Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (5): 792-797.doi: 10.12307/2022.129
Previous Articles Next Articles
Sarcopenia: age-related muscle mass loss and functional declines
Zheng Zhenquan, Rong Jiesheng
- Second Ward of Orthopedic Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150081, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2020-12-28Revised:2021-01-05Accepted:2021-01-30Online:2022-02-18Published:2021-12-02 -
Contact:Rong Jiesheng, MD, Associate professor, Second Ward of Orthopedic Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150081, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Zheng Zhenquan, Master, Second Ward of Orthopedic Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150081, Heilongjiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Zhenquan, Rong Jiesheng. Sarcopenia: age-related muscle mass loss and functional declines[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 792-797.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
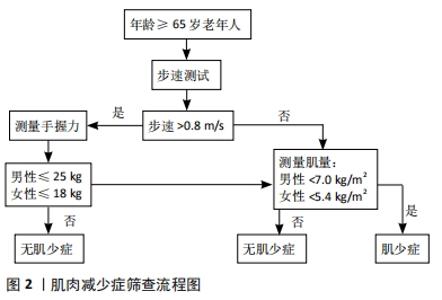
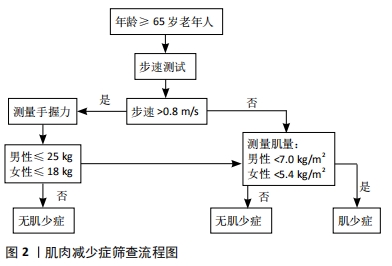
2.1 肌肉减少症的定义 肌肉减少症(Sarcopenia)这一术语由Rosenberg于1989年首次提出[6]。肌肉减少症缺乏特异的临床表现,患者可表现为虚弱、行走困难、步态缓慢、容易跌倒和无力等[7],其病因及发病机制十分复杂,缺乏体力活动和蛋白质摄入不足被认为是导致肌肉减少症的危险因素[8]。目前的研究表明,蛋白质合成和降解、线粒体功能障碍、骨骼肌干细胞自噬和卫星干细胞活化受损可能参与了肌肉减少症发生的分子机制[9]。随着人们对肌肉减少症认识程度的加深,它的定义也在逐步完善。2010年,欧洲老年肌少症工作组(EWGSOP)就肌肉减少症的定义和诊断标准达成了共识,将肌肉减少症定义为与年龄增长有关的进行性骨骼肌量减少、伴有肌肉力量和/或肌肉功能下降,并能引起一系列不良后果的综合征[10]。2018年EWGSOP 根据最新研究进展修订了欧洲肌少症共识(EWGSOP2),对肌肉减少症的定义做出了更新,认为肌力是衡量肌肉功能最可靠的指标,突出强调了肌力的减退是肌肉减少症的特征性的表现,骨骼肌质量及数量的减少是其临床诊断依据,机体功能降低是严重肌肉减少症的标志[11]。 2.2 肌肉减少症临床研究中常用的测量方法 自从肌肉减少症这一概念提出后,大部分学者认为,测定全身或四肢肌肉质量组成,是诊断肌肉减少症的一个重要依据[12]。根据2010年EWGSOP制定的标准化定义,诊断肌肉减少症除了要求具有低肌肉质量以外,还需满足低肌肉功能的条 件[10],而握力和步行速度测试最常见的肌肉功能测试,具有方便易行的特点。对于肌肉质量的检测,不同学者在研究中采用的方法还存有差异。Han等[13]学者在PubMed上以“sarcopenia”进行检索,纳入标准包括英语语言、原始数据、肌肉减少症的诊断,以及肌肉减少症对临床结果的影响。结果在283项研究中有264项(93.3%)使用骨骼肌质量作为诊断指标。骨骼肌质量的测量方法包括双能X射线吸收法(DXA)、生物电阻抗分析以及使用CT计算第三腰椎骨骼肌指数等,其中DXA是诊断肌肉减少症最常用的肌肉质量检测方法,占有43.6%的比例。 结合国内外的相关研究发现,不同地域人种的差异导致肌肉减少症诊断标准存在着不同[10-11,14-15]。2014年亚洲肌少症工作组(AWGS)确定了亚洲人肌肉质量减少的参考指标:使用 DXA测定出四肢骨骼肌质量,再除以身高的平方作为四肢骨骼肌指数(ASMI),若男性<7.0 kg/m2,女性<5.4 kg/m2 则考虑存在肌肉质量减少[14]。中国人群肌肉减少症的筛查与评估,同样参考此标准,并结合了男女握力及步速指标。具体流程推荐参照2016年发表的《肌少症共识》[7] (见图2)。"

2.3 肌肉减少症在人群中患病情况 研究人群的特点(如年龄、性别、种族等)以及用于评估肌肉减少症的方法会导致不同研究者对肌肉减少症患病率的统计出现很大的差异。不同国家及地区结合自身特点采用统一的诊断标准可以尽可能地得出真实的患病率。Shafiee等[1]检索了2009年1月至2016年12月期间的PubMed、Web of Science等电子数据库,纳入了35项研究进行Meta分析。这些研究均采用EWGSOP、IWGS、AWGS诊断标准来确定肌肉减少症,并且要求60岁及以上的正常人群参与研究,共有58 404人符合标准,其中男性32 642人(55.9%),女性25 762人(44.1%);35项研究中,21项来自亚洲,14项研究属于非亚洲国家;最终结果表明肌肉减少症的总体患病率男性为10%(95%CI:8%-12%),女性为10%(95%CI:8%-13%)。这说明肌肉减少症在60岁以上老年群体中占有很大比例,需要引起更多的注意。 2.4 肌肉减少症与骨折的相关性 肌肉力量不足、久坐不动的生活方式和较差的身体功能与较高的骨折风险相关[16]。而患有肌肉减少症的老年人肌肉质量减少、肌肉力量减弱、肌肉功能减退,导致他们更容易跌倒,加上老年群体骨量丢失,骨密度的下降,相较于年轻人有更大的概率发生骨折。最近的一项研究显示,肌肉减少症的发生率在髋部骨折中占41.5%、在脊椎骨折占35%,而在桡骨远端骨折中占29.6%[17]。 文章讨论肌肉减少症与骨折的相关性主要针对肌肉减少症和骨质疏松症对骨折造成联合影响,因为肌肉减少症与骨质疏松症常常密不可分,肌肉和骨骼系统,在生命过程中相互联系,它们起源于近轴中胚层的体节,协同发育,同时老化,在解剖和生化方面相互作用,通过肌动蛋白和骨因子等旁分泌信号相互协调。以肌肉生理改变为特征的疾病将会影响骨的重塑和结构,反之亦然[18]。虽然目前很少有临床数据证明骨质疏松症和肌肉减少症之间的因果关系,两者同时作用会极大增加骨折的风险,对患者造成严重的临床后果。在CHALHOUB等[19]的研究中,单独患有肌肉减少症或骨质疏松症的男性骨折风险分别为普通患者的1.20倍和1.82倍,但同时患有肌肉减少症和骨质疏松症的男性骨折风险显著增加到了4.08倍,肌肉减少症和骨质疏松症对骨折风险的联合影响大于单个风险的总和。