Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (20): 3143-3150.doi: 10.12307/2023.492
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network
Guo Shuhui1, Yang Ye1, Jiang Yangyang2, Xu Jianwen1
- 1The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-07-09Accepted:2022-08-27Online:2023-07-18Published:2022-11-21 -
Contact:Xu Jianwen, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Guo Shuhui, Master candidate, Physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960417 (to XJW); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 2018GXNSFAA050033 (to XJW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3143-3150.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
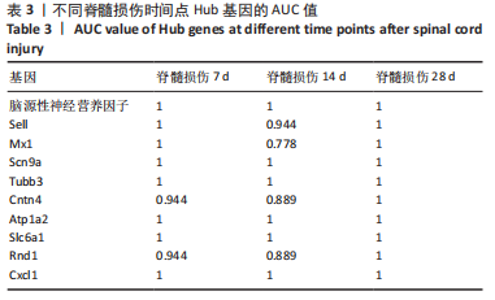
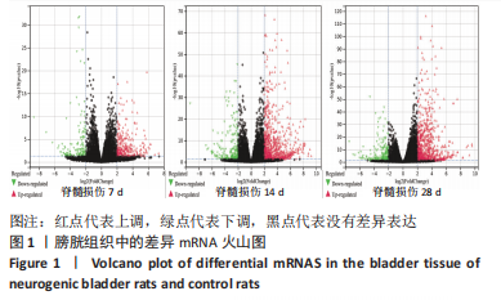
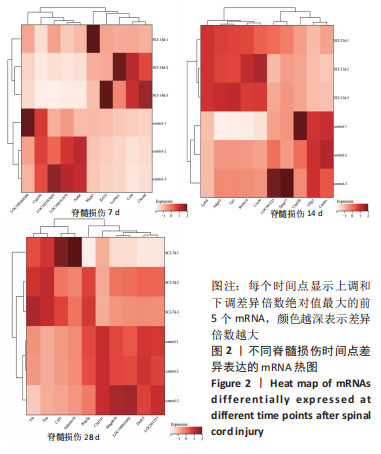
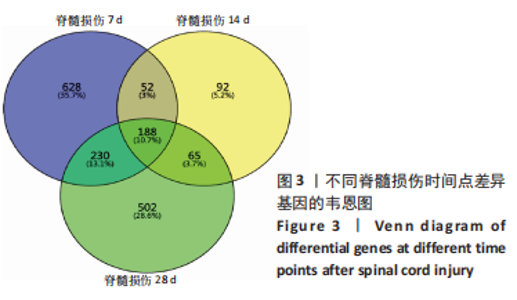
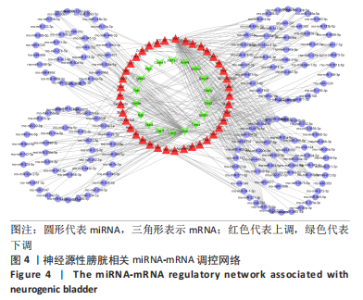
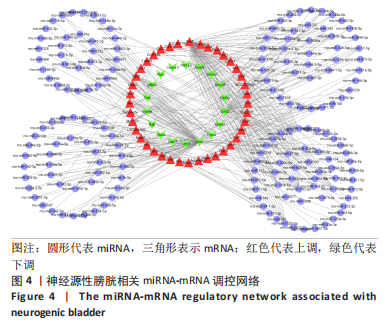
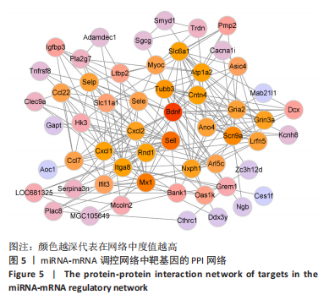
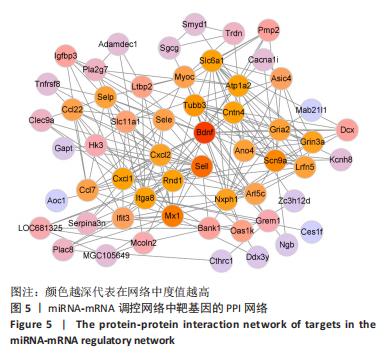
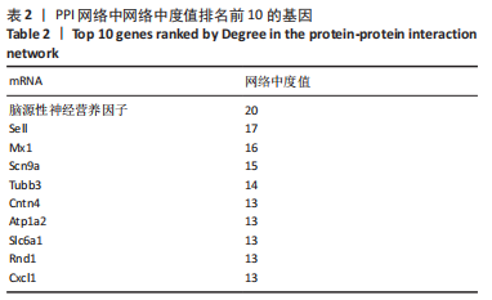
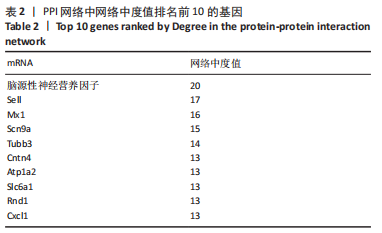
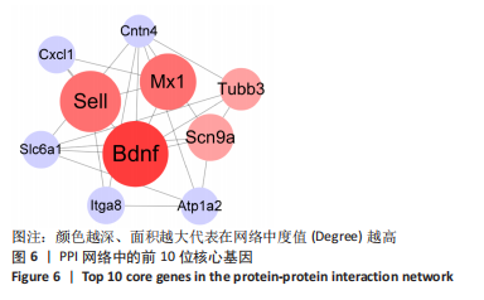
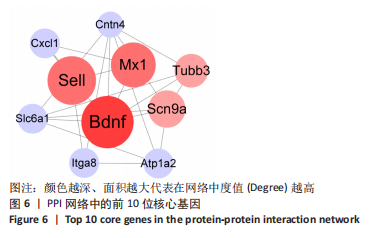
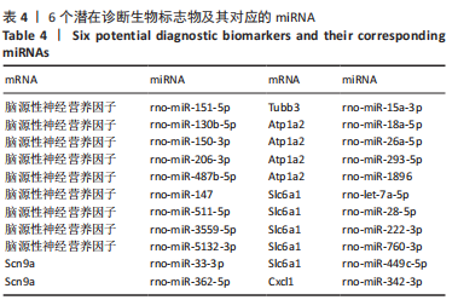
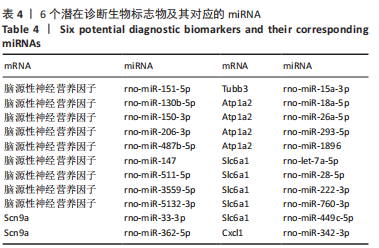
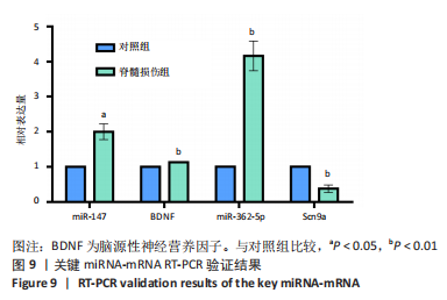
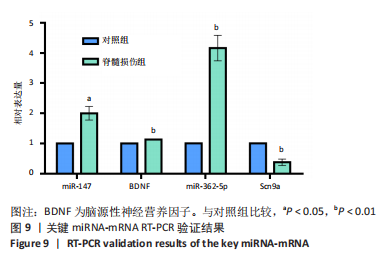
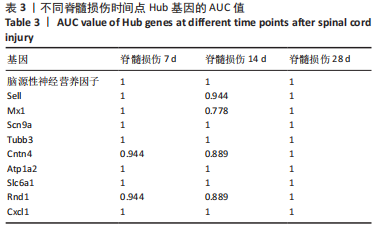
2.4 潜在诊断生物标志物筛选 ROC曲线结果表明,AUC值范围在0.778-1.000之间(表3),提示筛选出的Hub基因具有良好的诊断价值。其中,脑源性神经营养因子、Scn9a、Tubb3、Atp1a2、Slc6a1、Cxcl1在脊髓损伤后第7,14,28天的AUC 值都为1,表明这些基因可能是潜在诊断生物标志物;分析miRNA-mRNA网络,发现以上6个潜在诊断生物标志物共对应22个miRNA,具体见表4。通过文献查询对22个miRNA进一步交叉验证,采用SHANG等[7]通过 MiRs芯片检测神经源性膀胱组间差异表达的miRNAs数据作为验证数据,发现在 SHANG 等的研究中,rno-miR-147 和 rno-miR-362-5p在脊髓损伤后 7,14,28 d 表达量均明显上调。"
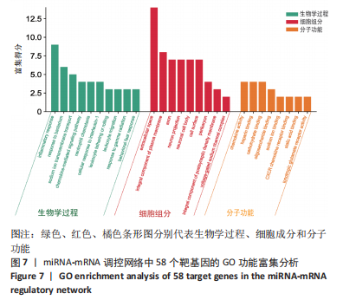
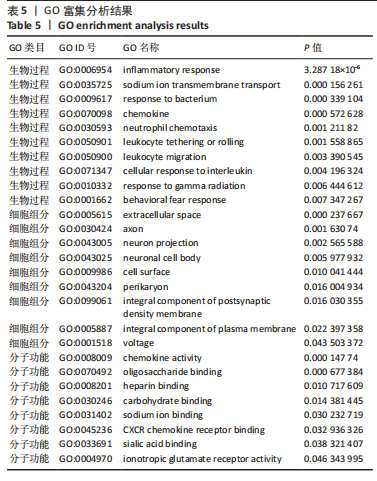
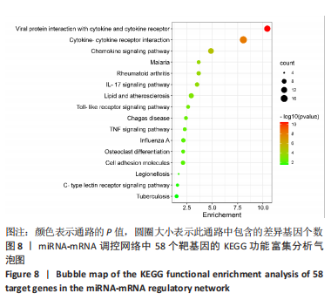
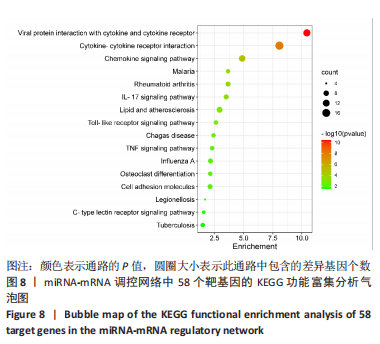
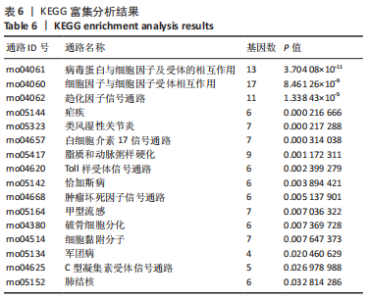
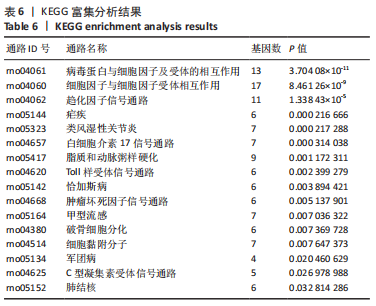
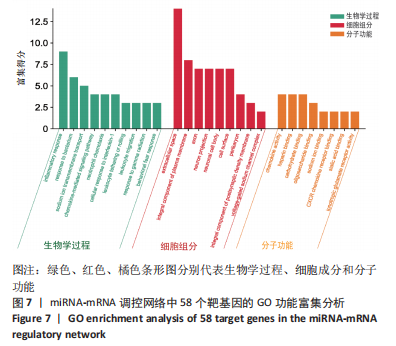
以上生信分析结果表明,相较于对照组,脊髓损伤组大鼠膀胱组织中rno-miR-147、rno-miR-362-5p、脑源性神经营养因子、Scn9a的表达量在脊髓损伤后7,14,28 d天都存在显著差异,提示rno-miR-147-脑源性神经营养因子与rno-miR-362-5p-Scn9a可能在脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的发生、发展过程中有重要作用,有望成为后续神经源性膀胱康复治疗的重要靶点,值得进一步研究。实验将从疾病早期入手,对生物信息学所预测到的rno-miR-147-脑源性神经营养因子、rno-miR-362-5p-Scn9a进行RT-PCR验证,以初步鉴定脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的miRNA-mRNA调控网络。 2.5 差异基因功能富集分析结果 将58个差异基因进行GO富集分析,经P < 0.05筛选后,共富集到23项生物过程、8项分子功能和9项细胞组分,见图7、表5(生物过程只列出前10项)。在分子功能方面,差异基因主要与炎症反应、钠离子的跨膜转运、中性粒细胞趋化性、细胞对白细胞介素1的反应等相关功能相关;在细胞功能方面,主要参与趋化因子活动,结合低聚糖、肝素、钠离子、碳水化合物以及与CXCR趋化因子受体结合相关;在细胞组分方面,差异基因主要参与构成细胞外空间、轴突、神经元胞体等重要细胞成分。"
