Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (16): 2601-2607.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1217
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of proprioceptive and balance training on rehabilitation of knee joint after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
Lu Yanyan1, 2, Xu Xuemeng2, Liu Wengang2, Du Jianping2, Chen Guocai1, 2, Chen Guoqian1, 2, Qiu Bofan1, 2, Zheng Yi1, 2, Wu Zugui1, 2
- 1the Fifth Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2019-06-08Published:2019-06-08 -
Contact:Xu Xuemeng, Master, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Lu Yanyan, Doctoral candidate, the Fifth Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China; Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Guangdong Provincial Industrial and Information Development Project, No. [2016]69 (to XXM)| Guangdong Provincial Famous Chinese Medicine Heritage Studio Construction Project, No. [2017]17 (to XXM)| the Scientific Research Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Bureau of Guangdong Province, No. 20183001 (to LWG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Yanyan, Xu Xuemeng, Liu Wengang, Du Jianping, Chen Guocai, Chen Guoqian, Qiu Bofan, Zheng Yi, Wu Zugui. Effect of proprioceptive and balance training on rehabilitation of knee joint after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2601-2607.
share this article
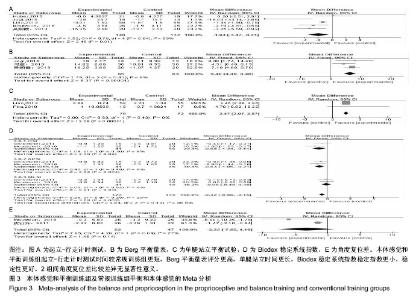
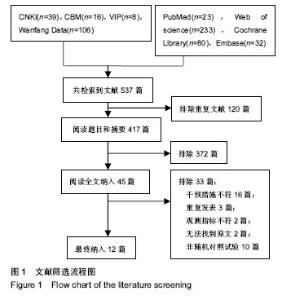
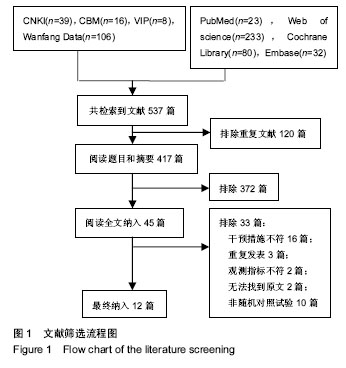
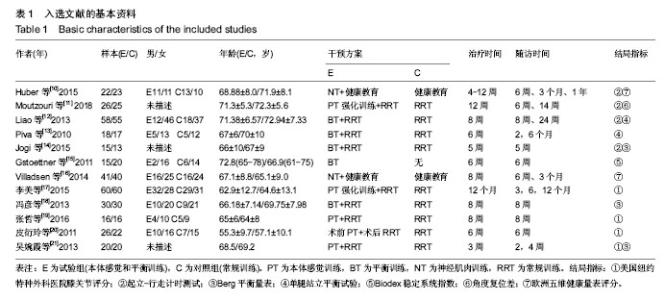
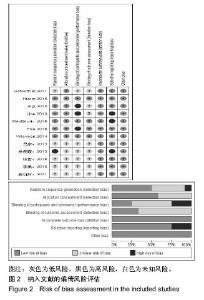
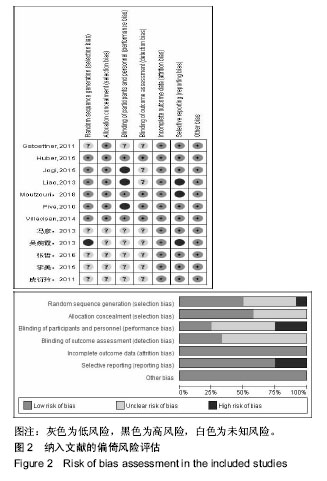
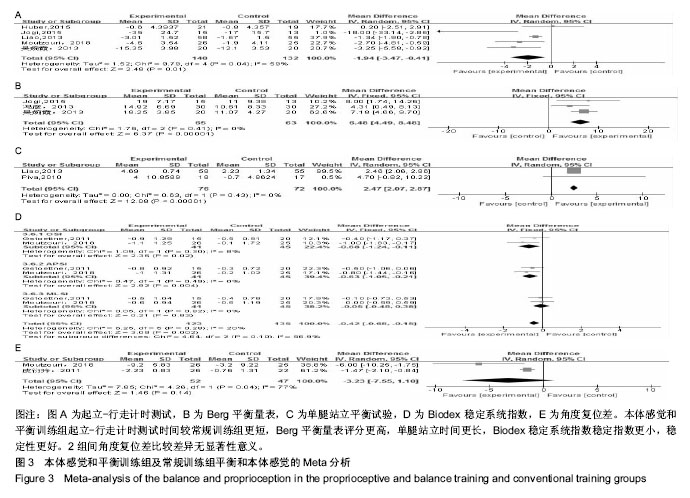
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 平衡和本体感觉 有8篇文献对治疗后平衡和本体感觉进行了报道[10-15,18,20],结局指标包括起立-行走计时测试、Berg平衡量表、单腿站立平衡试验、Biodex稳定系统指数、角度复位差。有5篇文献报道了起立-行走计时测 试[10-13,21],各研究间存在明显异质性(P=0.04,I2=59%),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示试验组起立-行走测试时间较对照组更短(WMD=-1.94,95%CI:-3.47至-0.41,P=0.01)。有3篇文献报道了Berg平衡量表[13,18,21],各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.41,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示试验组Berg平衡量表得分较对照组更高(WMD=6.48,95%CI:4.49-8.48,P < 0.000 01)。有2篇文献报道了单腿站立平衡试验[12,14],各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.43,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示试验组单腿站立时间更长,稳定性更好(WMD=2.47,95%CI:2.07-2.87,P < 0.000 01)。有2篇文献报道了Biodex稳定系统指数[11,15],各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.28,I2=20%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示试验组稳定指数较对照组更小(WMD=-0.42,95%CI:-0.68至-0.15,P=0.002),提示稳定性更好。有2篇文献报道了角度复位 差[11,20],各研究间存在明显异质性(P=0.04,I2=77%),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示2组间比较差异无显著性意义(WMD=-3.23,95%CI:-7.55-1.10,P=0.14)。平 A 衡与本体感觉Meta分析结果见图3。"
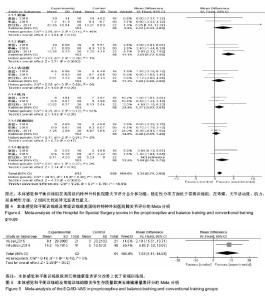
2.3.2 美国纽约特种外科医院膝关节评分 有3篇文献对术后美国纽约特种外科医院膝关节评分进行了报道[17,19,21],各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.20,I2=22%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示试验组美国纽约特种外科医院膝关节评分优于对照组(WMD=1.35,95%CI:0.71-2.00,P < 0.000 1)。各分项结果显示,在疼痛方面,2组间比较差异无显著性意义(WMD=2.22,95%CI:-0.43-4.86,P=0.10);在功能方面,试验组优于对照组(WMD=3.65,95%CI:1.72-5.58,P=0.000 2);在关节活动度方面,2组间比较差异无显著性意义(WMD=1.06,95%CI:-0.86-2.98,P=0.28);在肌力方面,2组间比较差异无显著性意义(WMD=1.27,95%CI:-0.03-2.57,P=0.05);在屈曲畸形方面,2组间比较差异无显著性意义(WMD=0.40,95%CI:-0.69-1.49,P=0.47);在稳定性方面,试验组优于对照组(WMD=1.35,95%CI:0.71-2.00,P < 0.000 1)。美国纽约特种外科医院膝关节评分Meta分析结果见图4。 2.3.3 欧洲五维健康量表评分 有2篇文献对欧洲五维健康量表评分进行了报道[10,16],各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.40,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示试验组欧洲五维健康量表评分高于对照组(WMD=7.83,95%CI:1.11-14.54,P=0.02)。欧洲五维健康量表评分的Meta分析结果见图5。"

