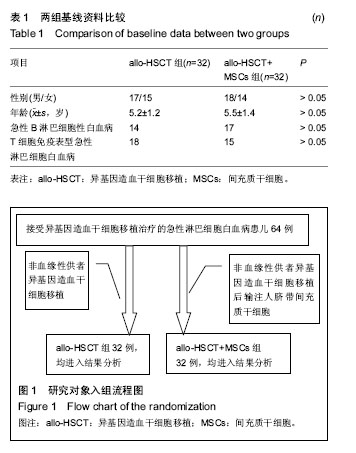
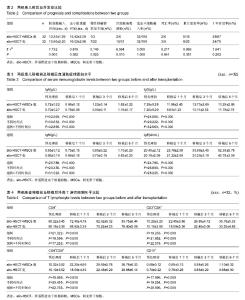
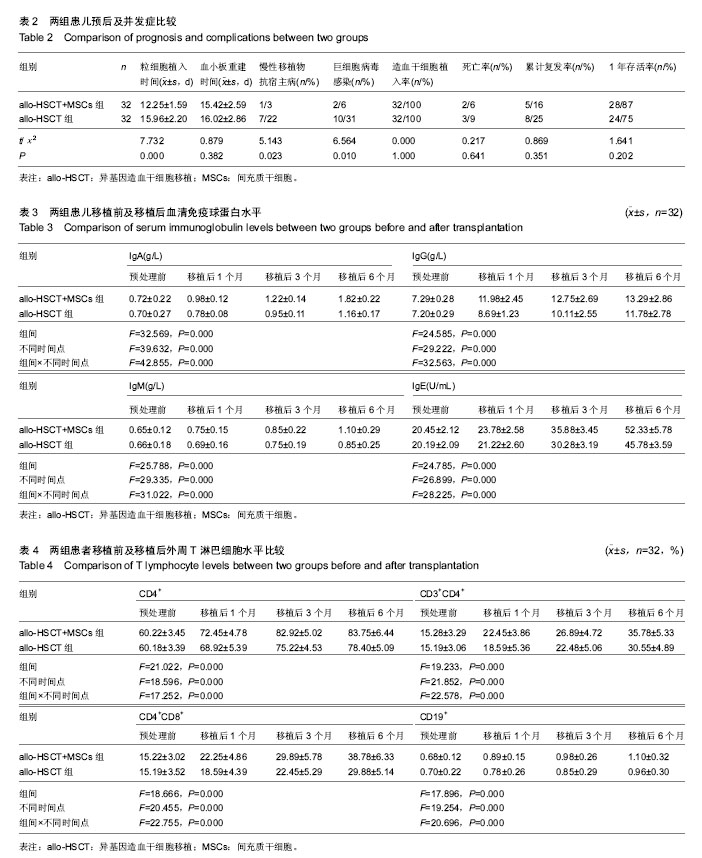
| [1] 崔蕾,张瑞东,高超,等.儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病早期治疗反应评估与预后价值[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2014,22(2):298-303.[2] 王晓雪,王萍萍,梁颖,等.成人急性淋巴细胞白血病免疫表型的特点分析[J].中国医科大学学报,2015,44(10):904-908.[3] 王婧,黄晓军,江滨,等.伊马替尼联合化疗治疗Ph染色体阳性急性淋巴细胞白血病的分子学疗效与预后因素分析[J].中华血液学杂志,2014,35(2):120-125.[4] 周华,周倩兰,唐晓文,等.allo-HSCT治疗进展期难治性急性髓系白血病的长期随访结果[J].浙江临床医学,2014,16(7): 1017-1018,1021.[5] 陈璇,袁茵,邵红伟,等.人脐带间充质干细胞培养上清对正常人淋巴细胞各亚群比例的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2014,30(5): 577-581.[6] 韩华,薛改,张俊勤,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的分离、培养及鉴定[J].河北医科大学学报,2015,36(1):21-23.[7] 张立新,栾正云,陈亚宝.人脐带基质间充质干细胞免疫调节机制及其相关应用的研究进展[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2012, 18(3):251-254.[8] 张晓婷,段连宁,丁丽,等.非血缘供者异基因外周血造血干细胞联合脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病临床研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2015,23(5):1445-1450.[9] 郑莹,王易,翟宗,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗急性移植物抗宿主病的疗效观察[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2015,17(8):869-872.[10] Yun JW, Ahn JH, Kwon E, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in acute liver injury: Hepatoprotective efficacy, subchronic toxicity, tumorigenicity, and biodistribution. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016;81:437-447.[11] Jones K, Wockner L, Brennan RM, et al. The impact of HLA class I and EBV latency-II antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells on the pathogenesis of EBV(+) Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016;183(2):206-220.[12] Shi W, Huang CJ, Xu XD, et al. Transplantation of RADA16-BDNF peptide scaffold with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells forced with CXCR4 and activated astrocytes for repair of traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2016;45:247-261.[13] Esmaeli A, Moshrefi M, Shamsara A, et al. Xeno-free culture condition for human bone marrow and umbilical cord matrix-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells using human umbilical cord blood serum. Int J Reprod Biomed (Yazd). 2016;14(9):567-576.[14] Yang J, Miao Y, Chang Y, et al. Condition medium of HepG-2 cells induces the transdifferentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into cancerous mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(8):3429-3438.[15] 唐伦,高蕾,张曦,等.Th17细胞及其相关的细胞因子在急性移植物抗宿主病中的作用[J].重庆医学,2015,44(36):5167-5170.[16] 冯秀梅,许洪志,张婧瑶,等.