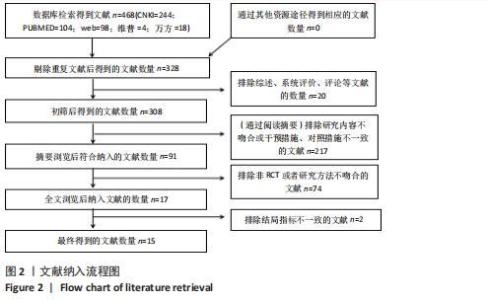
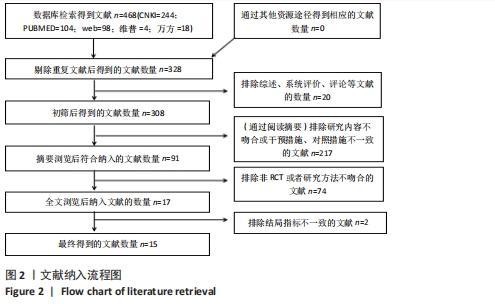
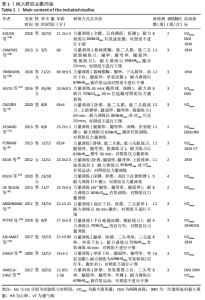
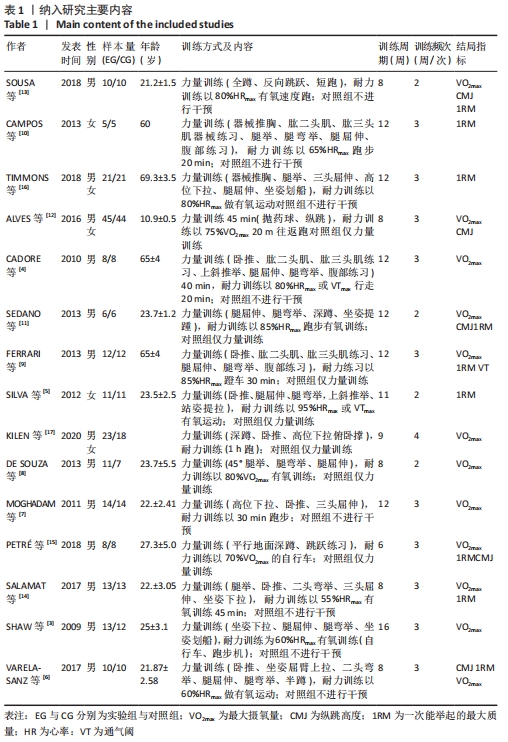
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (26): 4258-4264.doi: 10.12307/2022.832
Effects of concurrent aerobic and strength training on locomotor performance: a Meta-analysis
Li Gaofeng, Wang Jun
- Human Sports Science College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2021-09-08Accepted:2021-10-28Online:2022-09-18Published:2022-03-09 -
Contact:Wang Jun, Professor, Human Sports Science College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Li Gaofeng, Master candidate, Human Sports Science College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
Supported by:the 2018 National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. 2018YFF0300800
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Gaofeng, Wang Jun. Effects of concurrent aerobic and strength training on locomotor performance: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4258-4264.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
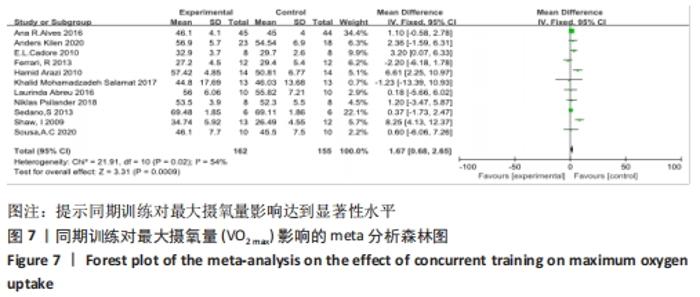
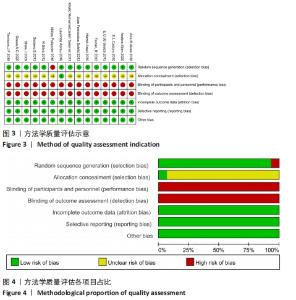
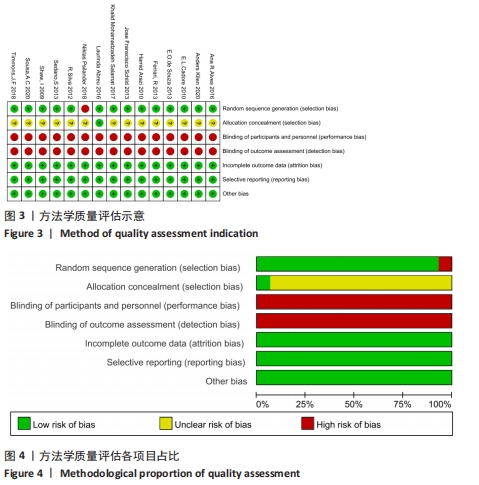
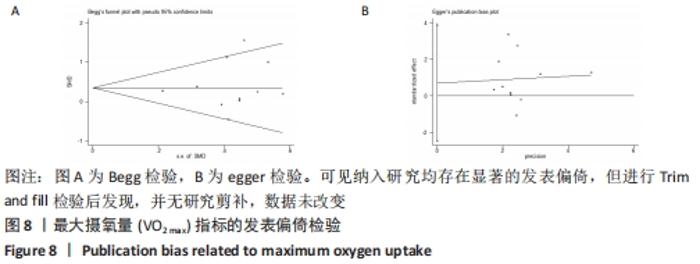
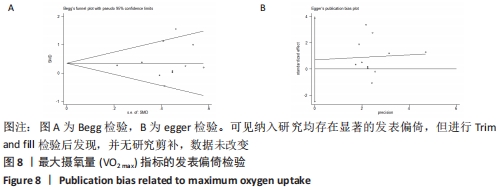
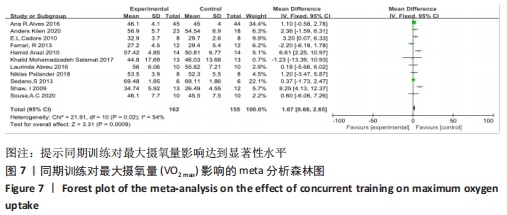
2.4.2 VO2 max效应量的Meta分析及发表偏倚评价 共有11篇研究纳入分析[3-4,6-7,9,11-15,17],Meta分析结果显示,存在中度异质性(I2=54%,P=0.02< 0.1),选择用随机效应模型进行分析。所有研究汇总的MD=1.67,95%置信区间为[0.68,2.65],Z=3.31,P < 0.01,具有非常显著的统计学意义。提示同期训练对VO2 max的影响达到显著性水平,见图7。通过begg以及egger检验结果(t=-8.73,P < 0.01)发现纳入研究均存在显著的发表偏倚,见图8,但进行Trim and fill检验后发现,并无研究剪补,数据未改变。 "

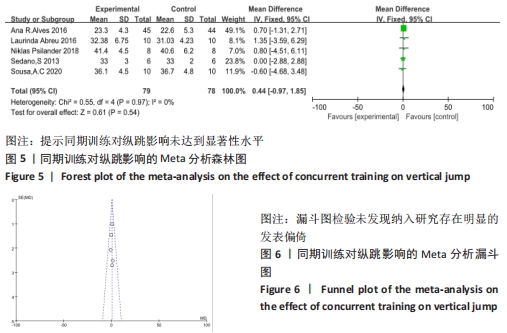
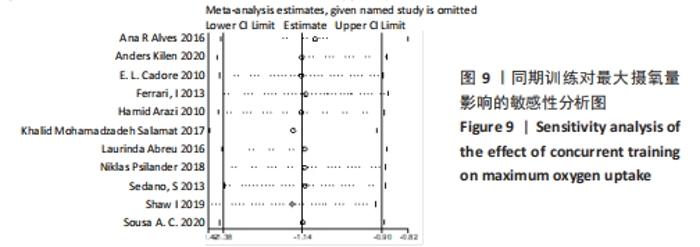
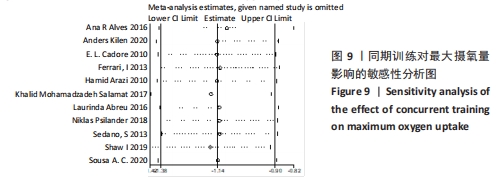
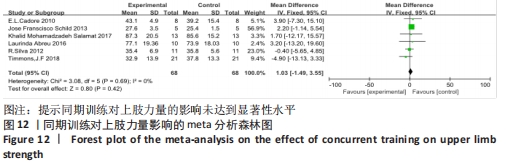
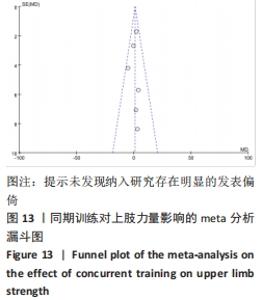
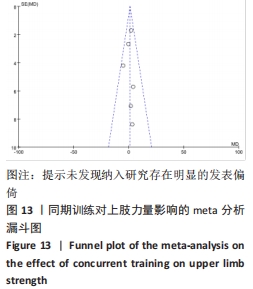
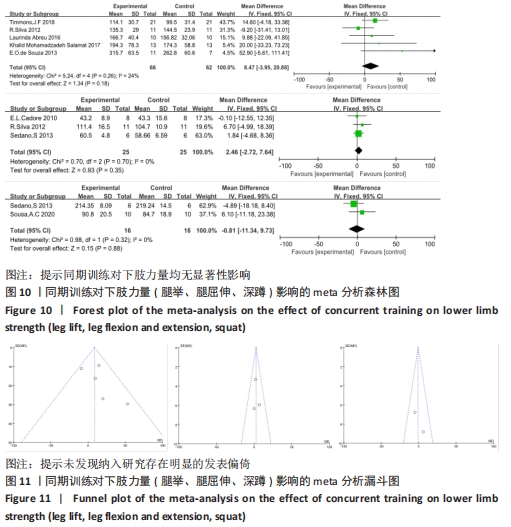
2.4.3 下肢力量效应量的Meta分析及发表偏倚评价 共有8篇研究纳入分析[4-6,8,11,13-14,16],由于不同研究的测试方法不同,分别通过腿举、腿屈伸、深蹲的方式衡量下肢力量,故此项研究对3个方式同时进行Meta分析。结果显示,腿举方式中存在低度异质性(I2=24%,P=0.26> 0.1),MD=8.47,95%置信区间为[-3.95,20.88],Z=1.34,P=0.18> 0.1;腿屈伸方式中无异质性(I2=0%,P=0.7< 0.1),MD=-0.81,95%置信区间[-11.34,9.73],Z=0.93,P=0.35> 0.1;深蹲方式中无异质性(I2=0%,P=0.32> 0.1),MD=2.46,95%置信区间为[-2.72,7.64],Z=0.15,P=0.88> 0.1。3种不同方式的Meta分析中均采用固定效应模型且结果均未达到显著性水平,提示同期训练对下肢力量的影响均无显著性影响,见图10。通过漏斗图检验未发现纳入研究存在明显的发表偏倚,见图11。"
