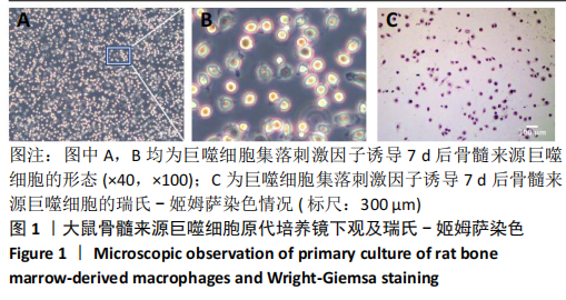
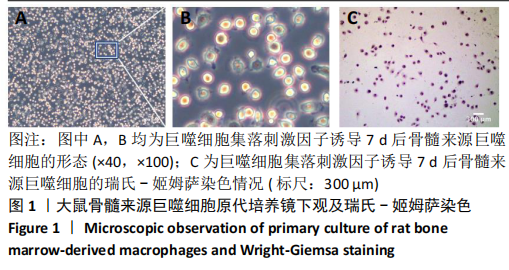
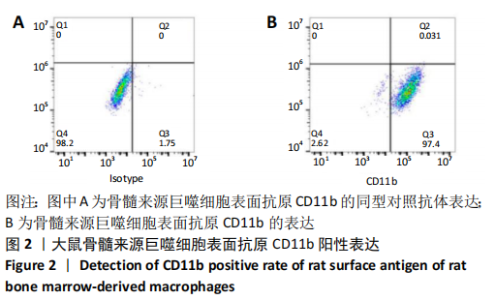
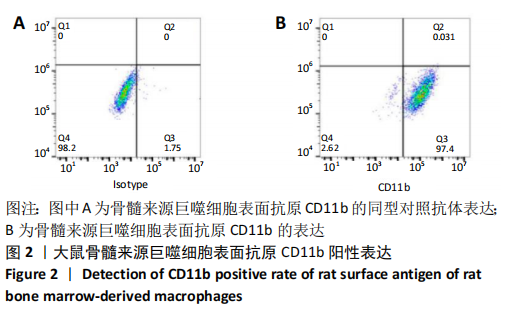
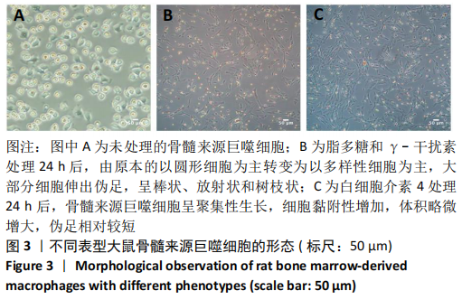
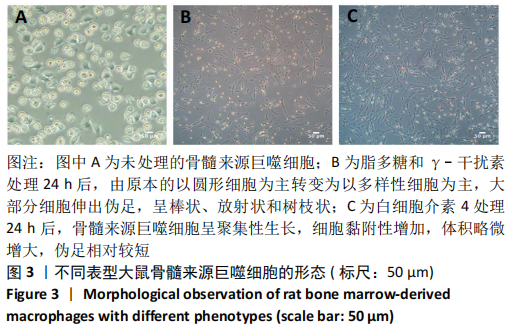
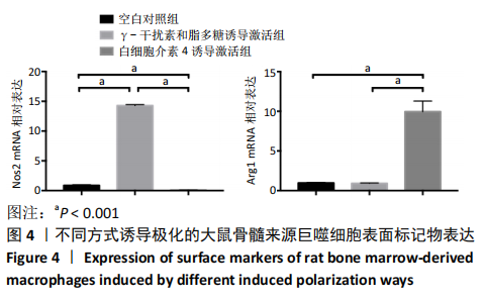
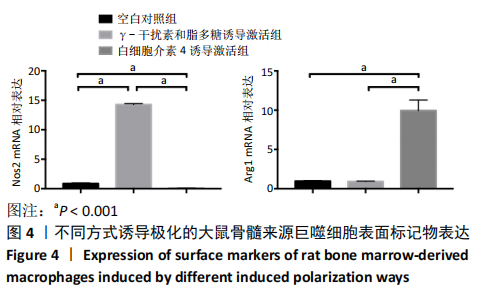
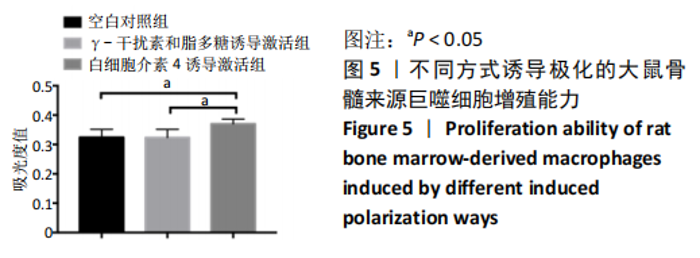
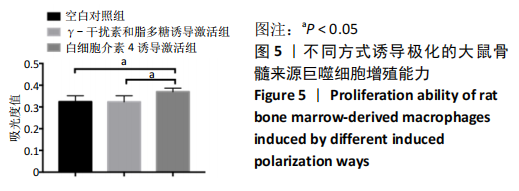
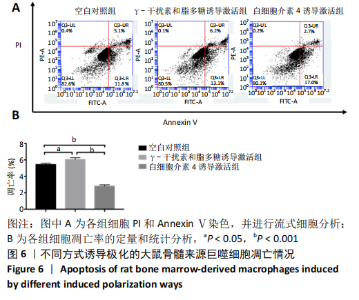
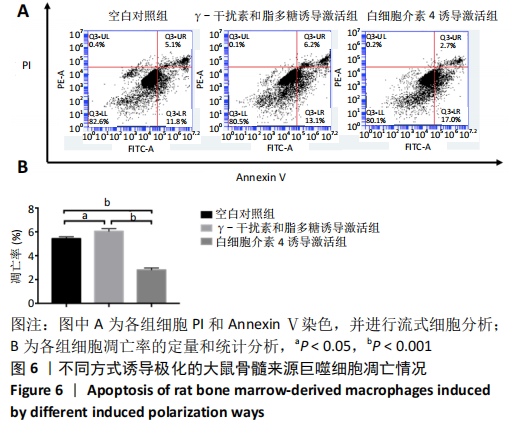
[1] OGLE ME, SEGAR CE, SRIDHAR S, et al. Monocytes and macrophages in tissue repair: Implications for immunoregenerative biomaterial design. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016;241(10):1084-1097.
[2] BROWN BN, RATNER BD, GOODMAN SB, et al. Macrophage polarization: an opportunity for improved outcomes in biomaterials and regenerative medicine. Biomaterials. 2012;33(15):3792-3802.
[3] JAMALPOOR Z, ASGARI A, LASHKARI MH, et al. Modulation of Macrophage Polarization for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;17(5):398-408.
[4] BLÉRIOT C, CHAKAROV S, GINHOUX F. Determinants of Resident Tissue Macrophage Identity and Function. Immunity. 2020;52(6):957-970.
[5] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969.
[6] MANTOVANI A, BISWAS SK, GALDIERO MR, et al. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol. 2013;29(2): 176-185.
[7] LOCATI M, CURTALE G, MANTOVANI A. Diversity, Mechanisms, and Significance of Macrophage Plasticity. Annu Rev Pathol. 2020;15:123-147.
[8] 周玲,许雄程,王松,等.骨质疏松大鼠骨髓巨噬细胞的体外培养研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(4):439-445.
[9] GRUBER R. Osteoimmunology: Inflammatory osteolysis and regeneration of the alveolar bone. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46 Suppl 21:52-69.
[10] ZHAO Z, ZHAO Q, GU B, et al. Minimally invasive implantation and decreased inflammation reduce osteoinduction of biomaterial. Theranostics. 2020;10(8):3533-3545.
