Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 301-308.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.02.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
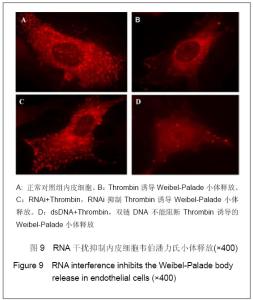
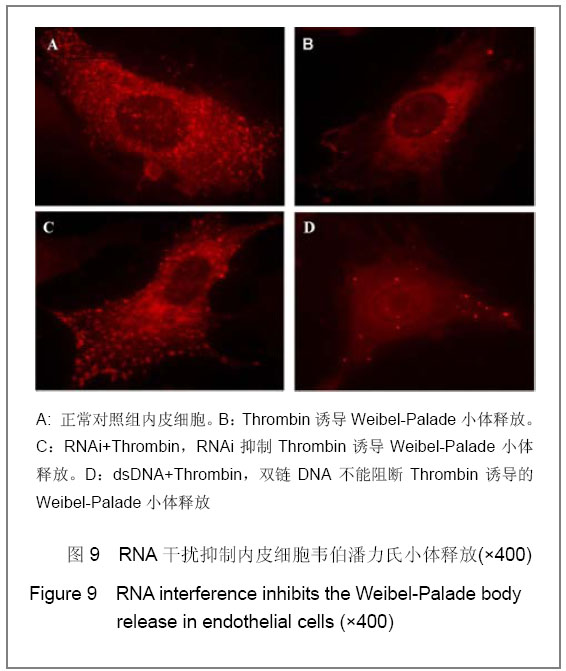
RNA interference inhibits Weibel-Palade body release from endothelial cells
Yang Shui-xiang, Wei Xiao-fei, Cui Yu-xia, Zhou Yong
- Department of Cardiology, Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Beijing 100038, China
-
Received:2012-05-04Revised:2012-06-05Online:2013-01-08Published:2013-02-25 -
About author:Yang Shui-xiang☆, Doctor, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiology, Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Beijing 100038, China sxyang68@163.com -
Supported by:Supported by: Beijing Natural Foundation Committee, No. 7083108
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Shui-xiang, Wei Xiao-fei, Cui Yu-xia, Zhou Yong. RNA interference inhibits Weibel-Palade body release from endothelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(2): 301-308.
share this article
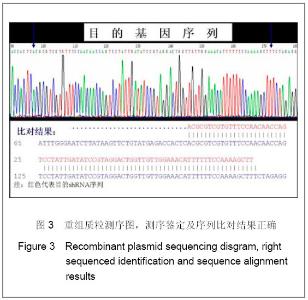
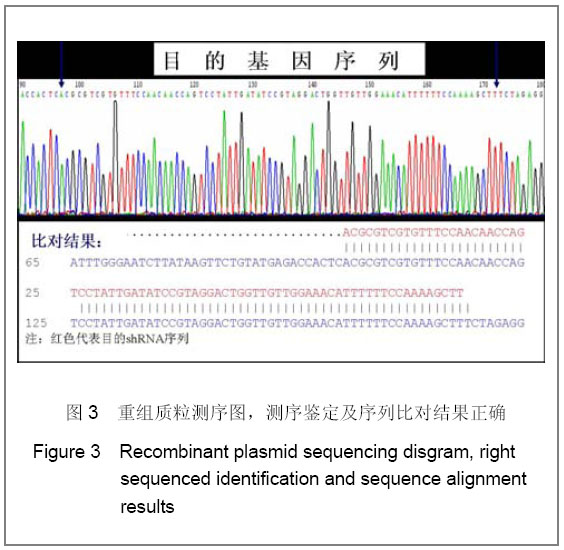
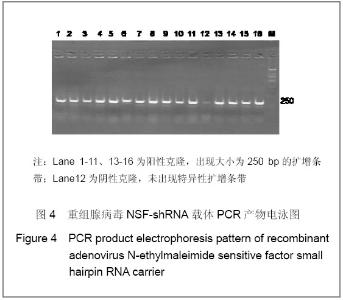
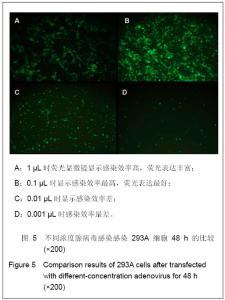
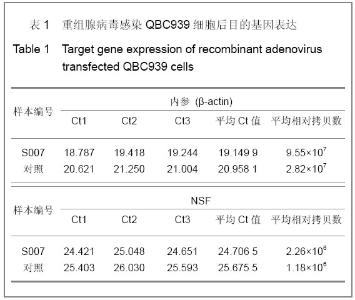
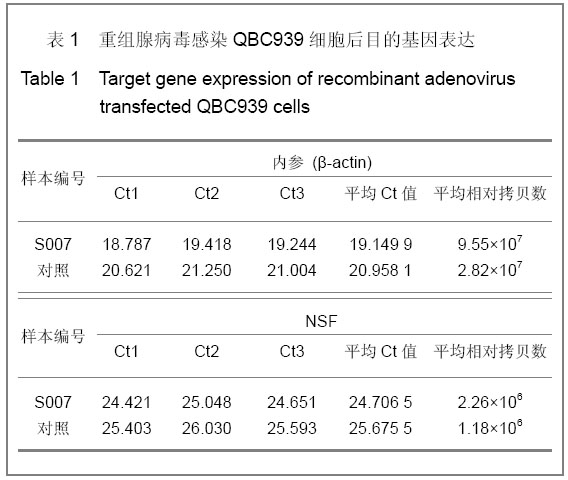
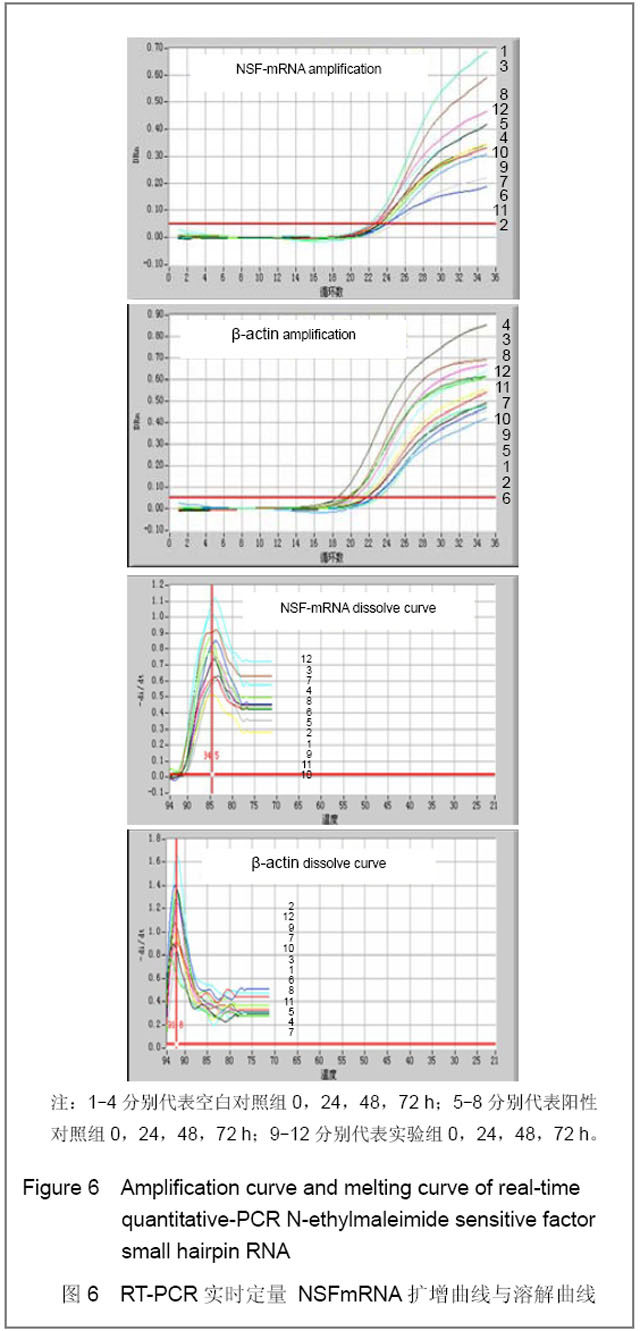
2.3 转染人主动脉内皮细胞后NSFmRNA的表达 总RNA质量检测:利用紫外分光光度计检测样品12份, A260/A280在1.8-2.0,均合格;2%凝胶电泳,18 s和28 s两条带明亮清晰,亮度比值2∶1,说明RNA质量良好(图省略)。 RT-PCR实时定量NSF-mRNA扩增曲线:实时荧光定量PCR(RT-PCR)根据反应体系中的荧光基团,建立实时扩增曲线,内参基因及NSF-mRNA的扩增曲线如下,见图6。该反应体系中,Ct值的重现性极好,即同一模板不同时间扩增或同一时间不同管内扩增,得到的Ct值恒定,并可利用标准曲线对未知样品进行定量测定。溶解曲线是内嵌染料在反应末尾时对扩增产物溶解而产生的溶解峰,单峰表明扩增产物特异性好。本实验各组中目的基因及对照基因的溶解曲线均为单峰,表明扩增结果具有特异性,见图6。"
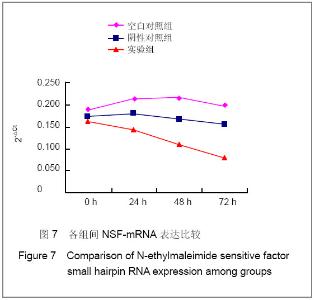
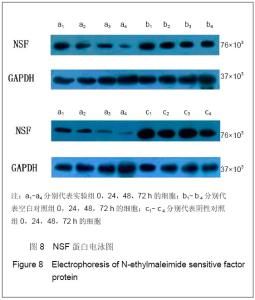
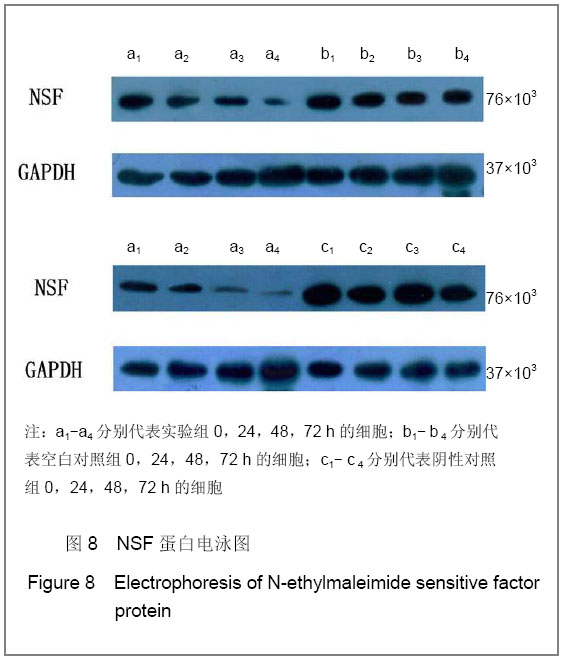
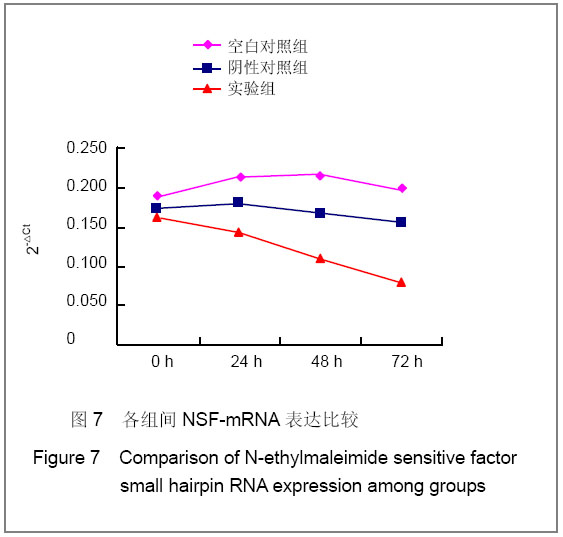
