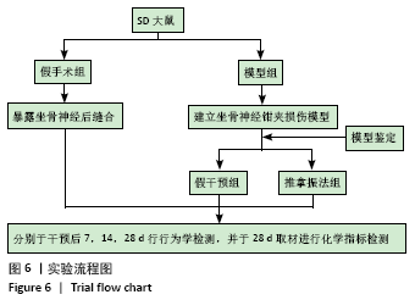
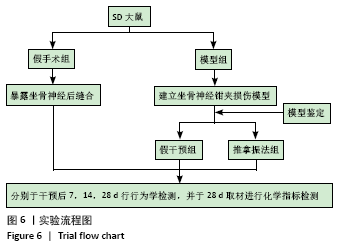
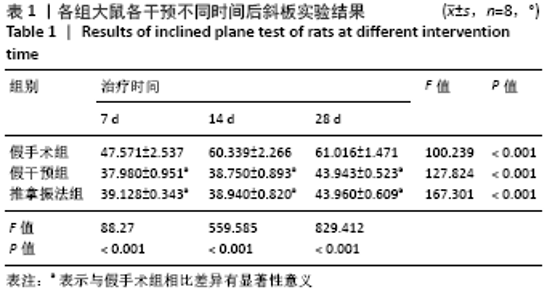
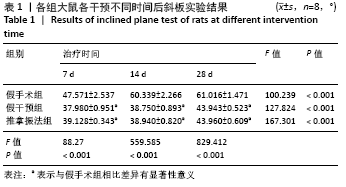
[1] PIOVESANA R, FARONI A, TATA AM, et al. Schwann-like adipose-derived stem cells as a promising therapeutic tool for peripheral nerve regeneration: effects of cholinergic stimulation.Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(6):1218-1220.
[2] LI L, XU Y, WANG X, et al. Ascorbic acid accelerates Wallerian degeneration after peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2021; 16(6):1078-1085.
[3] GARG K, SINHA S, SATYARTHEE GD, et al. Microsurgical Outcome of Post-traumatic Peripheral Nerve Injuries: An Experience of 23 Cases and Review of Literature. Turk Neurosurg. 2016;26(2):297-301.
[4] LI NY, ONOR GI, LEMME NJ, et al. Epidemiology of Peripheral Nerve Injuries in Sports, Exercise, and Recreation in the United States, 2009-2018. Phys Sportsmed. 2020;10(23):1-8.
[5] GOSWAMI N, ALEEM M, MANDA K, et al. Clinical relevance of chronic neuropathic pain phenotypes in mice: A comprehensive behavioral analysis. Behave Brain Resk. 2020;10(5):113055
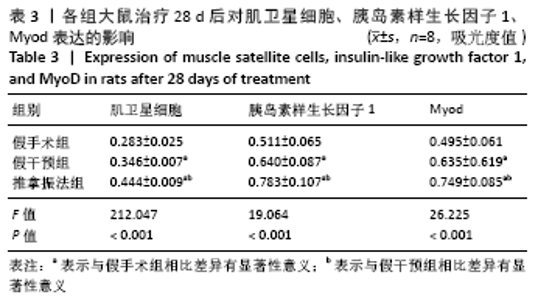
[6] 卢裕强,郭汝宝.推拿手法对家兔骨骼肌失神经支配后成肌调节因子Myf-5,Myogenin表达的影响[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2019, 29(12):979-984.
[7] 陆永嘉,严隽陶,马书杰,等.全程与间断推拿对延缓失神经大鼠骨骼肌萎缩的实验研究[J].上海中医药杂志,2017,51(10):97-99.
[8] 赵娜,张玮,庞赓,等.基于TGF-β1/CTGF作用途径探讨推拿干预骨骼肌纤维化的作用机制[J].辽宁中医杂志,2016,43(12):2539-2541.
[9] JANG MS, HAN JH, KIM DO, et al. Dexmedetomidine Improves Locomotor Function and Alleviates Thermal Hyperalgesia Following Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury in Rats. Int Neurourol J. 2020;24(Suppl 1): S11-18.
[10] RIVLIN AS, TATOR CH. Objective clinical assessment of motor function after experimental spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurosurg. 1977;47(4):577-581.
[11] TSUANG FY, CHEN MH, LIN FH, et al. Partial enzyme digestion facilitates regeneration of crushed nerve in rat. Transl Neurosci. 2020;11(1): 251-263.
[12] DE SOUZA LG, HENDLER KG, MARCOLINO AM, et al. Photobiomodulation promotes neural regeneration when compared to simvastatin treatment in a sciatic nerve crush model. Lasers Med Sci. 2020 Nov 18. doi: 10.1007/s10103-020-03176-y.
[13] 马颖,严隽陶,马书杰,等.推拿联合跑轮训练对大鼠失神经骨骼肌萎缩的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(5):530-534.
