Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 1720-1727.doi: 10.12307/2022.357
Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification and analysis of potential key genes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on miRNA-mRNA regulatory network
Liang Xuezhen1, Xie Guoxin2, Li Jiacheng1, Wen Mingtao2, Xu Bo1, Li Gang1, 3
- 1The First Clinical Medical School, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedic Microsurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2020-11-23Revised:2020-11-28Accepted:2021-03-27Online:2022-04-18Published:2021-12-11 -
Contact:Li Gang, MD, Professor, Chief physician, The First Clinical Medical School, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; Department of Orthopedic Microsurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liang Xuezhen, MD, Lecturer, Attending physician, The First Clinical Medical School, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82074453 (to LG); Shandong Provincial Medicine and Health Technology Development Project, No. 2019WS577 (to LXZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Xuezhen, Xie Guoxin, Li Jiacheng, Wen Mingtao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Identification and analysis of potential key genes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on miRNA-mRNA regulatory network[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1720-1727.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
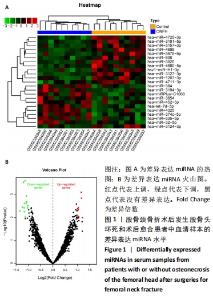
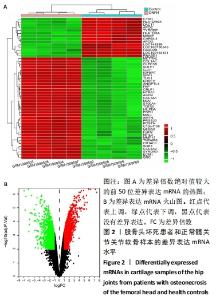
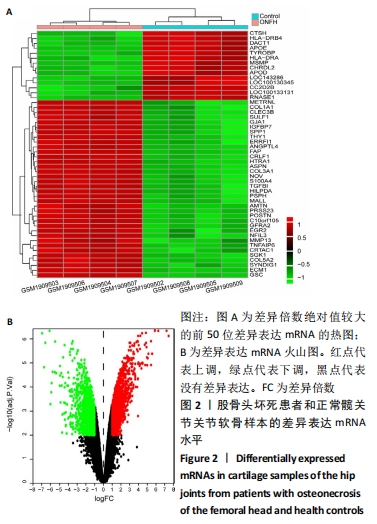
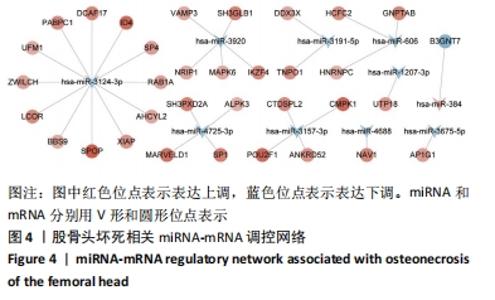
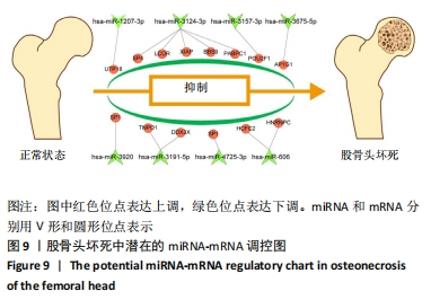
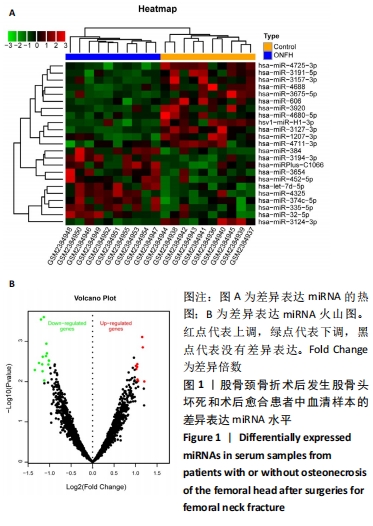
2.1 差异表达的miRNA GSE89587数据集中股骨颈骨折术后发生股骨头坏死和股骨颈骨折术后愈合患者的血清样本相比,获取差异表达 miRNA有23个,包括10个表达上调 (hsa-miR-4325,hsa-miR-3654,hsa-miR-3194-3p,hsa-miR-384,hsa-miR-335-5p,hsa-miRPlus-C1066,hsa-miR-32-5p,hsa-let-7d-5p,hsa-miR-374c-5p,hsa-miR-452-5p)和13个表达下调(hsa-miR-4680-5p,hsa-miR-4711-3p,hsa-miR-3127-3p,hsa-miR-3157-3p,hsa-miR-3920,hsa-miR-1207-3p,hsa-miR-4725-3p,hsa-miR-3124-3p,hsa-miR-606,hsv1-miR-H1-3p,hsa-miR-3191-5p,hsa-miR-3675-5p,hsa-miR-4688),各miRNA的火山图和聚类图,见图1。"
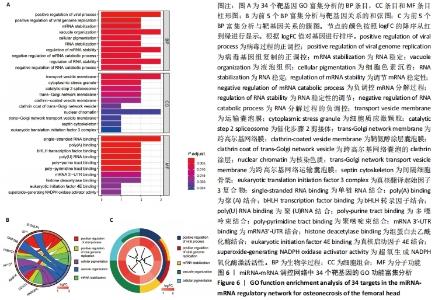
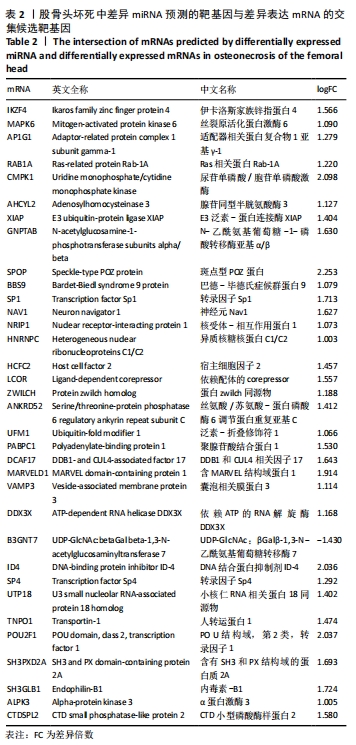
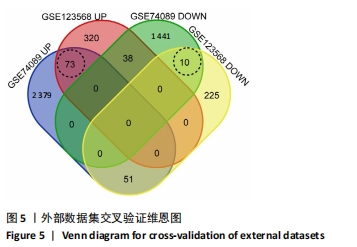
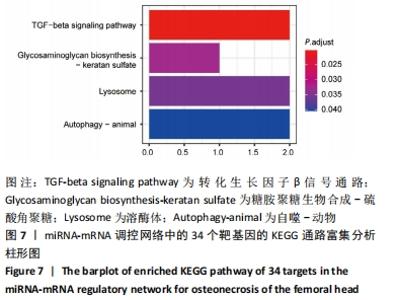
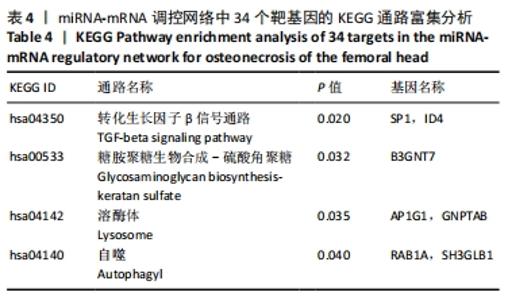
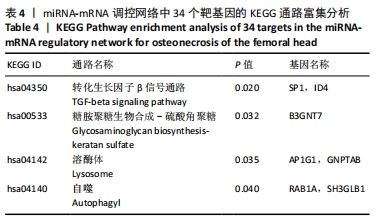
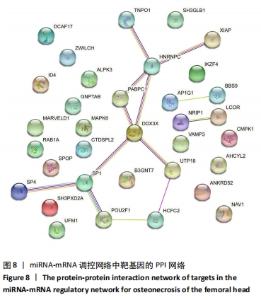
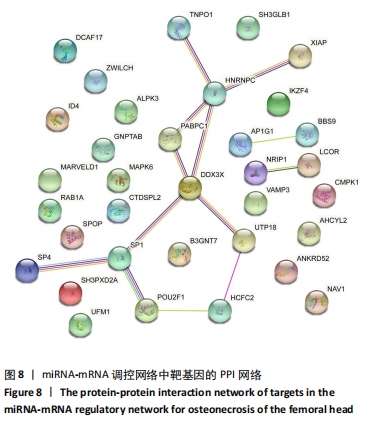
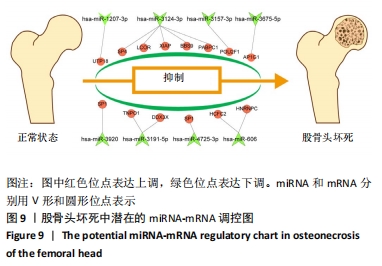
2.5 网络靶基因功能分析结果 通过R软件clusterProfiler包对miRNA-mRNA调控网络中的靶基因进行GO功能和KEGG通路富集分析,得到218个GO富集条目,其中包括150个BP条目、33个CC条目和35个MF条目。BP主要富集在病毒过程的正调控、病毒基因组复制的正调控、RNA稳定、液泡组织、细胞色素沉着、调节mRNA稳定性、负调控mRNA分解过程、RNA稳定性的调节、RNA分解过程的负调控及调节mRNA分解过程等方面;CC主要富集在运输囊泡膜、细胞质应激颗粒、催化步骤2剪接体、跨高尔基网络膜、鞘氨醇涂层囊泡膜、核染色质、跨高尔基网络运输囊泡膜及间隔细胞骨架等;MF主要富集在单链RNA结合、poly(A)结合、转录因子结合、poly(U) RNA结合及嘌呤束结合等,富集前5个BP、CC和MF条目见图6A。为显示更小的高维数据子集,使用R软件GOplot包绘制弦图(Chord)和簇图(Cluster)以展示最显著富集的5个GO结果,见图6B,6C。KEGG通路富集分析得到4条信号通路,主要为转化生长因子β信号通路、糖胺聚糖生物合成-硫酸角聚糖、溶酶体及自噬等,见图7,表4。"

