Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (26): 4118-4122.doi: 10.12307/2022.812
Previous Articles Next Articles
Up-regulating follicular regulatory T cells for treating antibody-mediated rejection after kidney transplantation
Xu Yuan1, Niu Yulin1, Yuan Zhihui1, Jia Lei2, Pan Guanghui1
- 1Department of Organ Transplantation, 2Department of Hepatological Surgery, the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-05Accepted:2021-08-21Online:2022-09-18Published:2022-03-08 -
Contact:Pan Guanghui, Chief physician, Department of Organ Transplantation, the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Xu Yuan, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Organ Transplantation, the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Young Science and Technology Talents Development Project of the Educational Department of Guizhou Province, No. KY[2018]190 (to XY); Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project of Guizhou Province, No. [2018]5779-47 (to XY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Yuan, Niu Yulin, Yuan Zhihui, Jia Lei, Pan Guanghui. Up-regulating follicular regulatory T cells for treating antibody-mediated rejection after kidney transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4118-4122.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
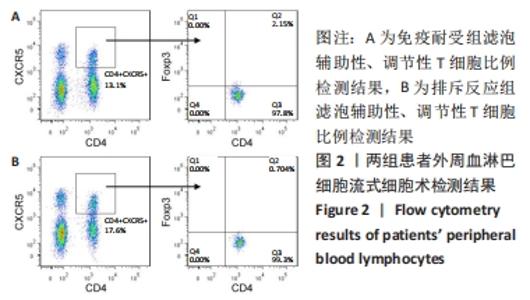
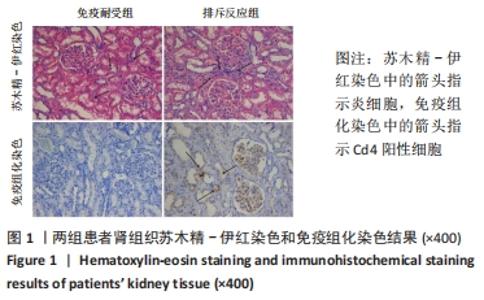
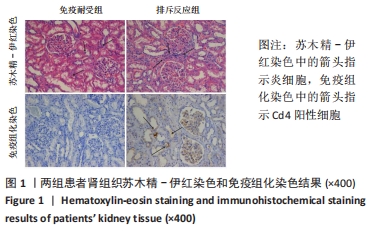
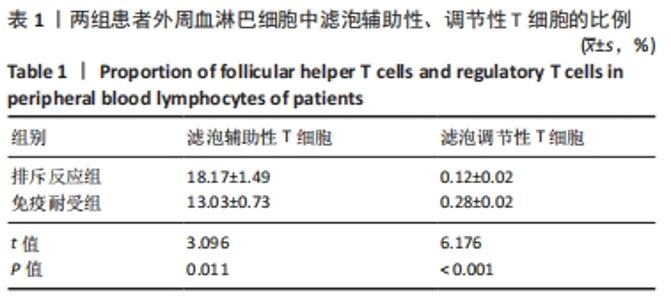
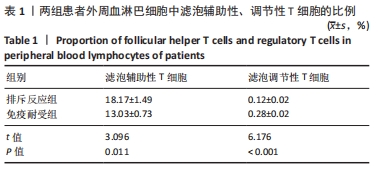
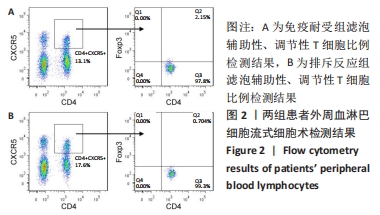
苏木精-伊红染色显示,排斥反应组患者肾组织内的炎细胞浸润数量多于免疫耐受组[(87.17±13.56),(18.11±3.95)个/视野,t=4.885,P < 0.001];免疫组化染色显示,排斥反应组患者肾组织内可见广泛的C4d阳性表达,免疫耐受组未见检测到C4d表达。 2.2 两组患者外周血淋巴细胞内的miR-4286 mRNA表达 RT-PCR检测结果显示,排斥反应组与免疫耐受组患者外周血淋巴细胞中的miR-4286 mRNA表达量分别为3.95±0.32,2.18±0.27,组间比较差异有显著性意义(t=4.331,P=0.002)。 2.3 两组患者外周血淋巴细胞中Tfh与Tfr细胞的比例 两组患者外周血淋巴细胞流式细胞术检测结果,见图2。"
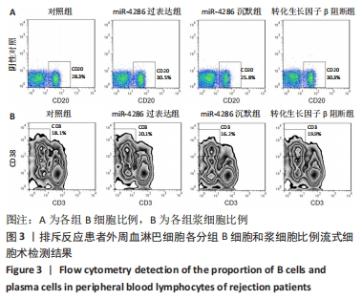
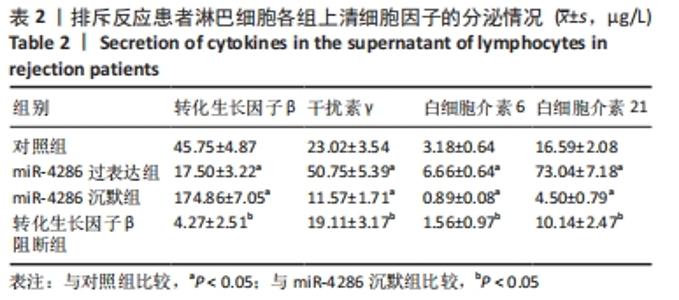
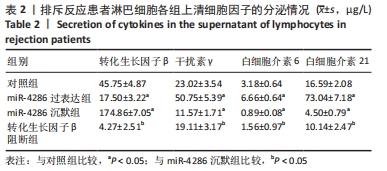
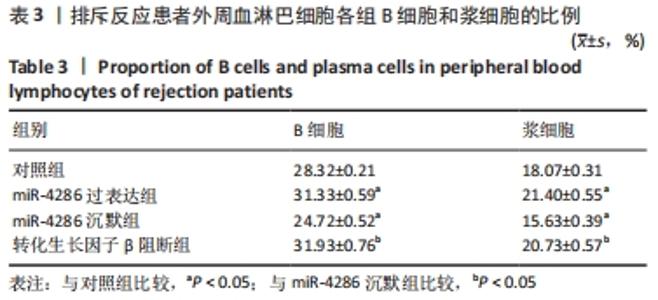
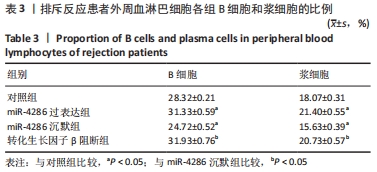
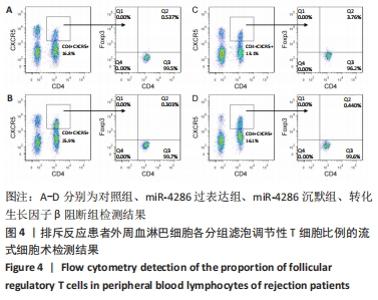
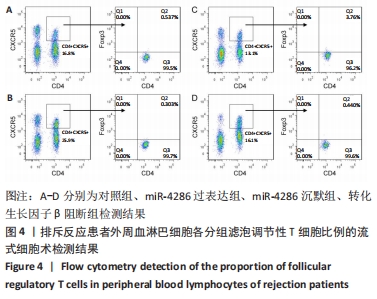
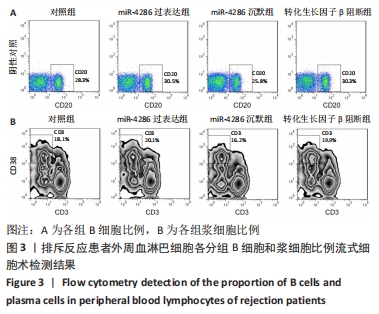
与对照组比较,miR-4286过表达组的转化生长因子β水平降低(t=4.846,P=0.003),干扰素γ、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素21水平升高(t=4.304,P=0.005;t=3.844,P=0.003;t=7.600,P < 0.001);miR-4286沉默组转化生长因子β水平升高(t=15.053,P < 0.001),干扰素γ、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素21水平降低(t=2.929,P=0.026;t=3.563,P=0.005;t=5.439,P < 0.001)。与miR-4286沉默组比较,转化生长因子β阻断组转化生长因子β水平降低(t=1.227,P < 0.001),干扰素γ、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素21水平升高(t=1.001,P < 0.05;t=2.441,P=0.005;t=1.554,P < 0.001)。 2.4.2 各组细胞中B细胞和浆细胞的比例 各组淋巴细胞B细胞和浆细胞比例流式细胞术检测结果,见图3。"