[14] 刘艳,谭曾德,刘琳,等.肌肉骨骼系统推拿病谱文献学研究[J].中医药信息,2011,28(2):133-134.
[15] WONG A, GARCIA SM, TAMAKI S, et al. Satellite Cell Activation and Retention of Muscle Regenerative Potential After Long Term Denervation. Stem Cells. 2020;10(16):1-18.
[16] YOSHIMURA K, HARII K. A Regenerative Change during Muscle Adaptation to Denervation in Rats. J Surg Res. 1999;81(2):139-146.
[17] ANNE SJ, ALEXANDRA H, ROSIN NL, et al. Macrophages Regulate Schwann Cell Maturation after Nerve Injury. Cell Rep. 2018;24(10): 2561-2572.
[18] DE OLIVEIRA PA, BLASCZYK JC, SOUZA JUNIOR G, et al. Effects of Elastic Resistance Exercise on Muscle Strength and Functional Performance in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2017;14(4):317-327.
[19] ALGHADIR AH, ANWER S, ZAFAR H,et al.Effect of localised vibration on muscle strength in healthy adults: A systematic review.Physiotherapy. 2018;104(1):18-24.
[20] TSUTSUMI S, URABE Y, MAEDA N, et al. The transition of tensor fasciae latae and iliotibial band hardness after hip abduction exercise and the effect of vibration stimulation. Japanese Journal of Physical Fitness and Sports Medicine. 2018;67(3):219-223 .
[21] JIAHUI A, XIANG Z, KEQI J, et al. Trichostatin A increases BDNF protein expression by improving XBP-1s/ATF6/GRP78 axis in Schwann cells of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133: 111062.
[22] 陈玄,叶笑然,黄晓卿,等.电针对大鼠失神经支配骨骼肌萎缩及IGF-1/PI3K/AKT表达的影响[J].中国针灸,2018,38(12):62-68.
[23] AGUERA E, CASTILLA S, LUQUE E, et al. Denervated muscle extract promotes recovery of muscle atrophy through activation of satellite cells. An experimental study. J Sport Health Sci. 2019;8(1):23-31.
[24] LANG F, ARAVAMUDHAN S, NOLTE H, et al. Dynamic changes in the skeletal muscle proteomeduring denervation-induced atrophy. Dis Model Mech. 2017;10(7):881-896.
[25] YOSHIDA T, DELAFONTAINE P. Mechanisms of IGF-1-Mediated Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy and Atrophy. Cells. 2020; 9(9):1970.
[26] CONG XX, GAO XK, RAO XS, et al. Rab5a activates IRS1 to coordinate IGF-AKT-mTOR signaling and myoblast differentiation during muscle regeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27(8):2344-2362.
[27] GU LJ, ZHANG YY, WANG L, et al. Changes of insulin-like growth factor 1 axis in chronic kidney disease and its role in skeletal muscle atrophy.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;98(10):749-754.
[28] YIN L, LIN LU, LIN X, et al. Crucial role of androgen receptor in resistance and endurance trainings-induced muscle hypertrophy through IGF-1/IGF-1R- PI3K/Akt- mTOR pathway. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020;17:26.
[29] ZAMMIT PS. Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;72:19-32.
[30] TSUKAMOTO S, SHIBASAKI A, NAKA A, et al. Lactate Promotes Myoblast Differentiation and Myotube Hypertrophy via a Pathway Involving MyoD In Vitro and Enhances Muscle Regeneration In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;9(11):3649.
[31] ZHAO Y, CHEN M, LIAN D, et al. Non-Coding RNA Regulates the Myogenesis of Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells, Injury Repair and Diseases. Cells. 2019;8(9):988.
[32] MUSARÒ A, CAROSIO S. Isolation and Culture of Satellite Cells from Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1553:155-167.
[33] FUJIMAKI S, SEKO D, KITAJIMA Y, et al. Notch1 and Notch2 Coordinately Regulate Stem Cell Function in the Quiescent and Activated States of Muscle Satellite Cells. Stem Cells. 2018;36(2):278-285.
[34] FENG X, NAZ F, JUAN AH, et al. Identification of Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells by Immunofluorescence with Pax7 and Laminin Antibodies. J Vis Exp. 2018;(134):57212.
[35] YASUO K, YUSUKE O. Visualization of PAX7 protein dynamics in muscle satellite cells in a YFP knock-in-mouse line. Skeletal Muscle. 2018;8(1): 26-32.
[36] 唐芳,高品操,潘同斌.钝挫伤对大鼠骨骼肌卫星细胞体外增殖的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(5):1091-1093
[37] RODRIGUES ADE C, SCHMALBRUCH H. Satellite cells and myonuclei in long-term denervated rat muscles. Anat Rec. 1995;243(4):430-437. |