Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (24): 4495-4501.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.24.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression in the degenerative intervertebral disc
Dai Qi-yu, Yang Ting-tong, Yu Fang-fang, Wang Quan-zhi, Wang Yuan, Zhang Xiao-shuang
- The 371 Central Hospital of PLA, Xinxiang 453000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2012-10-25Revised:2012-11-21Online:2013-06-11Published:2013-06-11 -
Contact:Yang Ting-tong, Professor, Master’s supervisor, the 371 Central Hospital of PLA, Xinxiang 453000, Henan Province, China yangtt@xxmu.edu.cn -
About author:Dai Qi-yu, Master’s supervisor, Chief technician, the 371 Central Hospital of PLA, Xinxiang 453000, Henan Province, China DQY716@sohu.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dai Qi-yu, Yang Ting-tong, Yu Fang-fang, Wang Quan-zhi, Wang Yuan, Zhang Xiao-shuang. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression in the degenerative intervertebral disc[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(24): 4495-4501.
share this article
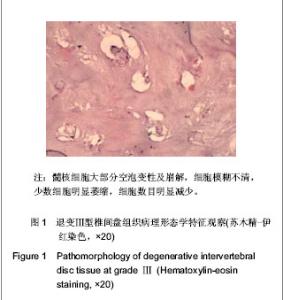
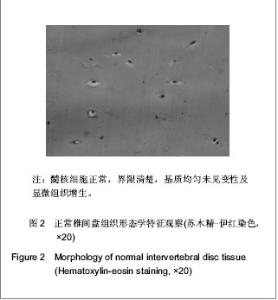
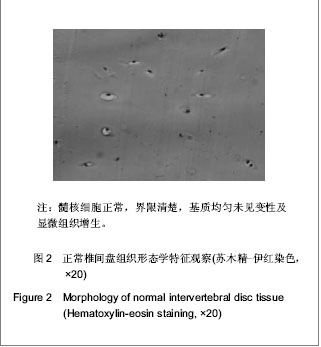
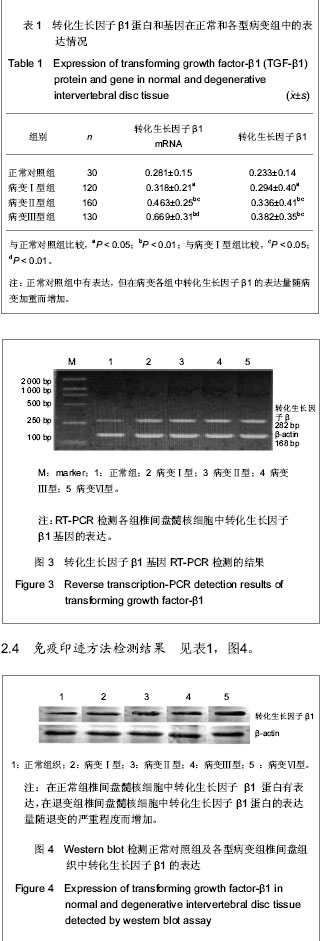
2.1 参与者或纳入样本数量分析 共收集椎间盘突出手术切除样本573例,在制片过程中由于蜡块处理不当26例,脱片17例,计43例被删除,最后纳入椎间盘突出530例为退变组。正常组中选取51例椎体爆裂性骨折患者椎间盘组织,不符合对照组标准的部分椎间盘组织被删除,最后选出镜下为正常椎间盘组织的30例作为对照组。实验过程中无脱失,均进入结果分析。 2.2 病理诊断与形态学分型 椎间盘退变病变Ⅰ型 120例,病理形态学特征:髓核细胞轻度变性、变大,部分细胞模糊,界限不清。椎间盘退变病变Ⅱ型160例,病理形态学特征:髓核细胞大部分空泡样变性,变大,少部分细胞崩解消失,细胞数目轻度减少。椎间盘退变病变Ⅲ型130例,病理形态学特征显示,髓核细胞大部分空泡变性及崩解,细胞模糊不清,少数细胞明显萎缩,细胞数目明显减少,见图1。 椎间盘退变病变Ⅳ型120例,病理形态学特征:髓核细胞数目极度减少,间质内胶原纤维重度增生。正常对照组30例,病理形态学特征正常,髓核细胞与周围组织界限清楚,未见变性,见图2。 "

| [1] Gembun Y,Nakayama Y,Shirai Y,et al.Surgical results of lumbar disc herniation in the elderly.J Nippon Med Sch.2001; 68(1):50-53.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11180701[2] Boos N,Weissbach S,Rohrbach H,et al.Classification of agerelated changes in lumbar intervertebral disca 2002 volvo Award in basic science.Spone.2002;27(2):2631-2644.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12461389[3] Antoniou J,Pike GB,Steffen T,et al.Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in the asseaament of degene rative disc disease.Magn Reson Med.1998;40(8):900-907.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9840835[4] Ma L,Zwahlen RA,Zheng LW,et al.Influence of nicotine on the biological activity of rabbit osteoblasts.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(3):338-342.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21561475[5] Kim IS,Song YM,Hwang SJ.Osteogenic reaponses of human mesenchymal stromal cell to static stretch.J Dent Res.2010; 89(10):1129-1134.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20639509[6] Bettina K,Tao Y,Elda M,et al.Interraction of TGF-B and BMP signaling pathways during chondrogenesis.Plos One.2011; 6(1):1-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21297990[7] Wang Y, Yu SY, Gao XJ, et al. Dongwuxue Zazhi. 2010;45(3): 127-132.王悦,俞诗源,高先军,等.Bax,TGF-B1和Ghrelin在饥饿后长耳鸪胃及小肠中的免疫组织化学[J].动物学杂志,2010,45(3): 127-132.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GWSX200102002.htm[8] Hu YG. Beijing: The Publishing House of People′s Health. 2004: 411.胡有谷.腰椎间盘突出症[M].第三版,北京:人民卫生出版社,2004: 411.[9] Nomura T,Mochida J,Okuma M,et al.Nuclus pulposus allograft vetards intervertebral disc degeneration.Spine. 2001;38(1): 94-101.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11501830[10] Yang H,wu J,Liu J et al.transplanted mesenchymal stem cells with pure fibrinous gelatin-transforming growth factor-betal decrease rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration.Spine J.2010; 10(9):802-810.