[11] WYNN TA, CHAWLA A, POLLARD JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496(7446):445-455.
[12] GORDON S, PLÜDDEMANN A. Tissue macrophages: heterogeneity and functions. BMC Biol. 2017;15(1):53.
[13] KANG S, KUMANOGOH A. The spectrum of macrophage activation by immunometabolism. Int Immunol. 2020;32(7):467-473.
[14] THIRIOT JD, MARTINEZ-MARTINEZ YB, ENDSLEY JJ, et al. Hacking the host: exploitation of macrophage polarization by intracellular bacterial pathogens. Pathog Dis. 2020;78(1):ftaa009.
[15] YU T, ZHAO L, HUANG X, et al. Enhanced Activity of the Macrophage M1/M2 Phenotypes and Phenotypic Switch to M1 in Periodontal Infection. J Periodontol. 2016;87(9):1092-1102.
[16] MARINO S, CILFONE NA, MATTILA JT, et al. Macrophage polarization drives granuloma outcome during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Infect Immun. 2015;83(1):324-338.
[17] CHANG X, XING L, WANG Y, et al. Nanoengineered immunosuppressive therapeutics modulating M1/M2 macrophages into the balanced status for enhanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis therapy. Nanoscale. 2020;12(16):8664-8678.
[18] WU RX, HE XT, ZHU JH, et al. Modulating macrophage responses to promote tissue regeneration by changing the formulation of bone extracellular matrix from filler particles to gel bioscaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:330-340.
[19] CHEN B, NI Y, LIU J, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exert Diverse Effects on Different Macrophage Subsets. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:8348121.
[20] MACMICKING J, XIE QW, NATHAN C. Nitric oxide and macrophage function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:323-350.
[21] BOGDAN C, RÖLLINGHOFF M, DIEFENBACH A. The role of nitric oxide in innate immunity. Immunol Rev. 2000;173:17-26.
[22] PESCE JT, RAMALINGAM TR, MENTINK-KANE MM, et al. Arginase-1-expressing macrophages suppress Th2 cytokine-driven inflammation and fibrosis. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5(4):e1000371.
[23] LI LX, XIA YT, SUN XY, et al. CXCL-10/CXCR3 in macrophages regulates tissue repair by controlling the expression of Arg1, VEGFa and TNFα. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(3):987-999.
[24] GALLI SJ, BORREGAARD N, WYNN TA. Phenotypic and functional plasticity of cells of innate immunity: macrophages, mast cells and neutrophils. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(11):1035-1044.
[25] WATANABE S, ALEXANDER M, MISHARIN AV, et al. The role of macrophages in the resolution of inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2019; 129(7):2619-2628.
[26] WANG LX, ZHANG SX, WU HJ, et al. M2b macrophage polarization and its roles in diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;106(2):345-358.
[27] SHRIVASTAVA R, SHUKLA N. Attributes of alternatively activated (M2) macrophages. Life Sci. 2019;224:222-231.
[28] MCCALL TB, BOUGHTON-SMITH NK, PALMER RM, et al. Synthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine by neutrophils. Release and interaction with superoxide anion. Biochem J. 1989;261(1):293-296.
[29] CHOI KS, SONG EK, YIM CY. Cytokines secreted by IL-2-activated lymphocytes induce endogenous nitric oxide synthesis and apoptosis in macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 2008;83(6):1440-1450.
[30] MILLS CD. Macrophage arginine metabolism to ornithine/urea or nitric oxide/citrulline: a life or death issue. Crit Rev Immunol. 2001;21(5): 399-425.
[31] RICHARDS DM, ENDRES RG. The mechanism of phagocytosis: two stages of engulfment. Biophys J. 2014;107(7):1542-1553.
[32] RICHARDS DM, ENDRES RG. How cells engulf: a review of theoretical approaches to phagocytosis. Rep Prog Phys. 2017;80(12):126601. |