| [1] WILSON JM, MARIN PJ, RHEA MR, et al. Concurrent training:A Meta-Analysis examining interference of aerobic and resistance exercises. J Strength Cond Res. 2021;26(8):2293-2307 [2] 郜卫峰,冯鑫,顾大成.同期耐力与力量训练对长跑运动员跑步经济性及耐力表现相关指标影响的Meta分析[J].体育科学,2019,39(9):68-81. [3] SHAW BS, SHAW I. Compatibility of concurrent aerobic and resistance training on maximal aerobic capacity in sedentary males. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2009;20(2):104-106. [4] CADORE EL, PINTO RS, LHULLIER FL, et al. Physiological effects of concurrent training in elderly men. Int J Sports Med. 2010;31(10):689-697. [5] SILVA RF, CADORE EL, KOTHE G, et al. Concurrent Training with Different Aerobic Exercises. Sports Med. 2012;33:627-634 [6] VARELA-SANZ A, TUIMIL JL, ABREU L, et al. Does Concurrent Training Intensity Distribution Matter? J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(1):181-195. [7] MOGHADAM MG, ARAZI H, SAMADI A, et al. Comparison of the effects of two different methods of concurrent training (continues&distinct)on body composition;aerobic power and muscle endurance in nonathlete male student. Electronic Physician. 2011;3(3):177. [8] DE SOUZA EO, TRICOLI V, ROSCHEL H, et al. Molecular adaptations to concurrent training. Int J Sports Med. 2013;34(3):207-213. [9] FERRARI R, KRUEL LF, CADORE EL, et al. Efficiency of twice weekly concurrent training in trained elderly men. Exp Gerontol. 2013;48(11):1236-1242 [10] CAMPOS ALP, DEL PONTE LS, CAVALLI AS, et al. Effects of concurrent training on health aspects of elderly women. Revista Brasileira de Cineantropometria e Desempenho Humano. 2013;15(4):437-447. [11] SEDANO S, MARÍN PJ, CUADRADO G, et al. Concurrent training in elite male runners: the influence of strength versus muscular endurance training on performance outcomes. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(9):2433-2443. [12] ALVES AR, MARTA CC, NEIVA HP, et al. Concurrent Training in Prepubescent Children: The Effects of 8 Weeks of Strength and Aerobic Training on Explosive Strength and V[Combining Dot Above]O2max. J Strength Cond Res. 2016;30(7):2019-2032. [13] SOUSA AC, MARINHO DA, GIL MH, et al. Concurrent