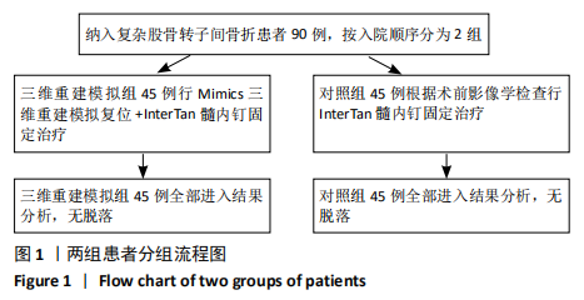
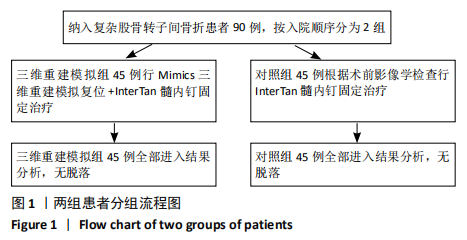
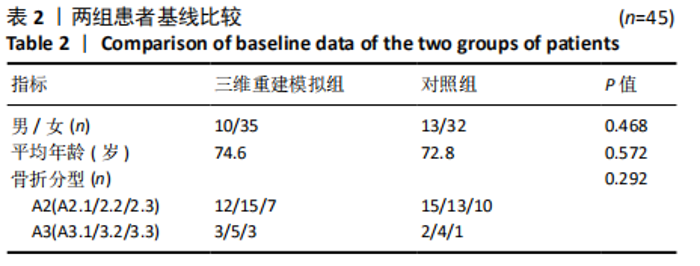
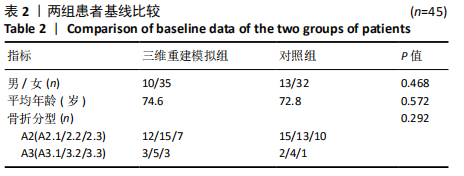
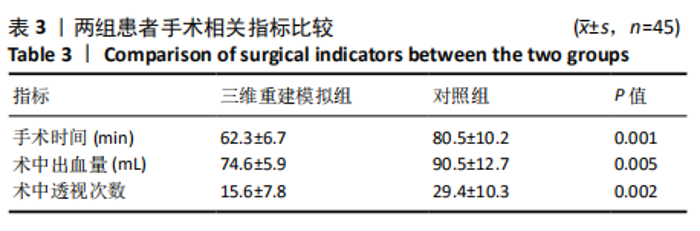
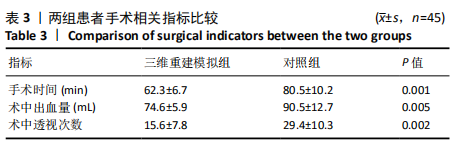
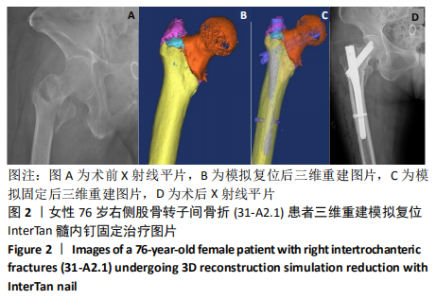
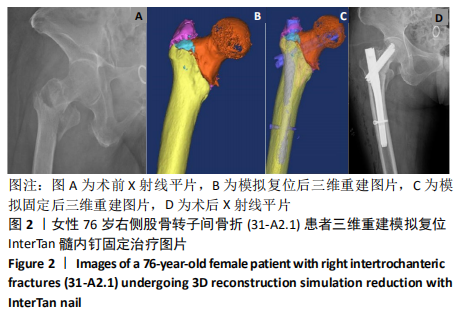
[1] VERONESE N, MAGGI S. Epidemiology and social costs of hip fracture. Injury. 2018;49(8):1458-1460.
[2] YOO JI, LEE YK, KOO KH, et al. Concerns for Older Adult Patients with Acute Hip Fracture. Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(10):1240-1244.
