Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (29): 4616-4623.doi: 10.12307/2022.845
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effects of tertiary butylhydroquinone on various organs in type 2 diabetic rats
Tian Min, Liu Yuting, Xie Like, Cao Yang, Lyu Hongbin
- Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-10-08Accepted:2021-11-13Online:2022-10-18Published:2022-03-27 -
Contact:Lyu Hongbin, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Tian Min, Master, Attending physician, Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:a grant from Sichuan Provincial Department of Education, No. 17ZA0428 (to LHB); Southwest Medical University Scientific Research Project, No. 2015-YJ006 (to LHB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Min, Liu Yuting, Xie Like, Cao Yang, Lyu Hongbin. Protective effects of tertiary butylhydroquinone on various organs in type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4616-4623.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
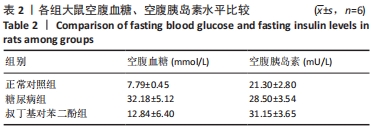
2.1 实验动物数量分析 纳入SD大鼠24只,饲养过程中死亡6只,其中正常组1只大鼠不明原因死亡;糖尿病组2只因为血糖太高而死亡,1只因为皮肤脓肿感染死亡;tBHQ组有2只大鼠死亡,其中1只大鼠解剖后发现一侧肾脏有肿瘤生长,另外1只死亡原因不明。最终18只大鼠进入结果分析,共3组,每组6只。 2.2 各组大鼠糖尿病相关生化指标的改变 各组大鼠干预治疗12周的空腹血糖水平有所不同,总体比较差异均有显著性意义(F=78.53,P=0.000);其中与正常对照组比较,糖尿病组及tBHQ组大鼠空腹血糖水平升高,差异均有显著性意义(均P < 0.05)。各组大鼠在干预后空腹胰岛素总体比较差异有显著性意义(F=22.48,P=0.000),其中糖尿病组及tBHQ组高于正常对照组(P < 0.05);tBHQ组较糖尿病组升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。"
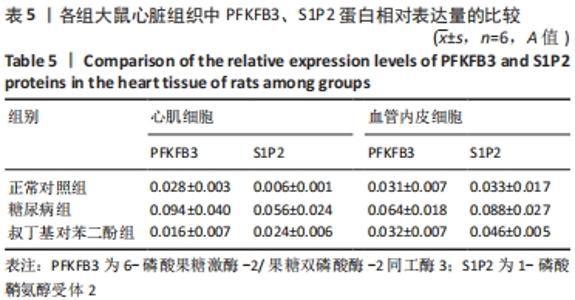
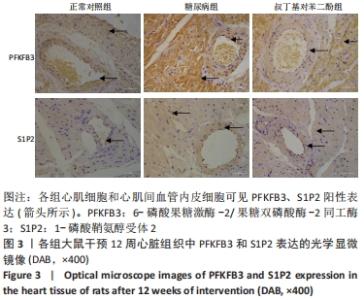
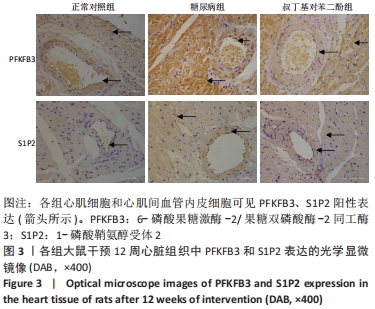
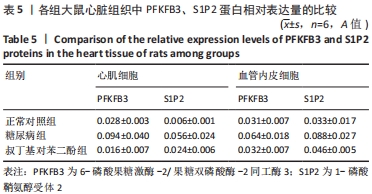
各组大鼠心肌细胞和心肌间血管内皮细胞中PFKFB3、S1P2蛋白的相对表达量的总体比较差异均有显著性意义(F心肌PFKFB =9.273,P心肌PFKFB=0.004;F心肌S1P2 =6.411,P心肌S1P2=0.014;F心肌血管内皮PFKFB =6.659,P心肌血管内皮PFKFB=0.02;F心肌血管内皮S1P2 =6.214,P心肌血管内皮S1P2=0.02)。 在大鼠心肌细胞中,糖尿病组PFKFB3(t=2.64,P=0.024)、S1P2(t=3.16,P=0.009)的表达均较正常对照组增加,差异有显著性意义;tBHQ组PFKFB3(t=3.95,P=0.002)、S1P2(t=2.32,P=0.04)的表达较糖尿病组降低,差异有显著性意义。 在大鼠心肌细胞间血管内皮细胞中,糖尿病组PFKFB3(t=2.77,P=0.025)、S1P2(t=3.04,P=0.016)的表达均较正常对照组增加,差异有显著性意义;tBHQ组PFKFB3(t=3.23,P=0.015)、S1P2(t=2.62,P=0.028)的表达较糖尿病组降低,差异有显著性意义,见表5。"
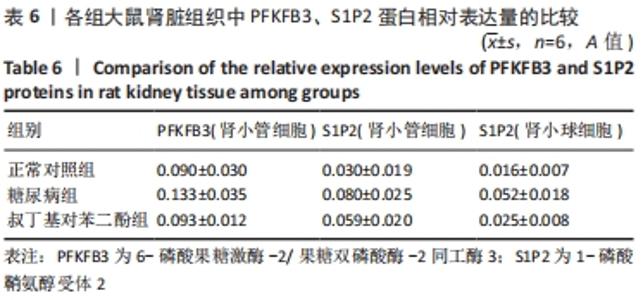
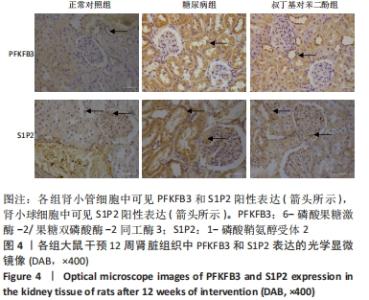
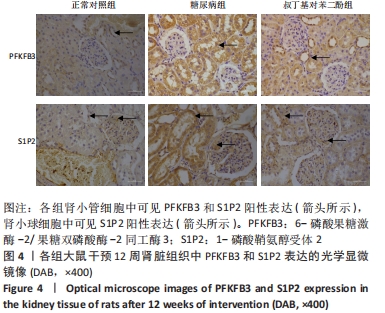
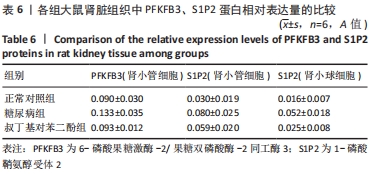