另有针对中国老年人的研究表明,在中国老年人髋部脆性骨折患者中,男性中有高达84.1%的人患有肌肉减少症,而女性人数占比相对较少,但也达到了41.9%[20]。 肌肉减少症合并骨质疏松症除了增加老年患者的跌倒和骨折风险以外,对骨折的治疗与恢复往往带来更为负面的影响。ZHANG等[21]学者以高龄骨质疏松症伴有肌肉减少症(SAMP8)/不伴肌肉减少症(SAMR1)的小鼠为动物模型,通过测量两个品系动物第5腰椎的骨密度和肌肉测试,来确定骨质疏松症和肌肉减少症的状况。人为造成8月龄动物右侧股骨闭合性骨折,骨折后每周拍1次X射线片,分别于骨折后2,4,6周进行股骨显微CT检查和组织学检查,并于骨折后4,6周进行双侧股骨力学测试。结果表明SAMP8组Ⅱ型肌纤维的肌肉质量和面积百分比减少,但Ⅰ型肌纤维增加;SAMR1组的骨痂在骨折后2周明显大于SAMP8组,而在第6周明显小于SAMP8组;骨折后第4周,SAMR1组的力学性能明显好于SAMP8组。这项研究验证了在肌肉减少症和骨质疏松性骨折共存的动物模型中,肌肉减少症可导致骨折愈合延迟。 患有肌肉减少症的骨质疏松症患者骨折后死亡率相比单纯骨质疏松症患者要更高。KIM等[22]对91例髋部骨质疏松性骨折患者在术后1年内进行CT检查,使用第3腰椎水平的骨骼肌指数来定义肌肉减少症,根据有无肌肉减少症对所有患者分为2组,比较1年和5年死亡率。在45例肌肉减少症患者中,1年和5年死亡率分别为22.2%和82.7%;在46例无肌肉减少症患者中,1年和5年死亡率分别为19.6%和52.7%;Kaplan-Meier分析结果显示,肌肉减少症对1年死亡率没有影响(P=0.793),但对5年死亡率却有着显著的影响(P=0.028)。 患有肌肉减少症的老年人发生骨折风险增加,而对于骨质疏松症的患者来说,肌肉减少症将会造成更坏的影响,这部分人群需要得到骨科医师更多的重视。 2.5 肌肉减少症的预防及治疗 2.5.1 营养干预 食欲不佳是居住在家里和疗养院的老年人以及医院住院患者的常见问题,这可能与年龄增长随之而来的生理和心理变化有关,它可以导致体质量减轻和营养缺乏,带来相关的不良医疗后果,包括死亡率增加等[23]。而营养不良的老年患者与营养状态正常的患者相比食欲也不如后者[24],食欲不振无疑会导致老年人进一步营养缺乏、体力下降,形成恶性循环。因此进行有效的营养干预对老年人十分重要,尤其是对于和衰老密切相关的老年肌肉减少症患者。 对肌肉减少症有潜在益处的营养素包括优质蛋白质、亮氨酸、β-羟基β-甲基丁酸、维生素D、omega-3脂肪酸等。更健康的饮食通常具有最佳的能量和蛋白质摄入量,更多的维生素D和omega-3脂肪酸的摄入量与更好的肌肉健康相关[25]。 (1)蛋白质和氨基酸干预:在碳水化合物和脂肪摄入量充足的情况下,膳食蛋白质在提供能量方面的作用很小,只有长时间不进食才消耗蛋白质提供能量。在消化过程中,食物中的蛋白质被分解成小肽和游离氨基酸,用来构建在所有器官和器官系统中完成各种功能的内源蛋白质。年龄较大人群的肌肉对蛋白质摄入的合成代谢刺激反应较差,可以称这种现象为合成代谢阻力,这可能会助长肌肉质量的丧失[26],因此老年人可能需要更大的蛋白质摄入量。 已有流行病学研究表明,蛋白质摄入量与老年人的四肢骼肌质量呈正相关[27]。在肌肉中,氨基酸是肌肉纤维形成的底物[28],而亮氨酸乳清蛋白在保持肌肉质量方面特别有价值,因其被认为可以通过刺激肌肉蛋白质合成进而保持肌肉质量[29]。支链氨基酸亮氨酸是多磺酸黏蛋白活化的信号分子,能够刺激有关肌肉蛋白质合成的调节蛋白质的激活,随年龄增长其含量的差异可能参与维持甚至增加肌肉质量[30]。MOORE等[31]通过年轻人与老年人的对比,48 h内避免运动前提下,一次性摄入不同质量(1-40 g)的优质蛋白,用输入L-[环13C6]苯丙氨酸来检测肌原纤维蛋白合成,得出的研究结果显示在老年人群中,补充优质蛋白可以导致肌肉质量的改善。一项随机、双盲的对照试验以老年人群为研究对象,试验组持续12周补充1.5 g/(kg?d)剂量蛋白质后,肌肉量与体能均得到了显著改善,所有此剂量的蛋白质摄入可能对肌肉质量的改善存在着积极意义[32]。补充蛋白质及氨基酸治疗及预防肌少症可作为一项被选择的方案,未来也期待更高质量的研究得到报道。 (2)维生素D干预:众所周知,维生素D是人体内钙和磷的调节剂,其在骨矿化过程中起着重要作用,并有益肌肉骨骼的健康发育[33]。目前补充维生素D对肌肉功能的作用文献中仍然缺乏明确的共识,有文献表明老年人补充维生素D对肌肉功能的加强改善有着积极的意义[34]。相反,一些文献则显示维生素D对肌肉功能的影响并不显著[35-36]。最近RANATHUNGA等[37]进行了一项双盲随机对照研究以确定每月补充维生素D3对70岁以上成年人肌肉功能的影响,参与者被随机分成3组,分别每月服用12 000,24 000 或48 000 IU维生素D3,为期12个月,最后测定补充维生素D3前后的标准化握力(GS)和起跳计时(TUG)。研究发现补充12 000,24 000 和48 000 IU剂量的维生素D 12个月可以显著增加老年人的血浆25(OH)D浓度,但对肌肉功能影响甚微。另一项随机试验的Meta分析结果表明,在基线血清25(OH)D水平< 10-12 μg/L的老年人中,补充维生素D对肌肉力量和功能的影响是有益的,在维生素D水平较高的人群中则没有意义[38]。造成以上结论不一致的原因有可能是选取的研究参与者的特征不同,其中包括基线维生素D状态不同。维生素D对肌肉功能的影响仍有待进一步研究。 2.5.2 运动干预 社会不断发展,人类生活工作方式也不断改变,现代生活中体育锻炼缺乏越来越常见,并成为导致社会大众体质下降的主要原因,它不仅影响着儿童及青少年的生长发育,也影响着广大成年人的身体健康和工作效率。同时,缺乏锻炼可以导致各种慢性病发病率的增加,势必增加医疗成本,增加社会负担。生活质量的下降通常与衰老过程有关,但这些下降在很大程度上可归因于体力活动减少的后果[39]。锻炼的好处适用于各个年龄段,其对改善一个人的生活质量来说从来不会晚[40]。有研究表明有氧运动可以增强人体血流量,降低外周血管阻力和血压,增加代谢链中的毛细血管数量、线粒体密度和氧化酶,有利于患者各项功能恢复,对神经系统、心血管系统、呼吸系统、骨关节系统等都有良好的康复效果[41]。 随年龄的增长老年人群肌肉质量的下降和功能水平的降低在一定程度上无法避免,但仍具有一定的可塑性,经过系统的抗阻力量训练后,老年人的肌肉力量和功能水平可得到改善,肌肉质量和功能的衰退可得到延缓,甚至是逆转[42]。抗阻运动是一种以发展肌肉力量为主的运动,具有强度大、时间短的特点,属于无氧代谢。抗阻运动对老年人群的益处在于可以引发肌肉肥大,而肌肉力量也有所改善[43]。有研究表明抗阻运动6 h后,肌肉组织miR-1表达增加,其可通过激活IGF-1/Akt信号通路促进骨骼肌蛋白质合成,进而促进骨骼肌肥大[44-45]。PAPA等[46]的研究表明阻力训练可以减轻与年龄相关的肌肉功能变化,提高日常生活活动能力,如步行耐力、步速和爬楼梯,即使90岁老年人,功能表现也可以显著提高。而NICHOLSON等[47]展示了经抗阻运动后步态速度和站立平衡的某些方面在老年人身上得到了改善。 耐力运动,又称有氧运动,是最基本、最主要的运动处方。在对老年人和啮齿动物的研究中,耐力运动已被证明能有效提高衰老机体骨骼肌中线粒体的酶活性、数量和功能,并增强老年人肌肉的抗氧化能力[48]。其他研究中,小鼠经4周耐力运动后,腓肠肌中转录激活因子pGC-1α在肌肉组织中表达增加,参与调节骨骼肌的生物学功能,抑制肌肉萎缩[49-50]。长期的耐力运动可以通过自噬促进代谢物的降解,减少代谢物在细胞内的积累,抑制活性氧的产生,最终抑制骨骼肌萎缩[51]。