Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (20): 3202-3208.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2558
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of hypoxic exercise on Nesfatin-1 and Ghrelin in hypothalamus of rats with alimentary obesity
Fan Jinqin1, Weng Xiquan2, Xu Guoqin2, Wu Juhua3, Lin Wentao2
- 1Shaoguan College of Physical Education, Shaoguan 512005, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou 510500, Guangdong Province, China; 3Sports College, Guangxi University of Science and Technology, Liuzhou 545006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-07-31Revised:2019-08-02Accepted:2019-09-07Online:2020-07-18Published:2020-04-13 -
Contact:Fan Jinqin, Shaoguan College of Physical Education, Shaoguan 512005, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Fan Jinqin, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Shaoguan College of Physical Education, Shaoguan 512005, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:2018-2019 Guangdong Provincial Sports Department Research Project, No. GDSS2018N022; 2018 Scientific Research Project of Shaoguan University, No. SZ2018KJ08
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Jinqin, Weng Xiquan, Xu Guoqin, Wu Juhua, Lin Wentao. Effects of hypoxic exercise on Nesfatin-1 and Ghrelin in hypothalamus of rats with alimentary obesity[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(20): 3202-3208.
share this article
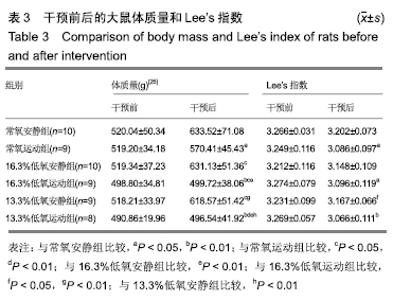
2.1 实验动物数量分析 干预结束时,剩余大鼠55只:常氧安静组10只、常氧运动组9只、16.3%低氧安静组10只、16.3%低氧运动组9只、13.3%低氧安静组9只和13.3%低氧运动组8只。流失大鼠5只,其中13.3%低氧安静组大鼠1只因在干预期间长有肿物死亡,16.3%低氧运动组大鼠1只和13.3%低氧运动组大鼠2只在运动时尾部被卷入跑台的转轴引致颈部折断而死亡。 2.2 干预前后大鼠体质量和Lee’s指数变化 由表3可知,干预前大鼠体质量和Lee’s指数组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。干预后大鼠体质量较干预前均有增加而Lee’s指数则有所下降,其中体质量增幅的排序为常氧安静组>16.3%低氧安静组>13.3%低氧安静组>常氧运动组>16.3%低氧运动组、13.3%低氧运动组,而Lee’s指数降幅的排序为13.3%低氧运动组>16.3%低氧运动组>常氧运动组>16.3%低氧安静组、13.3%低氧安静组、常氧安静组。 "
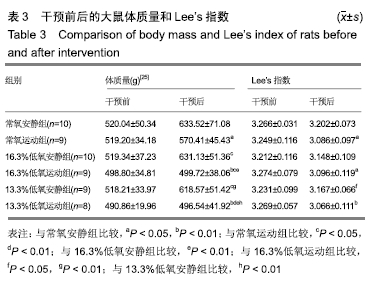

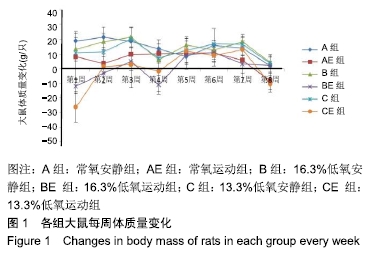
多重比较发现:与常氧安静组比较,常氧运动组、16.3%低氧运动组和13.3%低氧运动组的体质量及Lee’s指数均较低且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05和P < 0.01);与常氧运动组比较,16.3%低氧安静组、13.3%低氧安静组的体质量较高且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),16.3%低氧运动组、13.3%低氧运动组的体质量较低且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);与16.3%低氧安静组比较,16.3%低氧运动组、13.3%低氧运动组的体质量较低且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);与16.3%低氧运动组比较,13.3%低氧安静组体质量和Lee’s指数较高且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01,P < 0.05);与13.3%低氧安静组比较,16.3%低氧运动组、13.3%低氧运动组的体质量较低且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。结果提示,单纯低氧环境刺激对大鼠体质量、Lee’s指数的影响没有单纯有氧运动刺激明显,而当低氧和运动结合时,其效果优于单一刺激,如在氧气体积分数更低的常压环境中运动,其效果更为显著。 大鼠干预期体质量变化,见图1。8周干预期内,3个安静组的体质量为持续增加状态;3个运动组的体质量增幅均小于安静组,其中常氧运动组每只大鼠每周体质量增长保持在0-10 g之间;16.3%低氧运动组和13.3%低氧运动组的体质量在干预第1周即下降,尤以13.3%低氧运动组明显,随后两组的体质量降幅变缓,至第4周出现了体质量下降峰(下降幅度16.3%低氧运动组>13.3%低氧运动组),之后每只大鼠每周增长保持在0-10 g之间;在第8周时常氧运动组和13.3%低氧运动组大鼠体质量出现下降峰(下降幅度13.3%低氧运动组>常氧运动组)。结果提示运动和低氧均可抑制大鼠的体质量增长,而低氧抑制体质量增长的效果在干预初期较后期明显,且氧气体积分数较低时将更早出现体质量的负增长。 "

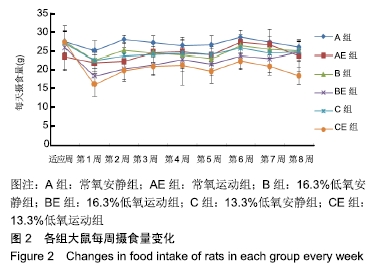
2.3 干预期间大鼠摄食量变化 干预前各组大鼠的日均摄食量(g/只):常氧安静组26.99±2.44、常氧运动组27.18±2.31、16.3%低氧安静组27.32±2.27、16.3%低氧运动组25.87±3.72、13.3%低氧安静组27.46±2.25、13.3%低氧运动组26.22±5.61,各组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。8周干预期内,各组大鼠每周的日均摄食量变化见图2。常氧安静组整体保持平稳;其余5组在第1周即明显下降,尤以16.3%低氧运动组和13.3%低氧运动组明显;随后常氧运动组、16.3%低氧安静组和13.3%低氧安静组每只大鼠日均摄食量保持在23-27 g之间,而16.3%低氧运动组和13.3%低氧运动组则保持在17-22 g之间。结果提示运动和低氧均可减少大鼠的摄食量,而二者结合的效果更显著。 "
