留,并且Akt磷酸化被Dex处理后显著上调,而且,Dex的这些作用可以被硫氧还蛋白1抑制剂给药所消除。从而指出,Dex的心脏保护作用至少部分通过硫氧还蛋白1依赖性Akt通路实现。 2.2 抗炎症相关信号通路 2.2.1 Toll样受体(Toll-like receptors,TLR)和核因子κB相关通路 越来越多的证据表明,TLR家族,尤其是TLR4,在缺血再灌注的有害作用中起着主导作用[14]。HMGB1是一种促炎因子,已经被假定为TLR4配体[15],两者结合可激活促炎细胞因子产生的信号通路。GU等[16]研究发现,在小鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤模型中,Dex提供细胞保护,改善肾缺血后的肾小管结构和功能。Dex可能通过α2肾上腺素能受体激活细胞存活信号磷酸化蛋白激酶B,以减少细胞死亡和HMGB1释放,通过HMGB1-TLR4炎症回路,随后抑制TLR4信号传导以提供肾脏保护。 核因子κB是一种蛋白,该蛋白家族可以选择性的结合在B细胞κ-轻链增强子上调控许多基因的表达。长期以来,核因子κB通路一直被认为是一种原型促炎信号通路[17],主要是由于核因子κB在调节促炎基因表达中的作用,核因子κB下游因子主要包括细胞因子、趋化因子和黏附分子,这些因子的激活进而引发炎症反应。KIM等[18]研究表明,地塞米松预处理降低了白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等细胞因子表达,Dex组TLR4、核因子κB和半胱天冬酶3水平明显低于其他组别;Dex预处理对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤提供神经保护作用,并抑制TLR4/核因子κB通路和促炎细胞因子的产生,还通过降低大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后半胱天冬酶3的表达来减少细胞凋亡。SUN等[19]在脊髓缺血再灌注损伤中得到了类似的结果,Dex通过抑制脊髓炎症和神经元细胞凋亡,对脊髓缺血再灌注损伤提供神经保护作用,TLR4介导的核因子κB炎症信号通路和半胱天冬酶3依赖性细胞凋亡的抑制都与此有关。Dex还可通过抑制HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB信号通路减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[20],与对照组相比,Dex组的神经功能评分、脑含水量、梗死面积以及环氧化酶2和IBA-1阳性细胞数量显著降低,同时伴有HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB通路的表达下调,减轻了炎症和脑组织氧化应激损伤。 细胞间黏附分子1是一种黏附分子,参与炎症病理过程;S100B蛋白是一种在中枢神经系统中特异性发现的酸性钙结合蛋白,S100B与脑损伤严重程度呈正相关。LI等[21]发现Dex治疗可改善缺血再灌注损伤大鼠脑病理损伤,降低神经缺陷评分、S100B和丙二醛水平,降低核因子κB和细胞间黏附分子1 mRNA的表达,并增加超氧化物歧化酶水平。该研究表明Dex神经保护作用与核因子κB信号通路有关,Dex可能通过抑制脑损伤后核因子κB和细胞间黏附分子1的表达,抑制炎症反应,减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤。最近研究表明,Dex预处理可抑制心肌缺血再灌注损伤所诱导的炎症反应,显著降低心肌梗死面积和组织学评分,降低血清白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平,减少HMGB1、TLR4、MyD88和核因子κB的表达,且这些作用被α2-肾上腺素能受体拮抗剂育亨宾部分逆转[22]。因此,Dex预处理通过减轻炎症来减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤,从机制上讲,这可能是由于下调了α2-肾上腺素能受体激活介导的HMGB1-TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB信号通路。 2.2.2 胆碱能抗炎通路 器官缺血再灌注损伤常引起局部和全身炎症反应,进而加重器官损伤。这些炎症反应可由中枢神经系统调节,尤其是迷走神经和烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,它们是胆碱能抗炎通路的关键组成部分。MA等[23]发现Dex在肾缺血再灌注损伤后保留了肾脏的大体形态和结构,增加了颈迷走神经的放电频率,还显著增加了乙酰胆碱释放,Dex抑制了炎症递质白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和血管内皮生长因子的上调,Dex的有效作用可以被迷走神经切断术或阿替美唑(一种α2-肾上腺素能受体拮抗剂)所消除,Dex激活胆碱能通路在肾缺血再灌注损伤中发挥抗炎作用。ZHANG等[24]通过大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤模型发现Dex预处理显著减轻心肌梗死面积、减少心肌肌钙蛋白Ⅰ释放、心肌细胞凋亡、心脏HMGB1表达、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α产生,这些影响可以被单侧迷走神经切断术或甲基乌头碱(α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体抑制剂)治疗部分逆转。表明Dex可以通过激活胆碱能抗炎通路抑制心脏HMGB1的产生,从而保护心脏免受缺血再灌注损伤。JU等[25]同样发现,Dex可通过激活胆碱能抗炎通路减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤,降低血清肌酸激酶和乳酸脱氢酶水平,从而对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤后的心肌组织产生保护作用。胆碱能通路是众多核因子κB信号通路的上游机制,该研究能更好地解释Dex抗炎作用的完整信号过程。 2.2.3 PI3K/AKt相关通路 最新研究发现,Dex减少了肝缺血再灌注损伤模型的细胞焦亡和炎症。Dex增加了miR-494的表达,并且miR-494靶向基因JUND,基因JUND 是激活蛋白1转录因子家族的成员,它通过靶向白细胞介素1β合成和巨噬细胞激活来调节炎症。Dex预处理上调了PI3K和AKT的磷酸化以及Nrf2的表达,而Nrf2的激活可以抑制NLRP3炎性体激活,结果表明Dex可以通过miR-494/JUND/PI3K/AKT/Nrf2信号通路抑制NLRP3炎性体并减轻肝脏缺血再灌注损伤[26]。Dex通过上调内皮型一氧化氮合酶表达来调控一氧化氮浓度,从而发挥抗缺血再灌注损伤作用。在心肌缺血再灌注损伤时,心肌梗死面积被Dex减弱,细胞因子及氧化产物白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、髓过氧化物酶和丙二醛均显著降低,抗氧化酶超氧化物歧化酶增加。