耐力运动还被证明可以抑制骨骼肌细胞的凋亡,促进骨骼肌IIb型纤维的合成,进而导致肌肉肥大,增强骨骼肌的质量和力量[52]。 对于患有肌肉减少症的老年人,通过阻力和平衡运动可以提高他们的肌肉力量,减少他们的身体脂肪[53]。最近VLIETSTRA等[54]通过系统回顾和Meta分析综合对比了多篇文献,结果显示运动疗法虽然没有显著改善全身的肌肉质量,却可以显著改善四肢骨骼肌肌肉质量。VIKBERG等[55]学者通过随机对照试验显示,通过为期10周的简易运动训练便可以增加患者的肌肉力量及肌肉质量。运动的简便、易行的特点无疑是治疗及预防肌肉减少症需要重点关注的治疗方案。 2.5.3 药物等相关治疗手段 目前除了运动锻炼和营养补充预防及治疗肌肉减少症以外,药物等相关治疗的研究也取得了一定的进展,多学科通过不同的研究角度力图解决人体肌肉衰减的问题。 (1)骨钙素治疗肌肉减少症的前景:骨钙素(OC)是一种成骨细胞特异性的非胶原蛋白。在血液循环中发现的骨钙素有两种形式:谷氨酸羧化骨钙素(γ-OC)和未羧化骨钙素 (Glu-OC)。羧化骨钙素在调节男性生育能力、胰岛素敏感性、能量代谢等方面发挥重要作用[56],其在肌肉中所起到的作用近年来也多有研究。小鼠动物实验表明骨骼中成骨细胞和骨细胞Cx43的缺失影响了骨骼肌在出生后发育过程中的质量和功能,导致肌肉质量和力量分别减少约30%和50%。研究进一步发现这些小鼠循环中的骨钙素显著减少,而用合成骨钙素治疗这些小鼠,可以挽救肌肉出现肌肉横截面积和握力减少等异常[57]。这也证明骨源性骨钙素是维持肌肉质量和功能所必需的。 LIU等[58]学者用CCK8法和免疫组织化学染色法检测外源性羧化骨钙素对成肌细胞(C2C12)增殖的影响;用PI3K/Akt或P38MAPK抑制剂预处理C2C12细胞,研究PI3K/Akt和P38MAPK信号通路在细胞增殖中的可能作用;形态学分析定量检测羧化骨钙素对成肌细胞分化的影响;此外研究对C2C12成肌细胞中GPRC6A的表达进行了沉默实验,用 qRT-PCR和Western blotting检测C2C12成肌细胞GPRC6A、肌球蛋白重链(MyHC)及其相关的ERK1/2信号通路的表达。首次证明了在C2C12中,羧化骨钙素通过依次激活PI3K/Akt和p38MAPK通路诱导成肌细胞增殖,羧化骨钙素通过GPRC6A-ERK1/2信号转导机制促进肌源性分化。 与年龄相关的肌肉减少症意味着负责细胞存活、增殖和分化的分子机制的进行性恶化。随着骨钙素研究不断取得新的进展,未来肌肉减少症的治疗或许可以在此方向上找到新的治疗切入点。 (2)激素领域的研究:激素参与人体生长发育的始终,在临床上的应用极其广泛,激素对肌肉的功能影响方面也有广泛研究。骨骼肌中被证实存在大量雌激素受体,雌激素可能直接参与肌肉新陈代谢,通过作用雌激素受体来控制和治疗更年期症状[54]。在绝经后妇女中已观察到血清雌二醇与肌肉质量和力量呈正相关[59],且绝经后的妇女长期使用激素疗法后可以提高肌肉质量和降低肌肉减少症的的患病率[60]。 生长激素和胰岛素样生长因子水平在维持骨骼肌质量方面起着至关重要的作用,特别是胰岛素样生长因子与骨骼肌质量独立相关[61]。睾丸间质细胞产生的睾丸素INSL3和肌肉萎缩原因关系密切[62],睾丸激素替代疗法可以增加老年男性的肌肉质量和力量,并最终减少体脂[63]。 肌肉生长抑素和激活素A是肌肉质量的负调节因子,作为配体可以与激活素ⅡB受体(ActRIIB)结合,通过激活Smad2/3信号通路而发挥作用[64-65]。有动物研究表明腹腔注射可溶性激活素ⅡB受体抗体(ActRIIB-Fc)能够增加小鼠的肌肉质量和骨量,提高骨强度[66]。PUOLAKKAINEN等[67]采用标准化闭合性胫骨骨折小鼠模型进行研究,实验分为治疗组与对照组2组,治疗组给予ActRIIB-Fc腹腔注射,而对照组给予PBS腹腔注射,每周1次,持续4周。结果证实了ActRⅡB-FC治疗可以增加骨密度,并且能显著促进闭合性长骨骨折的愈合。ActRIIB-Fc治疗对肌肉和骨骼均具有益处,给肌肉减少症、骨质疏松症及相关骨折的防治带来了新思路。 (3) omega-3多不饱和脂肪酸的作用:目前已经证实骨骼肌衰老过程与慢性低度性全身炎症以及胰岛素抵抗密切相关[68-69]。合理使用抗炎药物被发现可以预防肌肉减少症[70],这似乎可以进一步证明慢性炎症与肌肉减少症的关系。而omega-3多不饱和脂肪酸(omega-3 PUFAs)可以通过降低慢性炎症,也可以增强mTOR信号传导,降低胰岛素抵抗,与肌肉质量、肌肉力量和体能呈正相关[71]。omega-3多不饱和脂肪酸还可以增加老年人运动后线粒体和肌原纤维蛋白的合成,并增强老年人合成代谢反应[72]。此外,其他研究表明,在年轻人、中年人和老年人中,补充omega-3多不饱和脂肪酸的方案促进了肌肉蛋白质合成率[73]。补充omega-3多不饱和脂肪酸可以提高步行速度,改善肌肉质量和体能,是一种很有前途的治疗肌肉减少症的药物,且发生严重不良事件的风险很低[72]。 (4)干细胞移植治疗:再生医学是一个新兴的跨学科研究领域,致力于细胞、组织或器官的修复、替换或再生,以恢复受损的功能[74]。有研究探索在骨骼肌再生方向中实施干细胞移植治疗的可能性,卫星细胞作为位于肌肉纤维之上的肌肉干细胞,被注射到肌肉中时,可以有效地分化成收缩的肌肉纤维,显示出了巨大的治疗潜力,其再生能力在肌肉变性领域引起了特别的兴趣[75]。虽然目前还缺乏足够的证据证明这种再生策略在人类中的安全性和有效性,但干细胞移植在未来有可能成为治疗肌肉减少症的一个新的突破点,更多的基础及临床试验需要开展。"

| [1] SHAFIEE G, KESHTKAR A, SOLTANI A, et al. Prevalence of sarcopenia in the world: a systematic review and meta- analysis of general population studies. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2017;16(1):21. [2] HIDA T, SHIMOKATA H, SAKAI Y, et al. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic leg as potential risk factors for acute osteoporotic vertebral fracture among older women. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(11):3424-3431. [3] Olgun Yazar H, Yazar T. Prevalence of sarcopenia in patients with geriatric depression diagnosis. Ir J Med Sci. 2019;188(3):931-938. [4] VERONESE N, DEMURTAS J, SOYSAL P, et al. Sarcopenia and health-related outcomes: an umbrella review of observational studies. Eur Geriatr Med. 2019;10:853-862. [5] BRUYÈRE O, BEAUDART C, ETHGEN O, et al. The health economics burden of sarcopenia: a systematic review. Maturitas.2019; 119: 61-69. [6] Rosenberg IH. Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. J Nutr. 1997;127(5 Suppl):990S-991S. [7] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会 .肌少症共识[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(3):215-227. [8] DENNISON EM, SAYER AA, COOPER C. Epidemiology of sarcopenia and insight into possible therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017; 13(6):340-347. [9] RONG S, WANG L, PENG Z, et al. The mechanisms and treatments for sarcopenia: could exosomes be a perspective research strategy in the future? J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(2):348-365. [10] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAEYENS JP, BAUER JM, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People.Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412-423. [11] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31. [12] ABELLAN VAN KAN G, ANDRÉ E, BISCHOFF FERRARI HA, et al. Carla Task Force on Sarcopenia: propositions for clinical trials. J Nutr Health Aging. 2009;13(8):700-707. [13] HAN A, BOKSHAN SL, MARCACCIO SE, et al. Diagnostic Criteria and Clinical Outcomes in Sarcopenia Research: A Literature Review. J Clin Med. 2018;7(4):70. [14] FIELDING RA, VELLAS B, EVANS WJ, et al. Sarcopenia: an undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: prevalence, etiology, and consequences.International working group on sarcopenia.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2011;12(4):249-256. [15] CHEN LK, LIU LK, WOO J, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014; 15(2):95-101. [16] SZULC P, FEYT C, CHAPURLAT R. High risk of fall, poor physical function, and low grip strength in men with fracture-the STRAMBO study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2016;7(3):299-311. [17] YOON BH, LEE JK, CHOI DS, et al. Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Sarcopenia in Female Patients with Osteoporotic Fracture.J Bone Metab. 2018;25(1):59-62. [18] BATTAFARANO G, ROSSI M, MARAMPON F, et al. Bone Control of Muscle Function. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1178. [19] Chalhoub D, Cawthon PM, Ensrud KE, et al.Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study Research Group. Risk of Nonspine Fractures in Older Adults with Sarcopenia, Low Bone Mass, or Both. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(9):1733-1740. [20] HONG W, CHENG Q, ZHU X, et al. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Its Relationship with Sites of Fragility Fractures in Elderly Chinese Men and Women. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138102. [21] ZHANG N, CHOW SKH, LEUNG KS, et al. An animal model of co-existing sarcopenia and osteoporotic fracture in senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8). Exp Gerontol. 2017;97:1-8. [22] KIM YK, YI SR, LEE YH, et al. Effect of Sarcopenia on Postoperative Mortality in Osteoporotic Hip Fracture Patients. J Bone Metab. 2018; 25(4):227-233. [23] PILGRIM AL, ROBINSON SM, SAYER AA, et al. An overview of appetite decline in older people. Nurs Older People. 2015;27(5):29-35. [24] SIESKE L, JANSSEN G, BABEL N, et al. Inflammation, Appetite and Food Intake in Older Hospitalized Patients. Nutrients. 