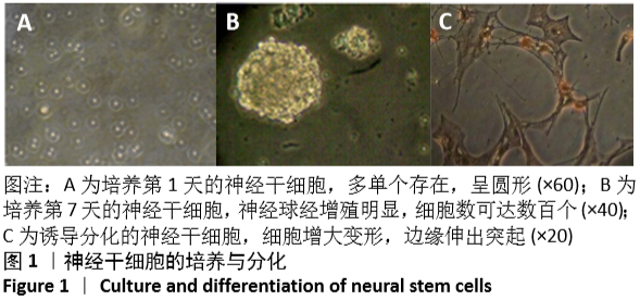
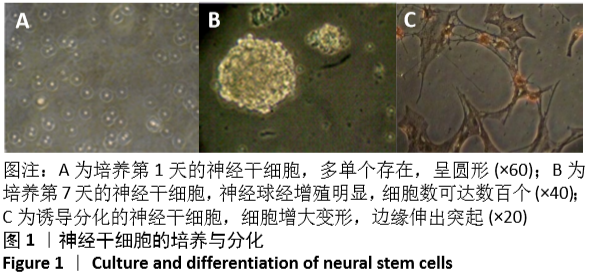
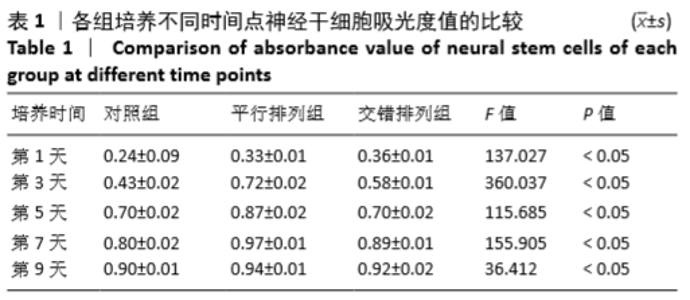
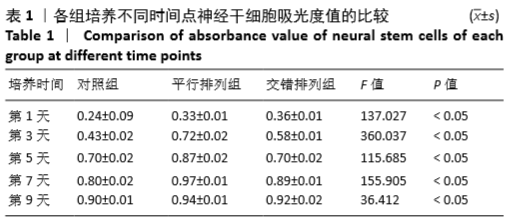
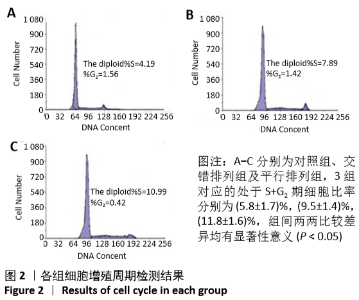
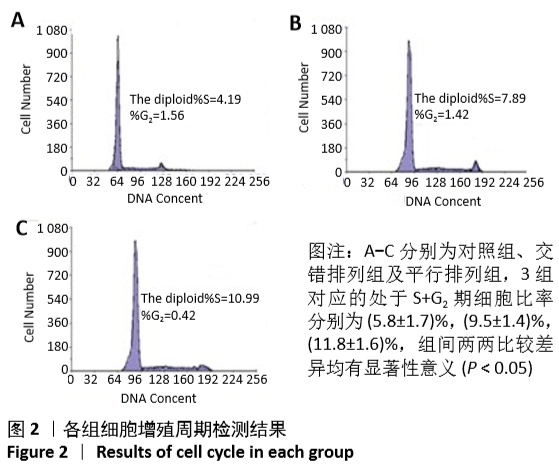
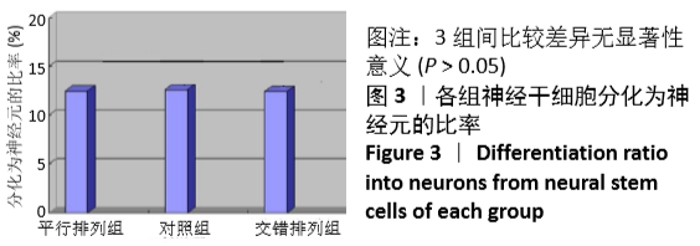
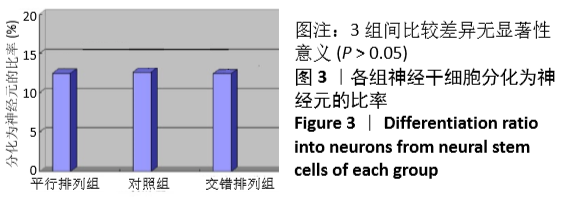
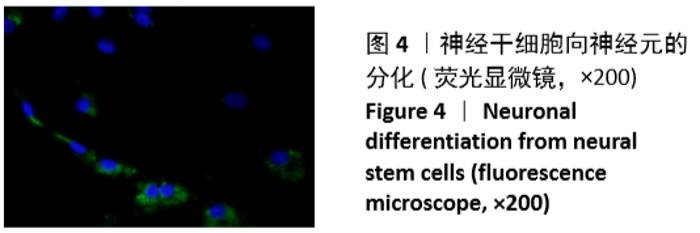
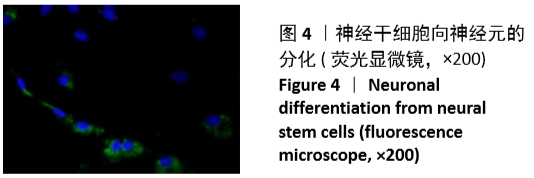
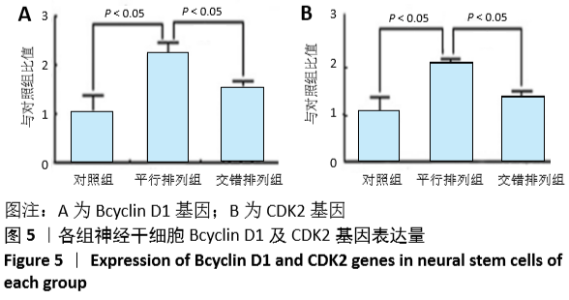
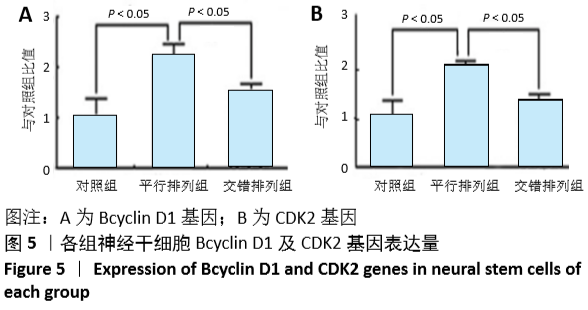
[1] 孙佳慧,林欣怡,邹剑龙,等.神经组织工程技术治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].解剖学研究,2016,38(6):480-483.
