Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5320-5326.doi: 10.12307/2023.493
Previous Articles Next Articles
Irisin/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha signaling pathway mediates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in mice
Wang Yao, Liu Danan, Zhao Guangjian, Zhou Bo, Wang Xiang
- Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Institute of Medical Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-05-23Accepted:2022-07-14Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-03-30 -
Contact:Liu Danan, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Institute of Medical Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Yao, Master candidate, Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Institute of Medical Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660083 (to LDN); Guizhou Science and Technology Innovation Talent Team Project, No. (2020)5014 (to LDN); Guizhou Province "One Hundred" Level Innovative Talent Training Program, No. (2015)4026 (to LDN); National Natural Science Foundation of Guizhou Medical University, No. TJ20073 (to LDN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yao, Liu Danan, Zhao Guangjian, Zhou Bo, Wang Xiang. Irisin/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha signaling pathway mediates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5320-5326.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
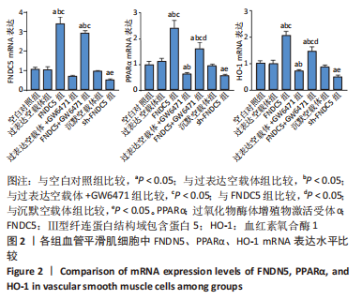
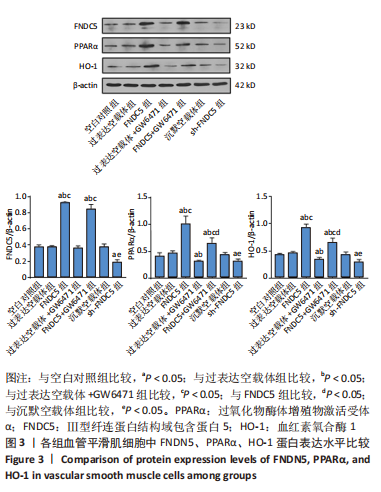
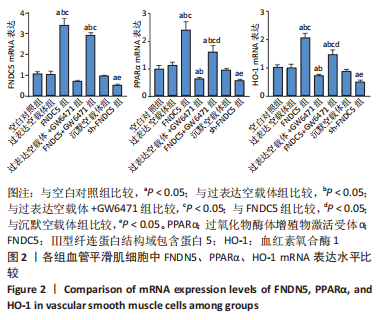
2.2 过表达、沉默FNDC5及在过表达FNDC5基础上下调PPARα表达对血管平滑肌细胞中FNDC5、PPARα、HO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达的影响 与空白对照组比较,过表达空载体组FNDC5、PPARα、HO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达水平无明显差异(均P > 0.05)。与空白对照组、过表达空载体组对比,FNDC5、FNDC5+ GW6471组FNDC5、PPARα、HO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达显著增加(均P < 0.05),过表达空载体+ GW6471组PPARα、HO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达显著降低(均P < 0.05),FNDC5 mRNA和蛋白表达无明显变化(均P > 0.05);与过表达空载体+GW6471组比较,FNDC5组、FNDC5+GW6471组FNDC5、PPARα、HO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达显著增高(均P < 0.05);与FNDC5组比较,FNDC5+GW6471组PPARα、HO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达显著降低(均P < 0.05),FNDC5 mRNA及蛋白表达变化不显著(均P > 0.05);与空白对照组、沉默空载体组比较,sh-FNDC5组FNDC5、PPARα、HO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达显著降低(均P < 0.05),FNDC5 mRNA和蛋白表达无明显变化(均P > 0.05)。见图2,3。"
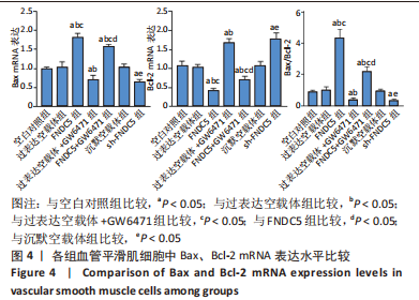
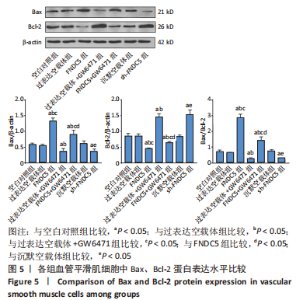
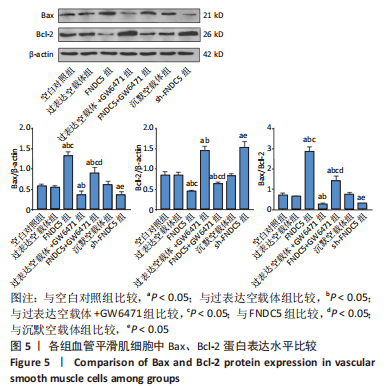
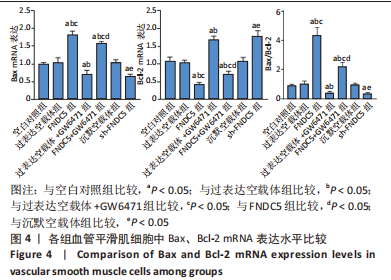
2.3 过表达、沉默FNDC5及在过表达FNDC5基础上下调PPARα表达对血管平滑肌细胞中Bax、Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达的影响 与空白对照组比较,过表达空载体组Bax、Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达水平、Bax/Bcl-2比值无明显差异(均P > 0.05);与空白对照组、过表达空载体组对比,FNDC5组、FNDC5+GW6471组Bax mRNA及蛋白表达水平、Bax/Bcl-2比值显著升高,Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(均P < 0.05),过表达空载体+GW6471组Bax mRNA及蛋白表达水平、Bax/Bcl-2比值显著降低,Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(均P < 0.05);与过表达空载体+GW6471组比较,FNDC5组、FNDC5+GW6471组Bax mRNA及蛋白表达水平、Bax/Bcl-2比值显著升高,Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(均P < 0.05);与FNDC5组比较,FNDC5+GW6471组Bax mRNA及蛋白表达水平、Bax/Bcl-2比值显著降低,Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(均P < 0.05);与空白对照组、沉默空载体组比较,sh-FNDC5组Bax mRNA及蛋白表达水平、Bax/Bcl-2比值显著降低,Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(均P < 0.05)。见图4,5。"