转染后NSF-mRNA的表达量:通过检测每个样品的对照基因,计算目的基因的相对表达量。计算方法:△Ct(相对表达量)=Ct(目的基因)-Ct(内参)。NSF-mRNA的表达情况,见图7(以2-△Ct为观察指标)。如图所示,各组比较,实验组与空白对照组(P =0.02)、实验组与阴性对照组(P=0.035)之间有显著性差异;而空白对照组与阴性对照组之间比较,差异无显著性意义(P=0.25)。在各组内部不同时间点的比较上,空白对照组(P=0.988)和阴性对照组(P=0.955)内各时间点NSF-mRNA的表达差异无显著性意义,实验组内NSF-mRNA的表达量随着时间的变化持续下降,差异具有显著性意义(P=0.048)。"
| [1] Sioud M. Promises and challenges in developing RNAi as a research tool and therapy. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;703: 173-187.[2] Shimizu H, Fujita T. New short interfering RNA-based therapies for glomerulonephritis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7(7): 407-415.[3] Katakowski JA, Palliser D. Optimizing siRNA delivery to the genital mucosa.Discov Med. 2011;11(57):124-132.[4] Yang SX, Hu DY, Tang CS. Zhongguo Xinxueguanbing Yanjiu Zazhi. 2004;2(12):1-3.杨水祥,胡大一,唐朝枢.基因组学研究的革命性工具-小分子RNA的研究进展(一)[J].中国心血管病研究杂志, 2004,2(12): 1-3.[5] Yang SX, Hu DY, Tang CS. Zhongguo Xinxueguanbing Yanjiu Zazhi. 2005;3(1):14-15.杨水祥,胡大一,唐朝枢.基因组学研究的革命性工具-小分子RNA的研究进展(二)[J].中国心血管病研究杂志, 2005,3(1): 14-15.[6] Yang SX, Yan J, Chen MZ, et al. Zhonghua Xinxueguanbing Zazhi. 2004;32(2):161-165.杨水祥,阎娟,陈明哲,等.Racl在内皮细胞韦伯潘力氏小体释放中的作用[J].中华心血管病杂志,2004,32(2):161-165.[7] Yang SX,Yan J,Deshpande SS, et al. Rac1 regulates the release of weibel-palade bodies in human aortic endothelial cells. Chinese Medical Journal.2004;117(8):1143-1150.[8] Matsushita K, Morrell CN, Cambien B, et al. Nitric oxide regulates exocytosis by S-nitrosylation of N-ethylmaleimdide-sensitive factor. CELL. 2003;115(2): 139-150.[9] Yang SX, Quick RA, Irani K, et al. Rac1 regulates the release of Weibel-Palade Bodies in human aortic endothelial cells. Cinese medical journal. 2004;117(8):1143-1150.[10] Qian Z, Gelzer-Bell R, Yang SX, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition of weibel-palade body release in cardiac transplant rejection. Circulation. 