Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (20): 3275-3280.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1158
Association between COL9A2 gene polymorphisms and intervertebral disc degeneration in Asian: a meta-analysis
Li Pengfei, Wang Tao, Ma Xinlong
- Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China
-
Online:2019-07-18Published:2019-07-18 -
Contact:Ma Xinlong, Professor, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China -
About author:Li Pengfei, Master, Attending physician, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81401792 (to LPF)| the Major Research and Development Project of Health of Tianjin, No. 16KG140 (to WT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Pengfei, Wang Tao, Ma Xinlong . Association between COL9A2 gene polymorphisms and intervertebral disc degeneration in Asian: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(20): 3275-3280.
share this article
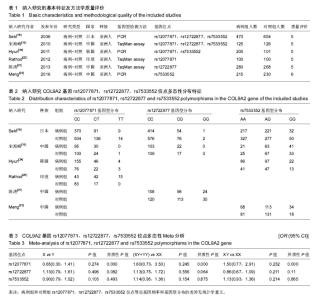
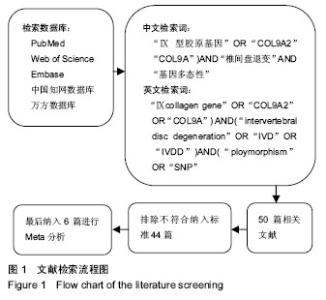
论文发表语种为4篇英语、2篇中文,研究对象均为亚洲人。纳入研究的COL9A2基因rs12077871,rs12722877,rs7533552位点多态性分布特征见表2。纳入研究质量评价结果显示6项研究中的椎间盘退变诊断标准明确,即均通过MRI诊断;基因检测方法合理、数据充分;符合H-W遗传平衡定律;6项研究组间进行了性别年龄匹配,组间可比性强;6项研究样本量均过百。 2.2 Meta分析结果 有4项研究报道了rs12077871位点多态性与椎间盘退变的相关性[18,20,22,24]。等位基因(C vs T)以及2种遗传模型[(CT+TT) vs CC,CT vs CC]的 Meta分析结果显示,病例组和对照组rs12077871位点等位基因频率和基因型分布的差异无统计学意义,见图2,表3。"
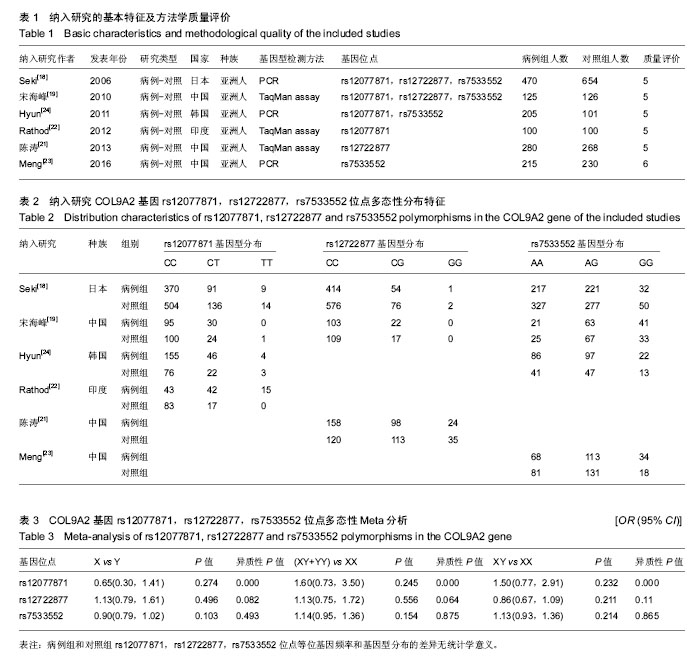
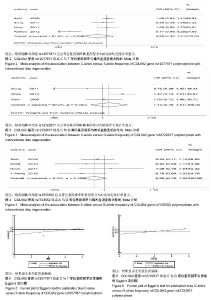
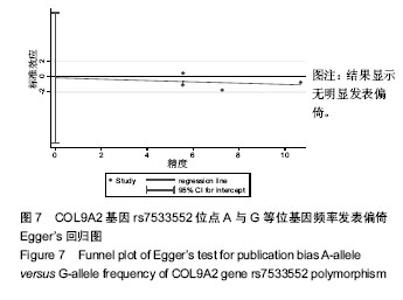
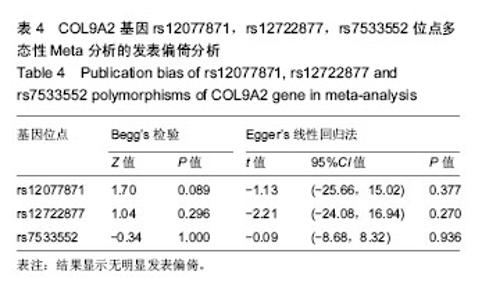
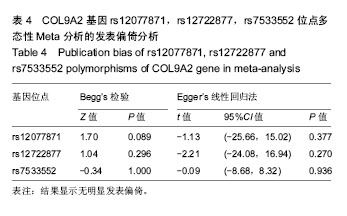
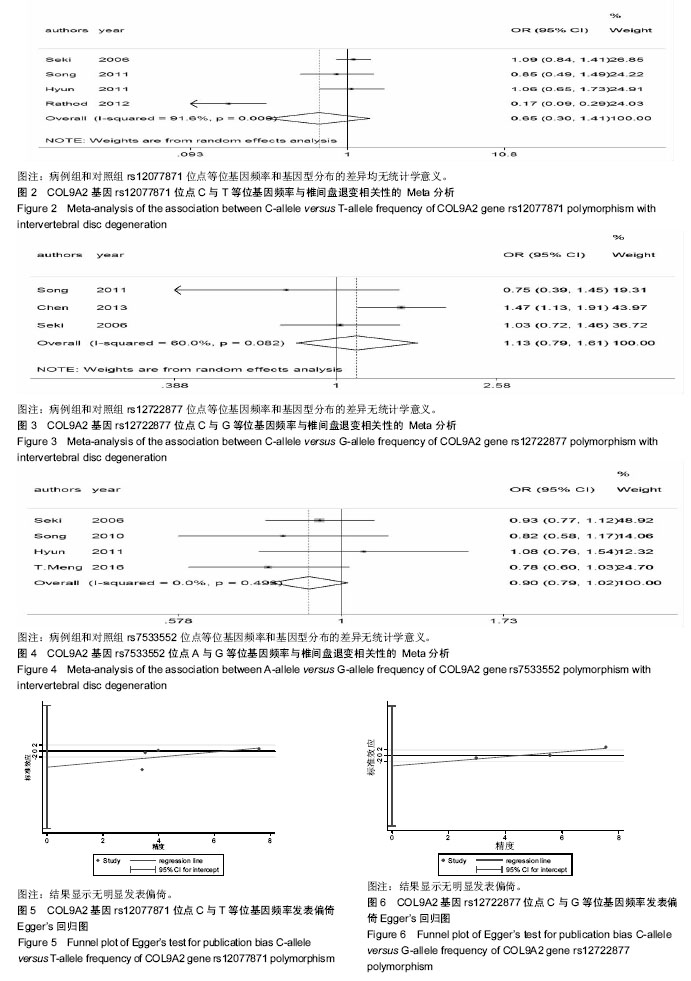
有3项研究报道了rs12722877位点多态性与椎间盘退变的相关性[18,20-21]。等位基因(C vs G)以及2种遗传模型[(CG+GG) vs CC,CG vs CC]的Meta分析结果显示,病例组和对照组rs12722877位点等位基因频率和基因型分布的差异无统计学意义,见图3,表3。 有4项研究报道了rs7533552位点多态性与椎间盘退变的相关性[18-19,23-24]。等位基因(A vs G)以及2种遗传模型[(AG+GG) vs AA,AG vs AA]的Meta分析结果显示,病例组和对照组rs7533552位点等位基因频率和基因型分布的差异无统计学意义,见图4,表3。 以rs12077871,rs12722877,rs7533552位点等位基因频率的OR值为效应量,应用Begg’s秩相关检验和Egger’s线性回归法评估发表偏倚情况,统计结果显示无明显发表偏倚,见图5-7,表4。使用逐一排除法进行敏感性分析,合并OR值后研究结果未发生改变,证明本次Meta分析结果较稳定。"
| [1] Heliövaara M. Risk factors for low back pain and sciatica. Ann Med. 1989;21(4):257-264. [2] 贾长青,王臣,陈勇,等.基质金属蛋白酶3和白细胞介素1在突出的腰椎间盘组织中的含量及其相关性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(12):1-2.[3] Sambrook PN, MacGregor AJ, Spector TD. Genetic influences on cervical and lumbar disc degeneration. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(2):366-372. [4] Tegeder I, Lötsch J. Current evidence for a modulation of low back pain by human genetic variants. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13(8B):1605-1619. [5] Kim NK, Shin DA, Han IB, et al. The association of aggrecan gene polymorphism with the risk of intervertebral disc degeneration. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011;153(1):129-133. [6] 程勇军,沈洪兴.椎间盘退变相关基因单核苷酸多态性的研究进展[J].