[3] CUMMINGS SR, MELTON LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet (London, England). 2002;359(9319):1761-1767.
[4] LEAL J, GRAY AM, HAWLEY S, et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Orthogeriatric and Fracture Liaison Service Models of Care for Hip Fracture Patients: A Population-Based Study. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(2):203-211.
[5] CHANG SM, HOU ZY, HU SJ, et al. Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Treatment in Asia: What We Know and What the World Can Learn. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(2):189-205.
[6] KAUFER H. Mechanics of the treatment of hip injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1980;(146):53-61.
[7] KWONG Y, YU D, SHAH J. Fracture mimics on temporal bone CT: a guide for the radiologist. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(2):428-434.
[8] MEINBERG EG, AGEL J, ROBERTS CS, et al. Fracture and Dislocation Classification Compendium-2018. J Orthop Trauma. 2018; 32 Suppl 1:S1-S170.
[9] SONG H, CHEN SY, CHANG SM. What should be filled in the blank of 31A2.1 in AO/OTA-2018 classification. Injury. 2020;51(6):1408-1409.
[10] 卫禛,陈时益,张世民.股骨转子间骨折治疗中前内侧皮质正性支撑复位的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(10):1216-1222.
[11] PARUK F, TSABASVI M, KALLA AA. Osteoporosis in Africa-where are we now. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05335-6.
[12] 赵凯平,袁蕊,马楠, 等.55岁以上原发骨质疏松性骨折患者特征及趋势分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(6):849-856.
[13] WU JC, STRICKLAND CD, CHAMBERS JS. Wrist Fractures and Osteoporosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 2019;50(2):211-221.
[14] STONE MA, NAMDARI S. Surgical Considerations in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Proximal Humerus Fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2019; 50(2):223-231.
[15] 唐佩福.股骨转子间骨折的治疗进展与策略[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2017,19(2):93-94.
[16] BHANDARI M, SWIONTKOWSKI M. Management of Acute Hip Fracture. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(21):2053-2062.
[17] JOHNELL O, KANIS J. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2005; 16 Suppl 2:S3-7.
[18] 孙健平,薛汉中,孙亮, 等.股骨近端解剖锁定钢板加自体髂骨植骨固定治疗股骨转子间骨折内固定失败[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(9): 771-776.
[19] MAVROGENIS AF, PANAGOPOULOS GN, MEGALOIKONOMOS PD, et al. Complications After Hip Nailing for Fractures. Orthopedics. 2016;39(1): e108-116.
[20] LEWIECKI EM, WRIGHT NC, CURTIS JR, et al. Hip fracture trends in the United States, 2002 to 2015. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(3):717-722.
[21] FU Y, LIU R, LIU Y, et al. Intertrochanteric fracture visualization and analysis using a map projection technique. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019;57(3):633-642.
[22] ZHENG SN, YAO QQ, MAO FY, et al. Application of 3D printing rapid prototyping-assisted percutaneous fixation in the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(4):3644-3650.
[23] CHEN Y, JIA X, QIANG M, et al. Computer-Assisted Virtual Surgical Technology Versus Three-Dimensional Printing Technology in Preoperative Planning for Displaced Three and Four-Part Fractures of the Proximal End of the Humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(22):1960-1968.
[24] QIANG M, ZHANG K, CHEN Y, et al. Computer-assisted virtual surgical technology in pre-operative design for the reconstruction of calcaneal fracture malunion. Int Orthop. 2019;43(7):1669-1677.
[25] LAU TW, LEUNG F, SIU D, et al. Geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway: the Hong Kong experience. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(Suppl 4):S627-636.
[26] SORG M, OSMERS J, FISCHER A. Methodical Approach for Determining the Length of Drill Channels in Osteosynthesis. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(16):3532.
[27] MAO W, NI H, LI L, et al. Comparison of Baumgaertner and Chang reduction quality criteria for the assessment of trochanteric fractures. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(10):502-508.
[28] LI H, WANG Q, DAI GG, et al. PFNA vs. DHS helical blade for elderly patients with osteoporotic femoral intertrochanteric fractures. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(1 Suppl):1-7.
|