各组大鼠肾小管细胞和肾小球细胞中PFKFB3、S1P2蛋白的相对表达量的总体比较差异均有显著性意义(F肾小管PFKFB=4.969,P肾小管PFKFB=0.019;F肾小管S1P2=11.403,P肾小管S1P2< 0.001;F肾小球S1P2=12.316,P肾小球S1P2=0.001)。 在大鼠肾小管细胞中,糖尿病组PFKFB3(t=2.92,P=0.009)、S1P2(t=4.97,P < 0.001)的表达均较正常对照组增加,差异均显著性意义;tBHQ组PFKFB3(t=2.36,P=0.039)、S1P2(t=2.13,P=0.043)的表达较糖尿病组降低,差异有显著性意义。 在大鼠肾小球细胞中,糖尿病组S1P2的表达均较正常对照组增加(t=4.45,P < 0.001),差异有显著性意义;tBHQ组S1P2的表达较糖尿病组降低(t=3.81,P < 0.001),差异有显著性意义,见表6。"
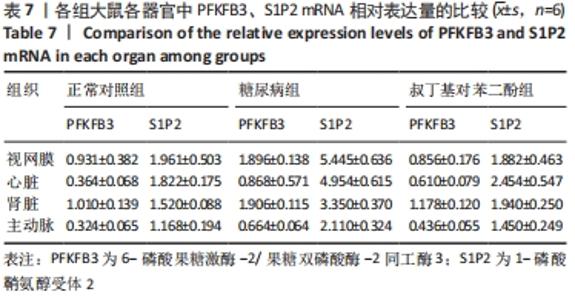
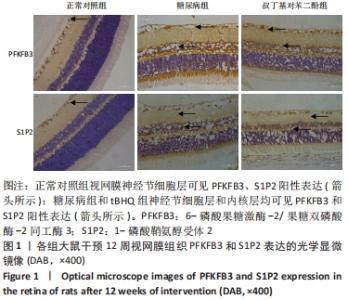
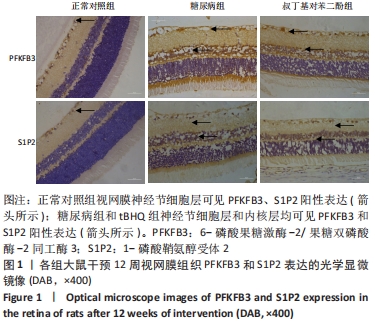
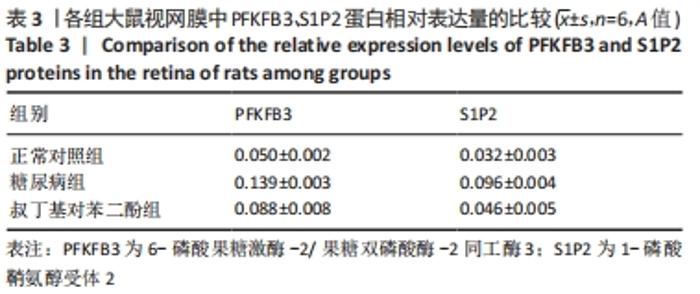
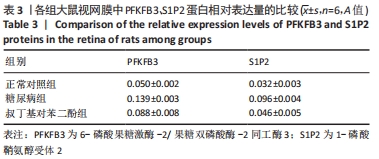
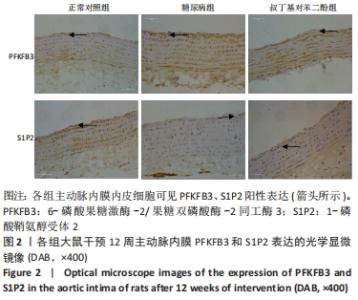
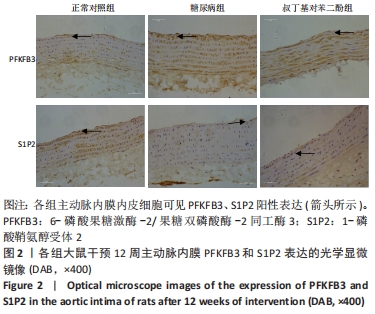
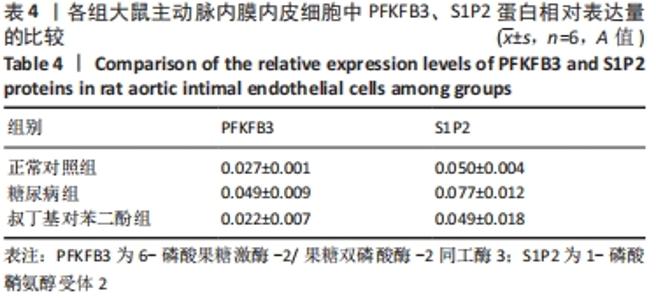
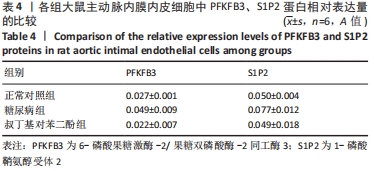
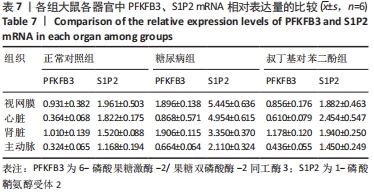
2.4 各组大鼠视网膜、主动脉、心脏、肾脏中PFKFB3、S1P2 mRNA的表达 qRT-PCR检测结果显示,各组大鼠视网膜、心脏、肾脏、主动脉等各器官中的PFKFB3、S1P2mRNA的表达总体比较差异有显著性意义(F视网膜PFKFB3=30.973,P视网膜PFKFB3< 0.001;F视网膜S1P2=53.268,P视网膜S1P2< 0.001;F心脏PFKFB3=66.859,P心脏PFKFB3< 0.001;F心脏S1P2=58.025,P心脏S1P2< 0.001;F肾脏PFKFB3=71.709,P肾脏PFKFB3< 0.001;F肾脏S1P2=64.539,P肾脏S1P2< 0.001;F主动脉PFKFB3=39.192,P主动脉PFKFB3< 0.001,F主动脉S1P2=17.087,P主动脉S1P2< 0.001)。糖尿病组(t视网膜PFKFB3=6.36,P视网膜PFKFB3< 0.001;t心脏PFKFB3=11.58,P心脏PFKFB3<0.001;t肾脏PFKFB3=11.27,P肾脏PFKFB3< 0.001;t主动脉PFKFB3=8.71,P主动脉PFKFB3< 0.001)较正常对照组增多;tBHQ组(t视网膜PFKFB3=6.85,P视网膜PFKFB3< 0.001;t心脏PFKFB3=5.93,P心脏PFKFB3< 0.001;t肾脏PFKFB3=9.16,P肾脏PFKFB3< 0.001;t主动脉PFKFB3=5.85,P主动脉PFKFB3< 0.001)较糖尿病组减少,差异均有显著性意义;糖尿病组(t视网膜S1P2=8.49,P视网膜S1P2< 0.001;t心脏S1P2=10.2,P心脏S1P2< 0.001;t肾脏S1P2=10.8,P肾脏S1P2< 0.001;t主动脉S1P2=5.7,P主动脉S1P2< 0.001)较正常对照组增多;tBHQ组(t视网膜S1P2=8.69,P视网膜S1P2< 0.001;t心脏S1P2=8.14,P心脏S1P2< 0.001;t肾脏S1P2=8.38,P肾脏S1P2< 0.001;t主动脉S1P2=4.02,P主动脉S1P2=0.002)较糖尿病组减少,差异均有显著性意义,见表7。"
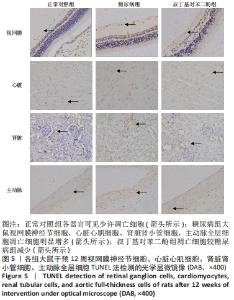
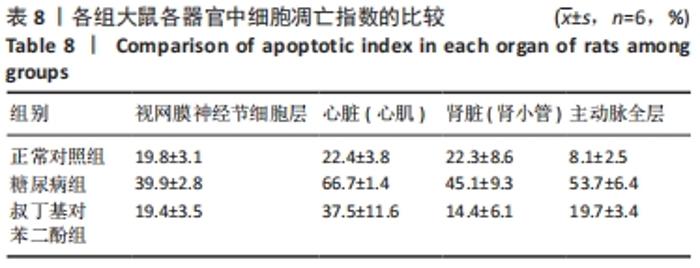
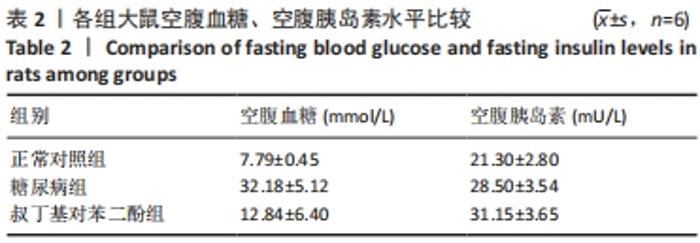
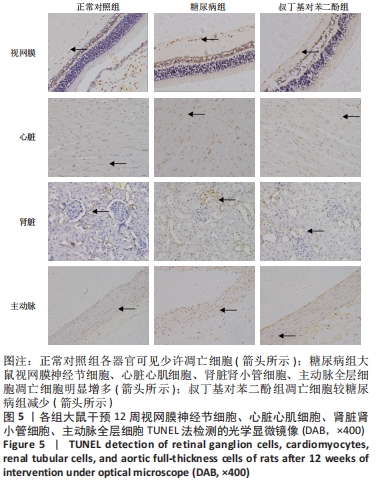
2.5 各组大鼠视网膜、主动脉、心肌、肾脏中细胞的凋亡指数 TUNEL法检测结果显示,各组大鼠视网膜神经节细胞、心脏心肌细胞、肾脏肾小管细胞、主动脉全层细胞凋亡指数各器官的总体比较差异有显著性意义(F视网膜=56.294,P视网膜< 0.001;F心脏=22.441,P心脏< 0.001;F肾脏=142.81,P肾脏< 0.001;F主动脉=19.28,P主动脉< 0.001)。糖尿病组(t视网膜=7.21,P视网膜< 0.001;t心脏=6.59,P心脏< 0.001;t肾脏=4.43,P肾脏=0.001;t主动脉=16.25,P主动脉< 0.001)较正常对照组增多;tBHQ组(t视网膜=7.36,P视网膜< 0.001;t心脏=4.34,P心脏=0.001;t肾脏=5.98,P肾脏< 0.001;t主动脉=12.11,P主动脉< 0.001)较糖尿病组减少,差异均有显著性意义,见图5及表8。"