第二军医大学学报,2012,32(11):1244-1248.[7] Kalb S, Martirosyan NL, Kalani M Y S, et al. Genetics of the degenerated intervertebral disc. World Neurosurg. 2012;77 (3-4):491-501. [8] Higashino K, Matsui Y, Yagi S, et al. The alpha2 type IX collagen tryptophan polymorphism is associated with the severity of disc degeneration in younger patients with herniated nucleus pulposus of the lumbar spine. Int Orthop. 2007;31(1):107-111. [9] Xu G, Mei Q, Zhou D, et al. Vitamin D Receptor Gene and Aggrecan Gene Polymorphisms and the Risk of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration-A Meta-Analysis. PloS one, 2012;7(11): e50243. [10] Cong L, Pang H, Xuan D, et al. Association between the expression of aggrecan and the distribution of aggrecan gene variable number of tandem repeats with symptomatic lumbar disc herniation in Chinese Han of Northern China. Spine.2010; 35(14):1371-1376. [11] Takahashi M, Haro H, Wakabayashi Y, et al. The association of degeneration of the intervertebral disc with 5a/6a polymorphism in the promoter of the human matrix metalloproteinase-3 gene. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(4):491-495. [12] 肖斌,田伟,赵丹慧,等.TIMP-1666C>T 单核苷酸多态性与腰椎间盘退变相关性分析[J].中华医学杂志, 2010,90(41):2939-2942.[13] Tokta? ZO, Ek?i M?,Y?lmaz B, et al. Association of collagen I, IX and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with radiological severity of intervertebral disc degeneration in Southern European Ancestor. Eur Spine J.2015;24(11):2432-2441. [14] 王兴盛,王想福,赵宁,等.甘肃汉族人群COL9A2基因多态性与腰椎间盘突出症术后复发的相关性研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2017,26(11):7-10.[15] Aladin DM, Cheung KM, Chan D, et al. Expression of the Trp2 allele of COL9A2 is associated with alterations in the mechanical properties of human intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(25):2820-2826. [16] Bagheri MH, Honarpisheh AP, Yavarian M, et al. MRI Phenotyping of COL9A2/Trp2 and COL9A3/Trp3 Alleles in Lumbar Disc Disease: A Case-control Study in South-Western Iranian Population Reveals a Significant Trp3-Disease Association in Males. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(21): 1661-1667. [17] Janeczko ?, Janeczko M, Chrzanowski R, et al. The role of polymorphisms of genes encoding collagen IX and XI in lumbar disc disease. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2014; 48(1):60-2. [18] Seki S, Kawaguchi Y, Mori M, et al. Association study of COL9A2 with lumbar disc disease in the Japanese population. J Hum Genet. 2006;51(12):1063-1067. [19] 宋海峰,吴志宏,费琦,等.中国汉族人群Trp2等位基因多态性与椎间盘退变性疾病的关联分析[J].中华医学杂志,2010,90(3):148-152.[20] 宋海峰,吴志宏,闫家智,等.腰椎间盘退变性疾病与COL9A2基因多态性的关系[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(8):1381-1383.[21] 陈涛,黎观保,梁科友,等.腰椎间盘退变与COL9A2基因单核苷酸多态性的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(9):1695-1702.