[1] 于勇,刘静华,赵罡.与基于模型定义技术相融合的工程图学课程教学探讨[J].图学学报,2019,40(4):816-821.
[2] 吴泽斌,张东亮,李基拓,等.复杂场景下的人体轮廓提取及尺寸测量[J].图学学报,2020,41(5):740-749.
[3] 张延恒,莫春晖,张莹,等.移动式康复训练机器人及下肢康复运动分析[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(3):6-11.
[4] ADOUNI M, FAISAL TR, GAITH M, et al. A multiscale synthesis: characterizing acute cartilage failure under an aggregate tibiofemoral joint loading. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2019;18(6):1563-1575.
[5] 白云峰,吴汉忠,刘建辉.一种可穿戴下肢外骨骼机器人的结构设计与仿真[J].毛纺科技,2021,49(7):68-74.
[6] 李书阁,赵鹏举,王伟强.基于连杆机构的四足仿生机器人的设计[J].装备制造技术,2021(6):23-26.
[7] 史亦凡,管小荣.外肢体机器人的运动分析与控制仿真[J].兵器装备工程学报,2021,42(4):218-223.
[8] WANG JP, WANG SH, WANG YQ, et al. A data process of human knee joint kinematics obtained by motion-capture measurement. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021;21(1):121.
[9] 王建平,梁军,张雁儒,等.人体膝关节股胫关节运动特性分析[J].中国临床解剖学,2017,35(1):62-68.
[10] 王建平,符龙,张雁儒,等.正常膝关节和人工膝关节髌股关节高屈曲运动特性及其比较分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(4): 432-438.
[11] BENOIT DL, RAMSEY DK, LAMONTAGNE M, et al. Effect of skin movement artifact on knee kinematics during gait and cutting motions measured in vivo. Gait Posture. 2006;24(2):152-164.
[12] ISAAC DL, BEARD DJ, PRICE AJ, et al. In-vivo sagittal plane knee kinematics: ACL intact, deficient and reconstructed knees. Knee. 2005; 12(1):25-31.
[13] REES JL, BEARD DJ, PRICE AJ, et al. Real in vivo kinematic differences between mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(432):204-209.
[14] 王建平,赵烜,胡海,等.基于MATLAB的人体膝关节运动捕捉测量与分析[J].河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,39(3):86-93.
[15] 劳峥,樊文慧.医学图像处理MIM软件和Velocity软件在弹性模体中形变配准精度的比较研究[J].中国医学装备,2021,18(6):47-51.
[16] ZHANG J, LIU F, YU X, et al. A 3D medical image registration method based on multi-scale feature fusion. Journal of Physics Conference Series. 1948(1):012057.
[17] LUO Y, CAO W, HE Z, et al. Deformable adversarial registration network with multiple loss constraints. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2021;91: 101931.
[18] 宋枭,朱家明,徐婷宜.基于B样条仿射和GANs的医学图像配准[J].无线电工程,2021,51(6):433-439.
[19] SAEIDI M, GUBAUA JE, KELLY P, et al. The influence of an extra-articular implant on bone remodelling of the knee joint. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2020;19(1):37-46.
[20] 骆健,王立华,王涛.不同材料赋值方法下踝关节三维有限元模型的应力及位移变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):2822-2826.
[21] 刘韵婷,郭辉,黄将诚.基于UG与ADAMS的人体下肢骨骼肌建模及仿真[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11):1719-1724.
[22] 余华,李少星,赵长义.胫骨远端关节面缺损有限元模型的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(43):7571-7580.
[23] WANG JP, GUO D, WANG SH, et al. Structural stability of a polyetheretherketone femoral component-A 3D finite element simulation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2019;70:153-157.
[24] 何晓宇,王朝强,周之平.三维有限元方法构建足部健康骨骼与常见疾病模型及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9): 1410-1415.
[25] 张吉超,董万鹏.膝关节有限元模型参数设置[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(30):4781-4786.
[26] 高辉,王晨艳.,不同屈曲状态下固定轴和移动轴膝关节胫-股关节的生物力学变化[J].太原理工大学学报,2021,52(1):144-150.
[27] 侯波,王毅,沈宇辉.膝关节动态有限元模型的力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(22):3998-4004.
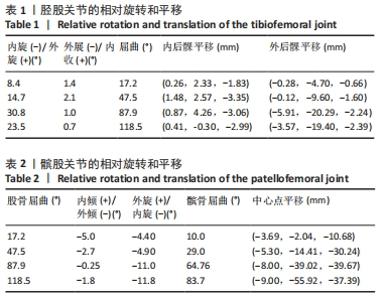
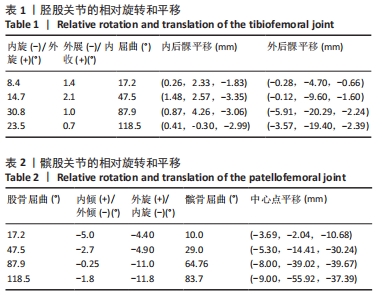
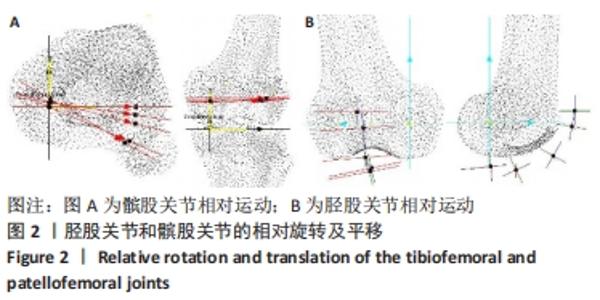
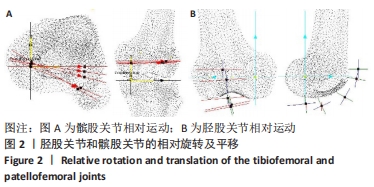
[28] 王建平,韩雪莲,季文婷,等.人体膝胫股关节相对运动的三维图像配准分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2009,26(6):1340-1344.
[29] ASANO T, AKAGI M, KOIKE K, et al. In vivo three-dimensional patellar tracking on the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(413):222-232.
[30] JOHAL P, WILLIAMS A, WRAGG P, et al. Tibio-femoral movement in the living knee. A study of weight bearing and non-weight bearing knee kinematics using ‘interventional’ MRI. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):269-276.
[31] ASANO T, AKAGI M, TANAKA K, et al. In vivo three-dimensional knee kinematics using a biplanar image-matching technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(388):157-166.
[32] IWAKI H, PINSKEROVA V, FREEMAN MA. Tibiofemoral movement 1: the shapes and relative movements of the femur and tibia in the unloaded cadaver knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(8):1189-1195.
[33] BULL AM, AMIS AA. Knee joint motion: description and measurement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 1998;212(5):357-372.
[34] CHURCHILL DL, INCAVO SJ, JOHNSON CC, et al. The transepicondylar axis approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(356):111-118.
|