Dex激活AMPK表达、内皮型一氧化氮合酶和Akt磷酸化,并且Dex对心脏功能的影响可以被内皮型一氧化氮合酶、AMPK和PI3K/Akt通路的抑制剂逆转。这些结果表明Dex保护了心肌缺血再灌注诱导的心脏功能、组织学变化、炎症和氧化应激,可能是通过激活AMPK/PI3K/Akt/eNOS通路来发挥作用[27]。SHAN等[28]在肾缺血再灌注损伤研究中发现了相似的结果,Dex激活PI3K和Akt的磷酸化,增加内皮型一氧化氮合酶表达,并减弱炎症反应,Dex对肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用被α2-肾上腺素受体拮抗剂消除。表明Dex通过激活PI3K/Akt-eNOS通路和通过肾微血管内皮细胞中的α2-肾上腺素受体抑制炎症反应来防止肾缺血再灌注损伤。哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR),是细胞生长和增殖的重要调节因子。ZHANG等[29]研究发现Dex可以通过PI3K-Akt-mTOR信号通路实现心脏保护作用。Dex预处理使缺血再灌注损伤心肌梗死面积显著减少,血清中肌酸激酶、肌酸激酶同工酶、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6水平明显降低,Dex组p-mTOR和p-Akt水平明显增高,通过PI3K-Akt-mTOR改善缺血再灌注大鼠心功能,清除氧自由基,减轻氧化应激损伤,抑制炎症反应。在肾缺血再灌注损伤中发现,Dex预处理使血尿素氮和肌酐水平下降,肾组织合成的炎症因子mRNA减少,分泌的血清炎症因子也减少,Akt和PI3K的磷酸化水平以及HIF-1α水平升高。最终表明Dex可通过PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α信号通路促进肾缺血再灌注损伤大鼠肾功能恢复,降低炎症水平[30]。星形胶质细胞连接蛋白43是大脑中最丰富的连接蛋白,在脑缺血再灌注损伤中发挥重要作用。ZHENG等[31]实验发现,星形胶质细胞连接蛋白43在体内和体外均因脑缺血再灌注损伤而下调,并且可以被Dex逆转,Dex预处理可减轻脑缺血后的神经损伤、脑损伤和炎症因子(白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α)的表达。这种作用是由Akt和糖原合成酶激酶3β(Glycogen synthase kinase-3β,GSK-3β)的磷酸化介导,使用LY294002(PI3K 抑制剂)或SB216763(GSK-3β抑制剂)可以抵消这种作用,认为Dex上调PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β在脑缺血再灌注损伤后星形胶质细胞连接蛋白43的调节中发挥重要作用。PI3K/Akt相关通路比较如表1所示。"
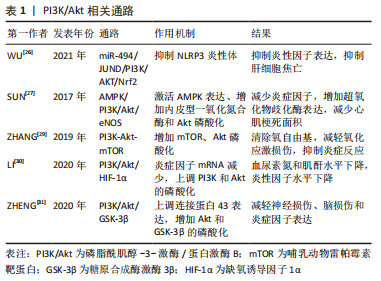

2.2.4 JAK2/STAT3相关通路 JAK2/STAT通路参与调控基因的表达与增殖、分化、免疫和凋亡相关。JAK2和STAT3被认为是JAK/STAT通路中最保守、最古老的成员。JAK2/STAT3信号通路的激活促进细胞凋亡、血管生成、氧化应激和神经炎症[32]。LIU等[33]研究指出Dex预处理降低了脑缺血再灌注损伤后的脑梗死面积,Dex预处理下调肿瘤坏死因子α表达、降低了JAK2和STAT3的磷酸化。推测Dex预处理通过负调节JAK2/STAT3信号通路抑制神经炎症,从而对脑缺血再灌注损伤提供神经保护。另外在肠缺血再灌注损伤中发现了相似的调节机制[34],Dex组肠缺血再灌注损伤大鼠JAK2、STAT1和STAT3的磷酸化受到影响,同时,JAK2或STAT抑制剂AG490和雷帕霉素表现出类似甚至更大的JAK2和STAT3调节作用,表明Dex发挥与JAK2/STAT3抑制剂相似作用。从而推测Dex抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路,发挥肾脏保护作用。 2.3 抗凋亡相关信号通路 PI3K/Akt信号通路已被证实通过调节细胞增殖、抑制细胞凋亡和减少氧自由基的释放对缺血再灌注发挥心脏保护作用[35]。GSK-3β是一种重要的细胞内蛋白,是Akt通路的下游,也与氧化应激和细胞凋亡有关[35]。PI3K依赖性Akt激活及其磷酸化可保持线粒体完整性并通过减弱细胞凋亡来保护心肌细胞。当Akt 被激活时,可能引起Bad或Bax残基的磷酸化,调节Bcl-2的活性,从而在心肌缺血时发挥抗细胞凋亡作用[36]。Bcl-2家族基因是细胞凋亡信号通路的主要基因,其主要通过Fas系统介导,引起凋亡蛋白酶半胱天冬酶3激活导致细胞凋亡,其成员在功能上可分为抗凋亡蛋白(Bcl-2蛋白为代表)和促凋亡蛋白(Bax为代表)两大类。CHENG等[37]研究发现,Dex降低血浆肌酸激酶同工酶、丙二醛浓度和乳酸脱氢酶水平,增加超氧化物歧化酶活性,Akt和GSK-3β的磷酸化增加,Bcl-2 mRNA和Bcl-2/Bax比率增加,Bax mRNA减少,使用PI3K抑制剂治疗后减弱了Dex引起的作用。Dex可能通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路增加 GSK-3β磷酸化,抑制心肌细胞凋亡和氧化应激,从而对大鼠心脏缺血再灌注损伤发挥保护作用。 PINK1可以通过线粒体膜电位进入线粒体,PINK1激酶还通过激活E3泛素连接酶Parkin促进受损线粒体中的选择性自噬[38]。通过SIRT3激活实现PINK1/Parkin上调对缺血再灌注损伤大鼠发挥心脏保护作用[39]。据报道,由PINK1介导的组蛋白去乙酰化酶3磷酸化增加了PINK1和p53之间的结合,随后导致p53的低乙酰化,并且这种减少已被证明在缺血再灌注损伤缓解中发挥关键作用[40]。ZHANG等[41]验证了这一通路,Dex通过激活SIRT3介导的PINK1/HDAC3/p53通路对肠神经胶质细胞中线粒体损伤和细胞凋亡发挥保护作用,降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和丙二醛水平,超氧化物歧化酶活性增加,最终减轻肠道缺血再灌注损伤。斯妍娜等[42]发现,Dex通过激活SIRT3,介导亲环素D去乙酰化,降低线粒体通透性转换孔开放程度,抑制细胞凋亡,减轻大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤。 HIF-1α是在缺氧环境下调节适应性反应的主要转录因子,可以调节下游众多的靶基因改善缺血再灌注损伤。Dex通过抑制HIF-1α减少神经元细胞凋亡,提高抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2水平,减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[43]。GAO等[44]发现,Dex预处理可以提高神经球蛋白Ngb水平,降低细胞色素C氧化酶及相关凋亡蛋白表达,通过激活HIF/p53信号通路抑制神经元凋亡,减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤反应。 