[22] Rathod TN, Chandanwale AS, Gujrathi S, et al. Association between single nucleotide polymorphism in collagen IX and intervertebral disc disease in the Indian population. Indian J Orthop.2012; 46(4):420-426. [23] Meng T, Ren Q, Wang JM, et al. Association between COL9A2 Gln326Arg mutations and the development of intervertebral disc disease in a Chinese population. Genet Mol Res. 2016 Dec 19;15(4). [24] Hyun SJ, Park BG, Rhim SC, et al. A haplotype at the COL9A2 gene locus contributes to the genetic risk for lumbar spinal stenosis in the Korean population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(16):1273-1278. [25] Buckwalter JA. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine.1995; 20(11):1307-1314. [26] Annunen S, Paassilta P, Lohiniva J, et al. An allele of COL9A2 associated with intervertebral disc disease. Science.1999; 285(5426):409-412. [27] Aladin DMK, Cheung KMC, Chan D, et al. Expression of the Trp2 allele of COL9A2 is associated with alterations in the mechanical properties of human intervertebral discs. Spine.2007;32(25): 2820-2826. [28] 吴成爱,王娜,肖斌,等COL9A2链19 外显子单核苷酸基因多态性与腰椎间盘退变相关性分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013, 23(7):644-647.[29] Janeczko ?, Janeczko M, Chrzanowski R, et al. The role of polymorphisms of genes encoding collagen IX and XI in lumbar disc disease. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2014; 48(1):60-62. [30] 秦集斌,宋洁富,荆志振,等.手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的术后早期复发率与COL9A2基因多态性相关性研究[J].中国现代医药杂志, 2017,20(5):1-5.[31] Zhang Z, Zhang J, Ding L, et al. Meta-analysis of the association between COL9A2 genetic polymorphisms and lumbar disc disease susceptibility. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(20):1699-1706. [32] Wu H, Wang S, Chen W, et al. Collagen IX gene polymorphisms and lumbar disc degeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):47. [33] Jim JJ, Noponen-Hietala N, Cheung KM, et al. The TRP2 allele of COL9A2 is an age-dependent risk factor for the development and severity of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005; 30(24):2735-2742. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [2] | Quan Zhanrou, He Liumei, Chen Hao, Hong Wenxu, Gao Suqing . Distribution characteristics of polymorphism of human leukocyte antigen C of hepatitis B virus carriers in patients from Shenzhen [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 482-486. |
| [3] | Wang Wei, Ma Junfeng, Cui Zijian, Zhang Lilong, Jiang Zehua, Lu Yun. Meta-analysis of posterior cervical laminectomy titanium mini-plate versus lateral mass screw fixation for treating multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2614-2624. |
| [4] | Tian Yi-xing, Bao Zhao-hua, Zou Jun, Ji Yi-ming, Mei Xin, Pan Jun, He Wen-ye, Yang Hui-lin. Short-term effectiveness of single-level Isobar TTL dynamic internal fixation in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(7): 1020-1025. |
