Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (9): 1455-1460.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1599
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell treatment for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: mechanisms of exosomes and factors
Zhang Changjiang, Liang Guiyou
- Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Revised:2018-11-21Online:2019-03-28Published:2019-03-28 -
Contact:Liang Guiyou, MD, Chief physician, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhang Changjiang, Master candidate, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Support Program, No. [2017]2969 (to LGY); Guizhou Provincial Social Development Research Project, No. Qian-ke-he-SZ-zi [2014]3022 (to LGY); the Science and Technology Plan Project of Zunyi City, No. Zun-shi-ke-he-she-zi[2018]69 (to LGY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Changjiang, Liang Guiyou. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell treatment for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: mechanisms of exosomes and factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1455-1460.
share this article

2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞概述及生物特性 2.1.1 骨髓间充质干细胞概述 骨髓间充质干细胞是一种来源于哺乳动物骨髓基质中的除造血干细胞以外的一类具有保留体外自我复制能力、多向分化潜能的干细胞[17]。在标准培养条件下,可表达细胞表面标记CD105、CD73 和CD90,而不表达细胞表面标记CD45、CD34、CD14或CD11b、CD79、CD19或HLA-DR[18],其具有自我更新、多向分化潜能、可体外大量扩增等干细胞生物学特性[19-21]。心肌梗死后移植骨髓间充质干细胞能够增加新生血管数量,减小梗死面积,减少瘢痕[22]。骨髓间充质干细胞在一定条件下被诱导分化为成骨细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞、心肌细胞、神经元及肝细胞等[23]。刘煜昊等[24]直接证据表明,人骨髓间充质干细胞能分化为心肌细胞和血管内皮细胞。研究显示,骨髓间充质干细胞具有低免疫原性[25]。骨髓间充质干细胞及其分化细胞表达的细胞外基质分子如黏附分子和整合素参与构成了支持造血的微环境,帮助造血干细胞的黏附和归巢以及细胞间的相互黏附。骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的细胞因子对造血干/祖细胞的自我更新与分化起重要调节作用。 2.1.2 归巢定植特性 骨髓间充质干细胞归巢是一种与造血干细胞相关的现象。造血干细胞被认为有能力从血液中迁移到不同器官,并在化学信号导航下返回到骨髓基质中。骨髓间充质干细胞被认为具有相似特征,这有助于它们迁移和移植到缺血心肌中并进行介导修复。实验研究结果显示,骨髓间充质干细胞在体外扩增之后,归巢能力严重受损。将未经过体外培养用绿色荧光蛋白转基因标记的骨髓间充质干细胞,移植到亚致死性辐射小鼠体内,55%-65%标记绿色荧光蛋白的细胞存活于骨髓间质中,4%-7%存活于脾脏中,而经体外培养24 h后用绿色荧光蛋白标记的骨髓间充质干细胞的存活率却下降到10%[26]。传代晚期的骨髓间充质干细胞已失去趋化因子受体CCR1、CCR9、CXCR6、CXCR5、CXCR4的表面表达,也就失去了对相应的趋化反应。因此,需要优化骨髓间充质干细胞的培养条件来维持趋化因子受体的归巢表达[27]。骨髓间充质干细胞在一定诱导条件下可以扩增分化为成骨细胞、软骨细胞、心肌细胞、脂肪细胞等。例如骨髓间充质干细胞在5-氮杂胞苷诱导下分化成心肌样细胞[28]。不同培养条件下骨髓间充质干细胞的分化能力也不相同。骨髓间充质干细胞通过归巢定植于心肌损伤位置,定向分化为心肌细胞,达到治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤的作用。 2.1.3 旁分泌特性 骨髓间充质干细胞发挥改善器官功能的效应依赖于其旁分泌作用。研究表明,骨髓间充质干细胞移植利用旁分泌作用改善心肌梗死后的心脏功能[29]。此外,旁分泌作用还可以解释许多与修复相关的作用机制,包括促进新生血管形成、减小梗死面积和瘢痕形成、改善心肌收缩功能等。有证据表明,骨髓间充质干细胞通过旁分泌相关因子来改善心脏功能,见表1,而不是通过直接分化成心肌细胞。骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体还携带miRNA基因,转录后参与抗凋亡和血管生成蛋白的调控[30-32],见表2。在这种情况下,外泌体作为一种运输心脏保护分子的载体获得了广泛的关注[33]。骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体可以通过抗凋亡、抗炎、促血管生成和免疫调节作用来保护心脏和大脑。骨髓间充质干细胞可能通过分泌卵泡抑素样分子1 (FSTL1)从而减少大鼠心肌梗死面积,进而起到心肌保护作用[34]。因此,骨髓间充质干细胞的旁分泌作用是治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤的又一重要机制。旁分泌特性可能成为骨髓间充质干细胞治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤的主要论点。"

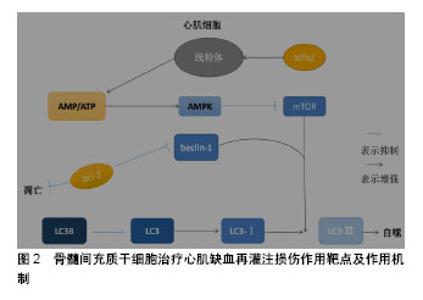