| [1] LA SELVA M, BELTRAMO E, PAGNOZZI F, et al. Thiamine corrects delayed replication and decreases production of lactate and advanced glycation end-products in bovine retinal and human umbilical vein endothelial cells cultured under high glucose conditions. Diabetologia. 1996;39(11):1263-1268. [2] OBINATA H, HLA T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate in coagulation and inflammation. Semin Immunopathol. 2012;34(1):73-91. [3] 侯云雷, 张昱, 夏娟娟, 等. 6-磷酸果糖-2-激酶3抑制剂的研究进展[J]. 中国药物化学杂志,2016,26(1):65-70. [4] ATSUMI T, CHESNEY J, METZ C, et al. High expression of inducible 6-phosphofructo-kinase/fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase(iPFK-2;PFKFB3) in human cancers. Cancer Res. 2002;62(20):5881-5887. [5] SHI L, PAN H, LIU Z, et al. Roles of PFKFB3 in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017;2:17044. [6] SCHNITZLER JG, HOOGEVEEN RM, ALI L, et al. Atherogenic Lipoprotein(a) Increases Vascular Glycolysis, Thereby Facilitating Inflammation and Leukocyte Extravasation. Circ Res. 2020;126:1346-1359. [7] BOCK KD, GEORGIADOU M,SCHOORS S, et al. Role of PFKFB3-driven glycolysis in vessel sprouting. Cell. 2013;154(3):651-663. [8] SCHOORS S, DE BK, CANTELMO AR, et al. Partial and transient reduction of glycolysis by PFKFB3 blockade reduces pathological angiogenesis. Cell Metab. 2014;19(1):37-48. [9] ZHOU ZY, WANG L, WANG YS, et al. PFKFB3:A Potential Key to Ocular Angiogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:628317. [10] EMINI VESELI B, VAN WIELENDAELE P, DELIBEGOVIC M, et al. The PFKFB3 Inhibitor AZ67 Inhibits Angiogenesis Independently of Glycolysis Inhibition. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:5970. [11] LIU Z, XU J, MA Q, et al. Glycolysis links reciprocal activation of myeloid cells and endothelial cells in the retinal angiogenic niche. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(555): eaay1371. [12] LI L, ZENG H, HE X, et al. Sirtuin 3 Alleviates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Regulating TIGAR and Cardiomyocyte Metabolism. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10: e018913. [13] HATOUM D, HADDADI N, LIN Y, et al. Mammalian Sphingosine Kinase (SphK) Isoenzymes and Isoform Expression: Challenges for SphK as an Oncotarget. Oncotarget. 2017;8:36898-36929. [14] AOKI M, AOKI H, RAMANATHAN R, et al. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling in Immune Cells and Inflammation: Roles and Therapeutic Potential. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:1-11 [15] MACEYKA M, HARIKUMAR KB, MILSTIEN S, et al. Sphingosine-1- phosphate Signaling and its Role in Disease. Trends Cel Biol. 2012;22:50-60. [16] KOWALSKI GM, CAREY AL, SELATHURAI A, et al. Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Is Elevated in Obesity. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(9):e72449 [17] SPIEGEL S, MILSTIEN S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate, a key cell signaling molecule. J Biol Chem. 2002;227(29):25851-25854. [18] SPIEGEL S, MILSTIEN S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate:an enigmatic signaling lipid. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(5):397-407. [19] SANCHEZ T, SKOURA A, WU MT, et al. Induction of vascular permeability by the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2(S1P2R)and its downstream effectors ROCK and PTEN. Arterioscler Thromb Vase Biol. 2007;27(6):1312-1318. [20] TERAO R, HONJO M, AIHARA M. Apolipoprotein M Inhibits Angiogenic and Inflammatory Response by Sphingosine 1-Phosphate on Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1):112. [21] QIAO Y, HU R, WANG Q, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate elicits proinflammatory responses in ARPE-19 cells. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:8200-8207. [22] SWANEY JS, MORENO KM, GENTILE AM, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a novel fibrotic mediator in the eye. Exp Eye Res. 2008;87:367-375. [23] KERAGE D, BRINDLEY DN, HEMMINGS DG. Review: Novel insights into the regulation of vascular tone by sphingosine 1-phosphate. Placenta. 2014;35:S86-S92. [24] IGARASHI J, MICHEL T. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and modulation of vascular tone. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;82:212-220. [25] KONO M, MI Y, LIU Y, et al. The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors S1P1, S1P2, and S1P3 function coordinately during embryonic angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(28):29367-29373. [26] ZHANG X, RITTER JK, LI N. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate pathway in renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018;315(4):F752-F756. [27] LIU W, LAN T, XIE X, et al. S1P2 receptor mediates sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced fibronectin expression via MAPK signaling pathway in mesangial cells under high glucose condition. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318(8):936-943. [28] LAN T, LIU W, XIE X, et al. Sphingosine kinase-1 pathway mediates high glucose-induced fibronectin expression in glomerular mesangial cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25(12):2094-2105. [29] YASUDA S, SUMIOKA T, IWANISHI H, et al. Loss of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 gene function impairs injury-induced stromal angiogenesis in mouse cornea. Lab Invest. 2021;101:245-257. [30] GAENGEL K, NIAUDET C, HAGIKURA K, et al. The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1PR1 restricts sprouting angiogenesis by regulating the interplay between VE-cadherin and VEGFR2. Dev Cell. 2012;23:587-599. [31] GREEN JA, SUZUKI K, CHO B, et al. The sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor S1P(2) maintains the homeostasis of germinal center B cells and promotes niche confinement. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:672-680. [32] SKOURA A, SANCHEZ T, CLAFFEY K, et al. Essential role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 in pathological angiogenesis of the mouse retina. J Clin Investig. 2007; 117:2506-2516. [33] CAO Y, ZHANG X, WANG L, et al. PFKFB3-mediated endothelial glycolysis promotes pulmonary hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2019;116:13394-13403. [34] RIERA L, MANZANO A, NAVARRO-SABATE A, et al. Insulin induces PFKFB3 gene expression in HT29 human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys. 2002; 1589:89-92. [35] TSUTSUI S, KUME M, ERA S. Prognostic value of microvessel density in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer. 2003;10:312-319. [36] OFFERSEN BV, BORRE M, OVERGAARD J. Quantification of angiogenesis as a prognostic marker in human carcinomas: a critical evaluation of histopathological methods for estimation of vascular density. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39:881-890. [37] FRAISL P, MAZZONE M, SCHMIDT T, et al. Regulation of angiogenesis by oxygen and metabolism. Dev Cell. 2009;16:167-179. [38] XU Y, AN X, GUO X, et al. Endothelial 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFKFB3) plays a critical role in angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(6):1231-1239. [39] SCHOORS S, DE BOCK K, CANTELMO AR, et al. Partial and transient reduction of glycolysis by pfkfb3 blockade reduces pathological angiogenesis. Cell Metab. 