| [1] SHANG Z, JIA C, YAN H, et al. Injecting RNA interference lentiviruses targeting the muscarinic 3 receptor gene into the bladder wall inhibits neurogenic detrusor overactivity in rats with spinal cord injury. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019;38(2):615-624. [2] STOVER SL, DEVIVO MJ, GO BK. History, implementation, and current status of the National Spinal Cord Injury Database. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80(11):1365-1371. [3] 孟祥志,崔慎红,侯晓倩,等.国际国内神经源性膀胱相关研究的可视化分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(4):439-446. [4] LIM V, MAC-THIONG J M, DIONNE A, et al. Clinical Protocol for Identifying and Managing Bladder Dysfunction during Acute Care after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(6):718-724. [5] GUO W, SHAPIRO K, WANG Z, et al. Restoring both continence and micturition after chronic spinal cord injury by pudendal neuromodulation. Exp Neurol. 2021;340:113658. [6] LIN L, HU K. MiR-147: Functions and Implications in Inflammation and Diseases. Microrna. 2021;10(2):91-96. [7] SHANG Z, OU T, XU J, et al. MicroRNA expression profile in the spinal cord injured rat neurogenic bladder by next-generation sequencing. Transl Androl Urol. 2020;9(4):1585-1602. [8] CRUZ C D, COELHO A, ANTUNES-LOPES T, et al. Biomarkers of spinal cord injury and ensuing bladder dysfunction. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015; 82-83:153-159. [9] KAMBOONLERT K, PANYASRIWANIT S, TANTISIRIWAT N, et al. Effects of Bilateral Transcutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation on Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity in Spinal Cord Injury: A Urodynamic Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(6):1165-1169. [10] GROSS O, LEITNER L, RASENACK M, et al. Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia: can a more specific definition distinguish between patients with and without an underlying neurological disorder? Spinal Cord. 2021;59(9):1026-1033. [11] BIRKHÄUSER V, LIECHTI MD, ANDERSON CE, et al. TASCI-transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in patients with acute spinal cord injury to prevent neurogenic detrusor overactivity: protocol for a nationwide, randomised, sham-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. BMJ Open. 2020;10(8):e039164. [12] WU SY, JIANG YH, JHANG JF, et al. Inflammation and Barrier Function Deficits in the Bladder Urothelium of Patients with Chronic Spinal Cord Injury and Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. Biomedicines. 2022;10(2):220. [13] TOGAN T, AZAP OK, DURUKAN E, et al. The prevalence, etiologic agents and risk factors for urinary tract infection among spinal cord injury patients. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014;7(1):e8905. [14] GONG L, LV Y, LI S, et al. Changes in transcriptome profiling during the acute/subacute phases of contusional spinal cord injury in rats. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(24):1682. [15] BAEK A, CHO SR, KIM SH. Elucidation of Gene Expression Patterns in the Brain after Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(7):1286-1300. [16] CAO S, YUAN J, ZHANG D, et al. Transcriptome Changes In Dorsal Spinal Cord Of Rats With Neuropathic Pain. J Pain Res. 2019;12:3013-3023. [17] BELADI RN, VARKOLY KS, SCHUTZ L, et al. Serine Proteases and Chemokines in Neurotrauma: New Targets for Immune Modulating Therapeutics in Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(11): 1835-1854. [18] RUTKOWSKI MD, DELEO JA. The Role of Cytokines in the Initiation and Maintenance of Chronic Pain. Drug News Perspect. 2002;15(10): 626-632. [19] KIGERL KA, LAI W, WALLACE LM, et al. High mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) is increased in injured mouse spinal cord and can elicit neurotoxic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;72:22-33. [20] NIE H, JIANG Z. Bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles deliver microRNA-23b to alleviate spinal cord injury by targeting toll-like receptor TLR4 and inhibiting NF-κB pathway activation. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):8157-8172. [21] STIRLING DP, CUMMINS K, MISHRA M, et al. Toll-like receptor 2-mediated alternative activation of microglia is protective after spinal cord injury. Brain. 2014;137(Pt 3):707-723. [22] STIVERS NS, PELISCH N, OREM BC, et al. The toll-like receptor 2 agonist Pam3CSK4 is neuroprotective after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2017;294:1-11. [23] HERMAN P, STEIN A, GIBBS K, et al. Persons with Chronic Spinal Cord Injury Have Decreased Natural Killer Cell and Increased Toll-Like Receptor/Inflammatory Gene Expression. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(15): 1819-2189. [24] BUTENSCHöN J, ZIMMERMANN T, SCHMAROWSKI N, et al. PSA-NCAM positive neural progenitors stably expressing BDNF promote functional recovery in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:11. [25] YOO JM, LEE BD, SOK DE, et al. Neuroprotective action of N-acetyl serotonin in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of both TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Akt/Nrf2/Antioxidant enzyme in neuronal cells. Redox Biol. 2017;11:592-529. [26] CAI H, WANG Y, HE J, et al. Neuroprotective effects of bajijiasu against cognitive impairment induced by amyloid-β in APP/PS1 mice. Oncotarget. 2017;8(54):92621-92634. [27] TIAN WJ, JEON SH, ZHU GQ, et al. Effect of high-BDNF microenvironment stem cells therapy on neurogenic bladder model in rats. Transl Androl Urol. 2021;10(1):345-355. [28] VIZZARD MA. Changes in urinary bladder neurotrophic factor mRNA and NGF protein following urinary bladder dysfunction. Exp Neurol. 2000;161(1):273-284. [29] LI F, WANG X, YANG L. MicroRNA-147 targets BDNF to inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2020;20(2):1931-1937. [30] LIU G, FRIGGERI A, YANG Y, et al. miR-147, a microRNA that is induced upon Toll-like receptor stimulation, regulates murine macrophage inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(37): 15819-15824. [31] JIANG C, WU X, LI X, et al. Loss of microRNA-147 function alleviates synovial inflammation through ZNF148 in rheumatoid and experimental arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 2021;51(8):2062-2073. [32] WU CG, HUANG C. MicroRNA-147 inhibits myocardial inflammation and apoptosis following myocardial infarction via targeting HIPK. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 24(11):6279-6287. [33] DU Y, YANG F, LV D, et al. MiR-147 inhibits cyclic mechanical stretch-induced apoptosis in L6 myoblasts via ameliorating endoplasmic reticulum stress by targeting BRMS1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2019; 24(6):1151-1161. [34] COX JJ, REIMANN F, NICHOLAS AK, et al. An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain. Nature. 