Training Followed by Detraining: Does the Resistance Training Intensity Matter? J Strength Cond Res. 2018; 32(3): 632-642. [14] SALAMAT KM. The Effect of Two Types of Concurrent Training on Vo2max, Maximal Strength and Body Fat Percentage in Young Men. Report of Health Care. 2017;3(1):17-22. [15] PETRÉ H, LÖFVING P, PSILANDER N. The Effect of Two Different Concurrent Training Programs on Strength and Power Gains in Highly-Trained Individuals. J Sports Sci Med. 2018;17(2):167-173. [16] TIMMONS JF, MINNOCK D, HONE M, et al. Comparison of time-matched aerobic, resistance, or concurrent exercise training in older adults. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28(11):2272-2283. [17] KILEN A, BAY J, BEJDER J, et al. Distribution of concurrent training sessions does not impact endurance adaptation. J Sci Med Sport. 2021;24(3):291-296. [18] TANAKA K, WATANABE H, KONISHI Y, et al. Longitudinal associations between anaerobic threshold and distance running performance. Eur J App Physiol Occup Physiol. 1986;55(3):248-252. [19] REICHERT T, COSTA RR, PREISSLER AAB, et al. Short and long-term effects of water-based aerobic and concurrent training on cardiorespiratory capacity and strength of older women. Exp Gerontol. 2020;142:111103. [20] HUNTER G, DEMMENT R, MILLER D. Development of strength and maximum oxygen uptake during simultaneous training for strength and endurance. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 1987;27(3):269-275. [21] MIKKOLA J, VESTERINEN V, TAIPALE R, et al. Effect of resistance training regimens on treadmill running and neuromuscular performance in recreational endurance runners. J Sports Sci. 2011;29(13):1359-1371. [22] NELSON AG, ARNALL DA, LOY SF, et al. Consequences of combining strength and endurance training regimens. Phys Ther. 1990;70(5):287-294. [23] DUDLEY GA, FLECK SJ. Strength and endurance training. Are they mutually exclusive? Sports Med. 1987;4(2):79-85. [24] 鲁成阳.同期训练对羽毛球专项大学生力量、耐力素质影响的实验研究[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2020. [25] 李荣辉.力量与耐力不同组合训练方式对下肢爆发力的影响[D].西安:西安体育学院,2014. [26] DUDLEY GA, DJAMIL R. Incompatibility of endurance- and strength-training modes of exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1985;59(5):1446-1451. [27] GARCÍA-PINILLOS F, LAREDO-AGUILERA JA, MUÑOZ-JIMÉNEZ M, et al. Effects of 12-Week Concurrent High-Intensity Interval Strength and Endurance Training Program on Physical Performance in Healthy Older People. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(5): 1445-1452. [28] HÄKKINEN K, ALEN M, KRAEMER WJ, et al. Neuromuscular adaptations during concurrent strength and endurance training versus strength training. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003;89(1):42-52. [29] SALE DG, JACOBS I, MACDOUGALL JD, et al. Comparison of two regimens of concurrent strength and endurance training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1990;22(3):348-356. [30] 于洪军.论同期力量和耐力训练及其在竞技体育中的训练策略[J].体育科学,2014, 34(2):18-33. [31] GARCÍA-PALLARÉS J, SÁNCHEZ-MEDINA L, CARRASCO L, et al. Endurance and neuromuscular changes in world-class level kayakers during a periodized training cycle. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009;106(4):629-638. [32] 王玮. 同期训练对肌肉力量、爆发力及体成分的影响[D].太原:中北大学,2016. [33] 赵启昌. 同期力量和速度训练对普通体育高考生下肢快速力量影响的研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2020. [34] 张海鹏,马继政,徐盛嘉.耐力和力量同时训练计划的设计[J].运动精品,2020, 39(12):87-88. [35] HICKSON RC. Interference of strength development by simultaneously training for strength and endurance. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1980;45(2-3):255-263. [36] 马继政,胡澄,乔箐.力量和耐力组合训练分子产生的干扰机制和训练学上的对策[J].体育科技文献通报,2012,20(6): 14-19+31. [37] 江健康.浅析耐力训练与力量训练相结合的训练模式[J].体育科技文献通报,2011, 19(8):24-25. [38] 单磊.抗阻训练在有氧耐力运动项目中的影响[J].运动,2012(24):48-49+10. |
| [1] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [2] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [3] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [4] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [5] | Wei Zhoudan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan, Guo Dong, Hao Min. Platelet-rich fibrin as a material for alveolar ridge preservation significantly reduces the resorption of alveolar bone height and width after tooth extraction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 643-648. |
| [6] | Ou Liang, Kong Dezhong, Xu Daoqing, Ni Jing, Fu Xingqian, Huang Weichen. Comparative clinical efficacy of polymethyl methacrylate and self-solidifying calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 649-656. |