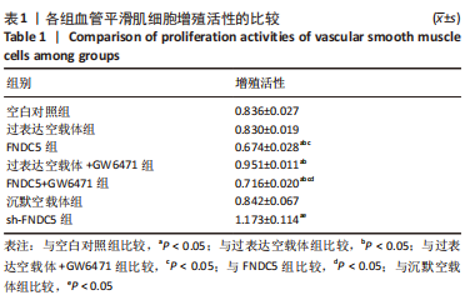
2.4 过表达、沉默FNDC5及在过表达FNDC5基础上下调PPARα表达对血管平滑肌细胞增殖活性的影响 CCK-8结果显示,与空白对照组比较,过表达空载体组血管平滑肌细胞增殖活性无明显差异(P > 0.05);与空白对照组、过表达空载体组比较,FNDC5组、FNDC5+GW6471组增殖活性显著降低(P < 0.05),过表达空载体+GW6471组血管平滑肌细胞增殖活性显著升高(P > 0.05);与过表达空载体+GW6471组比较,FNDC5组、FNDC5+GW6471组血管平滑肌细胞增殖活性降低(P < 0.05);与FNDC5组比较,FNDC5+GW6471组血管平滑肌细胞增殖活性升高(P < 0.05);与空白对照组、沉默空载体组比较,sh-FNDC5组血管平滑肌细胞增殖活性显著升高(P > 0.05)。见表1。"
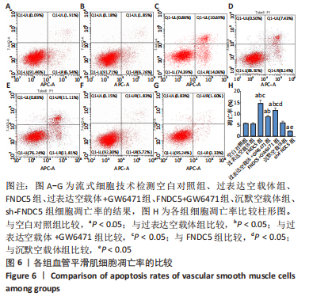
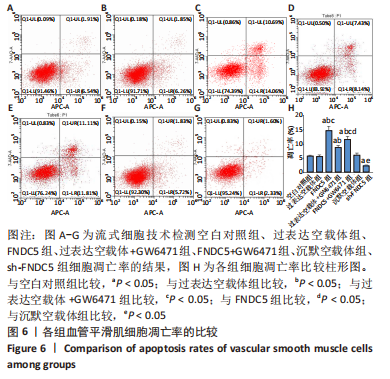
2.5 过表达、沉默FNDC5及在过表达FNDC5基础上下调PPARα表达对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响 与空白对照组比较,过表达空载体组血管平滑肌细胞凋亡率无明显差异(P > 0.05);与空白对照组、过表达空载体组比较,FNDC5组、FNDC5+GW6471组血管平滑肌细胞凋亡率显著升高(P < 0.05),过表达空载体+GW6471组血管平滑肌细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05);与过表达空载体+GW6471组比较,FNDC5组、FNDC5+GW6471组血管平滑肌细胞凋亡率升高(P < 0.05);与FNDC5组比较,FNDC5+GW6471组细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05);与空白对照组、沉默空载体组比较,sh-FNDC5组血管平滑肌细胞凋亡率明显降低(P < 0.05)。见图6。"
| [1] RUDIJANTO A. The Role of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells on the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Acta Med Indones. 2007;39(2):86-93. [2] MAYR M, XU Q. Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis in Arteriosclerosis. Exp Gerontol. 2001;36(7):969-987. [3] BENNETT MR, SINHA S, OWENS GK. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):692-702. [4] FALK E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(8 Suppl):C7-C12. [5] BOCHATON-PIALLAT ML, GABBIANI F, REDARD M, et al. Apoptosis participates in cellularity regulation during rat aortic intimal thickening. Am J Pathol. 1995;146(5):1059-1064. [6] BENNETT MR. Apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in vascular remodelling and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Cardiovasc Res. 1999; 41(2):361-368. [7] BENNETT MR, Evan GI, Schwartz SM. Apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells derived from normal vessels and coronary atherosclerotic plaques. J Clin Invest. 1995;95(5):2266-2274. [8] CHO A, COURTMAN DW, LANGILLE BL. Apoptosis (programmed cell death) in arteries of the neonatal lamb. Circ Res. 1995;76(2):168-175. [9] 杨思琪, 王健, 童兰, 等. 血管平滑肌细胞凋亡对动脉粥样硬化作用的研究进展[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版),2021,46(8):872-876. [10] CLARKE MC, FIGG N, MAGUIRE JJ, et al. Apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells induces features of plaque vulnerability in atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 2006;12(9):1075-1080. [11] BAI Y, ZHANG Q, SU Y, et al. Modulation of the Proliferation/Apoptosis Balance of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis by lncRNA-MEG3 via Regulation of miR-26a/Smad1 Axis. Int Heart J. 2019; 60(2): 444-450. [12] ASKARI H, RAJANI SF, POOREBRAHIM M, et al. A glance at the therapeutic potential of irisin against diseases involving inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis: An introductory review. Pharmacol Res. 2018;129:44-55. [13] 何青松,刘大男,谭娟.