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20655810[11] Delamarter R, Zigler JE, Balderston RA, et al. Prospective, random- ized, multicenter Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption study of the ProDisc-L total disc replacement compared with circumferential arthrodesis for the treatment of two-level lumbar degenerative disc disease: results at twenty-four months. J Bone Joint Surg (Am).2011;93(8):705-715.http://www.doc88.com/p-8095953936365.html[12] Gao CH, Lv M, Yang C, et al. Jizhu Waike Zazhi. 2012;10(6): 371-373.高春华,吕明,杨诚,等. 椎间盘内注射转化生长因子-β1诱导椎间盘退变[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(6):371-373.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JZWK201206017.htm[13] Li GF, Zhang SK, Fu CF, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(2):359-362.李高峰,张绍昆,付长峰,等. 细胞因子及基因治疗椎间盘退行性变的研究动态[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(2): 359-362.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDKF200902046.htm[14] Yan JW, Li AG, CHen HH, et al. ZHonguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2012;20(24):2268-2271.闫军伟,李爱国,陈鸿辉,等. 炎性细胞因子在椎间盘退变中的研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(24):2268-2271.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZJXS201224025.htm[15] Bobick BE,Kulyk WM. Regulation of cartilage formation and maturation by mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today.2008;84(2):131-154.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18546337[16] Guo Q, Jiang XF, Chen Y, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Huaxue ji Xibao Huaxue Zazhi. 2012;21(1): 69-73.郭琼,姜孝芳,陈艳,等.TGF-B1及其受体在大鼠整胚及软骨雏形发育过程中的表达[J].中国组织化学及细胞化学杂志,2012, 21(1): 69-73.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GGZZ201201015.htm[17] Mon SH,Nishida K,Gilbertson LG,et al.Biologicresponse of human intervertebral disc cells to gene therapy cocktail. Spine.2008;33(17):1850-1855.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18622355[18] Hu BS, Xu XJ, Guo YL, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2013;17(4):571-575.胡宝山,许喜筠,郭元利, 等. 各种腰椎间盘细胞可否自分泌产生白细胞介素1β[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):571-575.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDKF201304007.htm[19] Cheng SQ, Chen GB, Liu YH, et al. Hebei Yixue. 2013;19(2): 270-272.成善泉,陈国邦,刘亿华,等. 椎间盘退变的形态学分型中转化生长因子-β1表达的临床意义[J]. 河北医学,2013,19(2):270-272.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HCYX201302047.htm[20] SinghKM,MasodaKM.ThonarE.et al.Agerelated charges in the wxtracellularmatrix ofnucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus of human intervertebral disc.Spino.2009;34(1):10-16.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12193991[21] Yang Y,He XF,Li YH,et al.Association of transforming growth facto-B1 with pathological grading of intervertebral disc degeneration.Article in Chinese.2012;32(6):897-900.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22699080[22] Karamboulas K,Dranse HJ,Underhill TM.Regulation of BMP dependent chondrogenesis in early limb mesenchyme by TGF beta signals.Cell Sci.2010;123(12):2068-2076.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20501701[23] Baldridqe D,Shchelochkov O,Kelley B,et al.Signaling pathways in human skeletal dysplasias.Annu Res Genomics Hum Genet.2010;2991(1):189-217.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20690819[24] Song QX, Wu Y, Chen YZ.Zhongguo Yaoli Tongbao.2011; 27(3):378-382.宋清晓,吴勇,陈元仲.CD44抗体H144a对急性髓系白血病学报株HL-60细胞体外增值分化作用的研究[J].中国药理通报,2011, 27(3):378-382.http://www.doc88.com/p-605272455634.html[25] Heldin CH,Landstrom M,Moustakas A.Mechanism of TGF-beta signaling t growth arrest apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transtion.Curr Opin Cell Biol.2009; 21(2):166-176.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19237272[26] Li J, Yang SH, Zhao ZW.Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu.2003; 7(14):2079-2080.李进,杨述华,沼增务.细胞因子与椎间盘退行性变的关系[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(14):2079-2080.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDKF200314048.htm[27] Cui D,Zhang S,Ma J,et al.Short in terfering RNA targetting NF-kappa B induces apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells and attenuates extracellular matrix produetion.Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42(11):813-817.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20409762[28] Sing KM,Masuda KM,Thonar E,et al.Age-related changes in the extracellular matrix of nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus of human intervertebral disc.J Spine 2009;1(34): 10-16.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19127156[29] Xu JW,Zhong YM,Ji J,et al.Associations of transforming growth factor beta 1-509c/T site gene polymorphism with blood stasis syndrome of lumbar intervertebral dise protrusion and intervertebral dusc degeneration.J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res.2010;24(21):4524-4527.http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_xdkf201024040.aspx[30] Lin W, Wang WM, Zhuang YF, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(37): 7309-7313.林旺,王万明,庄颜峰,等.胰岛素样生长因子1,血血小板源性生长因子,转化生长因子β1对人退变纤维环细胞生物活性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(37):7309-7313.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDKF200937032.htm[31] Xu JW,Zhong YM,Ji J,et al.Associations of transforming growth factor bata1-509C/T site gene polymorphism with blood stasis syndrome of lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion and intervertebral disc degeneration. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res.2010;24(12):4524-4527.http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_xdkf201024040.aspx[32] Abbott RD,Purmessur D,Monsey RD,et al.Regenerative potential of TGF-B+Dex and notochordal cell conditioned media on degenerated human intervertebral disc cell.Jorthop Res.2012;30(3):482-488.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21866573[33] Hegewald AA,Endres M,Abbushi A,et al.Adequacy of herniated disc tissue as cell source for nucleus pulposu reqeneration. J Neurosurg Spine.2011;14(2):273-280.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21214312[34] Liu Y,Li JM,Hu YG.Transplantation of gene modified nucleus pulposus cells reverses rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration.Chin Med J (ENG1).2011;124(16):2431-2437http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21933582[35] He B, Yang J, Peng FL, et al.Xibao yu Fenzi Mianyixue Zazhi, 2012; 28(2):197-199.何斌,杨坚,彭方亮,等.退变髓核细胞与正常髓核细胞体外培养的生物学特性比较[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2012,28(2): 197-199.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBFM201202028.htm[36] Serigan K,Sakai D,Hiyama A,et al.Effector cell number on mesenchymal stem cell transplantatin in a canine disc degenration mode.Orthop Res.2010;28(10):1267-1275.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20839317[37] Gerald W.Apoptotic and non-apoptotic programmed cardiomyocyte death in ventricular remodelling.Cardiovasc Res.2009;81(3):465-473.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18779231[38] Feng G,Zhao X,Liu H,et al.Transplantation of masenchymal stem cells and nucleus pulposus cells in a degenerative disc model in rabbits:a comparison of cell types as potential candidates for disc regeneration.J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 14(3):322-329.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21250814[39] Gerald W. Apoptotic and non-apoptotic programmed cardiomyocyte death in ventricular remodelling.Cardiovasc Res.2009;81(3):465-473.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18779231[40] Shi YY, Dong X, Shi YH, et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2009;25(4):802-805.石永英,董颀,石永华,等.TGF-β1对体外培养的大鼠心肌细胞肥大和凋亡的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25(4):802-805.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZBLS200904047.htm[41] Dobaczewski M,Chen W,Frangogiannis NG. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-B signaling in cardiac remodeling.J Mol Cell Cardiol.2011;51(4):600-606.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22505689 |
