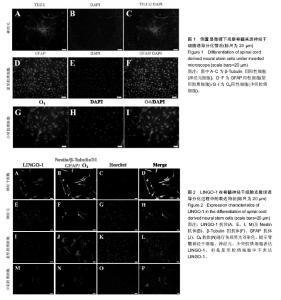
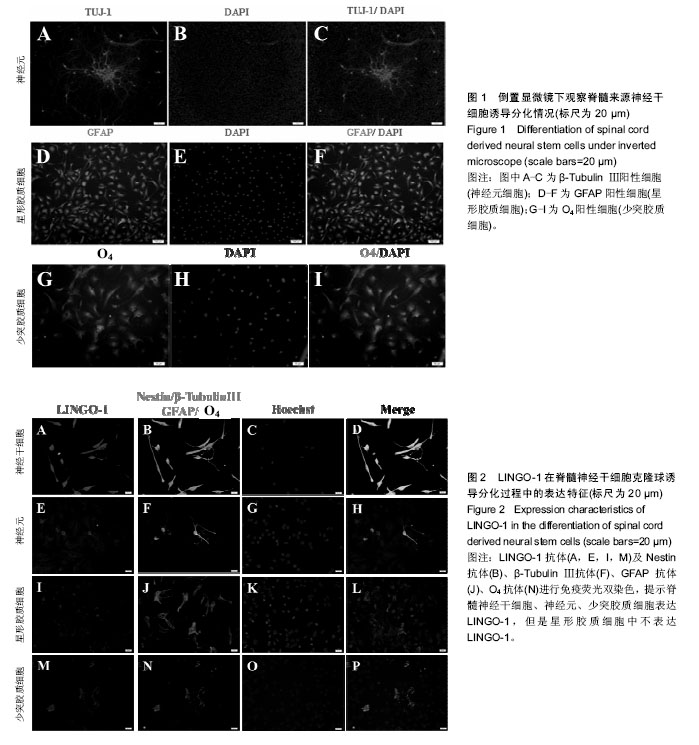
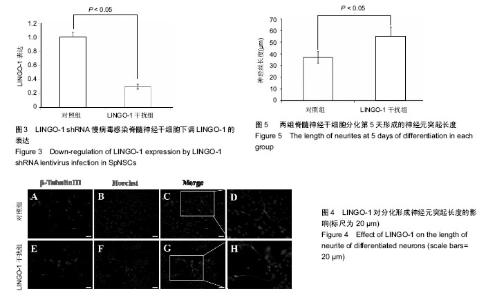
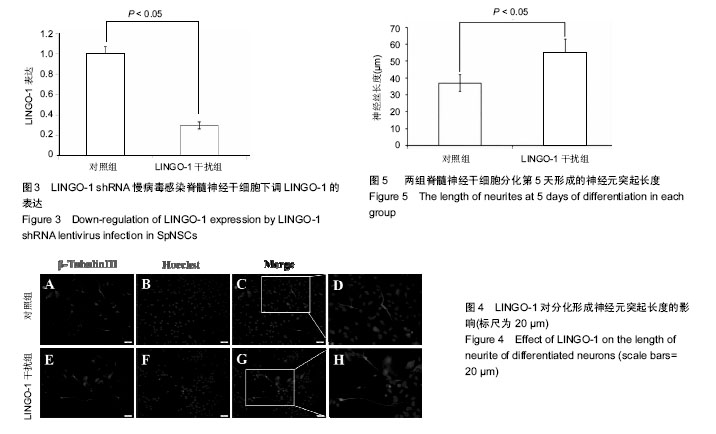
| [1] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system.Science. 1992;255(5052):1707-1710.[2] Sabelström H, Stenudd M, Frisén J. Neural stem cells in the adult spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 2014;260:44-49.[3] GrandPré T, Nakamura F, Vartanian T, et al. Identification of the Nogo inhibitor of axon regeneration as a Reticulon protein. Nature. 2000;403(6768):439-444.[4] Mi S, Lee X, Shao Z, et al. LINGO-1 is a component of the Nogo-66 receptor/p75 signaling complex. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7(3):221-228.[5] Ji B, Li M, Wu WT, et al. LINGO-1 antagonist promotes functional recovery and axonal sprouting after spinal cord injury. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006;33(3):311-320.[6] Zhao XH, Jin WL, Wu J, et al. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and up-regulation of LINGO-1 are involved in LINGO-1 antagonist regulated survival of cerebellar granular neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008;28(5): 727-735.[7] Scivoletto G, Miscusi M, Forcato S, et al. The Rehabilitation of Spinal Cord Injury Patients in Europe. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2017;124:203-210.[8] Sobhani A, Khanlarkhani N, Baazm M, et al. Multipotent Stem Cell and Current Application Acta Med Iran. 2017;55(1):6-23.[9] Salewski RP, Mitchell RA, Shen C, et al. Transplantation of neural stem cells clonally derived from embryonic stem cells promotes recovery after murine spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(1):36-50.[10] Nemati SN, Jabbari R, Hajinasrollah M, et al. Transplantation of adult monkey neural stem cells into a contusion spinal cord injury model in rhesus macaque monkeys. Cell J. 2014;16(2): 117-130.[11] Sabelström H, Stenudd M, Réu P, et al. Resident neural stem cells restrict tissue damage and neuronal loss after spinal cord injury in mice. Science. 2013;342(6158):637-640.[12] Sutter R, Yadirgi G, Marino S. Neural stem cells, tumour stem cells and brain tumours: dangerous relationships.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1776(2):125-137.[13] Mi S, Sandrock A, Miller RH. LINGO-1 and its role in CNS repair. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(10):1971-1978.[14] Mi S, Hu B, Hahm K, et al. LINGO-1 antagonist promotes spinal cord remyelination and axonal integrity in MOG-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat Med. 2007;13(10):1228-1233.[15] 叶正旭,李静,黄景辉,等.成年脊髓损伤大鼠脊髓神经干细胞的体外培养及分化研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009, 11(10): 956-959.[16] Lööv C, Fernqvist M, Walmsley A, et al. Neutralization of LINGO-1 during in vitro differentiation of neural stem cells results in proliferation of immature neurons. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29771.[17] Wang F, Zhu Y. The interaction of Nogo-66 receptor with Nogo-p4 inhibits the neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells. Neuroscience. 2008;151(1):74-81. |