冠心病患者血清鸢尾素水平变化观察[J].山东医药,2020,60(6):69-71. [14] 谭娟,刘大男,何青松,等.鸢尾素对载脂蛋白E基因敲除小鼠动脉粥样硬化的影响[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2017,25(8):773-777. [15] 向水,黄进启,蔡彦力,等.鸢尾素抑制血小板衍生生长因子BB诱导的血管平滑肌细胞增殖和炎性反应的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2018,35(11):2115-2118. [16] 王向,韦朝俊,王尧,等.构建过表达FNDC5慢病毒载体抑制平滑肌细胞的增殖与迁移[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35):5670-5675. [17] BOSTRÖM P, WU J, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):463-468. [18] SRIVASTAVA RA. Evaluation of anti-atherosclerotic activities of PPAR-α, PPAR-γ, and LXR agonists in hyperlipidemic atherosclerosis-susceptible F(1)B hamsters. Atherosclerosis. 2011;214(1):86-93. [19] ZHANG B, DONG Y, ZHAO Z. LncRNA MEG8 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis by targeting PPARα. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;510(1):171-176. [20] 刘大男,何作云,方颖,等.血红素氧合酶-1/一氧化碳系统对胰岛素样生长因子-Ⅰ诱导的兔血管平滑肌细胞增殖的抑制作用[J].中华心血管病杂志,2006,34(2):153-158. [21] LIU D, MO X, ZHANG H, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) alleviates vascular restenosis after balloon injury in a rabbit carotid artery model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018;11(5):2479-2487. [22] LIU D, HE Z, WU L, et al. Effects of induction/inhibition of endogenous heme oxygenase-1 on lipid metabolism, endothelial function, and atherosclerosis in rabbits on a high fat diet. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 118(1):14-24. [23] KRÖNKE G, KADL A, IKONOMU E, et al. Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human vascular cells is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27(6):1276-1282. [24] 覃铮,刘大男,肖金翠,等.FNDC5过表达慢病毒载体的构建及稳定转染THP-1细胞系[J].重庆医科大学学报,2020,45(2):212-216. [25] WU X, ZHENG X, CHENG J, et al. LncRNA TUG1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis by regulating miR-148b/IGF2 axis in ox-LDL-stimulated VSMC and HUVEC. Life Sci. 2020;243:117287. [26] GROOTAERT MOJ, BENNETT MR. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis: time for a re-assessment. Cardiovasc Res. 2021; 117(11):2326-2339. [27] SHI J, YANG Y, CHENG A, et al. Metabolism of vascular smooth muscle cells in vascular diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020;319(3): H613-H631. [28] AI TJ, SUN JY, DU LJ, et al. Inhibition of neddylation by MLN4924 improves neointimal hyperplasia and promotes apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells through p53 and p62. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(2):319-329. [29] MIANO JM, FISHER EA, MAJESKY MW. Fate and State of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2021;143(21): 2110-2116. [30] SAKUMA T, BARRY MA, IKEDA Y. Lentiviral vectors: basic to translational. Biochem J. 2012;443(3):603-618. [31] MILONE MC, O’DOHERTY U. Clinical use of lentiviral vectors. Leukemia. 2018;32(7):1529-1541. [32] THOMAS CE, EHRHARDT A, KAY MA. Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4(5):346-358. [33] 何青松,刘大男,谭娟.鸢尾素对高脂饮食诱导ApoE~(-/-)小鼠动脉粥样硬化形成的影响及其机制[J].