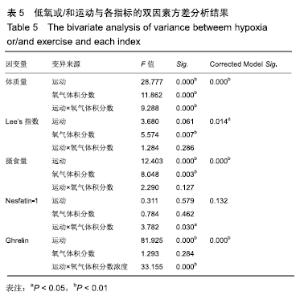
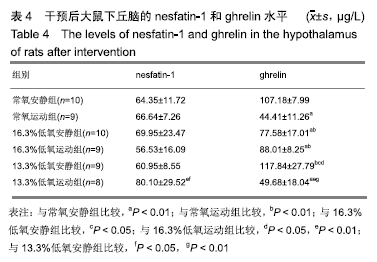
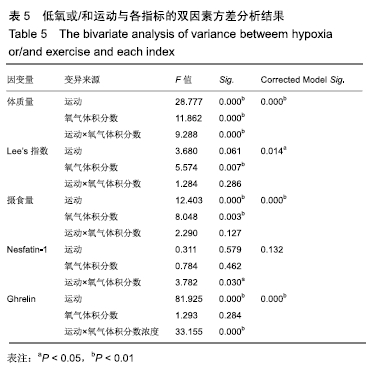
干预后各组大鼠下丘脑ghrelin水平进行多重比较,见表4。与常氧安静组比较,常氧运动组、16.3%低氧安静组、16.3%低氧运动组和13.3%低氧运动组的ghrelin水平均较低且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);与常氧运动组比较,16.3%低氧安静组、16.3%低氧运动组和13.3%低氧安静组的ghrelin水平均较高且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);与16.3%低氧安静组比较,13.3%低氧安静组的ghrelin水平较高且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与16.3%低氧运动组比较,13.3%低氧安静组ghrelin水平较高且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),13.3%低氧运动组ghrelin水平较低且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);与13.3%低氧安静组比较,13.3%低氧运动组ghrelin水平较低且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。结果提示单纯的运动或低氧均可影响大鼠下丘脑ghrelin水平,而单一运动刺激效果要强于单一低氧刺激,当二者结合时降低效果更明显,但这种效果在2种常压低氧组间没有显著差异。 2.5 低氧或/和运动与各指标的双因素方差分析结果 由表5可知,除nesfatin-1外,其余指标的Corrected Model Sig.均小于0.05,提示这些指标的组间差异有显著性意义。体质量受运动、氧气体积分数和运动×氧气体积分数的影响且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),提示运动和低氧干预均可影响大鼠体质量,两种因素有交互作用;Lee’s指数和摄食量受氧气体积分数影响且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),提示这两者对氧气体积分数改变敏感;Nesfatin-1受运动×氧气体积分数的影响且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),提示低氧和运动二者结合时,可影响大鼠下丘脑nesfatin-1水平;Ghrelin受运动和运动×氧气体积分数的影响且差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.05),提示运动或/和低氧结合可影响大鼠下丘脑ghrelin水平。 "
| [1] OHASHI K, SHIBATA R, MUROHARA T, et al. Role of anti-inflammatory adipokines in obesity-related diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014;25(7):348-355. [2] BHASKARAN K, DOUGLAS I, FORBES H, et al. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: a population-based cohort study of 5•24 million UK adults. Lancet.2014;384(9945):755-765. [3] NCD RISK FACTOR COLLABORATION (NCD-RISC). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19•2 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387 (10026):1377-1396. [4] HAMAD N, TRAVIS SP. Weight loss at high altitude: pathophysiology and practical implications. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;18(1):5-10. [5] LING Q, SAILAN W, RAN J, et al. The effect of intermittent hypoxia on bodyweight, serum glucose and cholesterol in obesity mice. Pak J Biol Sci. 2008;11(6):869-875. [6] MORTOLA JP. Implications of hypoxic hypometabolism during mammalian ontogenesis. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2004; 141(3):345-356. [7] COSTALAT G, LEMAITRE F, TOBIN B, et al. Intermittent hypoxia revisited: a promising non-pharmaceutical strategy to reduce cardio-metabolic risk factors? Sleep Breath. 2018; 22(1): 267-271. [8] KONG Z, ZANG Y, HU Y. Normobaric hypoxia training causes more weight loss than normoxia training after a 4-week residential camp for obese young adults. Sleep Breath. 2014; 18(3):591-597. [9] KOJIMA M, HOSODA H, DATE Y, et al. Ghrelin is a growth- hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402(6762):656-660. [10] KAMEGAI J, TAMURA H, SHIMIZU T, et al. Chronic central infusion of ghrelin increases hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and Agouti-related protein mRNA levels and body weight in rats. Diabetes. 2001;50(11):2438-2443. [11] 付鹏宇,龚丽景,朱镕鑫,等.Ghrelin-GHSR通路在急性低氧暴露大鼠胃炎症反应中的调节作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2018,34(10):1103-1110. [12] ALIPARASTI MR, ALIPOUR MR, ALMASI S, et al. Ghrelin Administration Increases the Bax/Bcl-2 Gene Expression Ratio in the Heart of Chronic Hypoxic Rats. Adv Pharm Bull. 2015;5(2):195-199. [13] OH-I S, SHIMIZU H, SATOH T, et al. Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature. 2006;443 (7112):709-712. [14] STENGEL A, TACHÉ Y. Nesfatin-1--role as possible new potent regulator of food intake. Regul Pept. 2010;163(1-3):18-23. [15] ZHANG T, WANG M, LIU L, et al. Hypothalamic nesfatin-1 mediates feeding behavior via MC3/4R-ERK signaling pathway after weight loss in obese Sprague-Dawley rats. Peptides. 2019;119:170080. [16] ÖZTÜRK ÖZKAN G. Effects of Nesfatin-1 on Food Intake and Hyperglycemia. J Am Coll Nutr. 2019 Aug 1:1-7. [17] 冯连世,张漓,高炳宏,等.不同环境下有氧运动对超重和肥胖青少年体重与体脂含量的影响[J].体育科学,2013,33(11):58-65. [18] DE GROOTE E, BRITTO FA, BULLOCK L, et al. Hypoxic Training Improves Normoxic Glucose Tolerance in Adolescents with Obesity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(11):2200-2208. [19] 吴娜娜,管延飞,朱欢,等.高住低练对肥胖青少年血浆食欲调节激素的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2015,31(3):281-283. [20] 王茹,刘冬梅,吴娜娜,等.高住低练对肥胖青少年内源性大麻素及相关食欲调节激素的影响[J].体育科学,2016,36(2):51-57,71. [21] URDAMPILLETA A, GONZÁLEZ-MUNIESA P, PORTILLO MP, et al. Usefulness of combining intermittent hypoxia and physical exercise in the treatment of obesity. J Physiol Biochem. 2012;68(2):289-304. [22] 王茹,王红霞,许亚丽,等.高住低练对肥胖青少年形态学指标和糖脂代谢的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2013,36(9):81-87. [23] 陈瑜文,林文弢,邱烈峰,等.间歇低氧运动对肥胖大鼠食欲的影响及其机制分析[J].体育学刊,2011,18(4):133-136. [24] WASSE LK, SUNDERLAND C, KING JA, et al. Influence of rest and exercise at a simulated altitude of 4,000 m on appetite, energy intake, and plasma concentrations of acylated ghrelin and peptide YY. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012; 112(4):552-559. [25] 吴菊花,杨亚南,翁锡全,等.低氧运动对营养性肥胖大鼠骨骼肌PGC-1α及其下游因子的影响[J].体育学刊, 2016,23(3) : 130-136. [26] 上官若男,苏全生,尚画雨,等.运动负荷强度与运动疲劳程度量化分级研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2013, 28(2): 188-192. [27] BEDFORD TG, TIPTON CM, WILSON NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283. [28] HØYDAL MA, WISLØFF U, KEMI OJ, et al. Running speed and maximal oxygen uptake in rats and mice: practical implications for exercise training. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007;14(6):753-760. [29] 何明,涂长春,黄起壬,等. Lee's 指数用于评价成年大鼠肥胖程度的探讨[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学杂志,1997,2(3):177-179. [30] 张静,沙继斌,张林,等.有氧运动与多糖干预对肥胖大鼠的血脂调节及抗炎作用[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2016,35(2):86-91. [31] 谢宜轩,李帅.持续和间歇低氧运动对肥胖大鼠体重及相关代谢指标的影响[J].扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2016,37(1): 31-34. [32] TAN BK, HALLSCHMID M, KERN W, et al. Decreased cerebrospinal fluid/plasma ratio of the novel satiety molecule, nesfatin-1/NUCB-2, in obese humans: evidence of nesfatin-1/NUCB-2 resistance and implications for obesity treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(4):E669-673. [33] 孙文娟,于普艳,戴红艳,等.肥胖症病人血浆nesfatin-1水平变化及与BMI关系[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2013,28(3):235-236,240. [34] 李娜,田字彬,孙桂荣,等.Nesfatin-1对肥胖大鼠胃排空及胃平滑肌条收缩性的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志,2012,20(8): 631-637. [35] CUI H, SOHN JW, GAUTRON L, et al. Neuroanatomy of melanocortin-4 receptor pathway in the lateral hypothalamic area. J Comp Neurol. 2012;520(18):4168-4183. [36] 习燕华,刘建英. Nesfatin-1在肥胖及血糖调节中的作用[J].