| [1] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [2] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [3] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [4] | Zhang Haitao, Chen Jinlun, Zhu Xingyang, Zeng Huiliang, Li Jie, Sun Xiaobo, Qi Xinyu, Zeng Jianchun, Zeng Yirong. Effect and molecular mechanism of Honeysuckle-Rhizoma coptidis in the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection based on molecular docking and network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3360-3367. |
| [5] | Fu Yuanfei, He Shenghua, Lai Juyi, Sun Zhitao, Feng Hualong, Lan Zhiming . Pheretima extract ameliorates nucleus pulposus cell degeneration in the intervertebral disc by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 264-268. |
| [6] | Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Chen Feng, Jiang Shunwan, Jiang Jinting, Gao Kun, Lin Zhanpeng. Research strategy of gene editing technology in the gene treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 298-303. |
| [7] | Li Lunyu, Jin Songlin, Huang Zenghao, Kang Liang, Hu Yushi, Ding Haili. Self-renewal and signal regulation of myosatellite cells: application hotspots and problems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 304-310. |
| [8] | Zhang Kai, Zhang Xiaobo, Shi Jintao, Wang Keping, Zhou Haiyu. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric and visualization analysis based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3031-3038. |
| [9] | Wang Liu, Song Dongzhe, Huang Dingming. Bone morphogenetic protein 9 regulates stem cell differentiation and bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3064-3070. |
| [10] | Chen Jie, Liao Chengcheng, Chen Zhiwei, Wang Yan. Bladder cancer stem cell markers and related signaling pathways: antibody targeted therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3090-3096. |
| [11] | Zhang Hui, Wang Shaohua, Wang Qian, Wang Hui, Gan Hongquan, Cui Yishuang, Li Qijia, Wang Zhiqiang. Porous tantalum coated with RGD polypeptide can activate the integrin/focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway of MG63 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2535-2540. |
| [12] | Li Shao, Liang Yongkang, Gao Yi, Peng Qing. Establishment and functional in vitro characteristics of three-dimensional collagen HepaRG microsphere [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2541-2547. |
| [13] | He Shenghua, Fu Yuanfei, Lan Zhiming, Sun Zhitao, Lai Juyi, Feng Hualong, Guo Zibin, Li Gai . Yaotu Granule deals with the proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via regulating the expression of microRNA-221 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2177-2182. |
| [14] | Liu Zhigang, Guo Qinggong, Chen Jingtao. Effect of Capparis spinosa total alkaloid on proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in an intervertebral disc degeneration rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1699-1704. |
| [15] | Chen Jiang, Xiao Huideng, Sun Qi, Zhang Fan, Zhu Yonggang, Liu Zhichao, Guo Feiyu, Liu Genzhe. Proliferative activity of nucleus pulposus cells in human intervertebral disc and intervention with Yishen Huoxue Tongluo Recipe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1200-1206. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||