[2] 张文龙,祁全.组织工程支架在脊髓损伤治疗的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(4):320-323.
[3] 周继辉,姚猛,王岩松,等.新型脊髓纳米组织工程支架的组织相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(21):3854-3861.
[4] HOU BR, JIANG C, WANG ZN, et al. Exosome-mediated crosstalk between microglia and neural stem cells in the repair of brain injury.Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(6):1023-1024.
[5] SUN X, BAI Y, ZHAI H, et al. Devising micro/nano-architectures in multi-channel nerve conduits towards a pro-regenerative matrix for the repair of spinal cord injury.Acta Biomater.2019;86:194-206.
[6] JØRGENSEN V, SLETTAHJELL HB, SKAVBERG ROALDSEN K, et al. Carboxy terminal collagen crosslinks as a prognostic risk factor for fall-related fractures in individuals with established spinal cord injury.Spinal cord. 2019;57(11):985-991.
[7] LIU XY, LIANG J, WANG Y, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging predicting neurological repair of spinal cord injury with transplanting collagen/chitosan scaffold binding bFGF.J Mater Sci.2019; 30(11):123.
[8] HUANG J, ZHOU X, SHEN Y, et al. Asiaticoside loading into polylactic-co-glycolic acid electrospun nanofibers attenuates host inflammatory response and promotes M2 macrophage polarization.J Biomed Mater Res A.2020;108 (1):69-80.
[9] XIE J, MACEWAN MR, SCHWARTZ AG, et al. Electrospun nanofibersforneural tissue engineering.Nanoscale.2010;2(1):35-44.
[10] CHRISTENSON EM, ANSETH KS, VAN DEN BEUCKEN JJ, et al. Nanobiomaterial applications in orthopedics.J Orthop Res.2007;1:11-22.
[11] SARACINO GA, CIGOGNINI D, SILVA D, et al. Nanomaterials design and tests for neural tissue engineering.Chem Soc Rev.2013;42(1):225-262.
[12] YOUSEFI F, LAVI ARAB F, JAAFARI MR, et al. Immunoregulatory, proliferative and anti-oxidant effects of nanocurcuminoids on adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.EXCLI J.2019;18:405-421.
[13] KOBAYASHI T, PIAO W, TAKAMURA T, et al. Enhanced lysosomal degradation maintains the quiescent state of neural stem cells.Nat Commun.2019;10(1):5446.
[14] MOHAN A, ASAKURA A. CDK inhibitors for muscle stem cell differentiation and self-renewal.J Phys Fit Sports Med.2017;6(2):65-74.
[15] VAN DEN HEUVEL S. Cell-cycle regulation.WormBook.2005:1-16.
[16] URBACH A, WITTE OW. Divide or Commit - Revisiting the Role of Cell Cycle Regulators in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:55.
[17] ANAM MB, AHMAD SAI, KUDO M, et al. Akhirin regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells/progenitor cells at neurogenic niches in mouse brain.Dev Growth Differ.2020;62(2):97-107.
[18] SANDQUIST EJ, SAKAGUCHI DS. Adult neural stem cell plasticity. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(2):256-257.
[19] HU YY, ZHENG MH, CHENG G, et al. Notch signaling contributes to the maintenance of both normal neural stem cells and patient-derived glioma stem cells.BMC Cancer.2011;11:82.
[20] CHEN YT, TSAI MJ, HSIEH N, et al. The superiority of conditioned medium derived from rapidly expanded mesenchymal stem cells for neural repair.Stem Cell Res Ther.2019;10(1):390.
[21] CUI Y, YIN Y, XIAO Z, et al. LncRNA Neat1 mediates miR-124-induced activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in spinal cord neural progenitor cells.Stem Cell Res Ther.2019;10(1):400.
|