Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (36): 5898-5904.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.36.027
Research advances in circular RNAs
Cheng Han-rong1, 2, 3, He Shao-ru2, 3, Wu Ben-qing1
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Shenzhen People’s Hospital, the Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, Shenzhen 518020, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Pediatrics, Guangdong General Hospital & Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 3Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2017-07-09Online:2017-12-28Published:2018-01-04 -
Contact:Wu Ben-qing, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Pediatrics, Shenzhen People’s Hospital, the Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, Shenzhen 518020, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Cheng Han-rong, Studying for doctorate, Associate chief physician, Department of Pediatrics, Shenzhen People’s Hospital, the Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, Shenzhen 518020, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Pediatrics, Guangdong General Hospital & Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific and Technological Program of Shenzhen, No. JCYJ20140416122812046
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Han-rong1, 2, 3, He Shao-ru2, 3, Wu Ben-qing1. Research advances in circular RNAs[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(36): 5898-5904.
share this article
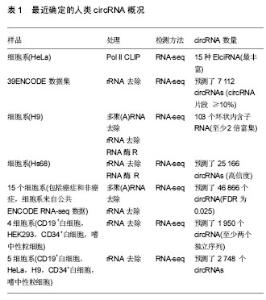
2.1 CircRNAs的多样性 CircRNAs表达水平低,并且最初认为是剪接体介导的剪接错误的副产物或从内含子脱壳脱离的中间体[29-30]。因此,circRNAs很少受到关注,认为不可能在生物过程中发挥关键作用。到2010年为止,几乎没有发现circRNAs,并且对circRNA生物发生的研究极少。 然而,随着高通量测序技术和计算分析的发展,已经发现了从古菌到人类的成千上万的circRNAs[6-11,31]。一些circRNA的表达比其相同基因的经典线性转录物的表达高10倍以上[7],见表1。 2.2 circRNAs的生物起源 最近的研究表明,通过反向剪接的circRNAs的生物发生不同于线性RNAs的规范剪接[12]。此外,认识了circRNA生物发生,特别是关于其调控和竞争反向剪接和规范剪接的几个最新进展[1]。例如Jeck等[7]提出了2种circRNA形成模型。模型1为“套索驱动的环化”或“外显子跳跃”,模型2为“内含子配对驱动的环化”或“直接后剪切”。Kelly[16]及其同事还发"

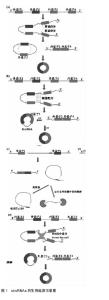
现外显子环化很广泛,并且与用肿瘤坏死因子α或肿瘤生长因子β处理的人脐静脉内皮细胞中的外显子跳跃相关。 一些证据表明内含子配对驱动的环化可能比套索驱动的环化发生更频繁[32],证据显示:内含子配对驱动的环化模型,指出反向互补序列,包括IRAlus,对circRNA生物发生很重要[12-15,17-19]。Zhang等[12]发现了一种新型的人类细胞circRNA,来源于内含子,被称为环状内含子RNA(ciRNA)。环状内含子RNA的生物合成依赖于在5'剪接位点附近7 nt富含GU的元件的共有基序和在分支点位点附近的11 nt富含C元件[9]。最近也发现外显子环化,内含子“保留”在外显子之间,这些称为外显子circRNA或EIciRNA,它们可以通过突变互补序列过表达[11]。然而,EIciRNA形成的机制仍然未知。这些机制显著增加了人类转录组的调节复杂性。 此外,研究人员已经鉴定出肌肉盲蛋白(MBL),其可以结合到circMb1侧面的内含子,以激发作为RNA结合蛋白的circRNA的形成,从而将两个内含子桥接在一起[17]。类似地,研究人员报道了另一种CircRNA生物发生模式,其中RNA结合蛋白之间的相互作用形成了内含子之间的桥梁,这导致剪接供体和剪接受体接近以促进circRNA的形成[33]。可是,Conn和其他人最近发现RNA结合蛋白 Quaking(QKI)调节circRNA的形成[20]。相反的,Ivanov[14]和其他人指出,RNA编辑酶ADAR1可以结合双链RNA,通过融化茎结构拮抗circRNA生物发生。 因此,在一些条件下,RNA结合蛋白可以用作circRNA形成的激活剂或抑制剂。 值得注意的是,Zhang等[12]首次提出了一种类似于可变剪接的替代性环化模型,通过互补序列(重复或非重"

| [1] Chen LL, Yang L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015;12(4):381-388. [2] Nigro JM, Cho KR, Fearon ER, et al. Scrambled exons. Cell. 1991;64(3):607-613.[3] Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, et al. Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell. 1993; 73(5):1019-1030.[4] Zaphiropoulos PG. Circular RNAs from transcripts of the rat cytochrome P450 2C24 gene: correlation with exon skipping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 93(13):6536-6341.[5] Pasman Z, Been MD, Garcia-Blanco MA. Exon circularization in mammalian nuclear extracts. RNA.1996;2(6):603-610.[6] Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, et al. Cell-Type Specific Features of Circular RNA Expression. PLoS Genetics. 2013; 9(9):e1003777.[7] Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19(2):141-157.[8] Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495(7441):333-338.[9] Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, et al. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2013;51(6):792-806.[10] Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H, et al. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014;15(7):409.[11] Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(3):256-264.[12] Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, et al. Complementary sequence- mediated exon circularization. Cell. 2014;159(1):134-147.[13] Liang D, Wilusz JE. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014;28(20):2233-2247.[14] Ivanov A, Memczak S, Wyler E, et al. Analysis of intron sequences reveals hallmarks of circular RNA biogenesis in animals. Cell Rep. 2015;10(2):170-177.[15] Starke S, Jost I, Rossbach O, et al. Exon circularization requires canonical splice signals. Cell Rep. 2015;10(1):103-111.[16] Kelly S, Greenman C, Cook PR, et al. Exon skipping is correlated with exon circularization. J Mol Biol. 2015;427(15): 2414-2417.[17] Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, et al. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 2014;56(1):55-66. [18] Vicens Q, Westhof E. Biogenesis of Circular RNAs. Cell. 2014;159(1):13-14.[19] Iverfeldt K, Serfözö P, Diaz A L, et al. RNA circularization strategies in vivo and in vitro. Nucl Acids Res. 2015;43(4): 2454-2465.[20] Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, et al. The RNA Binding Protein Quaking Regulates Formation of circRNAs. Cell. 2015; 160(6):1125-1134.[21] Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges Nature. 2013; 495(7441):384-388.[22] Burd CE, Jeck WR, Liu Y, et al. Expression of linear and novel circular forms of an ink4/arf-associated non-coding rna correlates with atherosclerosis risk. Plos Genet. 2010;6(12): e1001233.[23] Hansen TB, Kjems J, Damgaard CK. Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73(18):5609-5612.[24] Li F, Zhang L, Li W, et al. Circular RNA ITCH has inhibitory effect on ESCC by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6(8):6001-6013. [25] Bachmayr-Heyda A, Reiner AT, Auer K, et al. Correlation of circular RNA abundance with proliferation--exemplified with colorectal and ovarian cancer, idiopathic lung fibrosis, and normal human tissues. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8057.[26] Westholm JO, Miura P, Olson S, et al. Genomewide analysis of Drosophila circular RNAs reveals their structural and sequence properties and age-dependent neural accumulation. Cell Reports. 2014;9(5):1966-1980.[27] Bahn JH, Zhang Q, Li F, et al. The Landscape of MicroRNA, Piwi-Interacting RNA, and Circular RNA in Human Saliva. Clin Chem. 2015;61(1):221-230.[28] Li P, Chen S, Chen H, et al. Using circular RNA as a novel type of biomarker in the screening of gastric cancer. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2015;444:132-136.[29] Cocquerelle C, Mascrez B, Hétuin D, et al. Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. FASEB J. 1993;7(1):155-160.[30] Qian L, Vu MN, Carter M, et al. A spliced intron accumulates as a lariat in the nucleus of T cells. Nucl Acids Res. 1992; 20(20):5345-5350.[31] Danan M, Schwartz S, Edelheit S, et al. Transcriptome-wide discovery of circular RNAs in Archaea. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(7):3131-3142.[32] Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(5):453-461.[33] Lasda E, Parker R. Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. RNA. 2014;20(12):1829-1842.[34] Suzuki H, Tsukahara T. A view of pre-mRNA splicing from RNase R resistant RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(6):9331-9342.[35] Thomas LF, Sætrom P. Circular RNAs are depleted of polymorphisms at microRNA binding sites. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(16):2243-2246.[36] Chen CY, Sarnow P. Initiation of protein synthesis by the eukaryotic translational apparatus on circular RNAs. Science. 1995;268(5209):415-417.[37] Perriman R, Jr AM. Circular mRNA can direct translation of extremely long repeating-sequence proteins in vivo. RNA. 1998;4(9):1047-1054.[38] Wang PL, Bao Y, Yee MC, et al. Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. Plos One. 2014;9(6):e90859.[39] Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, et al. Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett. 2013; 339(2):159-166.[40] Taulli R, Loretelli C, Pandolfi PP. From pseudo-ceRNAs to circ-ceRNAs: a tale of cross-talk and competition. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013;20(5):541-543.[41] Hansen TB, Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, et al. miRNA-dependent gene silencing involving Ago2-mediated cleavage of a circular antisense RNA. Embo J. 2011;30(21):4414-4422.[42] Junn E, Lee KW, Jeong BS, et al. Repression of alpha-synuclein expression and toxicity by microRNA-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(31):13052-13057.[43] Jiang L, Liu X, Chen Z, et al. MicroRNA-7 targets IGF1R (insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Biochem J. 2010;432(1):199-205.[44] Chao CW, Chan D C, Kuo A, et al. The mouse formin (Fmn) gene: abundant circular RNA transcripts and gene-targeted deletion analysis. Mol Med. 1998;4(9):614-628.[45] Zhang Y, Yang L, Chen LL. Life without A tail: new formats of long noncoding RNAs. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;54(1): 338-349.[46] Wang Y, Wang Z. Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA.2015;21(2):172-179.[47] Abbas Z, Afzal R. Life cycle and pathogenesis of hepatitis D virus: A review. World J Hepatol. 2013;5(12):666-675.[48] Alves C, Branco C, Cunha C. Hepatitis delta virus: a peculiar virus. Adv Virol. 2013;2013(3):560105.[49] Hentze MW, Preiss T. Circular RNAs: splicing's enigma variations. Embo J. 2013;32(7):923-925.[50] Wilusz JE, Sharp PA. Molecular biology. A circuitous route to noncoding RNA. Science. 2013;340(6131):440-441.[51] Satoh J, Yamamura T. Gene expression profile following stable expression of the cellular prion protein. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2004;24(6):793-814.[52] Humphries B, Yang C. The microRNA-200 family: small molecules with novel roles in cancer development, progression and therapy. Oncotarget. 2015;6(9):6472-6498.[53] Garzon R, Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Ann Rev Med. 2009;60(1):167-179.[54] Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(4):259-269.[55] Dropcho EJ, Chen YT, Posner JB, et al. Cloning of a brain protein identified by autoantibodies from a patient with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84(13):4552-4556.[56] Lukiw WJ. Circular RNA (circRNA) in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Front Genet. 2013; 4(4):307.[57] Suto T, Yokobori T, Yajima R, et al. MicroRNA-7 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with poor prognosis and regulates cetuximab sensitivity via EGFR regulation. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36(3):338-345.[58] Hao Z, Yang J, Wang C, et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits metastasis and invasion through targeting focal adhesion kinase in cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):480-487.[59] Kalinowski FC, Brown RA, Ganda C, et al. microRNA-7: a tumor suppressor miRNA with therapeutic potential. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;54(8):312-317.[60] Fang XY, Pan HF, Leng RX, et al. Long noncoding RNAs: Novel insights into gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015;356 (2 Pt B):357-366.[61] Gla?ar P, Papavasileiou P, Rajewsky N. CircBase: a database for circular RNAs. RNA. 2014;20(11):1666-1670.[62] Ghosal S, Das S, Sen R, et al. Circ2Traits: a comprehensive database for circular RNA potentially associated with disease and traits. Front Genet. 2013;4(283):283. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaoyang, Tang Tian, Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Repair and regenerative therapies of the annulus fibrosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1582-1587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||