2014;19:37-48. [40] PERROTTA P, VAN DER VEKEN B, VAN DER VEKEN P, et al. Partial inhibition of glycolysis reduces atherogenesis independent of intraplaque neovascularization in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vascu Biol. 2020;40:1168-1181. [41] GANBAATAR B, FUKUDA D, SHINOHARA M, et al. Inhibition of S1P Receptor 2 Attenuates Endothelial Dysfunction and Inhibits Atherogenesis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2021;28:630-642. [42] GONG W, LI J, CHEN W, et al. Resveratrol Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Extracellular Matrix Accumulation and Inflammation in Rat Glomerular Mesangial Cells by SphK1/S1P2/NF-κB Pathway. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:4495-4505. [43] 田敏, 张思远, 韩佩晏, 等.叔丁基对苯二酚激活Nrf2信号通路增强对2型糖尿病大鼠视网膜的保护作用[J].眼科新进展,2017,37(3):220-224. [44] 李航, 任韫卓, 刘淑霞, 等. 叔丁基对苯二酚对糖尿病小鼠肾脏氧化应激损伤及Nrf2蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报,2009,25(10):1341-1345. [45] KOVACS L, CAO Y, HAN W, et al. PFKFB3 in Smooth Muscle Promotes Vascular Remodeling in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(5):617-627. [46] MUPPIDI JR, SCHMITZ R, GREEN JA, et al. Loss of signalling via Gα13 in germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma. Nature. 2014;516:254-258. |
| [1] | Gao Lei, Qin Xinyuan, Nie Xin, Wang Lei, Wang Jiangning. Extracorporeal circulation compression perfusion in the reconstruction of limb microcirculation from the mechanism of mechanical and chemical signal transduction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1334-1340. |
| [2] | Lü Yiyan, Li Hanbing, Ma Xiaoqing, Zhang Han, Zhang Yuhang, Li Genlin. Establishment and characteristic analysis of interior heat and diabetes mouse model using compound factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1187-1193. |
| [3] | Wang Shuo, Liu Wenying, Lü Chaofan, Li Jiacong, Geng Yi, Zhao Yungang. Cardioprotective effect of 3-nitro-N-methyl salicylamide on the isolated rat heart under cold ischemia preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1194-1201. |
| [4] | Chen Xianghe, Liu Bo, Yang Kang, Lu Pengcheng, Yu Huilin. Treadmill exercise improves the myocardial fibrosis of spontaneous type 2 diabetic mice: an exploration on the functional pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1210-1215. |