山东医药,2020,60(22):39-43. [34] ZHANG M, XU Y, JIANG L. Irisin attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein impaired angiogenesis through AKT/mTOR/S6K1/Nrf2 pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18951-18962. [35] ZHANG Y, MU Q, ZHOU Z, et al. Protective Effect of Irisin on Atherosclerosis via Suppressing Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein Induced Vascular Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction. PloS One. 2016;11(6):e0158038. [36] GIZARD F, NOMIYAMA T, ZHAO Y, et al. The PPARalpha/p16INK4a pathway inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by repressing cell cycle-dependent telomerase activation. Circ Res. 2008; 103(10):1155-1163. [37] CHENG C, XU BL, SHENG JL, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting miRNA-124-3p/PPARα axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(20):9025-9032. [38] BOCK FJ, TAIT SWG. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(2):85-100. [39] KIM N, HWANGBO C, LEE S, et al. Eupatolide inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of aortic smooth muscle cells through ROS-dependent heme oxygenase-1 induction. Phytother Res. 2013; 27(11):1700-1707. [40] LIU XM, CHAPMAN GB, WANG H, et al. Adenovirus-mediated heme oxygenase-1 gene expression stimulates apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 2002;105(1):79-84. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [4] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [5] | Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Lu Dahong, Xu Junrong, Liu Xiaocui, Wang Bingyun. Clinical-grade human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells affect the improvement of neurological function in rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 835-839. |
| [6] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [7] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [8] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [9] | Zhao Siqi, Du Juan, Qu Haifeng, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Effects of enriched environment combined with melatonin on learning and memory function and brain neuron apoptosis in SAMP8 mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 701-706. |
| [10] | Zhang Qing, Gao Chunlan, Yu Feifei, Zhang Zhenghao, Ma Fang, Gao Yuan, Li Guizhong, Jiang Yideng, Ma Shengchao. Ephrin A receptor 2 DNA methylation increases in pancreatic beta cell apoptosis induced by homocysteine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 714-719. |
| [11] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [12] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [13] | He Qin, Bu Yan, Lin Guanglei, Luo Jing, Yong Min, Huang Yongqing. Differential expression of RNA binding protein Lin28A regulates osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5283-5291. |
| [14] | Zhang Huiyu, Yu Jingwen, Bai Zhenjun, Li Liang, Mu Bingtao, Zhang Jinfeng, Xie Jiawei. Triptolide protects damaged neurons by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5342-5347. |
| [15] | Xu Luchun, Yang Yongdong, Zhao He, Zhong Wenqing, Ma Yukun, Yu Xing. Effect and mechanism of non-coding RNA in regulating neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5404-5412. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||