| [1] Wang J, Yang L, Li Q, et al. Construction of an adherence rating scale for exercise therapy for patients with knee osteoarthritis. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2018;19(1): 263.[2] Komang-Agung IS, Sindrawati O, William PS. Do age and co-morbidy, among other factors, affect length of hospital stay following total knee arthroplasty. Malays Orthop J. 2018; 12(2): 25-30.[3] Chan A, Jehu DA, Pang M. Falls after total knee arthroplasty: frequency, circumstances, and associated factors-a prospective cohort study. Phys Ther. 2018;98(9): 767-778.[4] Zemková E, Hamar D. Sport-Specific Assessment of the effectiveness of neuromuscular training in young athletes. Front Phys. 2018; 9:264.[5] Blasco J, Igualcamacho C, Roigcasasús S. In-home versus hospital preoperative balance and proprioceptive training in patients undergoing TKR; rationale, design, and method of a randomized controlled trial. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2017;18(1):518. [6] Bennell K, Dobson F, Hinman R. Measures of physical performance assessments: self-paced walk test (spwt), stair climb test (sct), six-minute walk test (6mwt), chair stand test (cst), timed up & go (tug), sock test, lift and carry test (lct), and car task. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63(S11):S350-S370.[7] Muir SW, Berg K, Chesworth B, et al. Use of the berg balance scale for predicting multiple falls in community-dwelling elderly people: a prospective study. Phys Ther. 2008;88(4): 449-459.[8] Vellas BJ, Wayne SJ, Romero L, et al. One-leg balance is an important predictor of injurious falls in older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997;45(6):735-738.[9] Higgins JPT, Green S(editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.1.0[updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.[10] Huber EO, Roos EM, Meichtry A, et al. Effect of preoperative neuromuscular training (NEMEX-TJR) on functional outcome after total knee replacement: an assessor-blinded randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013; 16(1):101.[11] Moutzouri M, Gleeson N, Coutts F, et al. Early self-managed focal sensorimotor rehabilitative training enhances functional mobility and sensorimotor function in patients following total knee replacement: a controlled clinical trial. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(7):888-898.[12] Liao CD, Liou TH, Huang YY, et al. Effects of balance training on functional outcome after total knee replacement in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2013;27(8):697-709.[13] Jogi P, Overend TJ, Spaulding SJ, et al. Effectiveness of balance exercises in the acute post-operative phase following total hip and knee arthroplasty: A randomized clinical trial. SAGE Open Med. 2015;3: 2102642769.[14] Piva SR, Gil AB, Almeida GJ, et al. A balance exercise program appears to improve function for patients with total knee arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Phys Ther. 2010;90(6): 880-894.[15] Gstoettner M, Raschner C, Dirnberger E, et al. Preoperative proprioceptive training in patients with total knee arthroplasty. Knee.2011; 18(4):265-270.