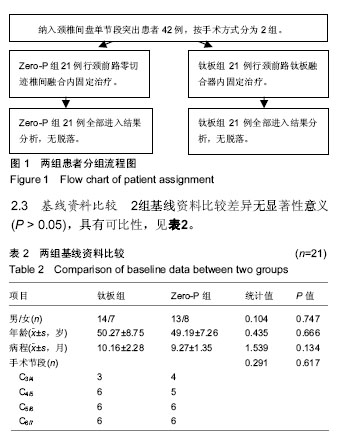
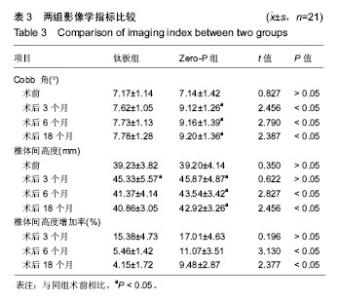
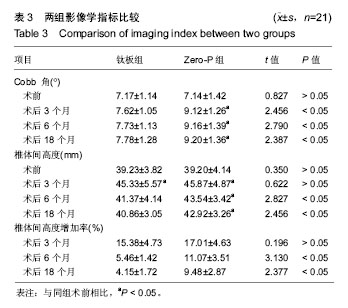
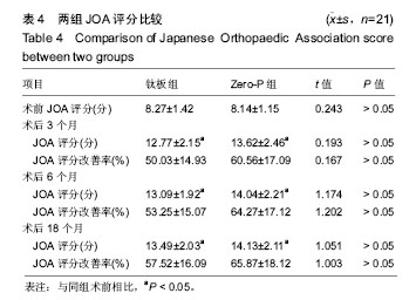
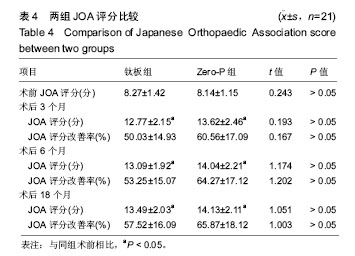
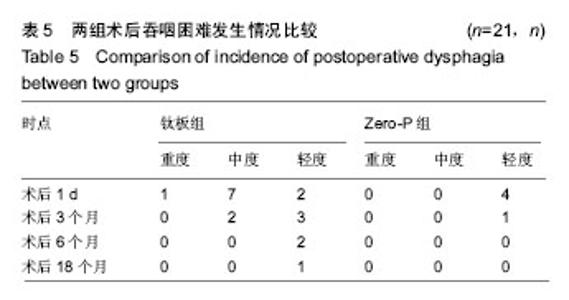
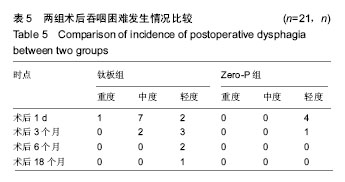
| [1] Kang DG, Anderson JC, Jr R AL. Return to play after cervical disc surgery. Clin Sports Med. 2016;35(4):529-543.[2] Goel A, Shah A, Patni N, et al. Immediate postoperative reversal of disc herniation following facetal distraction-fixation surgery: report of four cases. World Neurosurg. 2016;94(12):339-344.[3] Kawasaki T, Fukuda H, Kurosaki Y, et al. Acute compressive myelopathy caused by spinal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a combined effect of asymptomatic cervical spondylosis. World Neurosurg. 2016;95(7):619.e1-619.e4.[4] Wang BY, Wu TK, Liu H, et al. Intraoperative conversion of artificial cervical disc replacement to anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for iatrogenic fracture: A rare case report. Medicine. 2017;96(47): e8917.[5] 胡迪,王少飞,晁建虎,等. 2种颈前路椎间融合内固定治疗单节段颈椎间盘突出症的疗效比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015, 30(3): 295-296.[6] 邵海宇,张骏,杨迪,等. 零切迹颈椎前路融合固定系统与传统融合器钢板内固定系统治疗单节段颈椎间盘突出症的病例对照研究[J]. 中国骨伤, 2016, 29(6):530-537.[7] Zhang J, Meng F, Yan D, et al. Hybrid surgery versus anterior cervical discectomy and fusion in multilevel cervical disc diseases: a meta-analysis. Medicine. 2016; 95(21):e3621.[8] Ament JD, Yang Z, Pierce N, et al. Cost utility analysis of the cervical artificial disc vs fusion for the treatment of 2-level symptomatic degenerative disc disease: 5-year follow-up. Neurosurgery. 2016; 79(1):135-145.[9] Hou Y, Nie L, Pan X, et al. Effectiveness and safety of Mobi-C for treatment of single-level cervical disc spondylosis: a randomised control trial with a minimum of five years of follow-up. Bone Joint J. 2016; 98-B(6):829.[10] Hori M, Tsutsumi S, Yasumoto Y, et al. Cervical spondylosis: evaluation of microstructural changes in spinal cord white matter and gray matter by diffusional kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;32(5):428-432. [11] Yang JS, Chu L, Chen L, et al. Anterior or posterior approach of full-endoscopic cervical discectomy for cervical intervertebral disc herniation? A comparative cohort study. Spine. 2014;39(21): 1743-1750.[12] 刘威,盛伟斌,张健,等. 颈椎间盘置换及前路椎间融合治疗单节段颈椎间盘突出症:谁更多影响邻近节段发生退变[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(4):504-510.[13] 文天林,孙天胜. 脊髓型颈椎病的病理演变和治疗研究进展[J]. 