生理科学进展,2013,44(3):220-222. [37] CHAOLU H, ASAKAWA A, USHIKAI M, et al. Effect of exercise and high-fat diet on plasma adiponectin and nesfatin levels in mice. Exp Ther Med. 2011;2(2):369-373. [38] HAGHSHENAS R, JAFARI M, RAVASI A, et al. The effect of eight weeks endurance training and high-fat diet on appetite-regulating hormones in rat plasma. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014;17(4):237-243. [39] TSCHÖP M, SMILEY DL, HEIMAN ML. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000;407(6806):908-913. [40] 汪军,田吉明. 8周跑台运动对肥胖大鼠下丘脑ghrelin 和obestatin 的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2009,32(4):57-60. [41] 唐光旭,汪军.急性运动对肥胖大鼠下丘脑ghrelin和obestatin的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(5):551-555. [42] 王宁琦,胡扬,官余凌,等.4周低氧运动结合饮食控制对肥胖青年体重、血脂及胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2012, 31(4):289-294. |
| [1] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [2] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [3] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [4] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [5] | Huang Zhusong, Lin Yu, Chen Xiang, Lan Jinfu, Guan Yong, Gao Xi. Alcohol extract of Morinda officinalis improves lipid metabolism and bone metabolism in ovariectomized obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 205-210. |
| [6] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Liu Chao. Adipose-derived stem cells integrated with concentrated growth factors prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2982-2987. |
| [7] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| [8] | Jiang Tao, Wu Shuo, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Mayire·Nuermaimaiti, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB promotes the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1976-1981. |
| [9] | Yang Luyao, Fu Pengyu, Tang Shuning, Zhu Rongxin, Gong Lijing . Change of Ghrelin-GHSR pathway in 4-week intermittent hypoxic exposure improving obesity in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1733-1739. |
| [10] | Zang Jing, Luan Zuo, Wang Qian, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wu Youjia, Guo Aisong. Two kinds of stem cell nasal transplantation for treating white matter injury in premature rat infants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 101-107. |
| [11] | Wang Jing, Lu Changfeng, Peng Jiang, Zhu Chen, Xu Wenjing, Cheng Xiaoqing, Fang Jie, Zhu Yaqiong, Zhao Yanxu, Jiang Wen, Xu Hongguang, Wang Yu. Establishment and evaluation of traumatic neuroma model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 716-719. |
| [12] | Cao Qingjun, Yang Fenghua, Wang Hua. Hippocampal astrocytes in juvenile rats with persistent epilepsy: the role of cannabinoid receptor type 2 in regulating MAPK pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5179-5185. |
| [13] |
Li Ying, Lin Wentao, Weng Xiquan.
Effects of different exercise intensities on visfatin level and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4196-4200. |
| [14] | Jiang Tao, Shao Min, Chen Qingzhen, Ling Cuimin, Shen Zhen, Wang Gang, Huo Shaochuan, Lin Yanping, Liu Haiquan, Wang Qinsheng, Zeng Zhenming. Inokosterone effects on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts from neonatal Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3636-3642. |
| [15] | Yuan Guoqiang, Qin Yongsheng, Peng Peng. High-intensity interval training for treating pathological cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3708-3715. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||