2019;11(9):1986. [25] ROBINSON SM, REGINSTER JY, RIZZOLI R, et al. Does nutrition play a role in the prevention and management of sarcopenia?. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(4):1121-1132. [26] BURD NA, GORISSEN SH, VAN LOON LJ. Anabolic resistance of muscle protein synthesis with aging. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2013;41(3):169-173. [27] VALENZUELA RE, PONCE JA, MORALES-FIGUEROA GG, et al. Insufficient amounts and inadequate distribution of dietary protein intake in apparently healthy older adults in a developing country: implications for dietary strategies to prevent sarcopenia. Clin Interv Aging. 2013;8: 1143-1148. [28] DUAN Y, LI F, LI Y, et al. The role of leucine and its metabolites in protein and energy metabolism. Amino Acids. 2016;48(1):41-51. [29] GORISSEN SHM, WITARD OC. Characterising the muscle anabolic potential of dairy, meat and plant-based protein sources in older adults. Proc Nutr Soc. 2018;77(1):20-31. [30] PENNINGS B, BOIRIE Y, SENDEN JM, et al. Whey protein stimulates postprandial muscle protein accretion moreeffectively than do casein and casein hydrolysate in older men. Am JClin Nutr. 2011;93(5):997-1005. [31] MOORE DR, CHURCHWARD-VENNE TA, WITARD O, et al. Protein ingestion to stimulate myofibrillar protein synthesis requires greater relative protein intakes in healthy older versus younger men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015;70(1):57-62. [32] PARK Y, CHOI JE, HWANG HS. Protein Supplementation Improves Muscle Mass and Physical Performance in Undernourished Prefrail and Frail Elderly Subjects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018;108(5):1026-1033. [33] LEWIS RD, LAING EM.Conflicting reports on vitamin D supplementation: Evidence from randomized controlled trials. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015; 410:11-18. [34] CANGUSSU LM, NAHAS-NETO J, ORSATTI CL, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation alone on muscle function in postmenopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(10):2413-2421. [35] KOTLARCZYK MP, PERERA S, FERCHAK MA, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with functional decline and falls in frail elderly women despite supplementation. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(4):1347-1353. [36] ROSENDAHL-RIISE H, SPIELAU U, RANHOFF AH,et al. Vitamin D supplementation and its influence on muscle strength and mobility in community-dwelling older persons: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2017;30(1):3-15. [37] RANATHUNGA RMTK, HILL TR, MATHERS JC, et al. Vitamin D in Older People Study group. No effect of monthly supplementation with 12000 IU, 24000 IU or 48000 IU vitamin D3 for one year on muscle function: The vitamin D in older people study. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019; 190:256-262. [38] BEAUDART C, BUCKINX F, RABENDA V, et al. The effects of vitamin D on skeletal muscle strength, muscle mass, and muscle power: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(11):4336-4345. [39] MECHLING H, NETZ Y. Aging and inactivity-Capitalizing on the protective efect of planned physical activity in oldage. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2009;6(2):89-97. [40] KELL KP, RULA EY. Increasing exercise frequency is associated with health and quality-of-life benefits for older adults. Qual Life Res. 2019; 28(12):3267-3272. [41] PENEDO FJ, DAHN JR. Exercise and well-being: a review of mental and physical health benefits associated with physical activity. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2005;18(2):189-193. [42] BORDE R, HORTOBÁGYI T, GRANACHER U. Dose-Response Relationships of Resistance Training in Healthy Old Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2015;45(12):1693-1720. [43] STEWART VH, SAUNDERS DH, GREIG CA. Responsiveness of muscle size and strength to physical training in very elderly people: a systematic review. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014;24(1):e1-10. [44] ZHANG S, CHEN N. Regulatory Role of MicroRNAs in Muscle Atrophy during Exercise Intervention. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):405. [45] MATHENY RW JR, CARRIGAN CT, ABDALLA MN, et al. RNA transcript expression of IGF-I/PI3K pathway components in regenerating skeletal muscle is sensitive to initial injury intensity. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2017;32:14-21. [46] PAPA EV, DONG X, HASSAN M. Resistance training for activity limitations in older adults with skeletal muscle function deficits: a systematic review. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:955-961. [47] NICHOLSON VP, MCKEAN MR, BURKETT BJ. Low-load high-repetition resistance training improves strength and gait speed in middle-aged and older adults. J Sci Med Sport. 2015;18(5):596-600. [48] MENSHIKOVA EV, RITOV VB, FAIRFULL L,et al. Effects of exercise on mitochondrial content and function in aging human skeletal muscle. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006;61(6):534-540. [49] FANG Z, LI P, JIA W, et al. miR-696 plays a role in hepatic gluconeogenesis in ob/ob mice by targeting PGC-1α. Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(3):845-852. [50] PARK YM, PEREIRA RI, ERICKSON CB, et al. Time since menopause and skeletal muscle estrogen receptors, PGC-1α, and AMPK. Menopause. 2017;24(7):815-823. [51] FAN J, YANG X, LI J, et al. Spermidine coupled with exercise rescues skeletal muscle atrophy from D-gal-induced aging rats through enhanced autophagy and reduced apoptosis via AMPK-FOXO3a signal pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(11):17475-17490. [52] ZAMPIERI S, MOSOLE S, LÖFLER S, et al. Physical Exercise in Aging: Nine Weeks of Leg Press or Electrical Stimulation Training in 70 Years Old Sedentary Elderly People. Eur J Transl Myol. 2015;25(4):237-242. [53] HASSAN BH, HEWITT J, KEOGH JW, et al. Impact of resistance training on sarcopenia in nursing care facilities: A pilot study. Geriatr Nurs. 2016;37(2):116-121. [54] VLIETSTRA L, HENDRICKX W, WATERS DL. Exercise interventions in healthy older adults with sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Australas J Ageing. 