| [1] JORDAN SC, AMMERMAN N, CHOI J, et al. Novel Therapeutic Approaches to Allosensitization and Antibody-mediated Rejection. Transplantation. 2019;103(2): 262-272. [2] SCHINSTOCK CA, MANNON RB, BUDDE K, et al. Recommended Treatment for Antibody-mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation: The 2019 Expert Consensus From the Transplantion Society Working Group. Transplantation. 2020;104(5):911-922. [3] TSAI CC, CHEN TY, TSAI KJ, et al. NF-κB/miR-18a-3p and miR-4286/BZRAP1 axis may mediate carcinogenesis in Helicobacter pylori-Associated gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;132:110869. [4] AN X, GE J, GUO H, et al. Overexpression of miR-4286 is an unfavorable prognostic marker in individuals with non-small cell lung cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(10): 17573-17583. [5] LI Z, ZHAO S, WANG H, et al. miR-4286 promotes prostate cancer progression via targeting the expression of SALL1. J Gene Med. 2019;6:e3127. [6] KOMINA A, PALKINA N, AKSENENKO M, et al. Antiproliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Effects of MiR-4286 Inhibition in Melanoma Cells. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0168229. [7] HE Z, XUE H, LIU P, et al. miR-4286/TGF-β1/Smad3-Negative Feedback Loop Ameliorated Vascular Endothelial Cell Damage by Attenuating Apoptosis and Inflammatory Response. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020;75(5):446-454. [8] ZHANG M, TIAN H, LI R, et al. MicroRNA-4286 promotes esophageal carcinoma development by targeting INPP4A to evoke the JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation. Pharmazie. 2018;73(6):342-348. [9] LING C, WANG X, ZHU J, et al. MicroRNA-4286 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via PTEN regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2019;8(7):3520-3531. [10] JUNO JA, TAN HX, LEE WS, et al. Humoral and circulating follicular helper T cell responses in recovered patients with COVID-19. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1428-1434. [11] JI LS, SUN XH, ZHANG X, et al. Mechanism of Follicular Helper T Cell Differentiation Regulated by Transcription Factors. J Immunol Res. 2020;2020:1826587. [12] LOUPY A, HAAS M, ROUFOSSE C, et al. The Banff 2019 Kidney Meeting Report (I): Updates on and clarification of criteria for T cell- and antibody-mediated rejection. Am J Transplant. 2020;20(9):2318-2331. [13] 赵敏,厉永强,石贞玉.miR-4286靶向FOXO4对肺癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭及凋亡的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021,37(8):958-963. [14] GLOTZ D, RUSS G, ROSTAING L, et al. Safety and efficacy of eculizumab for the prevention of antibody-mediated rejection after deceased-donor kidney transplantation in patients with preformed donor-specific antibodies. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(10):2865-2875. [14] MARKS WH, MAMODE N, MONTGOMERY RA, et al. Safety and efficacy of eculizumab in the prevention of antibody-mediated rejection in living-donor kidney transplant recipients requiring desensitization therapy: A randomized trial. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(10):2876-2888. [16] NGUYEN VP, KOBASHIGAWA JA. Antibody-medicated rejection after heart transplantation: diagnosis and clinical implications. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2020;25(3):248-254. [17] PALADINI SV, PINTO GH, BUENO RH, et al. Identification of Candidate Biomarkers for Transplant Rejection from Transcriptome Data: A Systematic Review. Mol Diagn Ther. 2019;23(4):439-458. [18] WANG X, CAO J, YU Y, et al. Role of MicroRNA 146a in Regulating Regulatory T Cell Function to Ameliorate Acute Cardiac Rejection in Mice. Transplant Proc. 2019;51(3):901-912. [19] SALIMINEJAD K, KHORRAM KHORSHID HR, SOLEYMANI FARD S, et al. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5451-5465. [20] YU H, WANG K, LIU P, et al. miR-4286 functions in osteogenesis and angiogenesis via targeting histone deacetylase 3 and alleviates alcohol-induced bone loss in mice. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(6):e13054. [21] BENGONE-ABOGOURIN JG, CHELKHA N, VERDIN E, et al. Sequence Similarities between Viroids and Human MicroRNAs. Intervirology. 2019;62(5-6):227-234. [22] HU Z, LV X, CHEN L, et al. Protective effects of microRNA-22-3p against retinal pigment epithelial inflammatory damage by targeting NLRP3 inflammasome. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18849-18857. [23] FRASCÀ GM, BRIGANTE F, VOLPE A, et al. Kidney transplantation in patients with previous renal cancer: a critical appraisal of current evidence and guidelines. J Nephrol. 2019;32(1):57-64. [24] LIU Y, JI H, ZHAO P, et al. Follicular helper T cell and memory B cell immunity in CHC patients. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(3):397-407. [25] WU H, DENG Y, ZHAO M, et al. Molecular Control of Follicular Helper T cell Development and Differentiation. Front Immunol. 2018;9: 470. [26] ZHU Y, ZHAO Y, ZOU L, et al. The E3 ligase VHL promotes follicular helper T cell differentiation via glycolytic-epigenetic control. J Exp Med. 2019;216(7):1664-1681. [27] YANG J, BI L, HE X, et al. Follicular Helper T Cell Derived Exosomes Promote B Cell Proliferation and Differentiation in Antibody-Mediated Rejection after Renal Transplantation. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:6387924. |
| [1] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [2] | Yang Zhiwei, Liu Junchang, Gao Xiaolin, Jiang Taimao. Relationship between tacrolimus metabolic rate and early BK virus infection after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 712-716. |
| [3] | Liu Ya, Liu Xia, Deng Penghui, Ji Wei, Li Jianping. Exercise effects on myocardial type I, III collagen and angiotensin II/transforming growth factor beta1/Smad2 pathway in diabetic myocardial fibrosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4173-4179. |
| [4] | Zhang Rong, Liang Zhenting, Yang Chun, Liu Dongdong, Xi Yin, Zhang Jie, Wang Ya, Xu Yonghao, Liu Xiaoqing, Li Yimin. Effects of mechanical stretch on fiber proliferation in human lung epithelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3821-3825. |