骨髓间充质干细胞可以通过分泌多种可溶性因子与细胞表面分子及胞外基质组成特异性的微环境发挥治疗作用。研究发现,骨髓间充质干细胞通过产生一些细胞因子发挥其生物学效应,如血管内皮生长因子、干细胞因子、肝细胞生长因子、肿瘤坏死因子α、胰岛素样生长因子1等[35]。这些细胞因子间接的抗凋亡、抗炎、抗纤维化等作用均促进了组织的内源性修复。骨髓间充质干细胞的抗炎、抗凋亡特性是治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤的基础,可以减少炎症发生及心肌细胞凋亡,缓解心肌损伤发生。 许多学者通过研究骨髓间充质干细胞与各种不同免疫细胞的相互作用,以及与同种异体T细胞的相互影响来证明骨髓间充质干细胞的低免疫原性。骨髓间充质干细胞对T细胞应答具有较低的刺激阈,并且不能诱导同种异体T细胞的激活,要充分的激活T细胞,需2个信号途径:①T受体对主要组织相容性复合体(major histocompatibility complex,MHC)分子与抗原递呈细胞表面抗原相结合的识别;②T细胞激活需要一个共刺激的信号,包括激活在T细胞内的CD28和抗原递呈细胞内的CD80或CD86[36]。骨髓间充质干细胞表面虽然能表达较低水平的MHCⅠ类分子,但是其缺乏MHCⅡ类分子和共刺激分子CD80或CD86,CD40的表达就有利于形成骨髓间充质干细胞的低免疫原性。尽管干扰素γ可刺激MHCⅠ类分子和Ⅱ类分子的表达,但仍不能激起可引起免疫反应的骨髓间充质干细胞的免疫原性。自然杀伤细胞是先天免疫系统中重要的效应细胞,这类细胞对缺乏MHCⅠ类分子表达的细胞具有极强的溶解细胞能力。同时,自然杀伤细胞也是重要的造血细胞移植过程的调节物。在体外,骨髓间充质干细胞对自然杀伤细胞具有抑制作用,并能下调其增殖能力、细胞毒活性和细胞因子表达。由于骨髓间充质干细胞表面低表达MHCⅠ类分子,自然杀伤细胞又对其有极强的杀伤作用[37]。Wu等[38]揭示miR-21通过负调控转化生长因子β1来调控骨髓间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用,这为骨髓间充质干细胞的免疫调控作用提供了新的见解。因此,可以利用骨髓间充质干细胞的免疫调控、低免疫性、减少免疫应答、抑制自然杀伤细胞、减少炎症发生达到治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤的目的。 2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤作用靶点及作用机制 骨髓间充质干细胞治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤的作用机制知之甚少,结合实验室前期结果以及当前研究进行总结骨髓间充质干细胞治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤潜在作用机制,见图2。"
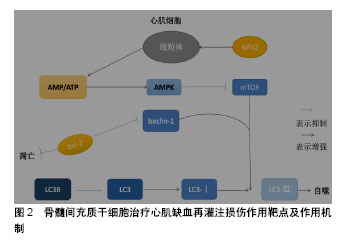
| [1] 陈伟伟,高润霖,刘力生,等.《中国心血管病报告2017》概要[J].中国循环杂志, 2018,33(1):1-8.[2] Chi HJ, Chen ML, Yang XC, et al. Progress in Therapies for Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18(15):1712-1721. [3] Zhou T, Chuang CC, Zuo L. Molecular Characterization of Reactive Oxygen Species in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:864946.[4] Okafor ON, Farrington K, Gorog DA. Allopurinol as a therapeutic option in cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;172:139-150.[5] Wang F, Liang GY, Liu DX, et al. Effect of Si-RNA-silenced HIF-1α gene on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion-induced insulin resistance. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(9):15514-15520.[6] Garcia-Dorado D, Ruiz-Meana M, Inserte J, et al. Calcium-mediated cell death during myocardial reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;94(2): 168-180.[7] Chouchani ET, Pell VR, Gaude E, et al. Ischaemic accumulation of succinate controls reperfusion injury through mitochondrial ROS. Nature. 2014;515(7527):431-435.[8] 陈福晖,刘达兴,容松.心肌缺血再灌注损伤发生机制的研究进展[J].安徽医药,2017, 21(12): 2145-2148.[9] 叶明,吴辉.心肌缺血再灌注损伤的研究新进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2016, 18(4): 434-437.[10] Tao H, Nuo M, Min S. Sufentanil protects the rat myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion injury via activation of the ERK1/2 pathway . Cytotechnology. 2018;70(1):169-176.[11] Li Y, Jiang T, Fu X, et al. Atorvastatin protects cardiomyocytes against OGD/R?induced apoptosis by inhibiting miR?199a?5p. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):3807-3816.[12] Penn MS, Dong F, Klein S, et al. Stem cells for myocardial regeneration. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;90(4):499-501.[13] 王娟,贾合磊,吉红亮,等.同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞移植在心肌梗死后心室重建中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(50): 7487-7493.[14] Karantalis V, Suncion-Loescher VY, Bagno L, et al. Synergistic Effects of Combined Cell Therapy for Chronic Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66(18):1990-1999.[15] Charwat S, Gyöngyösi M, Lang I, et al. Role of adult bone marrow stem cells in the repair of ischemic myocardium: current state of the art. Exp Hematol. 2008;36(6):672-680.[16] Salem HK, Thiemermann C. Mesenchymal stromal cells: current understanding and clinical status. Stem Cells. 2010;28(3):585-596.[17] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[18] Li X, Yu X, Lin Q, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into functional cardiac phenotypes by cardiac microenvironment. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;42(2):295-303.