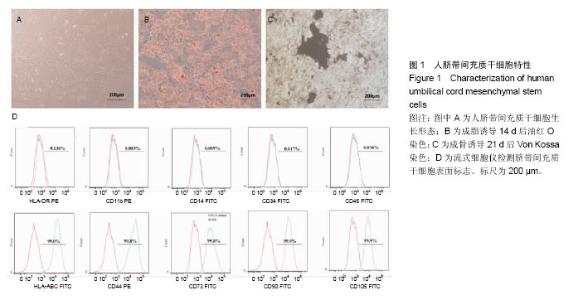
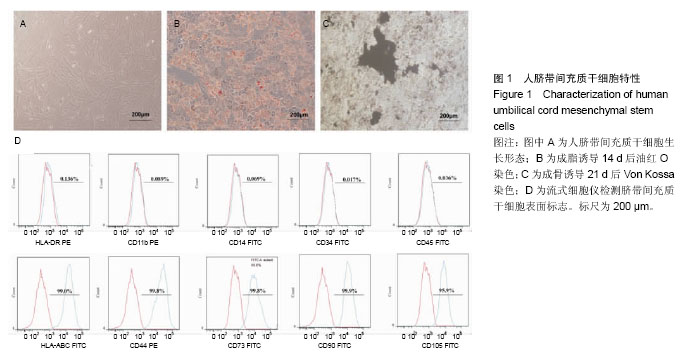
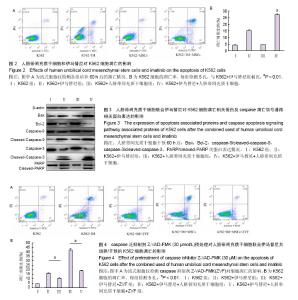
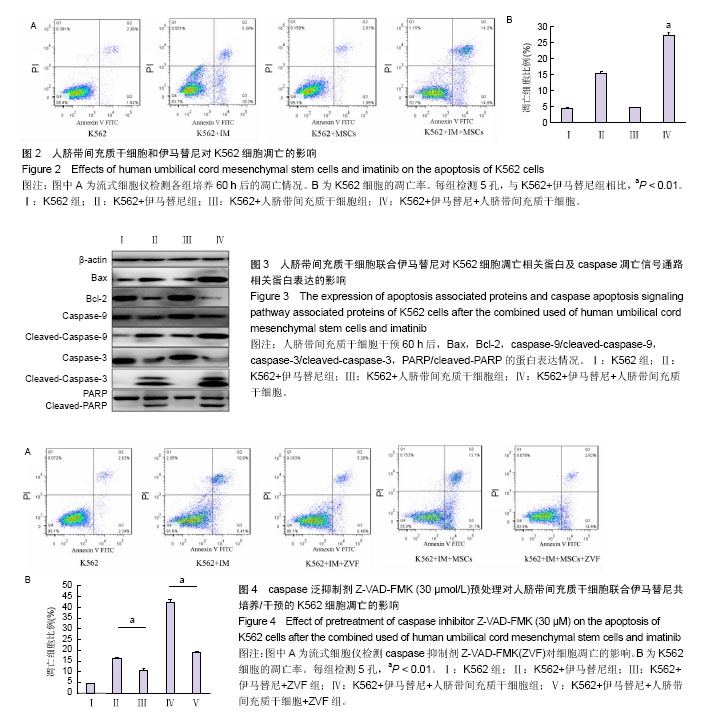
| [1] Kang ZJ, Liu YF, Xu LZ, et al. The Philadelphia chromosome in leukemogenesis. Chin J Cancer. 2016;35:48.[2] Mughal TI, Radich JP, Deininger MW, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: reminiscences and dreams. Haematologica. 2016; 101(5):541-558. [3] Jabbour E. Chronic myeloid leukemia: First-line drug of choice. Am J Hematol. 2016;91(1):59-66. [4] Polillo M, Galimberti S, Baratè C, et al. Pharmacogenetics of BCR/ABL Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):22811-22829. [5] Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276(5309):71-74.[6] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[7] Tian K, Yang S, Ren Q, et al. p38 MAPK contributes to the growth inhibition of leukemic tumor cells mediated by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;26(6):799-808. [8] Chen F, Zhou K, Zhang L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells induce granulocytic differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemic cells via IL-6 and MEK/ERK pathways. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(13):1955-1967. [9] Smith JR, Cromer A, Weiss ML. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Isolation, Expansion, Cryopreservation, and Characterization. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2017;41:1F.18.1-1F.18.23. [10] Maes ME, Schlamp CL, Nickells RW. BAX to basics: How the BCL2 gene family controls the death of retinal ganglion cells. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017;57:1-25. [11] Cheng CH, Cheng YP, Chang IL, et al. Dodecyl gallate induces apoptosis by upregulating the caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway and inhibiting the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins in human osteosarcoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(2):1495-1500. [12] Yuan J, Najafov A, Py BF. Roles of Caspases in Necrotic Cell Death. Cell. 2016;167(7):1693-1704. [13] Rascón-Valenzuela LA, Velázquez C, Garibay-Escobar A, et al. Apoptotic activities of cardenolide glycosides from Asclepias subulata. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;193:303-311. [14] Baksh D, Yao R, Tuan RS. Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2007;25(6):1384-1392. [15] Hoffmann A, Floerkemeier T, Melzer C, et al. Comparison of in vitro-cultivation of human mesenchymal stroma/stem cells derived from bone marrow and umbilical cord. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016. in press.