人民军医, 2017,11(1):75-76.[14] Hou Y, Nie L, Pan X, et al. Effectiveness and safety of Mobi-C for treatment of single-level cervical disc spondylosis: a randomised control trial with a minimum of five years of follow-up. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(6):829.[15] Lin SY, Chen DC, Lin CL, et al. Risk of acute coronary syndrome in patients with cervical spondylosis. Atherosclerosis. 2018;271(35): 136-141.[16] 金成春,鲍广全,徐宏光.颈前路减压椎间融合器植骨融合术治疗单节段脊髓型颈椎病临床观察[J]. 山东医药, 2017, 57(16):64-66.[17] 冷华平,段永壮,李宽宽,等.颈前路减压zero-p椎间植骨融合内固定治疗单节段神经根型颈椎病的疗效及影像学分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2018,26(5):154-155.[18] Miao Q, Qiang JH, Jin YL. Effectiveness of percutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation for neck pain relief in patients with cervical spondylosis. Medicine. 2018;97(26):e11080.[19] Liu B, Zhu D, Yang J, et al. Can Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Result in Decreased Lifting Capacity of the Shoulder? World Neurosurg. 2015;84(6):1636-1644.[20] 徐远金,杨俊峰. 前路减压植骨融合联合钢板置入内固定治疗脊髓型颈椎病的效果分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2017,9(6):598-599.[21] 王宁,何百祥,鲍刚,等. 颈前路“零切迹”椎间融合器与传统钛板融合器内固定治疗单节段颈椎病的疗效比较[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2016,11(2):174-177.[22] 孙柏寒,郑柏,黄栋,等. 零切迹颈椎融合器ROI-C与传统钢板内固定治疗颈椎病临床效果比较[J]. 中国医药导报, 2017, 14(6):100-103.[23] 庄超,周栋,汤雪明,等. 颈前路零切迹椎间融合内固定系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病的疗效分析[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,17(6):751-755.[24] 刘春雷,王建伟,郭安丰,等. Zero-P颈椎前路椎间融合固定系统在颈椎前路减压融合术中的效果观察[J]. 实用中西医结合临床, 2018,17(2): 503-504.[25] 张圣飞,冯新民,张亮,等. 颈椎Zero-P融合器与传统钛板融合内固定治疗双节段颈椎病的疗效比较[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2015, 9(11):2107-2112.[26] 季海龙,赵秀泉,张丽,等. 零切迹椎间融合器(Zero-P)治疗老年单节段脊髓型颈椎病的效果分析[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2017,32(4):504-506.[27] 周锋,传礼,世卿.应用Zero-P行颈前路椎间融合术治疗外伤性颈椎椎间盘突出并脊髓损伤[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2017, 15(6):344-347.[28] 许艺荠,张雪松,孙太存,等. 新型Zero-P与cage钛板椎间融合器修复颈椎病:早期稳定性对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(22): 3227-3234.[29] Barbagallo GM, Romano D, Certo F, et al. Zero-P: a new zero-profile cage-plate device for single and multilevel ACDF. A single Institution series with four years maximum follow-up and review of the literature on zero-profile devices. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(6):S868-S878.[30] 吴增志,赖茂松,熊浩,等. Zero-P椎间融合术治疗颈椎间盘突出并脊髓损伤的疗效观察[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2017, 23(4):363-365. |