| [5] | Yin Xun-lu1, Feng Min-shan1, 2, Zhu Li-guo1, 2, Li Xue-peng1, Chen Lin3, Li Ling-hui1, Zhan Jia-wen1, Wei Xu1. Animal models of intervertebral disc degeneration: economy, feasibility, reliability and controllability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 619-624. |
| [6] | Li Haitao, Liang Ting, Shao Yijie, Chen Xi, Yang Huilin, Luo Zongping. Influence of needle puncture versus abnormal mechanical compression on the biological properties of annulus fibrosus: a preliminary study at nano-scale [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5526-5517. |
| [7] | Wu Tao, Liu Jun, Wang Gang . Reliability of evaluating C2-7 Cobb angle for cervical degenerative disease with unclear C7 vertebrae on X-ray, CT and MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(31): 4993-4997. |
| [8] | Zhao Yin, Zhou Sheng-yuan, Yuan Bo, Xu Guo-feng, Xu Zheng, Lv Bi-tao, Jia Lian-shun, Chen Xiong-sheng. Lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration assessed by the nine-point system with X-ray [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(3): 450-455. |
| [9] | Guo Mei-yu, Li Zhong-hai. Biomarkers for lumbar disc degeneration: how to solve the influences of specificity, sensitivity and covariates [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4562-4567. |
| [10] | Chen Jun, Wu Guang-hui. Efficacy and safety of artificial total disc replacement in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 2961-2967. |
| [11] | Bai Rong-fei1, Zhang Zhen2, Lin Yi-feng3, Yuan Chao3, Wang Sheng-yu1, Fang Sheng1, Chi Li-ye1 . Establishing a rat model of intervertebral disc degeneration using three methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(16): 2514-2519. |
| [12] | Li Da-peng1, Wu Yan2, Yue Jia-wei2, Wang Jia-lun2, Hu Lang1, Huang Yong-hui1. Insulin-like growth factor-1 upregulates the expression of aggrecan and collagen type II in nucleus pulposus cells via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(8): 1202-1208. |
| [13] | He Sheng-hua1, Lai Ju-yi2, Wang Ye-guang1, Sun Zhi-tao1, Wang Jian1, Feng Hua-long2, Huang Fei-qiang2. Yaotu Granules regulate the Fas/FasL expression in a rabbit model of lumbar disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(32): 5140-5145. |
| [14] | Ma Liang-yu1, Wang Shan-zheng2, Guo Yu-dong2, Chen Xiang-xu2, Yu Jia-bin1, Jia Jun1, Wang Chen2. Platelet-rich-plasma for intervertebral disc degeneration: from bench to bedside [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(32): 5215-5220. |
| [15] | Song Hong-fang, Zhang Wen, Zhang Qiang, Liu Zhi-cheng. Comparison study of the effect of fusion and non-fusion fixation on the movement of injured lumbar spine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(31): 4963-4968. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||