| [5] | Yang Wei, Yuan Puwei, Du Longlong, Li Xuefeng, Gao Qimeng, Han Qingmin. Bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profile of peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3706-3713. |
| [6] | Yang Shukai, Wa Qingbiao, Yuan Xiaoyan. Moist exposed burn ointment intervenes with wound healing and expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin in burn model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3762-3767. |
| [7] | Wan Zhen, Wang Xuzhen, Zhang Xiaogang. CTLA4.FasL promotes the engraftment of xenogeneic hepatic oval cells in rat spleen [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3728-3732. |
| [8] | Zhao Jirong, Yang Tao, Xu Jiancheng, Zhao Ning, Xue Xu, Ma Tong. Action and mechanism of autologous bone marrow aspiration concentrate in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2938-2944. |
| [9] | Xiong Yang, Yang Yingli, Gao Yushan, Wang Xiumei, Yang Yongdong, Zhao Dingyan, Zhao He, Li Chuanhong, Yang Kaitan, Yu Xing. Histological changes of cervical disc tissue and underlying ossification mechanism in patients with cervical degenerative ossification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2868-2873. |
| [10] | Hu Yanan, Wang Ping, Du Haitao, Jing Tianyuan, Wang Chengcheng. Mechanism by which antler glue treats avascular necrosis of the femoral head induced by retinoic acid in rats: a serum proteomics study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2243-2251. |
| [11] | Hu Yihua, Yang Chunhua, Lu Yuanyuan, Sun Deyi. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with triptolide on transforming growth factor beta expression in synovium and synovial fluid in a mouse model of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2252-2258. |
| [12] | Hu Mingzhi, Zhang Jingying, Yang Guoan, Pang Chunyan, Zhang Wei, Wang Yongfu, Sun Xiaolin. Immunomodulatory effects of umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-1-5p on T lymphocyte subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4928-4938. |
| [13] | He Yixiang, Zhao Yuhao, Gao Zhao, Zhao Haiyan, Wang Wenji. Effect of B lymphocytes and related cytokines on osteoclast differentiation in the osteoimmunology system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4709-4714. |
| [14] | Liu Zhijun, Liu Shaojin, Wei Hewei, Wan Lei, Huang Hongxing, Qiao Rongqin. Effect of Bushen Jianpi Huoxue Recipe on transforming growth factor beta/bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in the muscle and skeleton of ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2219-2223. |
| [15] | Wang Xiaobo, Wang Changan, Han Jianle, Yang Qingyan, Yang Shuaiping, Yang Junwei. Influence of conversion from cyclosporine to tacrolimus on glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk profiles in stable kidney transplant patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2236-2240. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||