2018;37(3):169-183. [55] VIKBERG S, SÖRLÉN N, BRANDÉN L, et al. Effects of Resistance Training on Functional Strength and Muscle Mass in 70-Year-Old Individuals With Pre-sarcopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;20(1):28-34. [56] LI G, ZHANG L, WANG D, et al. Muscle-bone crosstalk and potential therapies for sarco-osteoporosis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(9):14262-14273. [57] SHEN H, GRIMSTON S, CIVITELLI R, et al. Deletion of connexin43 in osteoblasts/osteocytes leads to impaired muscle formation in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(4):596-605. [58] LIU S, GAO F, WEN L, et al. Osteocalcin Induces Proliferation via Positive Activation of the PI3K/Akt, P38 MAPK Pathways and Promotes Differentiation Through Activation of the GPRC6A-ERK1/2 Pathway in C2C12 Myoblast Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):1100-1112. [59] TAAFFE DR, NEWMAN AB, HAGGERTY CL, et al. Estrogen replacement, muscle composition, and physical function: The Health ABC Study. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(10):1741-1747. [60] KIM SW, KIM R.The association between hormone therapy and sarcopenia in postmenopausal women: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008-2011. Menopause. 2020;27(5): 506-511. [61] BIAN A, MA Y, ZHOU X, et al. Association between sarcopenia and levels of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in the elderly. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):214. [62] FERLIN A, DE TONI L, AGOULNIK AI, et al. Protective Role of Testicular Hormone INSL3 From Atrophy and Weakness in Skeletal Muscle. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:562. [63] BASUALTO-ALARCÓN C, VARELA D, DURAN J, et al. Sarcopenia and Androgens: A Link between Pathology and Treatment. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5:217. [64] LATRES E, MASTAITIS J, FURY W, et al. Activin A more prominently regulates muscle mass in primates than does GDF8. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15153. [65] SOUZA TA, CHEN X, GUO Y, et al. Proteomic identification and functional validation of activins and bone morphogenetic protein 11 as candidate novel muscle mass regulators. Mol Endocrinol. 2008;22(12):2689-2702. [66] PUOLAKKAINEN T, MA H, KAINULAINEN H, et al. Treatment with soluble activin type IIB-receptor improves bone mass and strength in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):20. [67] PUOLAKKAINEN T, RUMMUKAINEN P, LEHTO J, et al. Soluble activin type IIB receptor improves fracture healing in a closed tibial fracture mouse model. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0180593. [68] SAKUMA K, AOI W, YAMAGUCHI A. Current understanding of sarcopenia: possible candidates modulating muscle mass. Pflugers Arch. 2015;467(2):213-229. [69] BUDUI SL, ROSSI AP, ZAMBONI M. The pathogenetic bases of sarcopenia. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2015;12(1):22-26. [70] LANDI F, MARZETTI E, LIPEROTI R, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use and sarcopenia in older people: results from the ilSIRENTE study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013;14(8):626.e9-13. [71] DUPONT J, DEDEYNE L, DALLE S, et al. The role of omega-3 in the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019; 31(6):825-836. [72] LALIA AZ, DASARI S, ROBINSON MM, et al. Influence of omega-3 fatty acids on skeletal muscle protein metabolism and mitochondrial bioenergetics in older adults. Aging (Albany NY). 