[16] Villadsen A, Overgaard S, Holsgaard-Larsen A, et al. Postoperative effects of neuromuscular exercise prior to hip or knee arthroplasty: a randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1130-1137. [17] 李美,马磊,宋鑫,等. 本体感觉强化训练对全膝关节置换术后膝关节功能的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(3):275-278.[18] 冯彦,唐建华,陈亚丽. 平衡训练对初次全膝关节置换术后患者平衡功能的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2013, 28(11): 1060-1062.[19] 张哲,马辉,康一凡,等. 本体感觉训练在全膝关节置换术后康复中的应用价值[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2016, 10(4): 17-20.[20] 皮衍玲,王雪强,杨树芬,等. 全膝关节置换术前本体感觉训练对术后的影响[J]. 中国康复,2011,26(5):350-352.[21] 吴婉霞,徐武华,刘文权,等. 早期本体感觉训练对全膝关节置换术后患者步行能力的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(15): 1508-1512.[22] Lanting BA, Lieberman JR, Callaghan JJ, et al. Ensuring a winner: the abcs of primary total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2015;64:369-379.[23] Westby MD, Brittain A, Backman CL. Expert consensus on best practices for post-acute rehabilitation after total hip and knee arthroplasty: a canada and united states delphi study. Arthritis Care Res. 2014;66(3):411-423.[24] Rakel BA, Zimmerman MB, Geasland K, et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for the control of pain during rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty: A randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Pain. 2014; 155(12): 2599-2611.[25] Saleh KJ, Lee LW, Gandhi R, et al. Quadriceps strength in relation to total knee arthroplasty outcomes. Instr Course Lect. 2010;59:119.[26] Xu J, Zhang J, Wang XQ, et al. Effect of joint mobilization techniques for primary total knee arthroplasty: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Medicine. 2017;96(49): e8827.[27] Soison A, Riratanapong S, Chouwajaroen N, et al. Prevalence of fall in patients with total knee arthroplasty living in the community. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97(12):1338-1343.[28] Wodowski AJ, Swigler CW, Liu H, et al. Proprioception and knee arthroplasty: a literature review. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016; 47(2):301-309.[29] Pohl T, Brauner T, Wearing S, et al. Effects of sensorimotor training volume on recovery of sensorimotor function in patients following lower limb arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(1):1-9.[30] Nam D, Nunley RM, Barrack RL. Patient dissatisfaction following total knee replacement: a growing concern? Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(11-Supple-A):96-100. |
| [1] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [2] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [3] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [4] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [5] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [6] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [7] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [8] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [9] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [10] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [11] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [12] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [13] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [14] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [15] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||