2006;444(7121): 894-598. [35] DIB-HAJJ SD, RUSH AM, CUMMINS TR, et al. Gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons. Brain. 2005;128(Pt 8):1847-1854. [36] NASSAR MA, STIRLING LC, FORLANI G, et al. Nociceptor-specific gene deletion reveals a major role for Nav1.7 (PN1) in acute and inflammatory pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(34):12706-12711. [37] WEI X, WANG B, WANG Q, et al. MiR-362-5p, Which Is Regulated by Long Non-Coding RNA MBNL1-AS1, Promotes the Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth of Bladder Cancer by Targeting QKI. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11: 164. [38] CHEN Y, LIN L, HU X, et al. Silencing of circular RNA circPDE5A suppresses neuroblastoma progression by targeting the miR-362-5p/NOL4L axis. Int J Neurosci. 2021: 1-11.doi: 10.1080/00207454.2021.1896505. [39] LIU B, LUO C, LIN H, et al. Long Noncoding RNA XIST Acts as a ceRNA of miR-362-5p to Suppress Breast Cancer Progression . Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021;36(6):456-466. |
| [1] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [3] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [4] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [5] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [6] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [7] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [8] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [9] | Ruan Ling, Wang Guanghua, Wu Rongping, Jin Zhan, Lyu Zhenqing, Zhang Nan, Li Shoubang. Correlation between exercise intensity and lipid metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in a high-diet rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [10] | Tian Qinyu, Tian Xinggui, Tian Zhuang, Sui Xiang, Liu Shuyun, Lu Xiaobo, Guo Quanyi. Protection of manganese oxide nanoparticles for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell spreading against oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 821-826. |
| [11] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [12] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [13] | Li Xiaoyin, Yang Xiaoqing, Chen Shulian, Li Zhengchao, Wang Ziqi, Song Zhen, Zhu Daren, Chen Xuyi. Collagen/silk fibroin scaffold combined with neural stem cells in the treatment of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [14] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [15] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||