2017;9(4):1096-1129. [73] SMITH GI, ATHERTON P, REEDS DN, et al.Dietary omega-3 fatty acid supplementation increases the rate of muscle protein synthesis in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93(2):402-412. [74] COSSU G, BIRCHALL M, BROWN T, et al. Lancet Commission: Stem cells and regenerative medicine. Lancet. 2018;391(10123):883-910. [75] ROCHETEAU P, VINET M, CHRETIEN F. Dormancy and quiescence of skeletal muscle stem cells. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2015;56:215-235. [76] HIDAYAT K, CHEN GC, WANG Y,et al. Effects of Milk Proteins Supplementation in Older Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22(2):237-245. [77] LIAO CD, CHEN HC, HUANG SW, et al. The Role of Muscle Mass Gain Following Protein Supplementation Plus Exercise Therapy in Older Adults with Sarcopenia and Frailty Risks: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis of Randomized Trials. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1713. |
| [1] | Xu Xinzhong, Wu Zhonghan, Yu Shuisheng, Zhao Yao, Xu Chungui, Zhang Xin, Zheng Meige, Jing Juehua. Biomechanical analysis of different ways of inserting Steinmann Pins into the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Li Rui, Shi Wen, Yang Shicai, Lü Linwei, Zhang Chunqiu. Effect of splintage and Shenxiaosan cataplasm on fracture healing in rabbits with radial fracture model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1329-1333. |
| [3] | Yuan Jiabin, Zhu Zongdong, Tang Xiaoming, Wei Dan, Tan Bo, Xiao Chengwei, Zhao Ganlinwei, Liao Feng. Classification and reduction strategies for irreducible intertrochanteric femoral fracture based on anatomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1341-1345. |
| [4] | Liu Feng, Feng Yi. Finite element analysis of different Kirschner wire tension bands on transverse patella fractures during gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [5] | Lu Pan, Zhang Chunlin, Wang Yongkui, Yan Xu, Dong Chao, Yue Yisen, Li Long, Zhu Andi. Volume changes of cervical herniated discs after open-door laminoplasty and conservative treatment as assessed by three-dimensional volume method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1395-1401. |
| [6] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [7] | Yu Chengxiang, Liu Lehong, Li Wenbo, Chen Jinshi, Ran Chunlei, Wang Zhongping. Correlation between spine-pelvic sagittal parameters and prognosis of vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1412-1417. |
| [8] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [9] | Li Canhui, Wu Zhengjie, Zeng Yanhui, He Yinghao, Situ Xiaopeng, Du Xuelian, Hong Shi, He Jiaxiong. Advantage and disadvantage of robot-assisted sacroiliac screw placement and traditional fluoroscopy in orthopedic surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1434-1438. |
| [10] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [11] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [12] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [13] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [14] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [15] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||