再生障碍性贫血、骨髓增生异常综合征和急性髓系白血病患者CD4+T细胞亚群转录因子表达的变化及其临床意义[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2014,22(4):1038-1042.[17] Park SE, Jung NY, Lee NK, et al. Distribution of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUCB-MSCs) in canines after intracerebroventricular injection. Neurobiol Aging. 2016;47:192-200. [18] Carvalho MI, Pires I, Dias M, et al. Intratumoral CD3+ T-lymphocytes immunoexpression and its association with c-Kit, angiogenesis, and overall survival in malignant canine mammary tumors. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2015;2015: 920409.[19] 吴亚妹,曹永彬,李晓红,等.间充质干细胞联合单倍体异基因造血干细胞移植治疗27例重型再生障碍性贫血临床疗效[J].解放军医学院学报,2014,35(12):1191-1195.[20] 吴亚妹,曹永彬,李晓红,等.脐带间充质干细胞联合单倍体异基因造血干细胞移植治疗36例难治/复发髓细胞白血病临床疗效[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2014,22(4):1053-1057.[21] 乔淑敏,陈光华,王易,等.脐带间充质干细胞治疗儿童异基因造血干细胞移植后急性移植物抗宿主病疗效观察[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2013,21(3):716-720.[22] 李丹,王易,胡绍燕.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗白血病患儿异基因造血干细胞移植术后急性移植物抗宿主病疗效观察[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2012,27(12):937-939.[23] 边志磊,常英军,许兰平,等.高危和标危Ph阴性急性淋巴细胞白血病非体外去T细胞单倍型造血干细胞移植后早期免疫重建的比较研究[J].中华血液学杂志,2016, 37(8):650-655.[24] 曹晶,唐晓文,崔巍,等.移植前状态对难治复发急性淋巴细胞白血病异基因造血干细胞移植预后的影响[J].第三军医大学学报, 2016, 38(12):1374-1378.[25] 李文静,郭晓,李栋梁,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗急性淋巴细胞白血病的近期疗效及远期预后分析[J].空军医学杂志, 2017, 33(1):36-38.[26] 王晓刚.异基因外周血造血干细胞移植治疗45例急性白血病的临床研究[J].中华全科医学, 2016, 14(1):41-43.[27] 张燕,赵鹏,熊杰,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗Ph+急性淋巴细胞白血病的疗效观察[J].江西医药, 2016, 51(3):207-208.[28] 黄清昕,涂三芳,黄睿,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗100例白血病的临床总结[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2016, 24(2):556-561.[29] 马晓环,徐鑫,邹常咏,等.人脐带间充质干细胞对白血病细胞增殖分化的作用[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2016, 24(6):1710-1715.[30] 刘会兰,孙自敏.异基因造血干细胞移植后B淋巴细胞重建及其影响因素[J].国际输血及血液学杂志, 2016, 39(5):399-404.[31] 乔淑敏,宋秀玲,岳屹囡.脐带间充质干细胞在造血干细胞移植中的作用研究进展[J].心理医生, 2016, 22(20):296.[32] 沈耀耀,刘跃均,吴德沛,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后免疫重建的临床研究及急性移植物抗宿主病的危险因素分析[J].白血病•淋巴瘤, 2015, 24(6):346-351.[33] 何学鹏,杨凯,陈鹏,等. G-CSF诱导移植物抗白血病效应治疗异基因造血干细胞移植后复发白血病的临床研究[J].医学综述, 2015,21(14):2656-2658.[34] 李桥川,章忠明,刘练金,等.异基因外周血造血干细胞移植治疗急性淋巴细胞白血病95例疗效分析[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2015, 36(2):82-86.[35] 张博,赵晓甦,秦亚溱,等.急性T淋巴细胞白血病异基因造血干细胞移植后WT1基因表达及其与预后关系[J].中华血液学杂志, 2015,36(8):642-646.[36] 牛晓敏,何慧清,周睿卿,等.急性髓系白血病异基因造血干细胞移植后巨细胞病毒血症对白血病复发的影响[J].中华医学杂志, 2015,95(2):123-125.[37] 秘营昌,罗成伟.异基因干细胞移植与化疗作为急性髓系白血病缓解后治疗的前瞻性配对研究[J].循证医学, 2015, 15(2):79-82. |