2001;104(19):2369-75.[11] Ming X. Cellular delivery of siRNA and antisense oligonucleotides via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(4):435-449.[12] Samuel-Abraham S, Leonard JN. Staying on message: design principles for controlling nonspecific responses to siRNA. FEBS J. 2010;277(23):4828-4836.[13] Amin HM, Ahmad S, Walenga JM, et al. Soluble P-selectin in human plasma: effect of anticoagulant matrix and its levels in patients with cardiovascular disorders. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2000;6(2):71-76.[14] Russell FD, Skepper JN, Davenport AP. Evidence using immunoelectron microscopy for regulated and constitutive pathways in the transport and release of endothelin. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1998;31(3):424-430.[15] Wolff B, Burns AR, Middleton J, et al. Endothelial cell "memory" of inflammatory stimulation: human venular endothelial cells store interleukin 8 in Weibel-Palade bodies. J Exp Med. 1998;188(9):1757-1762.[16] Ito T, Yamakuchi M, Lowenstein CJ. Thioredoxin increases exocytosis by denitrosylating N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(13):11179-11184.[17] Lowenstein CJ. Nitric oxide regulation of protein trafficking in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;75(2): 240-246.[18] Ferlito M, Fulton WB, Zauher MA, et al. VAMP-1, VAMP-2, and syntaxin-4 regulate ANP release from cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;49(5):791-800. [19] Goel A, Su B, Flavahan S,et al. Increased endothelial exocytosis and generation of endothelin-1 contributes to constriction of aged arteries. Circ Res. 2010;107(2):242-251. [20] Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Morrell CN, et al. Exocytosis of endothelial cells is regulated by N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;440:203-215. [21] Calvert JW, Gundewar S, Yamakuchi M, et al. Inhibition of N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor protects against myocardial ischemia/ reperfusion injury. Circ Res. 2007;101(12): 1247-1254.[22] He GP, Zhang SZ. Shengwu Huaxue yu Shengwu Wuli Jinzhan. 2005;32(3):258-267.何国平,张思仲.短发夹RNA介导RNA干扰的时间和剂量效应研究[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2005,32(3):258-267. |
| [1] | Chen Ju, Zheng Jinchang, Liang Zhen, Huang Chengshuo, Lin Hao, Zeng Li. Effect and mechanism of beta-caryophyllene in mice with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [2] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [3] | Li Linzhen, Jiao Hongzhuo, Chen Weinan, Zhang Mingzhe, Wang Jianlong, Zhang Juntao. Effect of icariin-containing serum on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in human chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [4] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [5] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [6] | Lyu Xiaofan, Huang Yi, Ding Liucheng . Mitochondrial mechanism and intervention therapy in diabetic cystopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1508-1515. |
| [7] | Cao Xinyan, Yu Zifu, Leng Xiaoxuan, Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Liu Xihua. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation on motor function and gait in children with cerebral palsy: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1539-1548. |
| [8] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [9] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [10] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [11] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [12] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [13] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [14] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [15] | Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||