| [5] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [6] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [7] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng . Effects of aerobic and resistance exercises on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nuclear factor-kappa B and inflammatory cytokines in skeletal muscle of type II diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 669-675. |
| [8] | Yang Zhiwei, Liu Junchang, Gao Xiaolin, Jiang Taimao. Relationship between tacrolimus metabolic rate and early BK virus infection after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 712-716. |
| [9] | Du Shasha, Cai Zhiguo, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Pancreatic autophagy and protein expression of insulin-related genes in type 2 diabetic rats with periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4605-4610. |
| [10] | Zhang Xin, Ma Xiaoru, Xue Jingwen, Wang Fangfang, Wu Lan, Li Yue. Protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum spores on epididymis and authophage in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4632-4637. |
| [11] | Fu Yu, Shang Huayu, Li Shunchang. Aerobic and resistance exercises can alleviate liver inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4666-4671. |
| [12] | Zheng Haisheng, Lan Yuqing, Zhong Xingwu, Ding Hui. Effect of curcumin nanoparticles on proliferation of human retinal pigment epithelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4335-4339. |
| [13] | Liu Ya, Liu Xia, Deng Penghui, Ji Wei, Li Jianping. Exercise effects on myocardial type I, III collagen and angiotensin II/transforming growth factor beta1/Smad2 pathway in diabetic myocardial fibrosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4173-4179. |
| [14] | Xu Yuan, Niu Yulin, Yuan Zhihui, Jia Lei, Pan Guanghui. Up-regulating follicular regulatory T cells for treating antibody-mediated rejection after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4118-4122. |
| [15] | Duan Zhengwei, Liu Yunfei. Conventional versus marginal donor heart transplantation in patients with end-stage heart disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4211-4215. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||