| [1] LI R, LIN QX, LIANG XZ, et al. Stem cell therapy for treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head: from clinical applications to related basic research. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):291. [2] 孙笛,赵李奔,刘春晖,等.股骨头坏死危险因素流行病学分析[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2016,23(S1):10-11. [3] ZHAO DW, YU M, HU K, et al. Prevalence of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head and its associated risk factors in the chinese population: results from a nationally representative survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21):2843-2850. [4] 曾祥洪,梁博伟.股骨头坏死保髋治疗的新策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(3):431-437. [5] 张颖,张蕾蕾,柴玉娜,等.创伤性股骨头坏死中差异miRNA的筛选与验证[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(11):978-985. [6] GENNARI L, BIANCIARDI S, MERLOTTI D. MicroRNAs in bone diseases. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(4):1191-1213. [7] 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨循环与骨坏死专业委员会,中华医学会骨科分会骨显微修复学组,国际骨循环学会.中国区中国成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2020)[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(20): 1365-1376. [8] CUI D, ZHAO D, WANG B, et al. Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) polysaccharide attenuates cellular apoptosis in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head by targeting caspase-3-dependent signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;116:106-112. [9] ZHANG Y, YIN J, DING H, et al. Vitamin k2 ameliorates damage of blood vessels by glucocorticoid: a potential mechanism for its protective effects in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in a rat model. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(7):776-785. [10] LI GQ, WANG ZY. MiR-20b promotes osteocyte apoptosis in rats with steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head through BMP signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(11):4599-4608. [11] DONG Y, LI T, LI Y, et al. MicroRNA-23a-3p inhibitor decreases osteonecrosis incidence in a rat model. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(6): 9331-9336. [12] LIU Y, ZONG Y, SHAN H, et al. MicroRNA-23b-3p participates in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by suppressing ZNF667 expression. Steroids. 2020;163:108709. [13] XU W, LI J, TIAN H, et al. MicroRNA‑186‑5p mediates osteoblastic differentiation and cell viability by targeting CXCL13 in non‑traumatic osteonecrosis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(5):4594-4602. [14] WANG C, SUN W, LING S, et al. AAV-Anti-miR-214 prevents collapse of the femoral head in osteonecrosis by regulating osteoblast and osteoclast activities. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;18:841-850. [15] FANG SH, CHEN L, CHEN HH, et al. MiR-15b ameliorates SONFH by targeting Smad7 and inhibiting osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(22):9761-9771. [16] YU L, XU Y, QU H, et al. Decrease of MiR-31 induced by TNF-α inhibitor activates SATB2/RUNX2 pathway and promotes osteogenic differentiation in ethanol-induced osteonecrosis. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(4):4314-4326. [17] ZHANG Y, WEI QS, DING WB, et al. Increased microRNA-93-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation by targeting bone morphogenetic protein-2. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0182678. [18] LIAO W, NING Y, XU HJ, et al. BMSC-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-122-5p promote proliferation of osteoblasts in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019;133(18):1955-1975. [19] SUN Z, WU F, YANG Y, et al. MiR-144-3p Inhibits BMSC Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation Via Targeting FZD4 in Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(45):4806-4812. [20] ZHANG WL, CHI CT, MENG XH. miRNA‑15a‑5p facilitates the bone marrow stem cell apoptosis of femoral head necrosis through the Wnt/β‑catenin/PPARγ signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(6): 4779-4787. [21] MENG CY, XUE F, ZHAO ZQ, et al. Influence of MicroRNA-141 on Inhibition of the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in steroid-induced osteonecrosis via SOX11. Orthop Surg. 2020; 12(1):277-285. [22] XIE Y, HU JZ, SHI ZY. MiR-181d promotes steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by targeting SMAD3 to inhibit osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(13):4053-4062. [23] XU HJ, LIAO W, LIU XZ, et al. Down-regulation of exosomal microRNA-224-3p derived from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells potentiates angiogenesis in traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. FASEB J. 2019;33(7):8055-8068. [24] TIAN ZJ, LIU BY, ZHANG YT, et al. MiR-145 silencing promotes steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head repair via upregulating VEGF. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(17):3763-3769. [25] PENG WX, YE C, DONG WT, et al. MicroRNA-34a alleviates steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head by targeting Tgif2 through OPG/RANK/RANKL signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017; 242(12):1234-1243. [26] ZHA X, SUN B, ZHANG R, et al. Regulatory effect of microRNA-34a on osteogenesis and angiogenesis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(1):417-424. [27] KONG L, ZUO R, WANG M, et al. Silencing microRNA-137-3p, which targets RUNX2 and CXCL12 prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by facilitating osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(4):655-670. [28] CHAO PC, CUI MY, LI XA, et al. Correlation between miR-1207-5p expression with steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head and VEGF expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(7):2710-2718. [29] LIU XD, CAI F, LIU L, et al. MicroRNA-210 is involved in the regulation of postmenopausal osteoporosis through promotion of VEGF expression and osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2015;396(4):339-347. [30] GU C, XU Y, ZHANG S, et al. miR-27a attenuates adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis in steroid-induced rat BMSCs by targeting PPARγ and GREM1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38491. [31] SUN J, WANG Y, LI Y, et al. Downregulation of PPARγ by miR-548d-5p suppresses the adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and enhances their osteogenic potential. J Transl Med. 2014;12:168. [32] ZHAO SR, WEN JJ, MU HB. Role of Hsa-miR-122-3p in steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(3 Suppl): 54-59. [33] LI G, LIU H, ZHANG X, et al. The protective effects of microRNA-26a in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by repressing EZH2. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(5):551-566. [34] WEI JH, LUO QQ, TANG YJ, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-320 decreases the risk of developing steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head by inhibiting CYP1A2 both in vivo and in vitro. Gene. 2018;660:136-144. [35] HUANG S, LI Y, WU P, et al. microRNA-148a-3p in extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppresses SMURF1 to prevent osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(19):11512-11523. [36] 董政权,魏垒.骨关节炎基因差异谱的生物信息学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(3):335-340. [37] SAFE S, IMANIRAD P, SREEVALSAN S, et al. Transcription factor Sp1, also known as specificity protein 1 as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014;18(7):759-769. [38] LIU D, WANG Y, PAN Z, et al. cAMP regulates 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-2 and Sp1 expression in MLO-Y4/MC3T3-E1 cells. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(3):2166-2172. [39] 许灿宏,陈跃平,章晓云.成骨信号通路在非创伤性股骨头坏死中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(14):2235-2242. [40] TAO J, DONG B, YANG LX, et al. TGF‑β1 expression in adults with non‑traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16(6):9539-9544. [41] BAI Y, LIU Y, JIN S, et al. Expression of microRNA‑27a in a rat model of osteonecrosis of the femoral head and its association with TGF‑β/Smad7 signalling in osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):850-860. |
| [1] | Bao Xianguo, Gao Zengxin, Wu Zhanpo, Chen Youmin, Cheng Qinghua, Lu Haitao, Guo Changzheng, Xu Shuai. Correlation between lumbar posterior muscle and local kyphosis in patients with degenerative thoracolumbar kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1418-1423. |
| [2] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [3] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [4] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [5] | Li Huo, Wang Peng, Gao Jianming, Jiang Haoran, Lu Xiaobo, Peng Jiang. Relationship between revascularization and internal microstructure changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [6] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [7] | Li Zhiyi, He Pengcheng, Bian Tianyue, Xiao Yuxia, Gao Lu, Liu Huasheng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1202-1209. |
| [8] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [9] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [10] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [11] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [12] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [13] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [14] | Wen Xiaoyu, Sun Yuhao, Xia Meng. Effects of serum containing Wuzang Wenyang Huayu Decoction on phosphorylated-tau protein expression in Alzheimer’s disease cell model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1068-1073. |
| [15] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||