Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (9): 1313-1318.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.09.001
Effect of berberine on the proliferation and apoptosis of lung cancer stem cells and the possible mechanism
Sun Yan-zhen, Li Zhen, Yuan Zheng
- Department of Pathology, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
-
Online:2017-03-28Published:2017-03-31 -
About author:Sun Yan-zhen, Master, Attending physician, Department of Pathology, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Yan-zhen, Li Zhen, Yuan Zheng. Effect of berberine on the proliferation and apoptosis of lung cancer stem cells and the possible mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(9): 1313-1318.
share this article
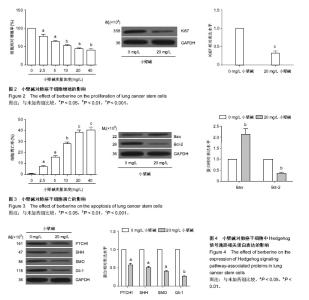
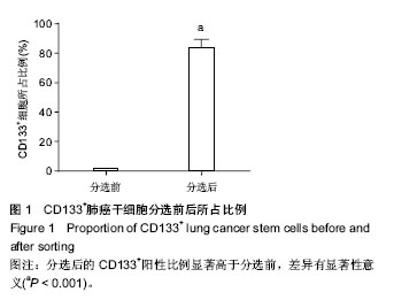
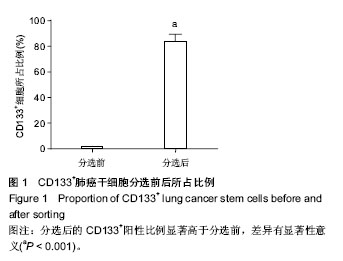
2.2 小檗碱抑制肺癌干细胞增殖 为了探究小檗碱对肺癌干细胞增殖的影响,将处于对数生长期的肺癌干细胞在含有不同质量浓度小檗碱的培养液中培养24 h,采用MTT法检测小檗碱对肺癌干细胞增殖的影响。结果发现含有2.5,5,10,20,40 mg/L小檗碱的培养液培养的活细胞分别为未加药组的78.5%,63.4%,52.1%,43.9%和40.7%,可见小檗碱能够抑制肺癌干细胞生长,并呈浓度依赖性。 采用免疫印迹检测未加药组和20 mg/L小檗碱组的增殖相关蛋白Ki67的表达水平,发现20 mg/L小檗碱组的Ki67表达水平显著低于未加药组,这也表明了小檗碱能够抑制肺癌干细胞增殖(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001,图2)。 2.3 小檗碱促进肺癌干细胞凋亡 为了探究小檗碱对肺癌干细胞凋亡的影响,将处于对数生长期的肺癌干细胞在含有不同质量浓度小檗碱(0,2.5,5,10,20,40 mg/L)的培养液中培养24 h,用流式细胞仪检测其凋亡率,各组的凋亡率分别为0.81%,7.21%,15.8%,28.2%,38.7%,40.5%,可见小檗碱能够促进肺癌干细胞凋亡,并呈浓度依赖性。 采用免疫印迹检测未加药组和20 mg/L小檗碱组的凋亡相关蛋白Bax和Bcl-2的表达水平。结果发现20 mg/L小檗碱组细胞中Bax蛋白的表达水平显著高于未加药组,而Bcl-2蛋白的表达水平显著低于未加药组,这也表明了小檗碱能够促进肺癌干细胞凋亡(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001,图3)。 2.4 小檗碱抑制肺癌干细胞中Hedgehog信号通路的活性 为了探究小檗碱是否通过调控Hedgehog信号通路对肺癌干细胞的增殖和凋亡起作用,将处于生长对数期的肺癌干细胞培养在未加药和加有20 mg/L小檗碱的培养液中培养24 h,检测两组细胞中Hedgehog信号通路中PTCH1、SHH、Gli-1和SMO蛋白的表达。结果发现这4种蛋白在加药组细胞中的表达水平明显低于未加药组,这表明小檗碱抑制了Hedgehog信号通路的活性(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,图4)。所以,作者推测小檗碱对肺癌干细胞增殖和凋亡的影响可能是通过调控Hedgehog信号通路起作用。"

| [1] 汤宇,李博,杨兴海,等.非小细胞肺癌脊柱转移治疗现状及进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(3):186-190.[2] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics.CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69-90.[3] Bareschino MA, Schettino C, Rossi A, et al. Treatment of advanced non small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2011; 3(2):122-133.[4] 刘杨,李玉芬,崔玲,等.肺癌术后营养支持对免疫功能的影响[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2014, 20(12): 1705-1706.[5] Pisters KM, Ginsberg RJ, Giroux DJ, et al. Induction chemotherapy before surgery for early-stage lung cancer: A novel approach. Bimodality Lung Oncology Team.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;119(3):429-439.[6] Shiozawa Y, Nie B, Pienta KJ, et al. Cancer stem cells and their role in metastasis. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;138(2):285- 293.[7] Memmi EM, Sanarico AG, Giacobbe A, et al. p63 Sustains self-renewal of mammary cancer stem cells through regulation of Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(11):3499-3504.[8] Osei-Sarfo K, Gudas LJ. Retinoic acid suppresses the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in embryonic stem cells and activates the noncanonical Wnt signaling pathway. Stem Cells. 2014;32(8):2061-2071.[9] Sturgeon CM, Ditadi A, Awong G, et al. Wnt signaling controls the specification of definitive and primitive hematopoiesis from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2014; 32(6):554-561.[10] Mo JS, Park HW, Guan KL. The Hippo signaling pathway in stem cell biology and cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014;15(6): 642-656.[11] Oskarsson T, Batlle E, Massagué J. Metastatic stem cells: sources, niches, and vital pathways. Cell Stem Cell. 2014; 14(3):306-321.[12] Stewart DJ. Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106(1):djt356.[13] Stewart DJ, Chang DW, Ye Y, et al. Wnt signaling pathway pharmacogenetics in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmacogenomics J. 2014;14(6):509-522.[14] Coscio A, Chang DW, Roth JA, et al. Genetic variants of the Wnt signaling pathway as predictors of recurrence and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(6):1284-1291.[15] Kugler MC, Joyner AL, Loomis CA, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling in the lung. From development to disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;52(1):1-13.[16] Xiong D, Ye Y, Fu Y, et al. Bmi-1 expression modulates non-small cell lung cancer progression. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(5):756-763.[17] Lee JJ, Perera RM, Wang H, et al. Stromal response to Hedgehog signaling restrains pancreatic cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(30):E3091-100.