| [7] | Yang Ruijia, Jiang Lingkai, Dong Zhengquan, Wang Yunfei, Ma Zhou, Cong Linlin, Guo Yanjing, Gao Yangyang, Li Pengcui. Open reduction and internal fixation versus circular external fixation for tibial plateau fractures: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 480-486. |
| [8] | Zhong Yuanming, He Bingkun, Wu Zhuotan, Wu Sixian, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Jack kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 487-492. |
| [9] | Zhao Shuying, Guo Guangling, Liu Chenchen, Zhang Chao, Dong Sirui, Gong Qinqin, Ji Luwei. Stem cell transplantation in the treatment of premature ovarian failure: a meta-analysis based on 13 animal studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4084-4092. |
| [10] | Shi Yao, Han Shufeng, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Jing Zhijie, Zhao Bichun, Zhang Ruxin, Zhang Yujuan, Wang Chunfang. Efficacy and safety of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4093-4100. |
| [11] | Liang Meifu, Guo Wenxia, Zhao Ningning, Pan Lei. Determination and characteristics of skeletal muscle output power in different strength training methods under optimal power load [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3638-3643. |
| [12] | Hao Zhixin, Wu Yixin, Wang Xin, Xia Zhongliang. Effect of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation on muscle strength and endurance: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3273-3280. |
| [13] | Diao Yulei, Zong Xiaorui, Deng Zhibo, Shu Han. Analgesic effect of adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block after autogenous bone-tendon-bone reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament: an updated Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 315-320. |
| [14] | Zhou Junli, Wang Xiaojun, Wang Haijiao, Li Chun. A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of new medical dressings for diabetic foot ulcers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2562-2569. |
| [15] | Zhai Haiting, Li Cheng, Xia Jixiang, Wei Hongwen, Qin Shuang. Integrative neuromuscular training for injury prevention of lower extremity in athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2454-2460. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||