[16] Pappa KI, Anagnou NP. Novel sources of fetal stem cells: where do they fit on the developmental continuum? Regen Med. 2009;4(3):423-433. [17] Nagamura-Inoue T, Mukai T. Umbilical Cord is a Rich Source of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Cell Therapy. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(8):634-642.[18] Arutyunyan I, Elchaninov A, Makarov A, et al. Umbilical Cord as Prospective Source for Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:6901286. [19] Aristizábal JA, Chandia M, Del Cañizo MC, et al. Bone marrow microenvironment in chronic myeloid leukemia: implications for disease physiopathology and response to treatment. Rev Med Chil. 2014;142(5):599-605. [20] Wang B, Hu Y, Liu L, et al. Phenotypical and functional characterization of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(6):1020-1028.[21] Han Y, Wang Y, Xu Z, et al. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from blastic phase chronic myelogenous leukemia on the growth and apoptosis of leukemia cells. Oncol Rep. 2013;30(2):1007-1013.[22] 张海梅,张连生.人骨髓间充质干细胞对慢性粒细胞白血病细胞增殖的影响及其机制探讨[J].癌症,2009,28(1):39-42.[23] 朱雅姝,孙昭,李振亚,等.脂肪MSCs分泌的DKK-1抑制慢性粒细胞白血病细胞K562的增殖[J].基础医学与临床,2009,29(5):479- 483.[24] 庞一琳,张斌,陈虎,等.间充质干细胞与肿瘤细胞相互作用:促进还是抑制[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2013,3(1):31-38. [25] Chen JR, Jia XH, Wang H, et al. Timosaponin A-III reverses multi-drug resistance in human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562/ADM cells via downregulation of MDR1 and MRP1 expression by inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 2016;48(5):2063-2070. [26] Zhang X, Dong W, Zhou H, et al. α-2,8-Sialyltransferase Is Involved in the Development of Multidrug Resistance via PI3K/Akt Pathway in Human Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. IUBMB Life. 2015;67(2):77-87. [27] Guerra B, Martín-Rodríguez P, Díaz-Chico JC, et al. CM363, a novel naphthoquinone derivative which acts as multikinase modulator and overcomes imatinib resistance in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncotarget. 2017;8(18):29679- 29698.[28] Shi X, Chen X, Li X, et al. Gambogic acid induces apoptosis in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells via inducing proteasome inhibition and caspase-dependent Bcr-Abl downregulation. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(1): 151-163. [29] Vida A, Márton J, Mikó E, et al. Metabolic roles of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;63: 135-143. [30] Beneke S, Bürkle A. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation, PARP, and aging. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ. 2004;2004(49):re9. |