内质网在缺血缺氧时,会导致细胞内未折叠或错误折叠的蛋白质积累,从而导致内质网应激,一旦内质网应激出现时间过长,它会诱导凋亡信号通路的表达,最终诱导细胞凋亡[45]。C/EBP同源蛋白的激活是内质网应激下游细胞凋亡的主要途径,当内质网应激发生时,它被诱导大量表达并转移至细胞核以调节其靶基因ERo1α和Bcl-2并诱导细胞凋亡[46]。C/EBP同源蛋白可以激活Ero1α,催化蛋白质二硫键异构酶的再氧化,最终调节细胞凋亡。C/EBP同源蛋白还上调促凋亡基因Bax,下调抗凋亡基因Bcl-2,导致内质网Bax/Bak的构象改变,引起内质网膜破坏和Ca2+外流,进而介导细胞凋亡[47]。LI等[48]研究表明,Dex可降低心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠肌酸激酶同工酶和心肌肌钙蛋白T的表达,减轻病理损伤,降低GRP78、C/EBP同源蛋白、ERO1α、ERO1β和蛋白质二硫键异构酶蛋白的表达,而且Dex对细胞凋亡的影响可被内质网应激激动剂阻断。猜测Dex通过减轻心肌内质网应激途径,减轻心肌细胞凋亡,进而减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤。类似的研究结果也被YANG等[49]发现,Dex预处理通过激活α2-肾上腺素能受体抑制大鼠缺血再灌注损伤的GRP78、p-PERK、C/EBP同源蛋白和半胱天冬酶3的心肌表达。从机制上讲,Dex提供的心脏保护作用是通过下调内质网应激信号通路的表达来抑制炎症和细胞凋亡来介导的。内质网定位蛋白同系物2参与内质网应激,内质网定位蛋白同系物2结合伙伴从GRP78转化为PERK,选择性启动PERK-CHOP介导的细胞凋亡信号。Dex可以抑制脊髓缺血再灌注损伤后内质网应激的激活,通过CNPY2-PERK信号减弱 C/EBP同源蛋白和半胱天冬酶3的表达,表明Dex可能通过抑制CNPY2-PERK凋亡通路来抑制内质网应激诱导的神经元损伤[50]。ZHAI等[51]还发现Dex通过激活Sigma-1受体抑制内质网应激诱导的细胞凋亡,从而减轻缺血再灌注24 h后的脑损伤。 2.4 其他 有研究发现皮质神经元损伤与永久性局灶性脑缺血中自噬的激活有关,表明抑制自噬可能有助于减轻缺血性脑损伤,Bcl-2/Beclin-1信号通路是自噬的经典调节途径之一[52]。Luo等[53]实验发现Dex在再灌注开始时抑制皮质神经元自噬而具有神经保护作用,同时还发现Dex通过上调HIF-1α和Bcl-2的表达,下调Beclin-1来介导自噬抑制,改善神经功能,减少梗死面积,从而保护小鼠大脑免受缺血再灌注损伤。Dex同样可以上调肠黏膜上皮细胞HIF-1α表达水平,Dex组的超氧化物歧化酶活性升高,丙二醛表达降低,减轻大鼠肠缺血再灌注损伤所致的肺损伤[54]。 此前有研究报告线粒体ATP敏感性钾通道参与Dex对缺血再灌注损伤的影响。YUAN等[55]发现Dex预处理丙二醛、髓过氧化物酶、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平显著降低,超氧化物歧化酶水平显著升高,粒体ATP敏感性钾通道阻断剂可以逆转Dex的作用,提示粒体ATP敏感性钾通道激活可能参与Dex对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用。袁峰等[56]同样发现粒体ATP敏感性钾通道参与了Dex减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的过程,但该过程不能被粒体ATP敏感性钾通道阻断剂完全阻断,提示Dex减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的机制除与粒体ATP敏感性钾通道有关,还存在其他通路参与。 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子是一种压力调节细胞因子,调节炎症细胞的激活和不同促炎细胞因子的启动。CHEN等[57]对心肌缺血再灌注损伤研究发现,Dex预处理可以减少白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的产生,减少心肌细胞坏死和凋亡,减轻炎性浸润;Dex组巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子、p-AMPKα、GLUT4和Bcl-2蛋白表达显著升高;最终指出Dex可能通过MIF/AMPK/GLUT4轴对幼鼠心肌发挥抗炎、抗凋亡等保护作用。"

| [1] LAND WG. The role of postischemic reperfusion injury and other nonantigen-dependent inflammatory pathways in transplantation. Transplantation. 2005;79(5):505-514. [2] WEERINK MAS, STRUYS MMRF, HANNIVOORT LN, et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56(8):893-913. [3] ENGELHARD K, WERNER C, EBERSPACHER E, et al. The effect of the alpha 2-agonist dexmedetomidine and the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist S(+)-ketamine on the expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins after incomplete cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats. Anesth Analg. 2003; 96(2):524-531. [4] 袁培根,薛彬彬,林碧,等. Nrf2/ARE通路介导右美托咪定减轻肢体缺血/再灌注损伤中的作用[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2016,32(3):250-254+293. [5] LI HX, WANG TH, WU LX, et al. Role of Keap1-Nrf2/ARE signal transduction pathway in protection of Dexmedetomidine preconditioning against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biosci Rep. 2022;42(9):BSR20221306. [6] YUAN PG, XUE BB, LIN B, et al. [Nrf2/ARE pathway mediates the reducing effect of Dexmedeto-midine on ischemia/reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle]. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2016; 32(3):250-254. [7] WANG X, ZHANG B, LI G, et al. Dexmedetomidine Alleviates Lung Oxidative Stress Injury Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion in Diabetic Rats via the Nrf2-Sulfiredoxin1 Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:5584733. [8] YANG JJ, ZHAO YH, YIN KW, et al. Dexmedetomidine inhibits inflammatory response and oxidative stress through regulating miR-205-5p by targeting HMGB1 in cerebral ischemic/reperfusion. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021;43(4):478-486. [9] LIU X, CHEN Z. The pathophysiological role of mitochondrial oxidative stress in lung diseases. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1):207. [10] ZHOU Y, CHUNG ACK, FAN R, et al. Sirt3 Deficiency Increased the Vulnerability of Pancreatic Beta Cells to Oxidative Stress-Induced Dysfunction. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017;27(13):962-976. [11] WANG L, DING Y, BAI Y, et al. The activation of SIRT3 by Dexmedetomidine mitigates limb ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung injury. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(6):319. [12] CHEN L, CAO J, CAO D, et al. Protective effect of Dexmedetomidine against diabetic hyperglycemia-exacerbated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: An in vivo and in vitro study. Life Sci. 2019;235: 116553. [13] WU ZL, DAVIS JRJ, ZHU Y. Dexmedetomidine Protects against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Cell Apoptosis through the Trx1-Dependent Akt Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:8979270. [14] ARSLAN F, KEOGH B, MCGUIRK P, et al. TLR2 and TLR4 in ischemia reperfusion injury. Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:704202. [15] YU M, WANG H, DING A, et al. HMGB1 signals through toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 and TLR2. Shock. 2006;26(2):174-179. [16] GU J, SUN P, ZHAO H, et al. Dexmedetomidine provides renoprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Crit Care. 2011;15(3):R153. [17] 游琼,吴铿,涂焰明,等.柚皮苷调控心肌核因子NF-κB炎症信号通路对糖尿病心肌病大鼠防治作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2013,29(2):121-124. [18] KIM E, KIM HC, LEE S, et al. Dexmedetomidine confers neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting inflammation through inactivation of the TLR-4/NF-κB pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2017;649:20-27. [19] SUN Z, ZHAO T, LV S, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury through both anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis mechanisms in rabbits. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):209. [20] ZHAI Y, ZHU Y, LIU J, et al. Dexmedetomidine Post-Conditioning Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Inhibiting High Mobility Group Protein B1 Group (HMGB1)/Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e918617. [21] LI Y, LIU S. The Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Oxidative Stress Response Following Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rats and the Expression of Intracellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and S100B. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:867-873. [22] ZHANG JJ, PENG K, ZHANG J, et al. Dexmedetomidine preconditioning may attenuate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by down-regulating the HMGB1-TLR4-MyD88-NF-кB signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0172006. [23] MA J, CHEN Q, LI J, et al. Dexmedetomidine-Mediated Prevention of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Depends in Part on Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms. Anesth Analg. 2020;130(4):1054-1062. [24] ZHANG J, XIA F, ZHAO H, et al. Dexmedetomidine-induced cardioprotection is mediated by inhibition of high mobility group box-1 and the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 2019;14(7):e0218726. [25] JU Y, XIAO F, LU J, et al. Effect of Dexmedetomidine and cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathways in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020;33(3(Special)):1377-1382. [26] WU Y, QIU G, ZHANG H, et al. Dexmedetomidine alleviates hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury via the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2-NLRP3 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(21):9983-9994. [27] SUN Y, JIANG C, JIANG J, et al. Dexmedetomidine protects mice against myocardium ischaemic/reperfusion injury by activating an AMPK/PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;44(9):946-953. [28] SHAN X, ZHANG J, WEI X, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through activating PI3K/Akt-eNOS signaling via α2 adrenoreceptors in renal microvascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2022;36(11):e22608. [29] ZHANG J, JIANG H, LIU DH, et al. Effects of Dexmedetomidine on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(15):6736-6743. [30] LI BY, LIU Y, LI ZH, et al. Dexmedetomidine promotes the recovery of renal function and reduces the inflammatory level in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury rats through PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(23):12400-12407. [31] ZHENG X, CAI X, YE F, et al. Perioperative Dexmedetomidine attenuates brain ischemia reperfusion injury possibly via up-regulation of astrocyte Connexin 43. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020;20(1):299. [32] 门运政,童旭辉,胡淼,等. JAK2/STAT3信号通路在右美托咪定抗小鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤中的作用[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版),2020, 49(6):662-666,699. [33] LIU H, LI J, JIANG L, et al. Dexmedetomidine pretreatment alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting neuroinflammation through the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022;55:e12145. [34] ZHANG X, ZHOU J, HU Q, et al. The Role of Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Signalling on Preventing Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury with Dexmedetomidine. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2020; 20(5):3295-3302. [35] HAUSENLOY DJ, YELLON DM. New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: targeting the Reperfusion Injury Salvage Kinase (RISK)-pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;61(3):448-460. [36] BRINKMANN K, KASHKAR H. Targeting the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway: a preferred approach in hematologic malignancies? Cell Death Dis. 2014; 5(3):e1098. [37] CHENG X, HU J, WANG Y, et al. Effects of Dexmedetomidine Postconditioning on Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Rats: Role of the PI3K/Akt-Dependent Signaling Pathway. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018:3071959. [38] KANE LA, LAZAROU M, FOGEL AI, et al. PINK1 phosphorylates ubiquitin to activate Parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. J Cell Biol. 2014;205(2):143-153. [39] DAS S, MITROVSKY G, VASANTHI HR, et al. Antiaging properties of a grape-derived antioxidant are regulated by mitochondrial balance of fusion and fission leading to mitophagy triggered by a signaling network of Sirt1-Sirt3-Foxo3-PINK1-PARKIN. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:345105. [40] CHOI HK, CHOI Y, KANG H, et al. PINK1 positively regulates HDAC3 to suppress dopaminergic neuronal cell death. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(4): 1127-1141. [41] ZHANG Q, LIU XM, HU Q, et al. Dexmedetomidine inhibits mitochondria damage and apoptosis of enteric glial cells in experimental intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via SIRT3-dependent PINK1/HDAC3/p53 pathway. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):463. [42] 斯妍娜,张媛,韩流,等. SIRT3介导CypD去乙酰化在右美托咪定减轻肾缺血再灌注损伤中的作用[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志,2016,36(2):239-241. [43] WANG YQ, TANG YF, YANG MK, et al. Dexmedetomidine alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(5):7834-7844. [44] GAO Y, YIN H, ZHANG Y, et al. Dexmedetomidine protects hippocampal neurons against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis through activation HIF-1α/p53 signaling. Life Sci. 2019;232:116611. [45] KIMURA M, ICHIMURA S, SASAKI K, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis contributes to a skeletal dysplasia resembling platyspondylic lethal skeletal dysplasia, Torrance type, in a novel Col2a1 mutant mouse line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;468(1-2):86-91. [46] HE YM, ZHANG Q, ZHENG M, et al. Protective effects of a G. lucidum proteoglycan on INS-1 cells against IAPP-induced apoptosis via attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress and modulating CHOP/JNK pathways. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;106:893-900. [47] XU X, LIU T, ZHANG A, et al. Reactive oxygen species-triggered trophoblast apoptosis is initiated by endoplasmic reticulum stress via activation of caspase-12, CHOP, and the JNK pathway in Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. Infect Immun. 2012;80(6):2121-2132. [48] LI J, ZHAO Y, ZHOU N, et al. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Diabetes Mellitus by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. J Diabetes Res. 2019;2019:7869318. [49] YANG YF, WANG H, SONG N, et al. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Myocardial Inflammation and Apoptosis Through Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14: 1217-1233. [50] ZHAO L, ZHAI M, YANG X, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates neuronal injury after spinal cord ischaemia-reperfusion injury by targeting the CNPY2-endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(12): 8173-8183. [51] ZHAI M, LIU C, LI Y, et al. Dexmedetomidine inhibits neuronal apoptosis by inducing Sigma-1 receptor signaling in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(21):9556-9568. [52] MALIK SA, SHEN S, MARINO G, et al. BH3 mimetics reveal the network properties of autophagy-regulatory signaling cascades. Autophagy. 2011; 7(8):914-916. [53] LUO C, OUYANG MW, FANG YY, et al. Dexmedetomidine Protects Mouse Brain from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting Neuronal Autophagy through Up-Regulating HIF-1α. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017;11:197. [54] Zhang W, Zhang J. Dexmedetomidine preconditioning protects against lung injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion through inhibition of autophagy. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(2):973-980. [55] YUAN F, FU H, SUN K, et al. Effect of Dexmedetomidine on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats by activating mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Metab Brain Dis. 2017;32(2):539-546. [56] 袁峰,付红光,孙凯,等. 线粒体ATP敏感性钾通道在右美托咪定减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤中的作用[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志,2014,34(4):500-502. [57] CHEN S, LI A, WU J, et al. Dexmedetomidine reduces myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in young mice through MIF/AMPK/GLUT4 axis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022;22(1):289. |
| [1] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [2] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [3] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [4] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [5] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [6] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [7] | Mu Bingtao, Yu Jingwen, Liu Chunyun, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Yang Pengwei, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Immunomodulatory effect of astragaloside IV on T cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1057-1062. |
| [8] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [9] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [10] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [11] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [12] | Chen Zepeng, Hou Yonghui, Chen Shudong, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treats spinal cord injury by reducing apoptosis of spinal cord neurons under glucose and oxygen deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [13] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [14] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 380-386. |
| [15] | Long Yi, Yang Jiaming, Ye Hua, Zhong Yanbiao, Wang Maoyuan. Extracellular vesicles in sarcopenic obesity: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 315-320. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||