[19] Niu H, Mu J, Zhang J, et al. Comparative study of three types of polymer materials co-cultured with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for use as a myocardial patch in cardiomyocyte regeneration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(6):1535-1542.[20] Gao S, Zhao Z, Wu R, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves radiation-induced heart injury through DNA damage repair in rat model. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2017;56(1):63-77.[21] Humphreys BD, Bonventre JV. Mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury. Annu Rev Med. 2008;59:311-325.[22] Wen Z, Zheng S, Zhou C, et al. Repair mechanisms of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(5):1032-1043.[23] 丁国永,郭丽,杜忠君,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对肾缺血再灌注损伤后肾功能及氧化应激水平的改善作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2009, 35(4): 587-590,572.[24] 刘煜昊,房佰俊,史明霞,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞在体内外分化为心血管组织[J].基础医学与临床, 2007,27(6):643-647.[25] He JG, Xie QL, Li BB, et al. Exosomes Derived from IDO1-Overexpressing Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Immunotolerance of Cardiac Allografts. Cell Transplant. 2018. doi: 10.1177/0963689718805375. [Epub ahead of print][26] Rombouts WJ, Ploemacher RE. Primary murine MSC show highly efficient homing to the bone marrow but lose homing ability following culture. Leukemia. 2003;17(1):160-170.[27] Honczarenko M, Le Y, Swierkowski M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells express a distinct set of biologically functional chemokine receptors. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4):1030-1041.[28] Bao L, Meng Q, Li Y, et al. C-Kit Positive Cardiac Stem Cells and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Synergistically Enhance Angiogenesis and Improve Cardiac Function After Myocardial Infarction in a Paracrine Manner. J Card Fail. 2017;23(5):403-415.[29] Suzuki E, Fujita D, Takahashi M, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Cardiovascular Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;998:179-185.[30] Henning RJ. Current status of stem cells in cardiac repair. Future Cardiol. 2018;14(2):181-192.[31] Kishore R, Khan M. More Than Tiny Sacks: Stem Cell Exosomes as Cell-Free Modality for Cardiac Repair. Circ Res. 2016;118(2):330-343.[32] Suzuki E, Fujita D, Takahashi M, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes as a therapeutic tool for cardiovascular disease. World J Stem Cells. 2016; 8(9):297-305.[33] Gong M, Yu B, Wang J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(28):45200-45212.[34] Zhang MQ, Chen H, Zhai CL, et al. Follistatin-like 1-engineered mesenchymal stem cells prevent myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016;96(25):2017-2022.[35] Liu JF, Ling B. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of myocardial infarction. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2015;37(1):108-112.[36] Jacobs SA, Roobrouck VD, Verfaillie CM, et al. Immunological characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells and multipotent adult progenitor cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013;91(1):32-39.[37] Ruggeri L, Mancusi A, Burchielli E, et al. NK cell alloreactivity and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008;40(1):84-90.[38] Wu T, Liu Y, Fan Z, et al. miR-21 Modulates the Immunoregulatory Function of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through the PTEN/Akt/TGF-β1 Pathway. Stem Cells. 2015;33(11):3281-3290.