[18] Matsushita S, Onishi H, Nakano K, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for gallbladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(3):272-280.[19] Heiden KB, Williamson AJ, Doscas ME, et al. The sonic hedgehog signaling pathway maintains the cancer stem cell self-renewal of anaplastic thyroid cancer by inducing snail expression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(11):E2178- 2187.[20] Raz G, Allen KE, Kingsley C, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway molecules and ALDH1A1 expression in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012;76(2):191-196.[21] 钟祥,李应东.小檗碱药理作用研究进展[J].亚太传统医药, 2012, 8(3):185-186.[22] Refaat A, Abdelhamed S, Yagita H, et al. Berberine enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 2013;6(3):840-844.[23] Zhang EB, Kong R, Yin DD, et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL indicates a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes tumor growth by epigenetically silencing of miR-99a/miR-449a. Oncotarget. 2014;5(8):2276-2292.[24] Chidambara Murthy KN, Jayaprakasha GK, Patil BS. The natural alkaloid berberine targets multiple pathways to induce cell death in cultured human colon cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;688(1-3):14-21.[25] Ma X, Zhou J, Zhang CX, et al. Modulation of drug-resistant membrane and apoptosis proteins of breast cancer stem cells by targeting berberine liposomes. Biomaterials. 2013;34(18): 4452-4465.[26] 吴澄,钟丰文,罗列. A549肺癌细胞株干细胞表面标志的初步研究[J].赣南医学院学报, 2015, 35(4): 529-531.[27] Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893-2917.[28] 谭宇蕙,陈冠林,郭淑杰,等.小檗碱对人胃癌MGC-803细胞生长抑制及诱导凋亡的作用[J].中国药理学通报, 2001,17(1): 40-43.[29] Kuo CL, Chou CC, Yung BY. Berberine complexes with DNA in the berberine-induced apoptosis in human leukemic HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 1995;93(2):193-200.[30] Kim HS, Kim MJ, Kim EJ, et al. Berberine-induced AMPK activation inhibits the metastatic potential of melanoma cells via reduction of ERK activity and COX-2 protein expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83(3):385-394.[31] Wang L, Cao H, Lu N, et al. Berberine inhibits proliferation and down-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor through activation of Cbl in colon tumor cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(2): e56666.[32] 蒋艳,王毅,郝钰,等.小檗碱对人高转移肺癌系(PG)细胞增殖的影响及机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2005, 21(11): 2170-2173.[33] Park SH, Sung JH, Chung N. Berberine diminishes side population and down-regulates stem cell-associated genes in the pancreatic cancer cell lines PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;394(1-2):209-215.[34] 邹宇辉,王琼,王伟民.小檗碱对U251胶质瘤干细胞的诱导分化作用[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志, 2016,21(12):559-562.[35] 顾红兵,李继坤.Hedgehog 信号通路与肿瘤的关系研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2011,19(4): 808-811.[36] 李悦,张宇,曹良启,等. Hedgehog信号通路转录因子Gli2表达对肝癌进展和生存预后的影响[J].中华普通外科学文献:电子版, 2016,10(3):174-178.[37] 黄少良,赵丽,郭青龙,等.Hedgehog信号通路参与肿瘤耐药机制研究的最新进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2016,47(3):259-266.[38] 邵欣宇,顾遷,丁希伟,等.Hedgehog信号通路与胰腺癌吉西他滨固有耐药的相关性研究[J].胃肠病学,2016,21(11):656-661.[39] 师海英,黄明莉,张广美,等. Hedgehog信号通路在卵巢癌中作用研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016,30(7):632-634.[40] 沈冰,刘陶文.Hedgehog信号通路Gli家族成员及其在恶性肿瘤中的作用研究进展[J].广西医学,2016,38(2):237-239.[41] Park KS, Martelotto LG, Peifer M, et al. A crucial requirement for Hedgehog signaling in small cell lung cancer. Nat Med. 2011;17(11):1504-1508.[42] Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Dasari V, Sidhu SS, et al. Wnt and Hedgehog are critical mediators of cigarette smoke-induced lung cancer. PLoS One. 2006;1:e93.[43] 郑晓文,陈一强,孔晋亮,等. Hedgehog信号通路成分SHH和Gli-1及血管内皮生长因子在人肺癌中的表达[J].中国全科医学, 2014, 17(18): 2096-2102.[44] Wang J, Peng Y, Liu Y, et al. Berberine, a natural compound, suppresses Hedgehog signaling pathway activity and cancer growth. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:595. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [5] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [6] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [7] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [8] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [9] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [10] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [11] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaoyang, Tang Tian, Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Repair and regenerative therapies of the annulus fibrosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1582-1587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||