[39] 巫宏坤,梁贵友,余丽梅,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞移植对犬体外循环再灌注肺损伤的影响[D]. 遵义:遵义医学院, 2016.[40] Ong SB, Subrayan S, Lim SY, et al. Inhibiting mitochondrial fission protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2010;121(18):2012-2022.[41] Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, et al. Distinct roles of autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: roles of AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy. Circ Res. 2007;100(6):914-922.[42] Zhang Z, Yang C, Shen M, et al. Autophagy mediates the beneficial effect of hypoxic preconditioning on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for the therapy of myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):89.[43] Jin Y, Wang H, Cui X, et al. Role of autophagy in myocardial reperfusion injury. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2010;2:1147-1153.[44] 赵海洋,张佳运,程姝娟.自噬在急性心肌梗死后无复流中的表达[J].广东医学,2016,37(11):1628-1630.[45] Cui X, He Z, Liang Z, et al. Exosomes From Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect the Myocardium Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2017;70(4):225-231.[46] Liu L, Jin X, Hu CF, et al. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Rescue Myocardial Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing Cardiomyocyte Autophagy Via AMPK and Akt Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(1):52-68.[47] Zhang Z, Yang M, Wang Y, et al. Autophagy regulates the apoptosis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxic condition via AMP-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2016;40(6):671-685.[48] Matsui Y, Kyoi S, Takagi H, et al. Molecular mechanisms and physiological significance of autophagy during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Autophagy. 2008;4(4):409-415.[49] 张文静,崔丽艳,张捷.自噬与缺血再灌注损伤[J].检验医学, 2014,29(2): 182-185.[50] Valentim L, Laurence KM, Townsend PA, et al. Urocortin inhibits Beclin1-mediated autophagic cell death in cardiac myocytes exposed to ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006;40(6): 846-852.[51] Maslov LN, Podoksenov IuK, Portnichenko AG, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning of stem cells as a new approach to increase the efficacy of cell therapy for myocardial infarction. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2013;(12):16-25.[52] Hu C, Li L. Preconditioning influences mesenchymal stem cell properties in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(3):1428-1442.[53] Epstein SE, Luger D, Lipinski MJ. Paracrine-Mediated Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Intravenously Administered Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Transformative Strategy for Cardiac Stem Cell Therapeutics. Circ Res. 2017;121(9):1044-1046.[54] Florea V, Rieger AC, DiFede DL, et al. Dose Comparison Study of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients With Ischemic Cardiomyopathy (The TRIDENT Study). Circ Res. 2017;121(11): 1279-1290.[55] Ciuffreda MC, Malpasso G, Chokoza C, et al. Synthetic extracellular matrix mimic hydrogel improves efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for ischemic cardiomyopathy. Acta Biomater. 2018;70:71-83.[56] Elmadbouh I, Ashraf M. Tadalafil, a long acting phosphodiesterase inhibitor, promotes bone marrow stem cell survival and their homing into ischemic myocardium for cardiac repair. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(21): e13480. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||